Abstract
The polycystic ovarian disorder (PCOS) is defined as a combination of hyperandrogenism (hirsutism and skin breakouts) and anovulation (oligomenorrhea, barrenness, and ineffective uterine leaking), with or without the presence of polycystic ovaries on ultrasound. It addresses the fundamental endocrine issue in the conceptional age, which affects 6%-15% of women in danger. It is the most generally recognized cause of barrenness due to anovulation and the predominant cause of female fruitlessness. PCOS is discovered in 30%-40% of individuals with essential or auxiliary amenorrhea and 80% of people with oligomenorrhea before the onset of a menstrual problem. PCOS should be diagnosed and treated early in life due to the conceptive, metabolic, and ontological issues that may be associated with it. Medication, food, and lifestyle changes are all possible treatment options. The likelihood of becoming pregnant varies among healthy young couples. In 2010, an estimated 48.5 million couples worldwide were infertile. This study provides a survey of barrenness causes, examinations, treatment modalities, and the role of a medical attendant birthing specialist in managing infertile couples. Barrenness (a condition of sub-richness) can be defined as the failure to become pregnant, the inability to maintain a pregnancy, or the failure to carry a pregnancy to term. Male and female infertility have various causes.
Keywords
Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), complication, causes and treatments.
Introduction
The first common endocrine disorder, polycystic ovarian syndrome (PCOS), affects 5.18% of women at reproductive age [1,2]. Hyperandrogenism and careful anovulatory behavior in women who are not fertile are symptoms of polycystic ovary syndrome.[3] The ovaries of a woman affect about 68% of people worldwide. increased testosterone, inconsistent menstruation, and small cysts. An overall knowledge that was undermined in 2003 by hyperandrogenic appearances included skin breakouts, hirsutism, dyslipidemia, diabetes, insult resistance, rotundity, illness, desolation, and coronary heart infections[4]. Please. In accordance with the Rotterdam Criteria of 2003, polycystic ovaries are defined as having at least 12 follicles in close proximity to one ovary, with a breadth of 2 to 9 mm, and an additional ovarian gauge of 10 milliliters (2004).[5] The symptoms of PCOS include oligo- or amenorrhea, polycystic ovaries, clinical or biochemical hyperandrogenism, and the presence of these conditions in close proximity. [6] According to ASRM (American Society of Regenerative Medicine), PCOS can be caused by a variety of etiologies, including Cushing disease, hyperprolactinemia, adrenal hyperplasia, thyroid brokenness, and androgen-releasing tumors. Polycystic ovaries, perpetual anovulation, and hyperdogenism (clinical or biochemical). As early as 1921, hyperandrogenism and insult were linked. Researchers have since deduced that the majority of women with hyperandrogenism exhibit symptoms of a disorder known as polycystic ovarian syndrome (PCOS).[7] The total power of deep rooted anovulation (CA) ranges from 2.2% to 26% in Western countries.2% to 7.5% in China; 6.3% in Sri Lanka; and 9.13% to 36% in India. [8,9] Patients with this condition have an increased risk of developing insult resistance (IR), obesity, dyslipidmia, cardiovascular disease (CVD), and endometrial carcinoma IR and hyperinsulinemia are skilled for the second rate rooted foundat. Aggravationof it’s first normal [9,10] The reason for desolateness is anovulation. In some nation it address the primary factor for female .

Fig No 1 ): Female Reproductive System: Polycystic ovarian Syndrome
There are four main types of PCOS that women can be diagnosed with, each with a Different Subset of Symptom And Treatmen

2. Pathophysiology and risk considerations:
One predominant characteristic of PCOS patients is their high androgen levels. Elevated blood levels of free (unbound) testosterone, a crucial hormone in the pathogenesis of PCOS, are indicative of hyperandrogenism. The primary pathophysiological components of this complex illness are broken down [11] .As shown in Fig2. , the predisposing risk factors for polycystic syndrome include genetics, neuroendocrine, lifestyle/environment, and obesity. Due to predominate genes, certain women are more likely to have PCOS ([12] According to a number of genome-wide association studies (Hayes et al., 2015, Shi et al., 2012, Dumesic et al., 2015), some loci and alleles are crucial in identifying the PCOS phenotype.Environmental elements, such as diet, lifestyle, and physicaactivity ,mighdiffergreatldepending on the population [13 ] . According to Rutkowska and Diamanti-Kandarakis [14].environmental variables can also result in genetic variation, disturbance of the metabolic and reproductive pathways, and endocrine-disrupting chemicals and glycotoxins, which can lead to PCOS phenotypes and associated difficulties. According to Dumesic et al. [15] .and androgen exposure can impair hormone levels and raise the high pulse frequency of GnRH, which affects the LH: FSH ratio and causes follicular arrest and dysplasia.

