Abstract
“The Study on the formulation and evaluation of dissolving oral film Containing Glutathione as skin Lightening Agent. Skin Whitening treatments are now readily accessible in markets as topical, Oral or injectable Formulation Multiple experiments Demonstrated that glutathione showed Antimelanogenic effects, thus it is associated with melanin production. The Solvent casting method and formulation was done with the several Evaluation tests such as, Organoleptic Properties, thickness, Folding endurance, Drug content Uniformity, Dryness/tack test, Tensile Strength Percent elongation, tear resistance, Young's modulus, In vitro dissolution studies, contact Angle, Transparency Scanning electron microscopy, permeation studies, percentage moisture loss & Stability Study. Above studies shows that, one of the best skin-whitening strips is film. Using an oral dissolving film to deliver Medication has various benefits. ODFs are excellent dose form for infants & the elderly because they are simple to swallow and pose no choking hazard. Adverse effects reported with Intravenous glutathione injection by the FDA. To overcome the adverse effects by IV route, the oral dissolving film formulated. Global glutathione market size was over USD 195 million in 2020 is estimated to grow at over % upto 2027 owing to wide application of glutathione in numerous industries such as pharmaceutical, cosmetic, food and nutraceuticals. Reduced glutathione market size should surpass USD 200 million by 2027 & is anticipated to show growth over 7.0?GR upto 2027.”
Keywords
GHS-Glutathione, Skin lightening, Cosmetics, Pharmaceuticals, oral dissolving film, evaluation, organoleptic, transparency, stability, solvent costing.
Introduction
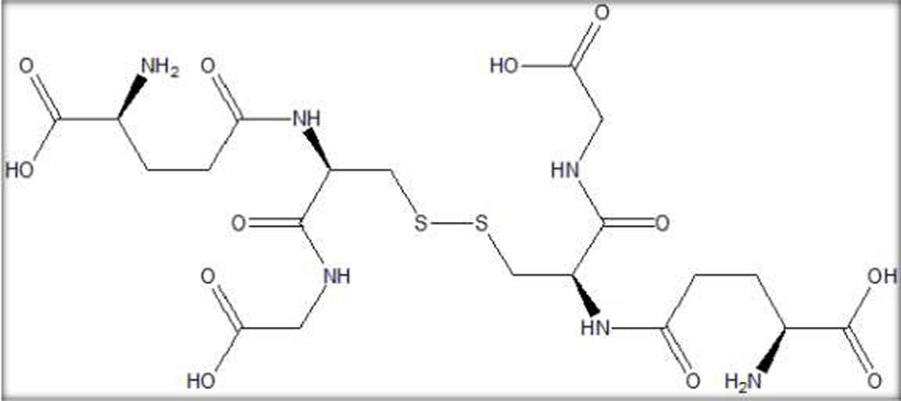
Fig. 1:- Structure of Glutathione
Chemical Name:
Pentonic acid, 2-amino-5-[(R)-(caroxymethylamino)-3-mercapto-1-oxopropan-2ylamino]- oxo, (S); N-(N-L-?-Glutamyl-l-cysteinyl) glycine.
Glutathione, a small, water-soluble thiol-tripeptide with low-molecular weight, is made from three amino acids: Glutamate, Cysteine, and Glycine. Glutathione is commonly found in two forms: reduced glutathione (GSH) and oxidized glutathione (GSSH). Its biological function serves as a potent antioxidant in human body. Melanin, a skin pigment, consists of blackish-brown eumelanin and reddish-yellow pheomelanin. Higher pheomelanin proportion will make skin brighter. Literature search on search engines revealed scarce results the fact that glutathione use as a skin-whitening agent is still rare and is yet to be researched extensively on human skin. The limitations of oral clinical trials are evident since the ability of GSH as an intact molecule decreases as it passes through the gastrointestinal tract. To pass the intestinal tract, glutathione has to be broken down into three amino acid components prior to absorption. Several animal studies showed that intact glutathione molecules may be absorbed through the small intestine, thus increasing plasma glutathione level. This would not be achieved if amino acid component is given in equivalent amount.
