Abstract
The fast-dissolving tablet (FDT) is an innovative and unique drug delivery system that is rapidly gaining attention in fast-dissolving technology research. Fast dissolving tablets are proving to be one of the most popular and widely accepted dosage forms, especially in pediatric patients due to incomplete development of muscles and nervous system and in geriatric patients suffering from Parkinson's disease or hand tremors. The oral dosage form and route is the most preferred route of administration for various drugs that have limitations such as e.g. First-pass metabolism, psychiatric patients, disabled and uncooperative patients. FDTs break down or quickly dissolve in saliva without the need for water. The FDTs formulation contains Superdisintegrants to increase the rate of dissolution of a tablet in the oral cavity. FDT have advantages such as easy portability and formulation, accurate dosage, good chemical and physical stability, and is an ideal choice for geriatric and pediatric patients. FDTs are rapidly degraded, rapidly absorbed and therefore improve the release time of the drug in vitro and this property of the drug (dosage form) increases bioavailability. This review article covers different FDT techniques, criteria of FDT, advantages and disadvantages of FDT, selection of superdisintegrants, different patented technologies, challenges faced FDT, evaluation parameters of FDT, marketed preparation of FDT.
Keywords
Fast Dissolving Tablet, Oral drug delivery system, super disintegrants.
Introduction
Oral administration of drugs has been known for decades as the most common route of administration. All pathways have been explored for the systemic distribution of drugs through various pharmaceutical products of different dosage forms[1]. It is very popular for good patient compliance, easy of administration, Self treatment, safety, and pain avoidance. FDT are Orodispersible tablet that can be dissolved or disperse in the mouth with in few seconds, with or without administration of water[2]. FDT mostly used those patients who have difficulties on swallowing dosage form such as older, pediatric and mentally ill patients[3].
FDT are designed to disintegrate or dissolve immediately in the mouth, in less than 60 seconds[4]. Most Fast dissolving delivery systems must contain substances to mask the taste of the active ingredient. This masked agent is then swallowed by the patient's saliva along with soluble and insoluble excipients[5]. According to European pharmacopoeia adopted the term "Orodispersible tablet" as a tablet are placed upon the tongue where it disperses rapidly, in the presence of saliva in the mouth. The importance of this drug delivery system includes disintegration of tablet without need water. Some drugs having low bioavailability due to the degradation of drug in GIT such as proteins and peptides are delivered by mouth dissolving tablet. These types of dosage forms are easily preferred by pediatric and geriatric patient due to the presence of flavourings and sweetening agents. The technologies used for manufacturing FDT are spray-drying, tablet molding, freeze-drying, sublimation, tablet compression sugar-based excipients [6,7].
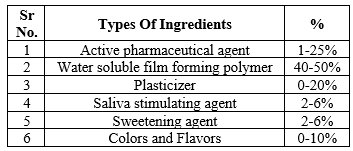
Table 1: Various Ingredients Used For FDTs[8]
Criteria for Fast dissolving Drug Delivery System:
- No need of water to swallow, but it should be dissolved in the mouth with in second.
- Be portable without fragility concern.
- It should be Compatible with Taste Masking.
- It should have Good Mouth Feel property with better Patient Compliance.
- After oral administration, no residues should remain in the mouth.
- Temperature and humidity exhibit low sensitive.
- Suitable for Conventional tablet packaging and processing.
- It should be economic[9].
Advantages of FDT
- No need of water to consume the tablet.
- easier for patients who cannot swallow the tablet such as older, bed-bound patients, stroke victims, kidney disease and patients who refuse to swallow.
- dissolution and absorption are rapid, with a fast onset of action.
- Convenient and accurate dosage form, when compared with liquids.
- It is Beneficial for coughs, allergic attacks, motion sickness, allergic attacks where ultra-fast action is required.
- The risk of choking due to physical blockage or during mouth administration of conventional formulations is avoided, thus providing superior protection.
- Increased bioavailability due to rapid dissolution of these tablets, especially in cases of hydrophobic drug and insoluble drugs.
- Long-term stability remains, because the drug is used as a solid dose until eating. So, it combines the benefits of concrete dose as stability and liquid dose in terms of bioavailability[10,11]
Disadvantages of FDT:
- There is an inadequate mechanical power in the tablet.
- FDT is very marginal and soft molded metrics, which is in a tablet with low compression, which makes the tablet to the friable and is brittle which is difficult to handle.
- FDT is hygroscopic in nature so must be put in dry place.
