Abstract
This study focuses on the development and assessment of an herbal soap that includes glycerin, coconut oil, lavender oil, beetroot powder, and ajwain oil (Trachyspermum Ammi), which is recognized for its antibacterial and antifungal qualities. The soap was made using the conventional saponification method, and its antibacterial activity, moisture content, foam retention, and physical attractiveness were evaluated. The finished soap had a good look, a pleasing smell, and a yellowish-brown tint. It retained a 12 cm foam height and 31% moisture content. Additionally, the soap demonstrated a strong antibacterial effect against Staphylococcus aureus, Escherichia coli, and Candida albicans. These results imply that herbal soap containing ajwain oil and other organic components can successfully improve skin health and offer antibacterial defense. The growing consumer preference for natural and environmentally friendly personal care products is in line with this, underscoring the potential applications of herbal formulations in the cosmetics and pharmaceutical industries.
Keywords
Herbal Soap, Features, Human skin, Ajwain, coconut oil, lavender oil, Antibacterial and Antifungal Activity.
Introduction
Health hygiene is critical due to the growing number of diseases caused by bacteria. [1] People have been using medicinal plants for healing purposes since the beginning of time. A wide range of illnesses and ailments have been naturally treated with the leaves, stems, and roots of several medicinal plants. Ayurvedic remedies are notable for their efficacy and safety, despite the fact that many plant-based medicines have been supplanted by synthetic counterparts. [2] These days, herbal compounds are the source of pharmaceuticals because synthetic drugs have many undesirable side effects. The interest in herbal medicines was growing among researchers as a result. The use of herbal remedies to cure a variety of illnesses gained traction due to its significance in folklore. In the current environment, plant-based formulations that take into account the active ingredients of the many herbal medications being manufactured are crucial to the growth of the pharmaceutical business. Medicinal oil, also known as vital oil, has been mentioned by numerous experts as one of the most often utilized ingredients in herbal compositions. Among the members of the Apiaceae family, tamam (ajwain) is the most widely known traditional plant. Ajwain is a traditional energetic plant used to treat a variety of human ailments. Ajwain, also known as ammi oil, is used to treat neurological conditions such as paralysis, tremor, and persistent pain.[3] There is a huge market for several types of bath soaps, including herbal soaps. Maintaining personal hygiene and being clean is a major business. However, soap users also experience a variety of skin-related problems. A dermatologist will recommend patients with skin conditions such dryness, itching, acne, or contact dermatitis and will counsel them to use certain skin care products, such as soap, based on their skin type and other associated conditions.[4]
Human skin:
The exterior layer of the human body, the skin, serves as the body's first line of protection against a variety of diseases.[5] The skin is continuously exposed to various environmental stimuli because it is the skin's interaction with the environment. This increases the risk of skin injury.[6] Severe skin damage will frequently attempt to heal by producing scar tissue, which is frequently depigmented and discolored. Since ancient times, people have utilized plants to cure illnesses and infections in humans. Plant-based formulations containing active ingredients can take the shape of lotion, ointment, cream, gel, soap, or crude/solvent extract. The use of phytoconstituents obtained from plant extracts has a promising future in the management of hyperpigmentation. The plant-based treatments found in ayurveda literature are becoming more and more well-liked in India these days because research has validated them in comparison to contemporary medicines. One type of cosmetic used in modern times to keep and improve skin vibrancy is soap. Thus, in Ayurveda, the plants listed under varnya are chosen for formulation.[7]