Inhibition of tyrosinase (the key enzyme of melanogenesis):
•Direct inhibition: Thiol group binding with the copper-containing active site of the enzyme
•Indirect inactivation: Exerted via the antioxidant effect of glutathione that leads to
•quenching of free radicals and peroxides
•Switching production of eumelanin to phaeomelanin
•Modulation of the depigmenting properties of other antimelanogenic principles
|
Parameters
|
Observation
|
|
Synonyms
|
L-glutathione ,GSH
|
|
Usage/application
|
skin lightening
|
|
Chemical formula
|
C10H17N306S
|
|
Physical state
|
powder
|
|
Color
|
white
|
|
Odor :
|
strong pungent odor
|
|
Molecular weight
|
307.32g/mol
|
|
Density
|
160kg/m?3;
|
|
Melting point
|
195 degree
|
|
Boiling point
|
754.5 degree
|
|
Solubility in water
|
free soluble
|
|
Acidity
|
2.12
|
|
Refractive index
|
1.572
|
|
Viscosity
|
960 cp
|
|
Surface tension
|
71mN/m
|

Fig. No. 2 :- Oral Dissolving Film
Many people find tablets and hard gelatin capsules difficult to chew and may not take their medications as advised. Approximately 35% of the general population suffers from swallowing difficulties, often known as dysphagia. A new oral dissolving dosage form such as dissolving film has been developed which offers the combined advantages of ease of dosing and convenience of dosing in the absence of water. “Oral dissolving film is relatively a new dosage form in which thin film is prepared using hydrocolloids, which rapidly dissolves on tongue or in buccal cavity” This are also known as Mouth dissolving films (MDF), oral strips, Orodispersible films (ODF).
The saliva containing the dissolved or dispersed medicament is then swallowed and the drug is absorbed in the normal way. Some drugs are absorbed from the mouth, pharynx, and esophagus as the saliva passes down into the stomach & it may produce rapid onset of action. In such cases, the bioavailability of the drugs is significantly greater than those observed from conventional tablets dosage form. The urge for the development of a mouth dissolving film is patients who find swallowing standard tablets and capsules troublesome for one purpose or another can benefit from fast dissolving dosage forms.
Special Features of Oral Dissolving Films
?Film should be thin and elegant.
?It should be available in various size and shapes.
?It should be Unobstructed.
?It should adhere to the oral cavity easily.
?It should processes fast disintegration without water.
?It should release rapidly.
Advantages of Oral Dissolving Film
?It is convenient form of dosing.
?It does not require water.
?There is no risk of chocking.
?With dosage form, we can mask the taste easily.
?It enhances stability.
?Improved patient compliance.
?The drug enters the systemic circulation with reduced hepatic first pass effect.
?It is site specific and has a local action.
?Availability of large surface area that leads to rapid disintegration and dissolution within oral cavity.
?Serves dose accuracy in comparison to liquid dosage form.
Disadvantages of Oral Dissolving Film
?The disadvantage of ODF is that high dose cannot be incorporated into the strip. The dose should be between 1-30 mg.
?There remain a number of technical limitations with use of film strips; the thickness while casting the film.
?The other technical challenge with these dosage forms is achieving dose uniformity.
?Packaging of films requires special equipment’s and it is difficult to pack.
?The drug should have pleasant taste.
