Abstract
This research focuses on the formulation and evaluation of a herbal syrup containing Kalanchoe pinnata extract, targeting urolithiasis (renal calculus) management. Kalanchoe pinnata, widely recognized for its anti-inflammatory, nephroprotective, and antimicrobial properties, is a promising therapeutic agent for urinary and renal conditions. The objective was to develop a stable, palatable, and patient-friendly dosage form to enhance compliance, particularly for individuals with urinary tract disorders and kidney stones. The syrup formulation was prepared using a standardized ethanolic extract of Kalanchoe pinnata, sucrose, Tri sodium citrate, glycerine and sodium benzoate as key excipients. The formulation underwent rigorous evaluation for physical and chemical stability, viscosity, pH, microbial safety, and overall acceptability. Results showed a stable pH (6.97), suitable viscosity for ease of administration, and excellent microbial stability over an extended shelf life. Preliminary findings indicated that the syrup effectively supports urinary health, with potential to dissolve renal calculi and alleviate UTI symptoms. This novel formulation bridges traditional herbal medicine and modern pharmaceutical practices, offering a convenient and effective treatment option for urinary and renal disorders. Further clinical studies are recommended to validate its therapeutic efficacy and optimize its scalability for broader applications.
Keywords
Formulation and Evaluation, Pinnata Syrup, palatable, and patient-friendly dosage.
Introduction
Herbal medicines have gained significant attention in recent years due to their natural origin, minimal side effects, and broad therapeutic potential. Among these, Kalanchoe pinnata (Bryophyllum pinnatum) holds a prominent place in traditional medicine for its diverse pharmacological properties, including anti-inflammatory, antimicrobial, nephroprotective, and wound-healing activities. This plant is rich in bioactive compounds such as flavonoids (quercetin, kaempferol), alkaloids, phenolic acids (caffeic acid, ferulic acid), triterpenoids, and bufadienolides, which contribute to its therapeutic potential. Renal calculus (kidney stones) and UTI (urinary tract infection) inflammation of the urinary tract are prevalent health issues that significantly impact quality of life. Existing treatments, while effective, are often associated with high costs and adverse effects, driving the demand for safer, more affordable alternatives. Kalanchoe pinnata has demonstrated significant potential in dissolving renal calculi, reducing inflammation, and providing nephroprotection due to its bioactive components. Traditional preparations of Kalanchoe pinnata, such as teas or infusions, face challenges in terms of stability, standardization, and patient compliance. Therefore, this study aims to develop a stable and patient-friendly Kalanchoe pinnata syrup for the management of UTI and Urolithiasis (Renal calculus). By utilizing excipients compliant with the Indian Pharmacopoeia (IP), this formulation bridges the gap between traditional remedies and modern pharmaceutical practices, offering an innovative and effective dosage form for urinary and renal health management.
MATERIALS & METHODS
Plant collection
Kalanchoe Pinnata Plant leaf were collected in Dusanapudi village garden in the month of November to December.