Fig.2. PCOS Risk change Factors
These factors produce hyperinsulinemia, hyperandrogenism, oxidative stress, and irregular periods, all of which contribute to the metabolic syndrome. PCOS was named after several ovarian cysts (undeveloped follicles) found during an ultrasound test. The follicles originated from primitive follicles, but due to impaired ovarian function, development stopped early.

Fig No. 3): Pathophysiology Of PCOS :
2.1) PCOS & Hyperandrogenis :
Impaired folliculogenesis is caused by excess androgens, which disturb normal androgen production. Excess androgens stimulate the formation of primordial follicles and an increase in antral follicles during the early gonadotropin stage [16]. GnRH discharge from the hypothalamus causes the pituitary gland to release gonadotropin hormones. Luteinizing hormone activates the LH receptor in ovarian theca cells, promoting androgen synthesis, whereas follicular stimulating hormone acts on the FSH receptor in ovarian granulosa cells, converting androgens to estrogens that drive follicle growth. [17].It is hypothesized that instability in the neuroendocrine system causes an imbalance in the hypothalamic-pituitary-ovarian axis, resulting in a surplus of gonadotropin. In PCOS, elevated GnRH levels boost the production of LH over FSH, leading to a significant increase in the LH:FSH ratio [18]
2.2)Insulin Resistance and type two Diabetes:
The primary cause of excess androgens is hyperinsulinemia since insulin raises GnRH indirectly and directly mimics the action of LH [19]Sex hormone binding globulin (SHBG), a major circulatory protein that regulates testosterone levels, is decreased by insulin. [20] decreased SHBG would therefore lead to an increase in free androgens, which cause clinical symptoms such hirsutism, alopecia, and acne. Patients with PCOS are more likely to develop diabetes and cardiovascular disease due to insulin resistance, which can also result in dyslipidemia [21]According to the NIH criteria, the AE-PCOS definition, and the ESHRE/ASRM criteria, respectively, the prevalence of PCOS in women with type 1 diabetes is 19%, 37%, and 41% [22]A cross-sectional study conducted in 1999 among women in the United States found that up to 35% of them had IGT and up to 10% had T2D. According to several research [23] managing insulin resistance will gradually reduce the excess androgens and ameliorate the disease.
2.3) Obesity and PCOS:
Obesity has been linked to aberrant hypothalamic-pituitary-ovarian axis function, resulting to PCOS development [24]. Obesity is associated with hyperinsulinemia, which raises the lipid profile and glucose intolerance in PCOS patients. Obesity increases androgen synthesis by activating LH, resulting in hyperandrogenism [25]. Leptin, an appetite-controlling adipokine, directly affects the neuroendocrine and reproductive function of obese PCOS women [26] Additionally, hyperleptinemia can impair ovarian follicular development [27]. Thus, reducing visceral fat would influence hunger, glucose levels, lipolysis, and raise SHBG, thereby regulating androgen action in the ovary.[28]
3) Evaluation Of polycystic ovarian Syndrome
3.1)Acne Vulgaris: Patient with pcos complain of inflammatory acne that responds minimally to standard therapy .[29]. Even if responsive, lesions return quickly after ceasing treatment, necessitating treatment With Oral.

Fig No .4): Acne With Hirsutism in a Patient with PCOS:
Isotretinoin and/or hormonal therapy. An essential feature found in these patients is the formation of many closed comedones that quickly turn into tender, lumpy nodules spread in the lower half of the face and jawline (V distribution) .[30] These typically last longer than 5-7 days. A premenstrual flare is also prevalent. Acne lesions can appear on the chest, shoulders, and back,well as the face. Prompt relapse after discontinuing treatment clearly supports a hormonal cause.Patients may also have a history of irregular periods, hirsutism, alopecia, or a PCOS-positive family [31]. The intensity of hirsutism may not equal the severity of acne and would be reliant on the balance of activity between the alfa-hydroxy type 2 vis-a-vis type.