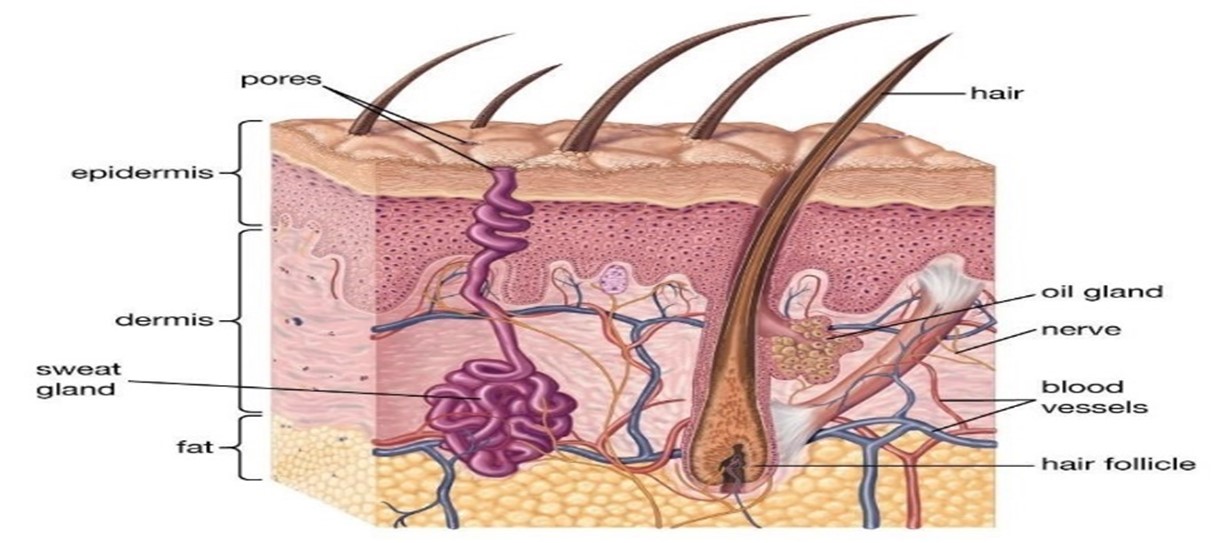
Fig. no.1- Structure of Skin [8]
Definition of soap:
soaps are cleaning agents solid, liquid, semi-solid powders that aid in the removal of dust, grime, microorganisms, stains, and other impurities while preserving appearance and wellbeing. When free fatty acids react with an alkaline base during the saponification process, soap is produced.
Qualities of soap are: -
- Ability of lather producing
- Color of the soap
- Fragrance of the soap
- Moisturizing ability
- Compatibility of the skin
- Storage Stability [9]
Features:
- Sodium salts of long-chain carboxylic acids are what make up soaps. Detergents are the sodium salts of long-chain benzene sulphonic acids.
- While some detergents cannot decompose naturally, soaps can.
- Detergents have a significant cleaning impact; soaps have a comparatively weak one.
- To obtain the appropriate hardness, we cure every soap that we sell. • A soap is not of high quality if it is hard to rinse off.[10]
Herbal Soap
Fatty acids combined with alkali salts that come from plants or vegetables and include organic or naturally scented substances are known as herbal soaps. Two processes the hot process and the cold process are used in the preparation process, which calls for the presence of bases like potassium and sodium hydroxides in addition to fatty acids to make soap.[9]
Saponification process
The chemical process known as saponification which happens when fats or oils are combined with an alkali, usually potassium hydroxide (KOH) or sodium hydroxide (NaOH) is what makes herbal soap.
Fats or Oils
Fats or oils, such as coconut oil, olive oil, palm oil, or shea butter, are commonly used to make herbal soaps. Triglycerides, which are made up of fatty acid chains and glycerol molecules, are present in these fats or oils.
An alkali, typically sodium hydroxide (NaOH) or potassium hydroxide (KOH), serves as a catalyst in the saponification process. The alkali reacts with triglycerides in fats and oils, breaking them down into constituent molecules.
Herbal soap preparation is a medication with antibacterial, anti-aging, antioxidant, and antiseptic qualities. It primarily uses plant parts, such as seeds, rhizomes, nuts, and pulps, to treat illnesses or injuries and promote overall health. Compared to the contents of commercial soap, herbal soap is free of artificial colors, flavors, fluorides, and other ingredients. Because of their great medicinal value, affordability, availability, and compatibility, herbs are the natural products that are typically used in the treatment of practically all diseases and skin issues.
Properties of herbal soap:
- Natural Ingredients: Herbal soaps are typically made from natural ingredients such as plant extracts, essential oils, and herbs. These natural ingredients are often chosen for their skinloving properties and are believed to provide various benefits for the skin.
- Mild and Gentle: Herbal soaps are usually formulated to be mild and gentle on the skin. They are typically free from harsh chemicals, sulfates, and synthetic fragrances, which can be irritating to the skin. This makes herbal soaps suitable for people with sensitive skin.
- Moisturizing: Many herbal soaps contain moisturizing ingredients such as shea butter, cocoa butter, and natural oils, which can help to hydrate the skin and prevent dryness.