Plan of Work
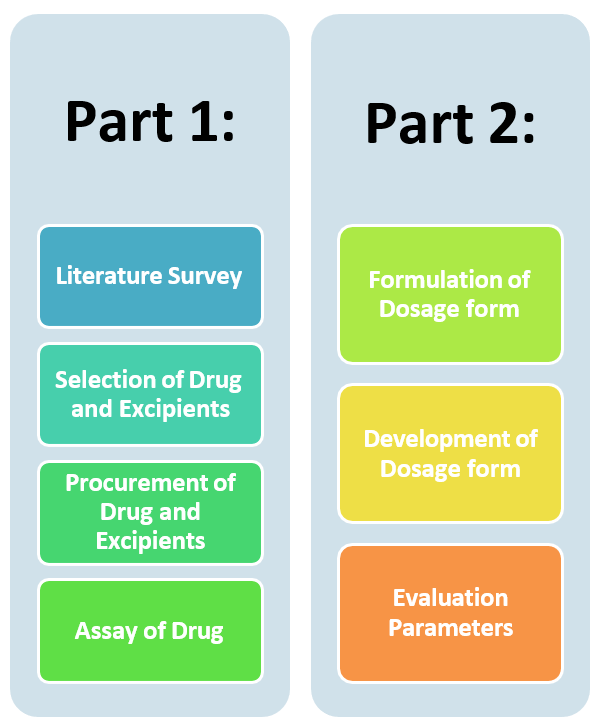
Objective
Hyperpigmentation is caused by the eposure to ultraviolet radiation, resulting in the formation of reactive oxygen and nitrogen species between cells. Oral antioxidants will reduce melanogenesis by suppressing those free radicals. Glutathione may affect skin pigmentation by inhibiting tyrosinase activity during melanogenesis, either directly or indirectly. Direct inactivation is done by binding to the active site of enzymes containing copper ion, while indirect inactivation eliminates free radicals and peroxides in ant oxidative manners. During melanogenesis, glutathione converts eumelanin to pheomelanin and modulates depigmentation of melanocytotoxic agents.
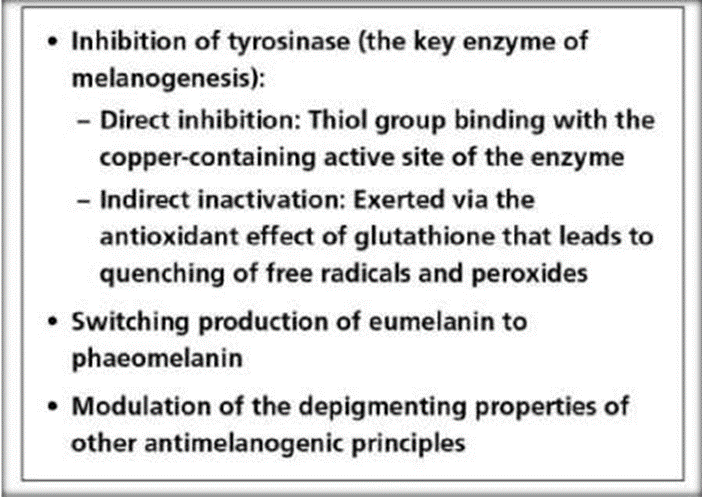
Fig. 3:- Mechanism of Action of Glutathione as Skin Lightening Agent
MATERIAL AND METHOD:
Selection of Drug and Excipient:
Drug candidate L-Glutathione obtained from Aseschem. Pvt. Ltd. Jodhpur, Rajasthan. Stevia was obtained from Dipa Enterprises, Aurangabad. Hydroxypropyl methyl cellulose, citric acid, sodium lauryl sulphate was obtained from Shreeyash Institute of Pharmaceutical Education and Research. Chemicals were the entire analytical grade. Glutathione, a small, water-soluble thiol-tripeptide with low-molecular weight, is made from three amino acids: Glutamate, Cysteine, and Glycine. Glutathione is capable of preventing damage to important cellular components caused by reactive oxygen species such as free radicals, peroxides, lipid peroxides, and heavy metals. HPMC, short for hydroxypropyl methylcellulose, is a semisynthetic, inert, viscoelastic polymer used as eye drops, as well as an excipient and controlled-delivery component in oral medicaments, found in a variety of commercial products. Citric acid is an organic compound with the chemical formula HOC(CH?CO?H)?. It is a colorless weak organic acid. It occurs naturally in citrus fruits. Citric acid stimulation was able to significantly increase salivary flow rate, pH value, sAA activities, sAA specific activity and sAA amount (including glycosylated and non-glycosylated sAA amount) in healthy children (P<0>
Fig. 4:- Drug and Excipients
Assay of Glutathione:
Sample: 500mg of glutathione. Blank: 50ml of metaphosphoric acid Mode: Direct Titration
Titrant: 0.1N Iodine VS End point detection: Visual
Analysis: Dissolve the sample in 50ml of metaphosphoric acid and titrate with titrant. Calculate the percentage of glutathione () in portion of glutathione taken.
Result = [{VU - Vb} * N * F * 100] / W Where
VU = Titrant volume of sample (ml) Vb = Titrant volume of blank (ml) N = Titrant Normality
F = Equivalence Factor
W = Weight of Sample (mg)
Acceptance Criteria: 98.0% - 101% on the dried basis.