3.2) Hirsutism:
Excessive facial hair is a racial feature found throughout the Indian subcontinent, particularly among certain ethnic groups.[32] This should be kept in mind while assessing individuals who complain of excessive facial/body hair. Androgens influence several elements of follicular activity. [33] stimulate hair growth, diameter, and melanization in areas sensitive to androgens via acting on androgen receptors and secretory factors. These dense, coarse, terminal hairs in androgen-dependent areas are ugly on females and indicate an underlying hyperandrogenic state . The degree of hirsutism is assessed using a modified Ferriman-Galway score, which analyzes nine body locations on a range of 1 to 4. If the total score exceeds 6 to 8, it is considered important
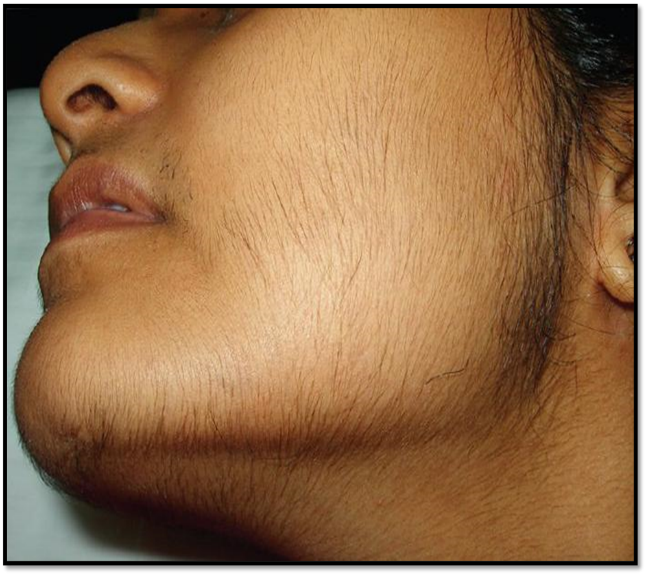
Fig No. 5): Hirsutism In a Patient with PCOS
3.2) Alopecia
Female pattern hair loss (FPHL) is not always caused by androgens. [34]Patterned hair loss in PCOS might be difficult to distinguish from that caused by other hyperandrogenic conditions [Figure 6]. Ludwig (diffuse), Hamilton (male pattern), and Olsen (frontal accentuation) all describe different clinical manifestations.] Women with early-onset FPHL are substantially more likely to exhibit hyperandrogenism. Hormonal effects cause terminal hair to change to vellus hair, giving the scalp the appea.

Fig No. 6) : Patterned Hair Loss Width bi – temporal in a Patient with PCOS
3.3) Acanthosis Nigricans :
Typically, thick black velvety skin on the nape of the neck, axillae, groins, and other frictional areas may be the first sign of insulin resistance [Figure 7)]. The thickening is caused by the activation of tyrosine kinase growth factor signaling pathways in the epidermis. Insulin-like growth factor receptor 1 (IGF1R) is found in numerous organs, including the epidermis and ovary[35]. High levels of insulin directly or indirectly stimulate the IGF1R, causing skin changes. Skin tags in frictional locations like the neck, axillae, groins, infra mammary, or even under a pendulous abdominal fold are widespread, especially in fat people.

Fig No.7) : Acanthosis Nigricans and Hirsutism in an obese girl with PCOS
3.5) Irregular Menses and Infertility:
PCOS is characterised by chronic menstrual irregularities or changes in menstrual pattern with reduced fertility. The anovulatory or oligoovulatory cycles result in continuous endometrial stimulation with estrogens, resulting in endometrial hyperplasia, thus increasing the risk of endometrial cancers. [36]
4) Physical Examination :
4.1) Anthropometry:
It is important to measure height (metres) and weight (kilograms), calculate body mass index (BMI) (kg/m?2;) and assess body fat distribution by waist, hip and the waist-to-hip ratio (WHR) [40] at baseline and during follow-up. [37]Waist circumference may add additional information as to the cardiovascular risk profile for individual women. In addition to truncal obesity, a buffalo hump and supraclavicular fat deposition may suggest the presence of Cushing's syndrome.