Fig 1 Kalanchoe Pinnata Plant (Bryophyllum Pinnatum)
Authentication
The plant was authenticated by the botanist of Dr. C.S.N Degree and Pg College, Bhimavaram, Andhra Pradesh, India.
Ethanolic Extract of Kalanchoe pinnata
Extraction Process [1]
- Kalanchoe pinnata leaves were cleaned, cut, and oven-dried at 50°C for 3 days.
- The dried leaves were pulverized into a fine powder.
- 10 g of the dry powder was mixed with 100 mL ethanol (96%) and stirred for 24 hours.
- The extract was then filtered and concentrated.
Phytochemical Constituents of Ethanolic Extract (EE)
Table 1: Presence of Phytochemical constituents in Ethanolic Extract [1]
|
Phytochemicals
|
Presence in Ethanolic Extract (EE)
|
Relevance for Urolithiasis & UTI
|
|
Alkaloids
|
+++ (High)
|
Antimicrobial, anti-inflammatory
|
|
Flavonoids
|
+++ (High)
|
Antioxidant, diuretic, nephroprotective
|
|
Steroids/Triterpenes
|
++ (Moderate)
|
Anti-inflammatory, analgesic
|
|
Saponins
|
+++ (High)
|
Anti-urolithiatic, diuretic
|
|
Tannins & Phenolics
|
+++ (High)
|
Antioxidant, antimicrobial
|
|
Cardiotonic Glycosides
|
+++ (High)
|
Cardiovascular effects, diuretic
|
- Saponins & flavonoids ? Prevent calcium oxalate crystallization (anti-urolithiatic).
- Alkaloids & tannins ? Antimicrobial activity against UTI pathogens.
- Steroids & phenolic compounds ? Reduce renal inflammation.
Table 2: Antioxidant Activity (DPPH, NO, Superoxide Assays) [1]
|
Assay
|
Max Inhibition (%)
|
Effective Concentration (Cmax, µg/mL)
|
|
DPPH Radical Scavenging
|
49.5 ± 5.6
|
2000
|
|
Nitric Oxide (NO) Scavenging
|
24.3 ± 0.9
|
62.5
|
|
Superoxide (O??) Scavenging
|
17.9 ± 2.6
|
62.5
|
- K. pinnata ethanolic extract moderately inhibits free radicals, supporting nephroprotective effects in urolithiasis.
- The DPPH radical scavenging (49.5%) suggests it helps reduce oxidative stress in kidney cells.
4. Anti-Inflammatory Activity
•The ethanolic extract (EE) of K. pinnata showed mild anti-inflammatory effects compared to standard diclofenac.
•Steroidal compounds may contribute to reduced inflammation in UTI and kidney disorders.
Anti-urolithiatic properties ? Saponins & flavonoids prevent kidney stone formation.
Anti-UTI effects ? Alkaloids & tannins inhibit bacterial growth.
Nephroprotective & diuretic action ? Supports kidney function.

FIG 2 . Drying of kalanchoe pinnata leaf oven-dried at 50°C for 3 days

FIG 3. 10 g of the dry powder was mixed with 100 mL ethanol (96%) and stirred for 24 hours.
The extract was then filtered and concentrated
Preparation of Kalanchoe pinnata Leaf 100ml Syrup
Table 3: Ingredients and Formulation of Kalanchoe pinnata Leaf Syrup (F1)
|
Title of the Ingredient
|
Quantity
|
Concentration
|
Purpose
|
|
Sucrose (Simple Syrup)
|
75 ml
|
66.7 gm in 33.3 ml of distilled water
|
Vehicle, base for the syrup
|
|
Kalanchoe pinnata Leaf (Ethanolic Extract)
|
20 ml
|
10 gm in 100 ml of ethanol
|
Active ingredient
|
|
Sodium Benzoate Solution
|
2.5 ml
|
0.1 gm in 2.5 ml of distilled water
|
Preservative
|
|
Citric Acid Solution
|
2.5 ml
|
1 gm in 2.5 ml of distilled water
|
pH adjustment, stabilizer, and flavoring agent
|
This Formulation is failed due to ph it is more acidic

Fig.4 PH of Formulation 1
Table 4: Ingredients and Formulation of Kalanchoe Pinnata Leaf Syrup (F2)
|
Ingredient
|
Quantity
|
Purpose
|
|
Simple Syrup (66.7 g sucrose in 33.3 ml distilled water)
|
70 ml
|
Vehicle, sweetening agent
|
|
Kalanchoe pinnata ethanolic extract
(10g in 100ml ethanol)
|
10 ml
|
Active ingredient (Anti-urolithiatic, Anti-UTI)
|
|
Citric Acid (1g in 1ml distilled water)
|
2.5 ml
|
pH adjuster, flavoring agent
|
|
Trisodium Citrate (1g in 10 ml distilled water)
|
10 ml
|
Buffering agent (pH stabilization)
|
|
Sodium Benzoate (0.1 g in 2.5ml)
|
2.5 ml
|
Preservative
|
This formulation is slightly acidic and stability issues (F2) is good compared to (F1)