METHOD:
Solvent Casting Method
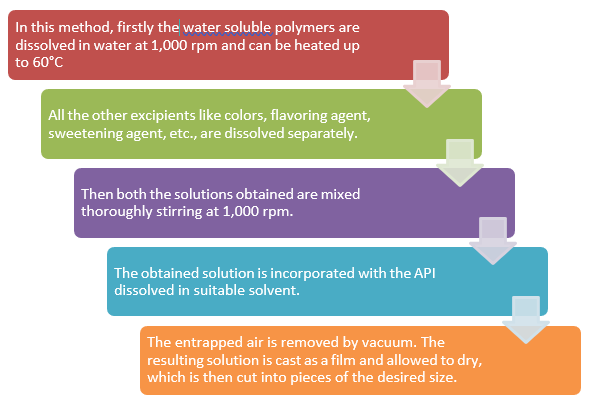
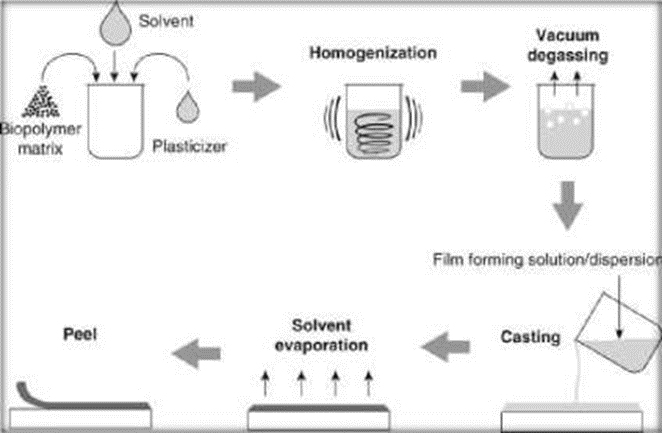
Fig. no. 5:- Schematic Diagram of Solvent Casting Method
Formulation Table:
Table No. 2
|
Ingredients
|
Amount
|
Role
|
|
L Glutathione
|
20-25 % w/w
|
Antioxidant, Skin
whitening
|
|
HPMC/E3
|
45-50% w/w
|
Water soluble
polymer
|
|
Polyethylene Glycol
|
0-20% w/v
|
Plasticizer
|
|
SLS
|
q.s.
|
Surfactant
|
|
Stevia
|
3-6 % w/w
|
Sweeting agents
|
|
Citric Acid
|
2-6% w/w
|
Saliva Stimulating
Agent
|
|
Orange Oil
|
Q.S.
|
Flavoring Agent
|

Fig. 6:- Casting of Solvent in drug Solution

Fig. 7:- Oral Films set in Petri Plates
Rganoleptic Properties:
Colour, flavour, and taste are the required organoleptic attributes for a fast dissolving formulation. The formulation should have acceptable organoleptic palatable characteristics because it will dissolve in the mouth. Hue helps patients accept a Formulation, and when oral films are given to youngsters, they should have appealing Colour. Therefore, the colour of the formulation should be consistent and appealing. Visual inspection can be used to assess colour. The smell is another organoleptic characteristic. The flavour added to the recipe should give it a pleasing aroma. By using a flavouring agent, the smell of the polymer, medication, and any other Excipient should be concealed. Taste is another crucial element that needs to be considered. A unique person is used to assess the taste.
Table No. 3
|
Parameter
|
Observation
|
|
Color
|
Slightly White
|
|
Taste
|
Sweet
|
|
Odour
|
Pleasant
|
|
Appearance
|
Glossy
|
Surface pH Test

Fig. 8 : - Evaluation of pH with pH meter
Evaluation of the surface pH of the film is required because the rapid dissolving strip's surface pH can have negative effects on the oral mucosa. The pH of the film's surface should be 7 or nearly neutral. A mixed pH electrode can be used for this. By using water to make the OS just a little damp, the pH was then determined by placing an electrode on the surface of the oral film. At least six films of each formulation should be used in this study so that the mean and standard deviation can be determined. Agar gel with a 1.5%weightvolume ratio is used as a base for the films, which are subsequently covered with pH paper to measure the surface pH.