4.2) Skin:
Excess terminal (thick pigmented) body hair in a male distribution is known as hirsutism. It is typically observed on the upper lip, chin, breast periareolar area, midsternum, and lower abdomen's linea alba. There is a significant ethnic variation in hirsutism; Asian women, for instance, typically exhibit lower levels of hirsutism [38] It's important to distinguish hirsutism from hypertrichosis, which is the excessive growth of vellus, androgen-independent hair that is prominent in non-sexual areas. Hypertrichosis is typically familial or brought on by medications (phenytoin, penicillamine, diazoxide, minoxidil, or cyclosporine) or systemic disorders (hypothyroidism, anorexia nervosa, malnutrition, porphyria, and dermatomyositis). The Ferriman and Gallway score is the most used semi-quantitative technique for hirsutism estimation [39] Recent research, however, lends credence to the theory that facial hair development may be more significant than that of other body areas [40]The effectiveness of the treatment can be readily measured and monitored with the use of this score. In descending order of severity, blackheads, whiteheads, inflammatory lesions, severe pustular lesions, and scars are typical acne lesions. Different stages of acne can be evaluated [41] and these grades are strongly by prior topical, systemic, and cosmetic therapies. Despite the lack of controlled trials, it is evident that women with PCOS require evaluation and therapeutic monitoring. The Ludwig score [42] is one well-known subjective approach for grading androgenic alopecia. Dermatologists can provide more advanced information since they are comfortable using far more involved diagnostic techniques, such as standardized hair removal and weighing in a specific area. taking pictures and determining the density of hair in specific scalp areas.Additional skin observations that need to be looked for are striae, thin skin, or bruises, which could indicate
Cushing's syndrome, seborrhea, and acanthosis nigricans. Particular importance is given to Acanthosis nigricans in the clinical assessment of PCOS. This is a typical finding in women with PCOS, especially in those who are obese, as previously described. It can be located in the axillary area and on the nape of the neck, as well as occasionally in other body regions like the hands, elbows, and skin folds. Its existence might serve as a cutaneous indicator of the metabolic syndrome and insulin resistance. However, a study comparing clinical staging with histological examination has shown that it may be poorly defined, and clinical skin examination may be particularly insensitive for diagnosing acanthosis nigricans.
4.3) Reproductive System:
When a diagnosis is made, a thorough examination of the reproductive system should be carried out, as well as any necessary follow-up exams depending on the initial results and symptom progression. Together with the required assessment for pathologic masses, the breast exam should include a special evaluation for atrophy, which is possible evidence of substantial hyperandrogenemia, and galactorrhea. Examining the external genitalia for signs of clitoromegaly should trigger a search for undetected class 21-hydrxilase deficiency or androgen-producing neoplasms. The presence of the internal genitalia—the uterus, ovaries, and vagina—should also be confirmed by the examination. If not, it is necessary to evaluate the possibility of other uncommon reasons of hyperandrogenism (ex testicular feminization) and amenorrhea.Pelvic ultrasound may help with the physical examination, thus the diagnosis of PCO should be made using the criteria provided by the Rotterdam Consensus Conference , until revised.
4.4) General:
PCOS is a systemic illness that necessitates a thorough physical examination from head to toe in an objective search for anomalies. Physical diagnosis skills are learned via experience, but success in eliciting signals is determined by more than technique, and it represents a way of thinking rather than a method of doing. The preceding paragraphs focused on anthropometry, symptoms of androgen excess, and a comprehensive study of the reproductive system. Always monitor arterial blood pressure and do a thorough examination of the cardiovascular system. The abdominal
examination should include a measurement of liver size (to rule out hepatic enlargement owing to NAFLD) as well as palpation for adrenal and pelvic masses, if possible.
4.5) Differential Diagnosis;[43]
PCOS is frequently diagnosed as an exclusionary condition. Other causes of hyperandrogenism include hyperprolactinemia, medications (danazol and androgenic progestins, valproate), non-classic congenital adrenal hyperplasia, Cushing's disease, and androgen secretory tumors (ovarian or adrenal). Acne rosacea (which typically responds to antibiotic therapy and is not a feature of PCOS), acne fulminans (which is most common in adolescent males and is associated with fever, arthalgias, and leukocytosis), and the SAPHO syndrome (defined as synovitis, acne, pustulosis, hyperostosis, and osteitis and necessitates referral for systemic therapy). Other reasons of menstruation dysfunction, such as pregnancy, ovarian failure, outflow track obstruction, and hypothalamic amenorrhea, should be evaluated in the appropriate therapeutic setting
- The differential diagnoses for polycystic ovarian disease include the following:
1) Use of androgenic steroids
2) Hypothyroidism
3)Late-onset congenital adrenal hyperplasia
4)Idiopathic/familial Hirsutism
5)Ovarian malignancies
1) Pelvic Examination:
During a pelvic exam, your doctor will examine your reproductive organs for lumps, growths, or other changes.