- Nourishing: Herbal soaps are often formulated with nourishing ingredients such as vitamins, minerals, and essential fatty acids that can provide nutrition to the skin. These nutrients can help to support the skin's health and vitality, promoting a radiant and healthy complexion.
- Aromatherapeutic: Herbal soaps often contain essential oils, which can provide aromatherapeutic benefits. The natural scents of essential oils can help relax the mind, uplift the mood, and provide a sensory experience during your skincare routine.
- Eco-Friendly: Many herbal soaps are formulated with biodegradable ingredients and are packaged in environmentally friendly materials, making them a more sustainable choice for personal care products.
- Customizable: Herbal soaps can be made at home or purchased from artisans, allowing for customization based on personal preferences or specific skin needs.[11]
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Ajwain
Synonym: - Ajwain, ajowan or Trachyspermum Ammi, also known as ajwain caraway, omam (in Tamil), thymol seeds, bishop's weed, or carom seeds.
Biological Source: - Dried ripe fruits of the plat Trachyspermum Ammi,
Family: - Apiaceae (or Umbelliferae)

Fig. no.2- Trachyaspermum Ammi (ajwain)
Chemical Constituents: - The major component was thymol (39.1%) followed by oleic acid
(10.4%), linoleic acid (9.6%), gamma-terpinene (2.6%), p-cymene (1.6%), palmitic acid (1.6%), and xylene (0.1%).
Scientific classification
- Kingdom: Plantae
- Sub-kingdom: Tracheobionta
- Division: Magnoliophyta
- Super division: Spermatophyta
- Order: Apiales
- Class: Magnolipsida
- Family: Apiaceae
- Genus: Trachyspermum
- Species: Ammi [12][13]
Pharmacological Activity
- Antioxidant
- Antimicrobial
- Cytotoxic
- Hypolipidemic
- Antihypertensive
- Antispasmodic
- Diuretic
- Antitussive
- Antifungal [14][15]
Coconut oil
Mostly for health and beauty, coconut oil has a wide range of uses. Firstly, applying coconut oil to our skin can help shield it from UV rays. According to a study, 20% of the UV radiation that the sun emits can be blocked by coconut oil. Since coconut oil will dissolve even the toughest waterproof mascara, it can also be used as a makeup remover. Coconut oil is utilized in non-toxic insect repellents for purposes other than health and beauty. Coconut oil is a good wound salve due to its antifungal and antibacterial characteristics. Coconut oil can also be used to make personal cleansing products including body wash products, shampoo, soaps, and detergents.[16]

Fig. no. 3- coconut oil
Lavender oil
For many years, essential oils have been a part of alternative medicine used by people all over the world. Adopting more natural substitutes rather than synthetic ones is a current trend. In place of rather dangerous pharmaceutical chemicals, essential oils provide a fresh, natural, and secure substitute. One of the often-studied therapeutic herbs is lavender, or Lavandula, which is a member of the Lamiaceae family.[17]

Fig. no. 4- Lavender oil
Sodium Hydroxide
Sodium hydroxide (NaOH) is an inorganic chemical that is also referred to as lye or caustic soda. It is a white solid ionic compound made up of hydroxide anions (OH?) and sodium cations (Na+ ion). Sodium hydroxide is an extremely alkaline and caustic base that breaks down proteins at room temperature and can result in very serious chemical burns. It easily collects moist moisture and carbon dioxide from the air and is highly soluble in water. NaOH is used as a drain cleaner and in various sectors to make textiles, drinking water, soaps, and detergents. It is also utilized in pulp and paper manufacturing.[18]
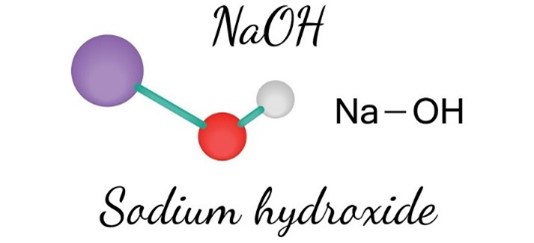
Fig. no. 5- Sodium Hydroxide
Beet Root Powder
One of the factors that significantly affects both food quality and consumer acceptance is food color. Many food products contain artificial food coloring, which poses a serious risk to human health due to its potential for allergies and cancer. As a result, attempts are being undertaken to employ natural food coloring derived from plants like saffron and turmeric. One such substance that contains betalain is beetroot, which is also a rich source of several bioactive and phytochemical components with numerous health advantages.[19]
Fig. no. 6- Beet Root Powder
Glycerine
"Glycerin Soap" is what all handcrafted soap is. Since the cold process soap producing procedure creates excess glycerin naturally, it is extracted from most commercial soap. Since handmade soap producers do not extract glycerin from their soap, all handmade soap is therefore high in glycerin. Glycerin soap is a phrase that is frequently used to describe clear soap in the market today. Usually, more glycerin is added to the clear soap to create a deeply nourishing and hydrating bar. One such "humectant" is glycerin. Glycerin soap is supposed to leave a thin coating on your skin after washing, which is why it attracts moisture to itself.[20]

Fig. no.7- Glycerine
Chemicals & Apparatus
All the Chemicals & Apparatus were collected from pharmacognosy & pharmaceutics lab of college itself.