Thickness
Micrometer screw gauges or calibrated digital Vernier Calipers are used to measure film Thickness.
The recommended range for film thickness is 5-200 mm. It is important to determine uniformity in the thickness of the film since this is directly Related to the accuracy of the dose distribution in the film. The thickness should be asses sed at five distinct points (four corners and one in the centre).
Folding Endurance
Folding endurance gives the brittleness of a film. The method followed to determine endurance value is that the film specimen (2 × 2 cm2) are repeatedly folded at the same place until it breaks or a visible crack is observed. The number of times the film is folded without breaking or without any visible crack is the calculated folding endurance value.
Drug Content Uniformity
Any standard assay method specified for the specific API in any of the standard Pharmacopoeia can be used to determine this. By measuring the API content in each individual strip, content consistency is Assessed. 85 to 115 percent is the maximum level of content uniformity.
In Vitro Disintegration Test
Table no. 4
|
Sr.
No.
|
Weight(mg)
|
Thickness(mm)
|
Surface pH
|
Folding Endurance
|
Drug Content Uniformity
|
Disintegration Time (sec)
|
|
1
|
120.27
|
0.53
|
6.3
|
145
|
91.45
|
21
|
|
2
|
129.63
|
0.45
|
6.2
|
142
|
90.88
|
29
|
|
3
|
128.13
|
0.46
|
6.3
|
143
|
92.01
|
26
|
|
4
|
121.77
|
0.51
|
6.5
|
151
|
89.98
|
31
|
When an oral film comes in contact with saliva or water, it begins to disintegrate at that point. The time of disintegration should be in the range of 5 to 30 seconds for a film that dissolves quickly. Disintegration time can be investigated using a USP (United States Pharmacopoeia) disintegration device. Another approach involves dipping the film in 25 ml of water in a beaker to visually assess the disintegration time. When the film begins to crack or dissolve, the beaker should be gently shaken and the moment noted.
Dryness/Tack
In all there have been eight stages identified for film drying and these are set-to-touch, dust-free, tack-free (surface dry), dry-to touch, dry-hard, dry-through (dry-to-handle), dry-to-recoat, and dry print-free. Tack is the tenacity with which the strip adheres to an accessory (a piece of paper) that has been pressed into contact with strip. Instruments are also available for this study.
Tensile Strength
Tensile strength is the maximum stress applied to a point at which the strip specimen breaks. It is calculated by the applied load at rupture divided by the cross-sectional area of strip as given in the equation below:
Tensile strength = Load at failure × 100/Strip thickness × Strip width
Percent Elongation
When stress is applied on a film (2 × 2 cm2) sample it gets stretched, this is referred to strain. Strain is basically the deformation of strip before it gets broken due to stress. It is measured by using hounsfield universal testing machine. Generally elongation of strip increases as the plasticizer content increases. It is calculated by the formula:
% Elongation = Increase in length of strip × 100/Initial length of strip
Tear Resistance
Tear resistance is the resistance which a film offers when some load or force is applied on the film specimen. The load mainly applied is of very low rate 51 mm/min. The unit of tear resistance is Newton or pounds-force. In other words it is the maximum force required to tear the specimen.
Young's Modulus
Young's modulus or elastic modulus is the measure of stiffness of strip. It is represented as the ratio of applied stress over strain in the region of elastic deformation as follows: Young's modulus = Slope × 100/Strip thickness × Cross head speed
Hard and brittle strips demonstrate a high tensile strength and Young's modulus with small elongation.
In Vitro Dissolution Studies
Dissolution is defined as the amount of drug substance that goes into the solution per unit time under standardized conditions of liquid/solid interface, temperature, and solvent concentration. The standard basket or paddle apparatus described in any of the pharmacopoeia can be used for dissolution testing. The selection of dissolution medium will essentially depend as per the sink conditions and highest dose of API. The temperature of dissolution medium should be maintained at 37 ± 0.5°C and rpm at 50.
When the paddle apparatus is employed, it has a disadvantage that oral films have a tendency to float over the dissolution medium.