2) Blood Test:
Hormone levels can be measured by blood tests. This testing can rule out potential causes of menstrual irregularities or androgen excess that resemble PCOS. You may also have other
blood tests, such as fasting cholesterol and triglyceride readings. A glucose tolerance test assesses your body's response to sugar.
3) Ultrasound:
An ultrasound can check the appearance of your ovaries and the thickness of the lining of your uterus. A wandlike device (transducer) is placed in your vagina. The transducer emits sound waves that are translated into images on a computer screen.
Treatment /Management:
1)Lifestyle Changes :
Exercise and calorie-restrictive diets are the most effective first-line therapies for weight loss and IGT in overweight and obese PCOS women and adolescents. Numerous studies have demonstrated that hirsutism can enhance and control ovulation and the menstrual cycle. In an attempt to better address hyperinsulinism, low-carb diets have been employed; however, research has not revealed any discernible differences in the results obtained from these diets.
2) Hormonal Contraceptive:
Every patient should be screened for hormonal contraceptive contraindications. Absolute contraindications include women 35 and older who smoke more than 15 cigarettes per day, uncontrolled hypertension more than 160/100, and uncontrolled diabetes with severe peripheral vascular disease. When numerous comorbidities are present, the United States Medical Eligibility Criteria For Contraceptive Use can be useful. Patients with diabetes who do not have vascular problems are not contraindicated from using hormonal contraceptives. In terms of hormonal contraception's metabolic consequences, increased estrogen activity raises HDL cholesterol while decreasing LDL cholesterol. There is no difference in body weight or fat distribution between PCOS and healthy women The initial oral contraceptive dose is 20 mcg of ethinyl estradiol mixed with a progestin that has antiandrogenic qualities, such as desogestrel and drospirenone, or has neutral effects, such as norethindrone acetate. Progestin with antiandrogenic effects has been linked to an increased risk of venous thromboembolism. If hyperandrogenic symptoms do not respond fully to this initial dose, ethinyl estradiol can be increased to 30 to 35 mcg.
Medication:
1) Metformin:
The Endocrine Society recommends that PCOS patients with DM2 or IGT who do not respond to lifestyle changes begin using metformin. It reduces the progression from IGT to DM2. Metformin also improves menstrual cycles, waist-to-hip ratio, and vascular indicators in non-obese women with PCOS.[19] Metformin is also used as a second-line treatment for menstrual abnormalities in people who cannot use hormonal contraception. It is often used in teenage monotherapy to restore normal menstrual cycles, promote weight loss, and minimize insulin resistance. Although it should not be used to treat clinical hyperandrogenism, it can alleviate androgen excess symptoms.
Therapeutic uses
- Restoring ovulation,
-Redusing weight
-reducing circulating androgen levels,
- reducing the risk of miscarriage and reducing the risk of gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM)
- To regulate your periods, your health care provider might recommend:
.2) Combination birth control pills.
Pills that include both estrogen and progestin reduce androgen production while regulating estrogen. Hormonal regulation can reduce the risk of endometrial cancer while also treating irregular bleeding, excessive hair growth, and acne.
2) Progestin therapy.
Taking progestin for 10 to 14 days every 1 to 2 months can help you regulate your periods and prevent endometrial cancer. This progestin medication does not reduce testosterone levels and will not prevent conception. If you want to avoid pregnancy, you should use a progestin-only minipill or an intrauterine device that contains progestin.
- To help you ovulate so that you can become pregnant, your health care provider might recommend:
3) Clomiphene.
Taking progestin for 10 to 14 days every 1 to 2 months can help you regulate your periods and prevent endometrial cancer. This progestin medication does not reduce testosterone levels and will not prevent conception. If you want to avoid pregnancy, you should use a progestin-only minipill or an intrauterine device that contains progestin.
Therapeutic uses
the first treatment recommended for women with PCOS who are trying to get pregnant.