Apparatus- Beaker, Soap Mould, Heating Mantle, Hot Air Oven, Test Tubes, Measuring
Cylinder, China Dish, Petri Plate etc.
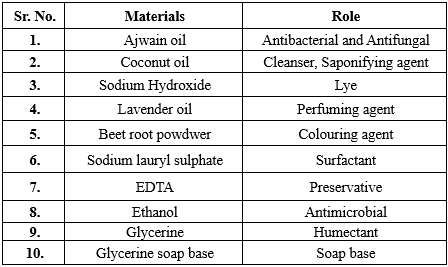
Table no.1-Formulation of Herbal Soap
METHODS:
Preparation of glycerine soap base:
- In a beaker, water and glycerin were combined.
With steady stirring, sodium hydroxide was gradually added to the mixture. The solution was mixed with coconut oil and ethanol. allowed to stand for ten minutes.
After adding the rose oil and fragrance ingredient to the mixture, pour mixture into Mold and cool at room temperature.[20]

Fig. no.8- Glycerine soap Base
Formula: - (For 50gm)
Table no. 2- Formulation of Ajwain Soap
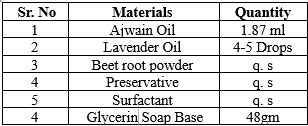

Fig. no. 9- Ajwain Soap
Ajwain Soap preparation: -
- Take glycerine soap base & melt them with help of microwave or Boiling
- Add lavender (Essential) oils in soap base
- Add Ajwain oil into Soap base.
- Add side by side sodium Lauryl sulfate & Colorants in mixture.
- Mix all ingredient in proper manner,
- Pour mixture into mold
- Let the soap cool at room temperature for about 1 or 2 hours or place the soap in the freezer for 30 minutes to cool it more quickly & soap will form.[21]
EVALUATION OF FORMULATED SOAP
1) Physical Examination
- The formulated soap was an evaluated for its color, odour and appearance was found by smelling the product.
- Determination of appearance, color & odour: -
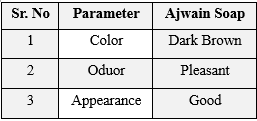
- Appearance & color was checked by naked eyes against white background, odor was smelled. Color - Yellowish Brown, Odour- Pleasant, Appearance- Good
2) Physical Evaluation
The formulation was dissolved in 100ml of distilled water & stored for 2hrs. The measurement of pH of the formulation was done in previously calibrated pH meter.[9]
Nature- pH -7.5 (Basic)
3) Skin Irritation Test
Soap was applied on skin of hands and legs of 5 volunteers and observed.[24]
4) Washing Capability
The herbal soap was put through a formulation test, as well as the simplicity with which it could be washed with water.[23]
5) Foam height
0.5g of sample of soap was taken, dispersed in 25ml distilled water. Then transferred it into 100ml measuring cylinder. Volume was adjusted to 50ml with water. Shaken the above sample solution 25 times and measured the foam height.
Foam height was shown in 9cm. After 1 hrs. 7 cm
6) Foam Retention Time
25 ml of the 1% soap solution was taken in to a 100 ml graduated measuring cylinder. The cylinder was covered with hand and shaken 10 times. The volume of foam at 10minute intervals for 50minutes was recorded.[22] Foam retention time was shown in 12cm.