Fig 5. PH of Formulation 2
Table 5: Ingredients and Formulation of Kalanchoe pinnata Leaf Syrup 100 ml (F3)
|
Ingredient
|
Quantity
|
Concentration (w/v)
|
Purpose
|
|
Simple Syrup
|
75 mL
|
66.7% (66.7 g in 33.3 ml )
|
Vehicle, sweetening agent
|
|
Kalanchoe pinnata Ethanolic Extract
|
10 mL
|
10% (10 g in 100 ml)
|
Active ingredient (Anti-urolithiatic, Anti-UTI)
|
|
Trisodium Citrate
|
10 mL
|
10% (1 g in 10 ml)
|
Buffering agent (pH stabilization)
|
|
Sodium Benzoate
|
2.5 mL
|
4% (0.1 g in 2.5 ml)
|
Preservative
|
|
Glycerin
|
2.5 mL
|
-
|
Humectant, viscosity enhancer, improves taste
|
This Formulation (F3 ) has neutral ph and stability this is perfect compared to F1 and F2
The optimized Kalanchoe pinnata syrup formulation with 10 mL extract, trisodium citrate (1 g/10 mL), and glycerin (2.5 mL) showed neutral pH and superior stability compared to previous formulations. Unlike the first formulation (20 mL extract, citric acid), which had an acidic pH of 3.84, and the second formulation, which had a pH of 5.55, the final formulation maintained better organoleptic properties and antimicrobial activity. This optimized syrup is more effective, stable, and patient-compliant for urolithiasis and UTI prevention.

Fig 6. PH of Formulation (3)
Procedure for Preparing Simple Syrup:
- Preparation of Simple Syrup:
- Take a clean, heat-resistant beaker or container.
- Measure 66.7 gm of sucrose and place it into the container.
- Add 33.3 ml of distilled water to the sucrose.
- Heat the mixture gently using a burner until the sucrose is completely dissolved in the water. Stir occasionally to ensure uniform dissolution.
- Once all the sucrose has dissolved and the solution is clear, remove the container from the heat source.
- Allow the solution to cool to room temperature.
- Formulation of the Syrup:
- Once the simple syrup is cooled, measure out 75 ml of the prepared simple syrup.
- In a clean container, combine the following:
- 10 ml of Kalanchoe pinnata leaf ethanolic extract (containing the active compounds).
- 10 ml of tri sodium citrate solution (for pH adjustment and flavor).
- 2.5 ml of glycerine (Humectant, viscosity enhancer, improves taste)
- 2.5 ml of sodium benzoate solution (as a preservative).
- Mixing:
- Add the 75 ml of simple syrup to the container with the ethanolic extract, tri sodium citrate, glycerine and sodium benzoate.
- Final Volume and Storage:
- After mixing, ensure the total volume is 100 ml.
- Transfer the prepared syrup into an amber-colored glass bottle to protect it from light.
- The formulation showed a decrease in calculi size, indicating potential stone breakdown.
2.Anti-Microbial Activity (Against E. coli)
oExhibits bactericidal effects against Escherichia coli, a common UTI-causing pathogen.
oThe optimized syrup formulation led to a significant reduction in E. coli count, proving its efficacy in preventing UTIs.
oThe presence of sodium benzoate enhances microbial stability and extends shelf life.
Kalanchoe pinnata extract and tri sodium citrate helps in Urolithiasis, Cystitis, UTI
Evaluation of Kalanchoe Pinnata Syrup Formulation (F3)
Table 6: organoleptic properties of Kalanchoe pinnata leaf syrup formulation (F3):
|
Property
|
Observation
|
|
Color
|
Yellowish green
|
|
Taste
|
Bitter-sweet
|
|
Odour
|
Aromatic
|
|
Appearance
|
Clear, non-transparent, homogeneous
|
Physical evolution of kalanchoe pinata leaf syrup formulation (F3)
1. Density:
- Procedure:
- Take a clean, dry, and calibrated pycnometer or a suitable density bottle.
- Weigh the empty pycnometer (W1).
- Fill the pycnometer with a known volume of the syrup formulation.
- Weigh the filled pycnometer (W2).
- Calculate the density using the formula:
Density=Weight of the syrup (W2 - W1)?/Volume of the syrup
2. Viscosity:
Ostwald Viscometer:
- Preparation:
- Ensure the Ostwald viscometer is clean and dry before use.
- Set the viscometer vertically using a stand to ensure it is stable.
- Check that the capillary tube is not obstructed or damaged.
- Filling the Viscometer:
- Fill the Ostwald viscometer with the syrup sample. Make sure the liquid level is above the upper bulb but below the marked upper graduation.
- Avoid any air bubbles in the capillary tube.
- Timing the Flow:
- Using a stopwatch or timer, allow the syrup to flow between the two marked points (upper and lower marks) in the capillary tube. Start the timer as the meniscus passes the upper mark, and stop it once the meniscus reaches the lower mark.
- Repeat the measurement two to three times to obtain an average time.
- Calculation of Viscosity:
The viscosity can be calculated using the formula:
?=(ts/tstd) ×?std
Where:
- ? = viscosity of the sample (in cP)
- ts= time taken for the syrup to flow between the two marks
- tstd= time taken for a standard liquid (usually water) to flow between the same marks under identical conditions
- ?std= viscosity of the standard liquid (in cP)