Clomifene encourages the monthly release of an egg from the ovaries (ovulation).
If clomifene is unsuccessful in encouraging ovulation, another medicine called metformin may be recommended.
4) Letrozole (Femara).
This breast cancer treatment may work to stimulate the ovaries.
Therapeutic uses
Letrozole oral medication used to treat infertility and ovulation problems in women with polycystic ovary syndrome
5)Gonadotropins.
These hormone medicines are administered by injection.
- To reduce excessive hair growth or improve acne, your health care provider might recommend.
1)Birth control pills.
These pills reduce testosterone production, which can cause excessive hair growth and acne.
2) Spironolactone (Aldactone).
This medicine inhibits the effects of androgens on the skin, preventing excessive hair growth and acne. Spironolactone can cause birth abnormalities, so use adequate birth control while using this drug. This drug is not suggested if you are pregnant or want to become pregnant.
3) Eflornithine (Vaniqa).
This lotion can reduce the growth of facial hair.
4) Hair removal.
There are two options for hair removal: electrolysis and laser. Electrolysis involves inserting a small needle into each hair follicle. The needle generates an electrical current pulse. The current damages and eventually destroys the follicle. Laser hair removal is a medical procedure that uses a focused beam of light to eliminate unwanted hair. Electrolysis or laser hair removal may require numerous treatments. Other techniques include shaving, plucking, or utilizing hair removal products. However, these are only temporary, and hair may thicken as it comes back.
5) Acne treatments.
Medication, such as tablets and topical gels or lotions, may help reduce acne. Discuss your choices with your healthcare practitioner.
CONCLUSION:
A prevalent disorder known as polycystic ovarian syndrome is characterized by oligo- or anovulation and hyperandrogenism. The morphologic appearance of the ovaries is included in the recently introduced Rotterdam criteria as one of the potential distinguishing characteristics of the condition. Clinical issues that could come up while providing care for impacted women include severe metabolic disorders, decreased fertility, and endometrial hyperplasia. The first line of treatment for prevention is lifestyle therapy.The use of common diagnostic criteria for PCOS that were created for teenagers is highlighted by this review. PCOS should be evaluated in all teenage females with oligo-anovulation and chronic HA. Clinicians should reevaluate all patients with features that are similar to PCOS in order to avoid overdiagnosing or incorrect treatment using specific criteria recommended for this age group. This is because early detection and treatment of PCOS in these girls can prevent the long-term reproductive, metabolic, and psycho-emotional complications associated with this syndrome. The key clinical symptoms and complaints should guide the recommendation of appropriate therapy alternatives for adolescents with PCOS.
REFERENCES
- Conway G, Dewailly D, Diamanti-Kandarakis E, Escobar-Morreale HF, Franks S, Gambineri A, et al. The polycystic ovary syndrome: A position statement from the European society of endocrinology. Eur | Endocrinol 2014; 171:P1-29.
- MarchWA, MooreVM, WillsonKJ, PhillipsDI, NormanRJ, Davies MJ. The prevalence of polycystic ovary syndrome in a community sample assessed under contrasting diagnostic criteria. Hum Reprod. 2010; 25:544-551.
- Kumarapeli V, Seneviratne Rde A, Wijeyaratne CN, Yap RM, Dodampahala SH. A simple screening approach for assessing community prevalence and phenotype of polycystic ovary syndrome in a semi-urban population. in Sri Lanka. Am J Epidemiology 2008;168:321-8
- Demirel MA, Ilhan M, Suntar I, Keles H. Akkol EKcienttico.asp (2016) Activity of Corylus avellana seed oil in letrozole-induced polycystic ovary syndrome model in rats. Revista Brasileira de Farmacognosia 26(1): 83-88
- Rotterdam ESHRE/ASRM-Sponsored PCOS Consensus Workshop Group (2004) Revised 2003 consensus on diagnostic criteria and long-term healthrisks related to in polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS). Human Reproduction 19(1): 41-47.
- Londe P, Shubhi Agarwal (2017) Invitro photochemical study on Berberis aristata root extracts: An effective neutraceutical for the treatment of polycystic ovarian syndrome.
- Achard C, Thiers J. Le virilisme pilaire et son association a' l'insuffisance glycolytique (diabe te des femme a barbe). Bull Acad Nati Med. 1921; 86:5183.
