Abstract
Escitalopram is a selective serotonin-reuptake inhibitor (SSRI) and an antidepressant used to treat Major Depressive Disorder. In 2011, escitalopram was approved in over 100 countries. Different analytical methods are being developed to identify the physicochemical properties of escitalopram in pharmaceutical dosage forms, chemical substances, and synthetic compositions. The Literature Review survey provides the most appropriate techniques for estimating escitalopram and identifies the most efficient solvents used to estimate escitalopram
Keywords
Treatment, Resistance Escitalopram, Analytical
Introduction
Escitalopram is the S-enantiomer of citalopram, a selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor (SSRI) used to treat Major Depressive Disorder with high overall tolerability. Escitalopram medication is less likely than many other antidepressants to result in clinically significant drug interactions. The key isoenzymes involved in escitalopram metabolism are cytochrome P450 (CYP) 2C19, CYP3A4, and CYP2D6. Escitalopram wasapproved in 100 countries across Europe, North America, and other regions as of November 2011. Escitalopram is used to treat generalized anxiety disorder, social anxiety disorder, obsessive-compulsive disorder, panic disorder, premenstrual dysphoric disorder, and major depressive disorder. Escitalopram inhibits SERT with great selectivity and dose-dependent efficacy. Its antidepressant properties derive from its suppression of serotonin reuptake into presynaptic nerve endings, which increases serotonin activity in the central nervous system. Radioligand binding experiments evaluated that escitalopram had significantly higher selectivity for SERT than citalopram and several other SSRIs. Two decision-analytic investigations conducted in Finland and Sweden discovered that when used to treat addiction, escitalopram had a higher cost utility than the other three medicines. Escitalopram should not be used in conjunction with irreversible monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs), and at least 2 weeks should pass between discontinuing escitalopram and starting an irreversible MAOI.