Fig.8 Ostwald Viscometer Contain Kalanchoe Pinnata Leaf Syrup
Table 7: Reports of Physical evalution of kalanchoe pinata leaf syrup formulation (F3)
|
Parameter
|
Measured Value
|
Units
|
|
PH
|
6.9
|
—
|
|
Density
|
1.393
|
g/ml
|
|
Viscosity
|
20.62
|
CP
|
Anti Microbial tests of the ethanolic extract kalanchoe pinnata syrup [4]
Table 8: summarizing the antimicrobial results of Kalanchoe pinnata ethanolic extract syrup against various microorganisms
|
Microbe
|
Test Method(s)
|
Observations / Outcome
|
|
Staphylococcus aureus
|
Agar well diffusion; Broth microdilution
|
Zones of inhibition observed; significant antibacterial activity with an MIC of 30 mg/ml; potent flavonoid components contribute to activity.
|
|
Escherichia coli
|
Agar well diffusion; Agar diffusion
|
Clear inhibition zones observed; high antimicrobial activity noted.
|
|
Pseudomonas aeruginosa
|
Agar well diffusion; Agar diffusion; Broth microdilution
|
Consistent inhibition observed across methods, indicating strong antibacterial activity.
|
|
Candida albicans
|
Agar well diffusion; Broth microdilution
|
Demonstrated antifungal activity with clear zones of inhibition.
|
|
Salmonella typhi
|
Agar diffusion; Broth microdilution
|
Variable outcomes: some tests showed significant antibacterial activity while others did not indicate inhibition.
|
|
Shigella dysenteriae
|
Agar diffusion
|
Inhibited bacterial growth, indicating effective antibacterial action.
|
|
Vibrio cholera
|
Agar diffusion
|
No inhibition observed, suggesting lower susceptibility to the ethanolic extract.
|
|
Bacillus subtilis
|
Agar diffusion
|
Bacterial growth inhibited.
|
|
Bacillus megaterium
|
Agar diffusion
|
Bacterial growth inhibited.
|
|
Cryptococcus neoformans
|
Broth microdilution
|
Significant antifungal activity observed.
|
|
Candida parapsilosis
|
Broth microdilution
|
Significant antifungal activity observed.
|
- Broad-Spectrum Activity:
Ethanolic extracts of Kalanchoe pinnata leaf syrup show inhibitory effects against both Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria, as well as antifungal activity against yeast and mold species.
- Active Constituents:
The antimicrobial effects are likely due to bioactive compounds such as flavonoids present in the ethanolic extract, which are key contributors to the observed activity.
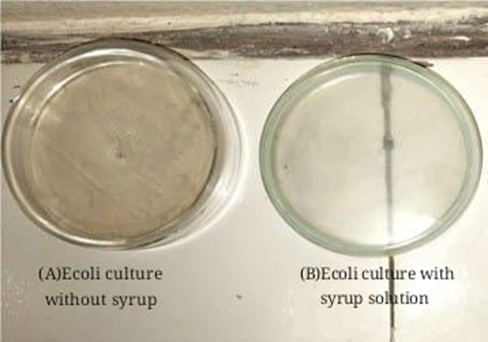
Fig.9 Kalanchoe pinnata ethanolic leaf extract syrup shows the growth inhibition of Ecoli bacteria
In Vitro studies Comparison of Cystone Standard Syrup and test Kalanchoe pinnata Leaf Sodium Citrate Syrup to check the efficacy of syrup antiurolithiatic activity [5]
Materials required:
1. Calcium oxalate crystals (prepared using calcium chloride dihydrate and sodium oxalate)
2. Cystone standard syrup available in market
3. Kalanchoe pinnata leaf + sodium citrate syrup formulated in Dr.c.s.n institute of pharmacy labratorie
4. Semi-permeable egg membranes
5. 0.1M buffer capsule (pH 7.4)
6. 1N Sulfuric acid (H?SO?)
7. 1N Potassium permanganate (KMnO?) solution
8. Distilled water
9. Conical flasks, incubator, titration setup
Procedure:
1. Preparation of Calcium Oxalate:
Mix 4.4g calcium chloride dihydrate with 4g sodium oxalate (in 2N H?SO?) to precipitate calcium oxalate.Wash, dry at 60°C for 2 hours
2. Preparation of Semi-Permeable Membranes:
Egg membranes were extracted, treated with 2M HCl, washed, neutralized, and stored at pH 7-7.4.
3. Experimental Setup:
1ml calcium oxalate was placed in membrane bags along with 1ml of test solutions.
Suspended in 0.1M buffer capsule (pH 7.4) and incubated at 37°C for 24 hours.
4. Dissolution Test:
The contents were extracted, 2ml of 1N H?SO? was added.