- Knochenhauer ES, Key TJ, Kahsar-Miller M, Waggoner W, Boots LR, Azziz R, et al. Prevalence of the polycystic ovary syndrome in unselected black and white women of the southeastern United States: A prospective study.
- Diamanti-Kandarakis E, Kouli CR, Bergiele AT, Filandra FA, Tsianateli TC, Spina GG, et al. A survey of the polycystic ovarysyndrome in the Greek island of Lesbos: Hormonal and metabolic profile. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 1999;84:4006-11
- ovary syndrome in women in China: A large community-based study. Hum Reprod 2013;28:2562-9
- L. Ibáñez, S.E. Oberfield, S. Witchel, R.J. Auchus, R.J. Chang, E. Codner, P. Dabadghao, F. Darendeliler, N.S. Elbarbary, A. Gambineri, CG. RudazAn international consortium update: pathophysiology, diagnosis, and treatment of polycystic ovarian syndrome in adolescence Hormone Res.Paediat., 88 (2017), pp. 371-395,
- M.H. van Hooff, CB. LambalkLength of gestation and polycystic ovaries in adulthood Lancet North Am. Ed., 351 (9098) (1998 Jan 24), p. 296,
- M.G. Hayes, M. Urbanek, D.A. Ehrmann, L.L. Armstrong, J.Y. Lee, R. Sisk, T. Karaderi, T.M. Barber, M.I. McCarthy, S. Franks, CM. Lindgren Genome-wide association of polycystic ovary syndrome implicates alterations in gonadotropin secretion in European ancestry populations
- D.A. Dumesic, S.E. Oberfield, E. Stener-Victorin, J.C. Marshall, J.S. Laven, RS. Legro Scientific statement on the diagnostic criteria, epidemiology, pathophysiology, and molecular genetics of polycystic ovary syndrome Endocr. Rev., 36 (5) (2015 Oct 1), pp
- H.F. Escobar-Morreale, M. Luque-Ramírez, J.L. San Millán The molecular-genetic basis of functional hyperandrogenism and the polycystic ovary syndrome Endocr. Rev., 26 (2) (2005 Apr 1), pp.
- R.L. Rosenfield, DA. Ehrmann The pathogenesis of polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS): the hypothesis of PCOS as functional ovarian hyperandrogenism revisited Endocr. Rev., 37 (5) (2016 Oct 1), pp.
- D.A. Dumesic, S.E. Oberfield, E. StenerVictorin, J.C. Marshall, J.S. Laven, RS. LegroScientific statement on the diagnostic criteria, epidemiology, pathophysiology, and molecular genetics of polycystic ovary syndrome
- AP. Cheung Polycystic ovary syndrome: a contemporary view J. Obstet. Gynaecol. Can, 32 (5) (2010 May 1), pp. 423-425,
- K.A. Walters, R.B. Gilchrist, W.L. Ledger, H.J. Teede, D.J. Handelsman, RE. Campbell New perspectives on the pathogenesis of PCOS: neuroendocrine origins Trends in Endocrinol.Metabol., 29 (12) (2018 Dec 1), pp. 841-852,
- R. Tsutsumi, NJ. Webster GnRH pulsatility, the pituitary response and reproductive dysfunction Endocr. J., 56 (6) (2009), pp. 729-737,
- M. Puttabyatappa, V. Padmanabhan Ovarian and extra-ovarian mediators in the development of polycystic ovary syndrome J. Mol. Endocrinol., 61 (4) (2018 Nov 1), 10.1530/JME-18-0079 R161-84
- T.M. Barber, M.I. McCarthy, J.A. Wass, S. Franks Obesity and polycystic ovary syndrome Clin. Endocrinol. (Oxf), 65 (2) (2006 Aug), pp. 137-145,
- A.L. Rocha, F.R. Oliveira, R.C. Azevedo, V.A. Silva, T.M. Peres, A.L. Candido, K.B. Gomes, FM. Reis advances in the understanding and management of polycystic ovary syndrome F1000Research, 8 (2019) https://dx.doi.org/10.12688/f1000research.15318.1
- C.R. McCartney, JC. Marshall Polycystic ovary syndrome N. Engl. J. Med., 375 (1) (2016 Jul 7), pp. 54-64,
- R.S. Legro, A.R. Kunselman, W.C. Dodson, A. Dunaif Prevalence and predictors of risk for type 2 diabetes mellitus and impaired glucose tolerance in polycystic ovary syndrome: a prospective, controlled study in 254 affected women J.Clin. Endocrinol.Metabol., 84 (1) (1999 Jan 1), pp. 165-169