Drug Profile[4] :
Escitalopram is an anti-depressant medication used to treat major depressive disorder. Amongst the SSRIs, escitalopram has the highest degree of selectivity for the serotonin transporter (SERT) compared to other off-targets, which may explain why it has lower rates of side effects than other drugs in its class.
Table 1: Drug Profile of Escitalopram

Current studies on Escitalopram
A recent study investigated the cognitive effects of chronic escitalopram administration in healthy volunteers. Another study explored escitalopram's effects on synaptic density in the human brain. Research has also examined the long-term effects of escitalopram on cardiac outcomes in patients who have experienced acute coronary syndrome (ACS).
Literature Review
Table 2: Reported UV method for Escitalopram

Table 3: HPLC method of escitalopram
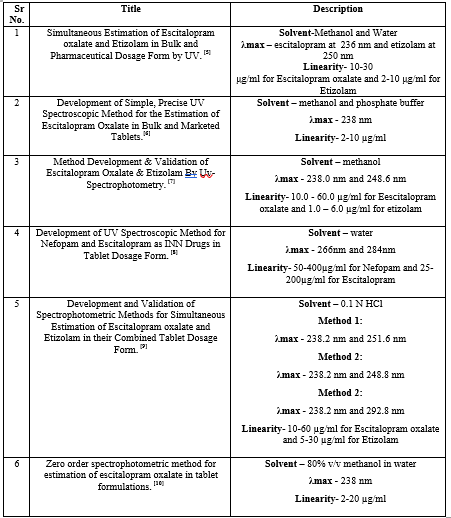
Table 4: HPTLC method of Escitalopram

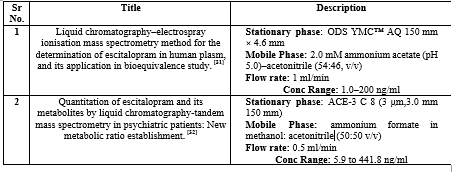
Table 5 LC/MS method of Escitalopram
Graphical Evaluation of Analytical Methods Found in Review
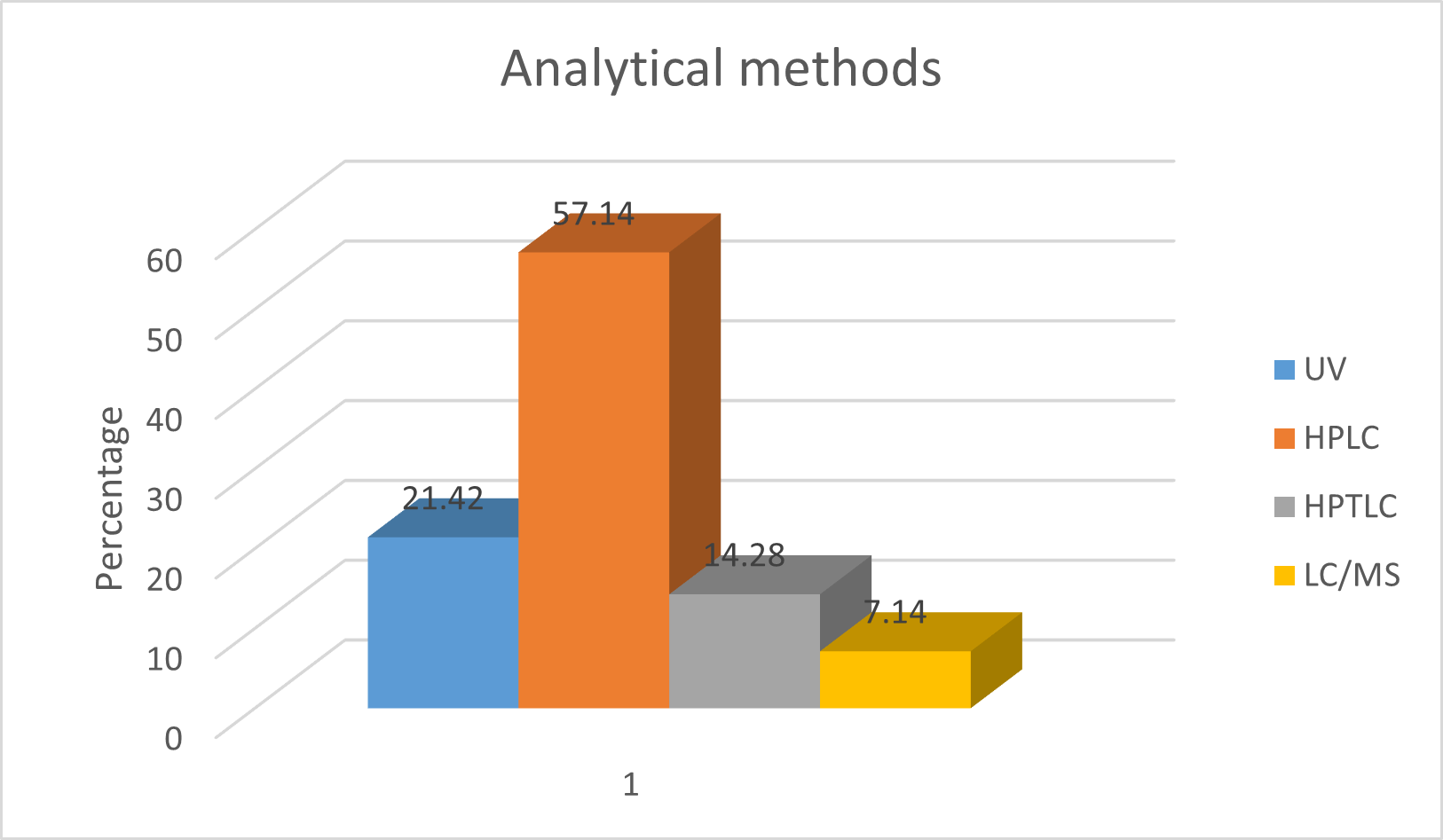
Fig 1. Methods found for Escitalopram.
CONCLUSION
Escitalopram is the selective serotonin-reuptake inhibitor (SSRI) used as first line medication for the treatment of Major Depressive Disorder. In 2011, escitalopram was approved in 100 countries in Europe, North America, and other regions. There are many analytical methods available for estimation of escitalopram alone or in combination with other drugs. Among these methods HPLC assisted with UV and PDA detector are abundant analytical techniques available in literature review for estimation in pharmaceutical dosage forms as well as in synthetic composition. On the basis of literature review we found that most of the methods are developed using phosphate buffer and methanol as solvents.
REFERENCE
- Eiji Kirino, “Escitalopram for the management of major depressive disorder: a review of its efficacy, safety, and patient acceptability”, Patient Preference and Adherence, 2012(6) 853–861.