7) Moisture content
The moisture content was used to estimate the percentage of water in the soap by drying the soap to a constant weight. The soap was weighed and recorded as wet weight of sample and was dried from 100 to 115°C using a dryer. The sample was cooled and weighed to find the dry weight to sample. The moisture content was determined using the formula.[24] %Moisture content= Initial weight–Final weight/Final weight × 100
8) Determination of alcohol insoluble matter
5g of sample was taken in a conical flask, added it to 50ml of warm ethanol & shaken vigorously to dissolve. The solution was filtered through a filter paper with 20ml warm ethanol and dried it at 105°C for 1hr. [2]
% Alcohol insoluble matter = wt. of residue / wt. of sample x 100 9)
9) Saponification value determination:
The amount of Potassium Hydroxide in milligrams which is required for the complete saponification of fat or oil of 1 gm. In either word it is defined as the mean of molecular weight of fatty acid which is present in oil or fat. For the determination of saponification value about 2 gm of the soap sample was taken in a conical flask and 0.5M KOH solution was added to it. This mixture was heated to about 55 degrees Celsius along with stirring continuously on a hot water bath. Then the temperature was further increased 1000C and boiling was continued for about 1-hour Titration was performed with phenolphthalein was an indicator and 0.5M HCl.
The end point observed is pink colour disappearance.[4]
10) Activity of Antimicrobial and Antifungal
Anti-bacterial and anti-fungal activity Bacterial strains Escherichia Coli, Staphylococcus Aureus, Fungal strains Candida albicans were chosen based on their clinical and pharmacological importance. The bacterial microorganisms were cultured on nutrient agar by using spread plate technique and fungal stock cultures were incubated for 48 hours at 37°C on potato dextrose agar (PDA) medium following refrigeration storage at 4°C. The bacterial strains were grown in MuellerHinton agar (MHA) plates at 37°C (the bacteria were grown in the nutrient broth at 37°C and maintained on nutrient agar slants at 4°C), whereas the yeasts and molds were grown in Sabouraud dextrose agar and PDA media, respectively, at 28°C. The stock cultures were maintained at 4°C. [25]
RESULT AND DISCUSSION
1) Physical Examination-
Physical parameter of Ajwain soap were evaluated. It occurs as yellowish brown color.it has pleasant odor. Appearance-good.
Table no.3- Physical Parameter
2) Foam Retention Test-
Foam height was found to be 12cm.
Table no.4- Foam Retention Time
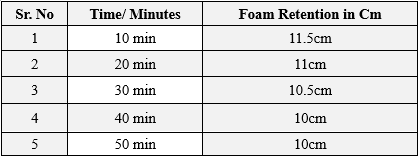
Fig. no.10- Foam Height

3) Moisture Content
%Moisture content = Initial weight–Final weight/Final weight × 100
= 10-7.6/7.6 x100
= 2.4/7.6 x 100
= 0.31 x 100
%Moisture content = 31%
4) Alcohol Insoluble Matter
% Alcohol Insoluble Matter = wt. of residue / wt. of sample X 100
= 0.31gm/5gm X 100
= 0.062 X 100
% Alcohol Insoluble Matter = 6.2%
5) Result of Antibacterial and Antifungal:
Table no.5- Antibacterial and Antifungal Activity
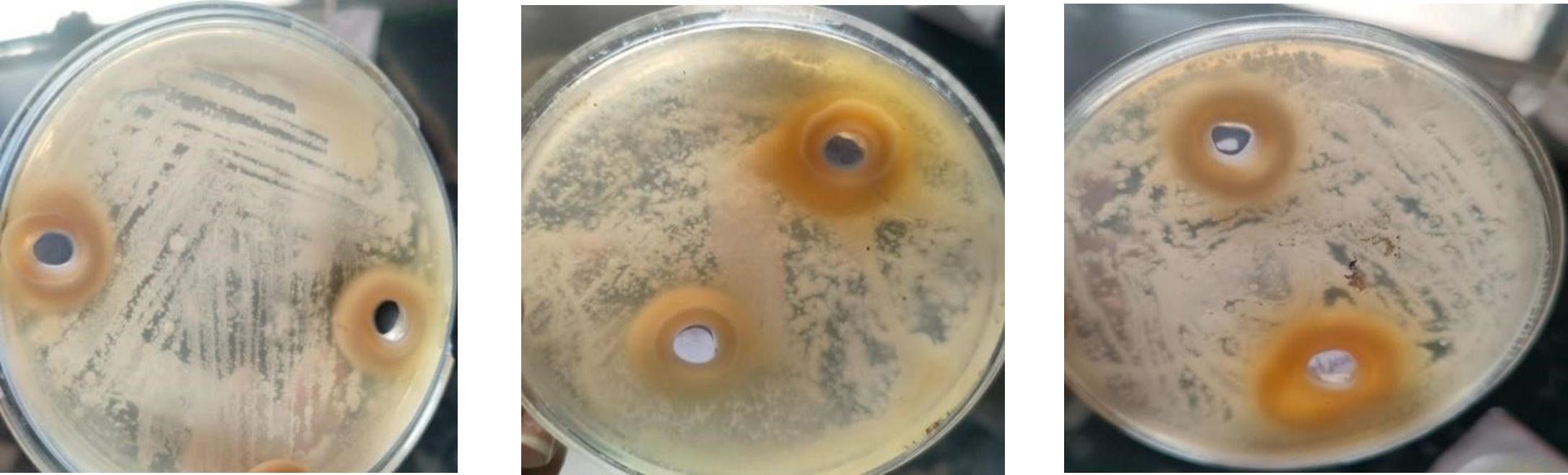
Fig. no.11- Candida Albicans Fig. no.12- E. coli Fig. no.13- S. aureus
CONCLUSION
The current effort produced herbal soaps that were antibacterial and antifungal, with the right amount of weight, thickness, and size and form as well as good foam-producing capabilities. Herbal soaps made from Ajwain were created with the intention of treating bacterial infections and cleanser due to their antibacterial and antifungal content. The formulations showed good results when evaluated for many characteristics, including size and shape, ZpH, clarity, color, and odor. Good antibacterial and antifungal characteristics were demonstrated by the herbal soap, which also had a pleasing scent and a dark brown color. According to the study, herbal products with superior antibacterial and antifungal qualities can be successfully prepared utilizing the heat process method to create medicated herbal soaps.
REFERENCE
- Dabhoya Sainbanu., Dalal Kinjal., Dasu Hasnain., Dhakal Harish., Jimisha Kher, Hemangi Sohil., Formulation and Evaluation of Antibacterial Paper Soap. Journal of Emerging Technologies and Innovative Research (JETIR), 2023; 10(4): 32-42.
- Safal Sharma., Sushilta Pradhan., Bibhas Pandit., and Mohanty., Formulation and Evaluation of Herbal Soap Taking Different Bioactive Plants by Cold Saponification Method. Int J Curr Pharm Res, 2022;14(5):30-35.
- Monawara Begum., B. P. Sharma., S. M. Barbhuiya Aziz., Ethonobotanical, Phytochemical and Pharmacological Trachyspermum Ammi a Synthetic Review. Interntional Journal of Pharmaceutical Science and Research, 2021; 12(11):5690-5697.
- Patel Anu., Patel Anar., Patel Jahanvi., Bhavsar Hemal., Formulation and Evaluation of Herbal Soap. International Journal of Scientific research and Review, 2022; 11(2):42-72.
- Ehrhardt Proksch., Johanna M. Brandner., Jens Michael Jensen., The Skin: An Indispensable Barrier. Journal Compilation, 2008; 17: 1063-1072.
- Avish D. Maru., Swaroop R. Lahoti., Formulation and Evaluation of Moisturizing Cream Containing Sunflower Wax. International Jouranal of Pharmacy and Pharmaceutical Sciences,2018; 10(11): 54-59.
- Gana Manjusha k., Bal Krishnaiah P., Syamala R., Mounik N., Ravi Chandra T., Formulation and Evaluation of Herbal Bath Soap Containing Methanolic Extracts of Three Ayurvedic Varnya Herbs. Asian Journal of Pharmaceutical and Clinical Research, 2019; 12(11): 213-215.
- Montagna, William and Ebling, F. John G... "Human skin". Encyclopedia Britannica, 9 Apr. 2024, https://www.britannica.com/science/human-skin. Accessed 18 May 2024.
- Prachi Bhimte., Prerana Sahu., Shashank Yadav., Shweta Sarparaj., Nemendra Sahu., Harish Sharma., Gyanesh Kumar Sahu., Formulation of Polyherbal Soap and of Its Physico-Chemical Evaluation. Acta Scientific Pharmaceutical Sciences, 2023; 7(5):13-19.
- Kiran Gaurav., Pranjal Dalave., Dyaneshwar Kattikar., A Review on Formulation of Herbal Soap. International Journal of Pharmaceutical research and Applications,2024; 9(1):15841592.