- S. Ashraf, M. Nabi, F. Rashid, S. Amin Hyperandrogenism in polycystic ovarian syndrome and role of CYP gene variants: a review Egypt. J.Med.Hum. Genetics, 20 (1) (2019 Dec 1), p. 25,
- P. Baillargeon, D.J. Jakubowicz, M.J. Iuorno, S. Jakubowicz, JE. Nestler Effects of metformin and rosiglitazone, alone and in combination, in nonobese women with polycystic ovary syndrome and normal indices of insulin sensitivity Fertil. Steril., 82 (4) (2004 Oct 1), pp. 893-902,
- RS. Legro Obesity and PCOS: implications for diagnosis and treatment In Seminars in reproductive medicine, Vol. 30, NIH Public Access (2012 Dec), p. 496
- C.J. Glueck, N. Goldenberg Characteristics of obesity in polycystic ovary syndrome: etiology, treatment, and genetics Metabolism, 92 (2019 Mar 1), pp. 108-12\
- Rojas, M. Chávez, L. Oliver, M. Rojas, J. Morillo, J. Mejías, M. Calvo, V. Bermúdez Polycystic ovary syndrome, insulin resistance, and obesity: navigating the pathophysiologic labyrinth Int. J.Reprod.Med., 2014 (2014 Jan 28),
- T.M. Barber, M.I. McCarthy, J.A. Was, S. Franks Obesity and polycystic ovary syndrome Clin. Endocrinol. (Oxf), 65 (2) (2006 Aug), pp. 137-145.
- Archer JS, Chang RJ. Hirsutism and acne in polycystic ovary syndrome. Best Pract Res Clin Obstet Gynaecol 2004;18:737-54.
- Azziz R. The evaluation and management of hirsutism. Obstet Gynecol 2003;101:995-1007.
- Morin-Papunen LC, Vauhkonen I, Koivunen RM, Ruokonen A, Martikainen HK, Tapanainen JS. Endocrine and metabolic effects of metformin versus ethinyl estradiol-cyproterone acetate in obese women with polycystic ovary syndrome: A randomized study. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2000;85:3161-8.
- Olsen EA. Female pattern hair loss. J Am Acad Dermatol 2001;45:70-80.
- Park JC, Lim SY, Jang TK, Bae JG, Kim JI, Rhee JH. Endometrial histology and predictable clinical factors for endometrial disease in women with polycystic ovary syndrome. Clin Exp Reprod Med 2011;38:42-6.
- Taylor AE Clinical evaluation of polycystic ovary syndrome. It. Insulin Resistance and Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome: Patho genesis, Evaluation, and Treatment. Diamanti-Kandarakis E, Nestler JE, Panidis D, Pasquali R eds. The Humana. Press, 2007; 131-143
- Ferriman D, Gallwey JD. Clinical assessment of body hair growth in women. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1961; 21:1440,
- DeUgarte CM, Woods KS, Bartolucci AA, Azziz R. Degree of facial and body terminal hair growth in unselected black and white women: toward a populational definition of hirsutism. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2006; 91:1345-50.
- Pochi PE, Shalita AR, Strauss JS, Webster SB, Cunliffle WI. Katz HI, Kligman AM, Leyden JJ, Lookinghill DP, Plewing G et al. Report of the consensus conference on acne classification, Washington DC, March 24 and 25, 1990
- Ludwig E. Classification of the types of androgenic alopecia (common boldness) occurring in the female sex. Br J Dermatol1977:97:247-254
- Dunaif A. Green G. Phelps RG, Lebwohl M, Futterweit W, Lewy L.. Acanthosis Nigricans, insulin action, and hyperandro genism: clinical, histological, and biochemical findings. J Clin Endocrinol Metah. 1991, 73:590-595
- https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/pcos/diagnosis-treatment/drc-20353443


 Punam Raut * 1
Punam Raut * 1
 Shivprasad Deokar 2
Shivprasad Deokar 2
 Dr.kawade Rajendra 3
Dr.kawade Rajendra 3








 10.5281/zenodo.14211805
10.5281/zenodo.14211805