- John Waugh and Karen L. Goa, “Escitalopram A Review of its Use in the Management of Major Depressive and Anxiety Disorders, CNS Drugs, 2003, 17 (5), 343-362.
- DS Baldwin et al., “Escitalopram Therapy for Major Depression and Anxiety Disorders”, Ann Pharmacother 2007, (41):1583-92.
- Drug Bank, “Escitalopram” 2024, https://go.drugbank.com/drugs/DB01175.
- Amruta More et. al., “Simultaneous Estimation of Escitalopram oxalate and Etizolam in Bulk and Pharmaceutical Dosage Form by UV”, vidyapharma, 2024, 2(2), 14-22.
- KUmaret al, “Development of Simple, Precise UV Spectroscopic Method for the Estimation of Escitalopram Oxalate in Bulk and Marketed Tablets”, Asian Journal ofPharmaceutical Research and Development. 2024; 12(3): 29-34
- K. Vikram, P. SinghH, “Method Development & Validation Of Escitalopram Oxalate & Etizolam By Uv- Spectrophotometry”, Kumar V, Singh HP, Rathore RPS, Method development & validation of escitalopram oxalate & etizolam by UV-spectrophotometry, International Journal of InstitutionalPharmacy and Life Sciences, 2015; 5(2):12-42.
- Fatema et al., “Development of UV Spectroscopic Method for Nefopam and Escitalopram as INN Drugs in Tablet Dosage Form”, S. J. Pharm. Sci., 2010, 3(1): 4-10
- Sakhreliya B. D. et al, “Development and Validation of Spectrophotometric Methods for Simultaneous Estimation of Escitalopram oxalate and Etizolam in their Combined Tablet Dosage Form”, JPSBR, 2012, 2(5) (195-200)
- Sharma S, Rajpurohit H, Sonwal C, Bhandari A, Choudhary V, Jain T., “Zero order spectrophotometric method for estimation of escitalopram oxalate in tablet formulations.”, J Young Pharm. 2010, 2(4):420-3.
- Sellappan et al., “Development and Validation of Rp-Hplc Method for The Estimation of Escitalopram Oxalate and Flupentixol Dihydrochloride in Combined Dosage Form and Plasma.”, Int J Pharm Pharm Sci, 2021. Vol 13, Issue 2, 61-66
- Bhimanadhuni et al., “Development and validation of an RP-HPLC method for the simultaneous determination of Escitalopram Oxalate and Clonazepam in bulk and its pharmaceutical formulations.”, International Current Pharmaceutical Journal 2012, 1(8): 193-198
- Rahman et al., “Development and Validation of a Chiral HPLC Method for Quantitative Analysis of Enantiomeric Escitalopram.” J. Pharm. Sci., , 2017, 16(2): 165-172
- Bhupendrasinh et al., “Development and Validation of Stability Indicating Rp-Lc, Short Runtime Method for The Estimation of Escitalopram in Escitalopram Dosage Form.”, World Journal of Pharmaceutical research, 2013, 2(4), 1018-1030.
- Perumal, Durga Devi, Manikandan Krishnan, and K.S. Lakshmi. 2022. “Eco-Friendly Based Stability-Indicating RP-HPLC Technique for the Determination of Escitalopram and Etizolam by Employing QbD Approach.” Green Chemistry Letters and Reviews, 2022, 15 (3): 671–82
- Rajendra B. Kakde*, Dinesh D. Satone, Kamalesh K. Gadapayale and Megha G. Kakde, “Stability-Indicating RP-HPLC Method for the Simultaneous Determination of Escitalopram Oxalate and Clonazepam”, Journal of Chromatographic Science 2013;51:490–495.
- Pgeetha Swarupa et al.,” Development and Validation of Stability Indicating Rp-Hplc Method for Simultaneous Estimation of Escitalopram and L-Methylfolate In Bulk and Tablet Dosage Form”, Rasayan J. Chem., 2019, 12(4), 2338-2347
- Kamboj Sweta ET. AL., “Development and Validation of Analytical Method by Reverse Phase HPLC for the Estimation of Escitalopram oxalate in Bulk and Dosage form.,” Research Journal of Pharmacy and Technology, 2023, 16(10), 4549-4553
- Nareshkuma et al., “Stability Indicating Chromatographic Method Development and Validation for The Simultaneous Estimation of Escitalopram Oxalate and Flupentixol in Its Pharmaceutical Dosage Form by Hplc”, WJPS, 2017, 6(17), , 549-566.