Contact Angle
Contact angle measurement predicts the wetting behavior, disintegration time, and dissolution of oral film. These measurements are performed with help of goniometer (AB Lorentzen and Wettre, Germany) and the measurements should be done at room temperature. The water used to determine contact angle should be double distilled water.A drop of double distilled water is placed on the surface of dry film. Images of water droplet are recorded within 10 s of deposition by means of digital camera. Digital pictures can be analyzed by image 1.28v software (NIH, USA) for angle determination.
Transparency
To determine transparency of oral film, a simple ultraviolet (UV) spectrophotometer can be used. The film specimen is placed on the internal side of spectrophotometer cell. The transparency of films is calculated as follows:
Transparency = (log T600)/b = ?€c
Where T600 is the transmittance at 600 nm and b is the film thickness (mm) and c is concentration.
Scanning Electron Microscopy
To study the surface morphology of film between different excipients and drug scanning, electron microscopy can be used. The film sample should be placed in sample holder and at ×1000 magnification; various photomicrographs can be taken using tungsten filament as an electron source.
Permeation Studies
Even though permeability of oral mucosa is 4-1000 times greater than that of skin, permeation studies should be carried out. To study the permeability, modified Franz diffusion cell can be used along with porcine buccal mucosa. The Franz diffusion cell consists of a donor and a receptor compartment. In between the two compartments, mucosa is mounted and the size of the mucosa should be of the same size as that of the head of receptor compartment. The receptor compartment is filled with buffer and maintained at 37 ± 0.2°C and to maintain thermodynamics a magnetic bead stirring at a speed of 50 rpm is used. A film specimen moistened with a few drops of simulated saliva should be kept in contact with mucosal surface. The donor compartment should consist of 1 ml simulated saliva fluid of pH 6.8. At particular interval, samples are withdrawn and replaced by same amount of fresh medium. By suitable analytical method, percentage of drug permeated can be determined.
Percentage Moisture Loss
To determine percentage moisture loss films of area 2 × 2 cm2 are cut and weighed accurately on an electronic balance. After weighing, the films were kept in desiccators containing fused anhydrous calcium chloride. The films should be kept for 72 h in the desiccator. After 72 h, they are taken out and again weighed and the percentage moisture loss of films was measured by using the formula:
Percent moisture loss = (Initial weight ? Final weight)/Initial weight × 100
The percentage moisture loss studies are done to determine physical stability and integrity of the film. Determination of percentage yield of buccal patches Percentage yield of buccal patches can be calculated by the following formula:
% yield = Mass of the buccal patches obtained/Total weight of drug and polymer × 100
Stability Study
Stability study should be carried out according to the International Conference on Harmonization (ICH) guidelines. The prepared formulation was wrapped in a special way. Firstly, it was wrapped in a butter paper then above it an aluminum foil was wrapped and the packing should be placed in an aluminum pouch and make it heat sealed. The storage conditions at which formulations are kept should be 30°C/60% relative humidity (RH) and 40°C/75% RH. After 3 months, the films were evaluated for drug content, disintegration time, and physical appearance observation.
Storage And Packaging Of ODF:
Oral dissolving films can be packed using single pouches, blister card with multiple units, multiple-unit dispenser, and continuous roll dispenser. There are certain patented packaging systems for fast dissolving films such as Rapidcard by Labtec and Core-peel by Amcor flexible. The rapid card is of same size as a credit card and holds three films on each side. Every dose can be taken out individually.

Fig. 9 :- Packaged Oral Film
DISCUSSION AND RESULT:
One of the best skin-whitening strips is film. It is a face-whitening supplement in the form of a film that works similarly to an injection. It has Glutathione and Vitamin C for the best whitening and brightening effect on the face. Aging causes the body's ability to accumulate glutathione, which has a combination structure of glutamic acid, cysteine, and glycine, to decline. Digestive enzymes in the stomach and intestines break down the nutrients we consume before being absorbed through liver metabolism. The required elements are directly absorbed through the oral mucosa when film is swallowed, skipping the digestion process. "Unlike the intestinal mucosa, which has many natural barriers, the oral mucosa is easy to access and has a short length to reach blood vessels.