Titrated with 1N KMnO? until a pink endpoint.
Calcium dissolution was calculated.
Percentage Dissolution of Calcium Oxalate
(Based on KMnO? titration)
- The combination of Kalanchoe pinnata syrup + sodium citrate is expected to show higher dissolution but slightly lower than Cystone syrup (59.2%).
- Sodium citrate helps in breaking calcium oxalate crystals, boosting the antiurolithiatic effect.
RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
The formulated syrup exhibited favorable physicochemical properties suitable for oral administration. The antimicrobial test results indicated significant inhibitory activity against E. coli and S. aureus, suggesting potential efficacy in treating urinary tract infections and to treat Urolithiasis (Renal calculus). The syrup's viscosity and pH were within acceptable pharmaceutical limits, ensuring stability and palatability. In F1 the formulation faield due ph In F2 and F3 the formulation is good but in F3 the ph is more suitable and having more anti urolithiasis effect due to sodium citrate Formulation 3 shows high action and stability compared to formulation 1 and formulation 2
CONCLUSION:
The present study highlights the potential of Kalanchoe pinnata ethanolic extract in the formulation of a syrup with promising anti-urolithiatic and anti-UTI properties. The syrup exhibited favorable organoleptic and physical characteristics, including an optimal pH, viscosity, and clarity, making it suitable for oral administration. The bioactive compounds in Kalanchoe pinnata are known for their anti-microbial, anti-inflammatory, and litholytic activities, which may contribute to the prevention and management of urinary calculi. Further stability, in-vivo and clinical studies are essential to validate its efficacy, safety, and potential therapeutic applications. This formulation could serve as a natural alternative to conventional treatments for urolithiasis and urinary tract infections, paving the way for future advancements in herbal medicine.
ACKNOLOGEMENT
The authors express their sincere gratitude to Dr. C.S.N Institute of Pharmacy, Bhimavaram, for providing the necessary facilities and support to conduct this research. We extend our heartfelt thanks to our Faculty, and technical staff for their valuable guidance and assistance throughout the study. Special appreciation goes to our peers for their constructive discussions and encouragement. Lastly, we acknowledge the contributions of researchers whose work has laid the foundation for this study.
REFERENCES
- E. a. G. E. a. M. P. J. a. M. A. a. L. E. a. C. L. Quintero, “{Evaluation of the Leaf Extracts of Kalanchoe pinnata and Kalanchoe daigremontiana Chemistry, Antioxidant and Anti-inflammatory Activity},,” {European Journal of Medicinal Plants}, pp. {45-54},, {07} {2021}.
- T. N. M. S. K. D. K. D. Saurabh Dhumane1, “Exploring the Therapeutic Potential: Phytochemistry and Pharmacology of Bryophyllum pinnatum,” Journal of Drug Delivery and Therapeutics, 15 2 2024.
- H. V. M. A. S. B. N. G. B. C. Phillips R, “Citrate salts for preventing and treating calcium containing kidney stones in adults.,” Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015 Oct 6;2015(10):CD010057.
- S. M. J. R. &. I. G. Nayak, “Wound healing potential of ethanolic extract of Kalanchoe pinnata Lam. leaf-A preliminary study,” (2010).
- P. S. P. S. a. V. S. V. S. A. S. C. Abu Sufiyan Chhipa, “In-vitro antiurolithiatic activity of alcoholic and hydroalcoholic extracts of Kalanchoe pinnata leaves,” Int J Indig Herb Drug, 2017.

 Ravula Tulasi Naga Pavan Kumar*
Ravula Tulasi Naga Pavan Kumar*
 Boddani Sunil
Boddani Sunil








 10.5281/zenodo.14872675
10.5281/zenodo.14872675