- Gulshan Kumar Mishra, Ritu Verma, Gaurav bhaduka, Rakesh Goyal., Review on Herbal Soap. International Journal of Innovative Research in Technology, 2023; 10(1): 1058-1062.
- Aditya Khedekar., Prathmesh Tivale, Rutuja R. Shah., An Overview on Ajwain (Trachyspermum Ammi): Pharmacological Activity and Medicinal Benefits. International Journal of Pharmacy and Pharmaceutical Research, pp- 22-26.
- Abhijeet Kumar., Dr. Ambrish Kumar Singh., Trachyspermum Ammi (Ajwain): A Comprehensive Review. World Journal of Pharmaceutical Research, 2021; 10(6): 724-736. Kanika Nag., Charu Gupta., Antimicrobial and antioxidant properties of
- Trachyspermum ammi leaf extracts against some plant pathogens. Journal of Nutritional Health & Food Engineering,2023;13(1):1- 4.
- Mohammad M. Zarshenas., Mahmoodreza Moein., Soliman Mohammadi Samani., Peyman Petramfar., An Overview On Ajwain (Trachyspermum Ammi) Pharmacological Effects; Modern And Traditional. Journal Of Natural Remedies, 2014; 14(1): 98-105.
- Yan Jer Ng., Pei En Tham., Kuan Shiong Khoo., Chin Kui Cheng., Kit Wayne Chew., Pau Loke Show., A comprehensive review on the techniques for coconut oil extraction and its application; Bioprocess and Biosystems Engineering (2021) 44:1807–1818.
- Shweta Kajjari., Riddhi S Joshi., Shivayogi M Hugar., Niraj Gokhale., Priya Meharwade., and Chaitanya Uppin., The Effects of Lavender Essential Oil and its Clinical Implications in Dentistry; A Review; international journal of clinical pediatric dentisty 2022 May-Jun; 15(3): 385–388.
- Majid Ahmadi., Seyed Hadi Seyedin., Investigation of NaOH Properties, Production and Sale Mark in the world; Journal of Multidisciplinary Engineering Science and Technology (JMEST) 2019;6(10):10809-10813.
- Gajanan P. Deshmukh., Priyanka., Rohit Sindhav and Naveen Jose., Application of Beetroot as Natural Coloring Pigment and Functional Ingredient in Dairy and Food Products; International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences; (2018) 7(12): 2010-2016.
- Nikam Manoj Madhukar, Shinde Vaibhavi Maheshkumar, Namrata Bapu Hegade, Ananda Bhimrao Waghmode., A research on formulation and evaluation of herbal soap; International Journal of Advanced Research and Development; 2023:8(2): 1-5
- Dinesh. Borkar., A Research on Formulation and Evaluation of Herbal Soap; International Journal of Research Publication and Reviews, 2023; 4(12): 4360-4367.
- Ashlesha Ghanwat*, Sachin Wayzod and Vanjire Divya., Formulation and Evaluation of Herbal Soap; Current Trends in Pharmacy and Pharmaceutical Chemistry, 2020; 2(2):21- 26.
- Margret Chandira., Lokeshwaran S2 and S. Gracy Gladin., Formulation and Evaluation of Herbal Soap by using Melt and Pour Method; Indian Journal of Natural Sciences, 2022; 13(72): 44244- 44257.
- Shaikh Nihal Nijam., Dr. Prachi Udapurkar., Formulation and Evaluation Of Herbal Antimicrobial Soap; International Journal of Creative Research Thoughts (IJCRT),2023; 11(5): 1656-1668.
- LK Sharma, D Agarwal, SN Saxena, Hanwant Kumar, Manish Kumar, JR
- Verma and B Singh., Antibacterial and Antifungal activity of ajwain in different solvent Journal of Pharmacognosy and Phytochemistry 2018;7(3): 2672-2674.


 Ankita R. Tandekar*
Ankita R. Tandekar*
 Ashika A. Khursam
Ashika A. Khursam
 Ashwini B. Sarve
Ashwini B. Sarve
 Priyanka A. Somkuwar
Priyanka A. Somkuwar
 Anil G. Dhawade
Anil G. Dhawade














 10.5281/zenodo.13224350
10.5281/zenodo.13224350