Clinical Implication:
Using an oral dissolving film to deliver medication has various benefits. ODFs are excellent dose forms for infants and the elderly because they are simple to swallow and pose no choking hazard. They typically include a film-forming polymer, a plasticizer, and an additional excipient. Adverse effects reported with intravenous glutathione injections by the Food and Drug Administration
1.Cutaneous—Ranging from skin rashes to serious and potentially fatal Stevens- Johnson syndrome (SJS) and toxic epidermal necrolysis (TEN).
2.Severe abdominal pain in patients receiving twice-weekly IV glutathione
3.Thyroid dysfunction
4.Kidney dysfunction with potential for development of renal failure
5.Liver dysfunction—reported in 32% of the treated subjects in the IV GSH trial by Zubair et al.
6.Lethal complications—Air embolism, blood-borne infections and potentially fatal sepsis stemming from incorrect technique of injections by untrained staff, use of unsterile or used needles, and use of counterfeit intravenous glutathione. To overcome this adverse effect by IV route, the Oral Dissolving Film formulated.
CONCLUSION AND FUTURE SCOPE:
Global Glutathione Market size was over USD 195 million in 2020 and is estimated to grow at over 7?GR up to 2027 owing to wide application of glutathione in numerous industries such as pharmaceutical, cosmetic, food and nutraceuticals. Reduced glutathione market size should surpass USD 200 million by 2027 and is anticipated to show growth over 7.0?GR up to 2027. The demand for manufacturing drugs in the region in high, owing to the presence of several pharmaceutical manufacturers including Johnson and Pfizer & Johnson. Hence, wide presence of pharmaceutical manufacturers in the region generates huge opportunity for glutathione market as the product is highly utilized in the manufacture of many pharmaceutical products.
REFERENCES
- Rajni Bala, Pravin Pawar, Sushil Khanna, and Sandeep Arora International Journal of Pharmaceutical Investigation 2013 Apr-Jun; 3(2): 67–76.
- I. B. S. Sitohang and S. Ninditya 2Dermatology Research and Practice Vol.2020; 2020::8547960.
- Arwa Ibrahim Al-Mogherah, Mohamed Abbas Ibrahim,Maha Abdelzeem Hassan Saudi Pharmaceutical Journal 28 (2020) 1374-1382
- Tarjani S Naik, Anubha Khale, Hema Kanekar International journal of Pharmaceutical and phytopharmacological Research 2249-6084
- Muzammil Husain,Vinit V. Agnihotri,Sameer N. Goyal,Yogita O.Agrawal Food Hydrocolloids for Health 2 (2022) 100064
- Guoyao Wu,Yun-Zhong Fang,Sheng Yang,Joanne R. Lupton,Nancy D.Turner The Journal of Nutrition,vol.134,issue 3 March 2004,pages 489-49
- Mehmet Ali Ockun,Hasan KirmizibekmezJournal of Drug Delivery Science and Technology vol.72, June 2022,1034288 )
- Eman Zmaily Dahmash, Affiong Lyire, Hamad S. Alyami Saudi Pharmaceutical Journal vol.29,issue 7 July 2021,pages 635-647
- Minako Nishigaki, Yoshinori Itoh, Masahito Nawa,Kana Kawahara International Journal of Pharmaceutical vol.424,issues 1-2,15 March 2012,Pages 12-17
- Sinee Weschawalit, MD, Division of Dermatology, Department of Medicine, Faculty of Medicine, Chulalongkorn University, Bangkok, Thailand; Pravit Asawanonda, MD, Division of Dermatology, Department of Medicine, Faculty of Medicine, Chulalongkorn University, Bangkok, Thailand Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology.vol.74,issues 5,supplement,May 2016,Page AB16
- Sirje Kaur, Maigi Eisen Journal of Investigative Dermatology. Vol.116,issues 6,June 2001, Pages 886-890
- Oranuch Nakchat, Nonthaneth Nalinratana, Duangdeun Meksuriyen, Sunanta Pongsamart Asian Pacific Journal of Tropical Biomedicine. Vol.4, issue 5,May 2014,Pages 379-385
- Anja Gobel, Jessica Bassi da Silva, Micheal Cook, Jorg Breitkreutz. International journal of Pharmaceutics. Vol.610,15 December 2021,121233
- Singh RJ. Glutathione: a marker and antioxidant for aging. J Lab Clin Med. 2002 Dec;140(6):380- 1. doi: 10.1067/mlc.2002.129505. PMID: 12486403.