- Wrushali A. Panchale 1, Shivrani W. Nimbokar 1, Bhushan R. Gudalwar 2, Ravindra L. Bakal 1 and Jagdish V. Manwar 2, *, “RP-HPLC method for simultaneous determination of escitalopram oxalate and flupentixol HCl in tablet dosage form.” GSC Biological and Pharmaceutical Sciences, 2021, 14(01), 169–174
- Mondal Prasenjit*, Kola Venu, “A New Stability Indicating Validated RP-HPLC Method for Simultaneous Estimation of Escitalopram and Clonazepam in Bulk and Tablet Dosage Form.” Asian Journal of Pharmaceutical Analysis, 2019, 9(4), 193-198
- Epuru Manoharreddy1,2, Reddy V Ravinder2, Reddy P Nagarjuna3, Ravada Kishore4, Kashanna Jajula5, Pilli V V N Kishore1, *, “RP-HPLC method development and validation for simultaneous estimation of escitalopram oxalate and atazanavir sulphate in bulk and dosage form.” AJRC, 2023, 16(2), 163-168
- Gandhi et al, “Spectrophotometric and Reversed-Phase High-Performance Liquid Chromatographic Methods for Simultaneous Determination of Escitalopram Oxalate and Clonazepam in Combined Tablet Dosage Form,” Journal of AOAC International, 2008, 91(1), 33-38.
- Kale et al., “Analytical Method Development and Validation for Simultaneous Estimation of Olanzepine and Escitalopram Oxalate by Using HPLC and UV Spectrophotometric Method.” World Journal of Pharmacy and Pharmaceutical Sciences, 2019, 8(7), 1558-1567.
- Devi et al, “Development and Validation of HPLC Method for The Estimation of Escitalopram Oxalate and Tolterodine Tartrate in Oral Dosage Forms.” WJPR, 2019, 8(3), 1132-1145.
- Seema Sheladia, Bhavesh Patel, “Determination of Escitalopram Oxalate and L-Methylfolate in Tablet by Spectrophotometric and Reverse Phase High-Performance Liquid Chromatographic Methods.” Journal of Chromatographic Science, 2017, 55(5), 550–555,
- Malathi S.*, Ananthi H, “Development and validation of HPTLC method for the estimation of escitalopram oxalate and flupentixol dihydrochloride in pharmaceutical formulation.” Research Journal of Pharmacy and Technology 2022, 15(11), 5255-5259
- Mahadik, Dhaneshwar & Kulkarni, “Application of Stability Indicating HPTLC Method for Quantitative Determination of Escitalopram Oxalate in Pharmaceutical Dosage Form.” Eurasian Journal of Analytical Chemistry, 2007, 2(2), 101-117.
- Rajendra Kakde, Dinesh Satone & Nilesh Bawane, “HPTLC Method for Simultaneous Analysis of Escitalopram Oxalate and Clonazepam in Pharmaceutical Preparations.” JPC – Journal of Planar Chromatography – Modern TLC, 2009, 22, 417–420
- Nilesh Dhavale, Santosh Gandhi, Shweta Sabnis & Kailash Bothara, “Simultaneous HPTLC Determination of Escitalopram Oxalate and Clonazepam in Combined Tablets.” Chromatographia, 2008, 67, 487–490
- SonuSundd Singh, Hiten Shah, Sapna Gupta, Manish Jain, Kuldeep Sharma, Purav Thakkar, Ruchy Shah, “Liquid chromatography–electrospray ionisation mass spectrometry method for the determination of escitalopram in human plasm, and its application in bioequivalence study.” Journal of Chromatography B, 2004, 811(2), 209-215
- Fadime Canbolat, Dilek Meltem Tasdemir Erinç, Alper Evrensel, Ahmet Ayd?n, Ka?if Nevzat Tarhan, “Quantitation of escitalopram and its metabolites by liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry in psychiatric patients: New metabolic ratio establishment.” Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol. 2019, 124, 285–297


 Mahima Dave*
Mahima Dave*
 Priyanka Patil
Priyanka Patil






 10.5281/zenodo.14000510
10.5281/zenodo.14000510