- Zubair S, Hafeez S, Mujtaba G. Efficacy of intravenous glutathione vs. placebo for skin tone lightening. J Pak Ass Dermatol. 2016;26:177-181.
- Taylor SC, Arsonnaud S, Czernielewski J; Hyperpigmentation Scale Study Group. The Taylor Hyperpigmentation Scale: a new visual assessment tool for the evaluation of skin color and pigmentation. Cutis. 2005;76:270-274.
- GRAS notice for Glutathione. (2009) URL http://www.fda. gov/ucm/groups/fdagov- public/@fdagov-foods-gen/documents/ document/ucm269318.pdf . Accessed on April 26, 2017.
- Lenzi A, Lombardo F, Gandini L, Culasso F, Dondero F. Glutathione therapy for male infertility. Arch Androl. 1992;29:65-68. . Cook GC, Sherlock S. Results of a controlled clinical trial of glutathione in cases of hepatic cirrhosis. Gut. 1965;6:472-476.
- Potterf SB, Virador V, Wakamatsu K, et al. Cysteine transport in melanosomes from murine melanocytes. Pigment Cell Res. 1999;12:4–12.
- Wellner VP, Anderson ME, Puri RN, Jensen GL, Meister A. Radioprotection by glutathione ester: Transport of glutathione ester into human lymphoid cells and fibroblasts. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1984;81:4732–4735.
- Chung BY, Choi SR, Moon IJ, Park CW, Kim YH, Chang SE. The glutathione derivative, GSH monoethyl ester, may effectively whiten skin but GSH does not. Int J Mol Sci. 2016;27;17:629. 18;8(1):4 4
- CDSCO list of approved drug from 01-01-2011 to 31-12-2011. http://www.cdsco.nic.in/writereaddata/LISTOF-APPROVED- DRUG-FROM-2011.pdf. Accessed on April 26, 2017.
- Lazo SH. Safety on the off-label use of glutathione solution for injection (IV). Food and Drug Administration, Department of Health, Republic of the Philippines; 2011. http://www.doh.gov.ph/sites/ default/files/Advisories_cosmetic_DOH- FDA Advisory No. 2011-004.pdf. Accessed on February 26, 2017.
- Sonthalia S, Sarkar R. Glutathione for skin lightening: an update. Pigment Int. 2017;4:3-6. 7. Exner R, Wessner B, Manhart N, Roth E. Therapeutic potential of glutathione. Wien Klin Wochenschr. 2000;112:610-616.
- Villarama CD, Maibach HI. Glutathione as a depigmenting agent: an overview. Int J Cosmet Sci. 2005;27:147-153.
- Sonthalia S, Daulatabad D, Sarkar R. Glutathione as a skin whitening agent: Facts, myths, evidence and controversies. Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol. 2016;82:262-272.
- Arjinpathana N, Asawanonda P. Glutathione as an oral whitening agent: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. J Dermatolog Treat. 2012;23:97- 102.
- Handog EB, Datuin MS, Singzon IA. An open-label, single-arm trial of the safety and efficacy of a novel preparation of glutathione as a skin-lightening agent in Filipino women. Int J Dermatol. 2016;55:153-157.
- Watanabe F, Hashizume E, Chan GP, Kamimura A. Skin-whitening and skin- condition-improving effects of topical oxidized glutathione: a double-blind and placebo- controlled clinical trial in healthy women. Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol. 2014;7:267- 274.
- O Skin Med Spa website. http://www.oskinmedspa.com/portfolio/ iv-glutathione- injections/ Accessed on September 8, 2017. 14. Magic Beauty website. http://www.magicbeauty.in/Product/GSH- Ultima-1500mg. Accessed on September 8, 2017..


 Lalita Patil*
Lalita Patil*
 Kunal Rathod
Kunal Rathod
 Ganesh Patil
Ganesh Patil
 Chetan Narkhede
Chetan Narkhede











 10.5281/zenodo.14874958
10.5281/zenodo.14874958