Selection of Superdisintegrants in FDTs [12]
FDT are depended on Superdisintegrants affected by the rate of disintegration of tablet, but when used at high concentration it can also affect the tablet hardness, mouth feel property and tablet friability.
Various ideal factors to be select a Superdisintegrants for a formulation should be:
- When the tablet comes in contact with saliva, the tablet rapidly dissolve in the mouth.
- Be sufficiently compacted to form less friable pills.
- Have good flow, as it improves the characteristics of flow of the aggregate mixture.
- Produce good mouth feel to the patients. Thus, smaller particle size is preferred to achieve patient compliance.
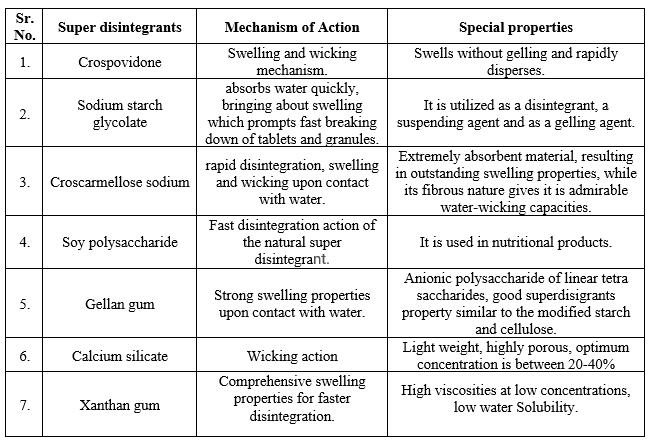
Table: 2 List of Superdisintegrants [12]
Techniques For Preparation of Fast Dissolving Tablet
- Direct Compression
- Freeze drying
- Spray drying
- Molding
- Sublimation
- Mass-extrusion
Direct Compression:
Direct compression represents the easiest way to tablet and most cost-effective tablet manufacturing technique. Superdisintegrants and other common sugar -based excipients Increase the availability of ODT.
- Superdisintegrants:
Superdisintegrant are used to increase disintegration and Tablet dissolution and compression techniques are directly used to compress tablets With Superdisintegrant, effervescent material and other water-soluble excipients.
- Sugar -Based Excipients:
Sugar -based excipients are also used to form ODT with direct compression techniques. Sugar -based excipients are fructose, lactilol, maltose, sorbitol, dextrose, starch, Hydrolysis, isomalt, maltilol, mannitol, xylitol, and, polydextrose which has bulking Agents, sweetener agents with high solubility. Sugar -Based Excipients are classified excipients becomes two types based on printing and dissolution rates.
- Type 1 Saccharides (lactose and mannitol) show the low mouldability but high dissolution speed.
- Type 2 Saccharides (maltose and maltilol) show low dissolution rate but high mouldability[13].
Steps involved by direct compression method:
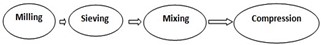
Direct compression method
Lyophillization or Freeze-Drying:
Freeze drying or Lyophilization technology in which tablet are prepared which disintegrate in saliva rapidly due to extremely porous open matrix network. Matrix are prepared through Freeze drying, it is water-soluble in which drug are entrapped uniformly and drug are dispersed or release from matrix when come in contact .with saliva. To improve the characteristics of final tablet other excipients are also incorporated such as antioxidants, wetting agents, preservatives, suspending agents, colors and flavors. Characteristics of drug for freeze drying technique are water insoluble, physically and chemically stable, small particle size, low dose and tasteless[14].
Spray drying:
Spray dryers technique are widely used to prepare rapidly disintegrating tablets. Spray drying is used for microsphere preparation. Spray drying technique used in pharmaceutical processing because it only requires one-step process and can be easily controlled and improved. The number of factors, including the size of the nozzle used in processing. Very porous fine powder is obtained by this method. Wang and Allen use this process to prepare FDT. The FDT formulation consists of gelatin which is hydrolyzed/ UN hydrolyzed as supporting agent for matrix, mannitol as bulking agent, and Sodium Starch glycolate and croscarmellose sodium as disintegration agents. Disintegration and dissolution are further enhanced by adding the component of the effervescent, namely; sodium bicarbonate (alkaline), citric acid (acid).The formulation spray is dried to produce porous powder. FDT made from this method is disintegrated in <20>
Tablet Molding:
In this technology tablet disintegrate and dissolve rapidly due to the presence of water-soluble excipients. Hydro alcoholic solvents are used to moist the blends and tablets are molded by compression. Air drying process is used to remove the solvent. Tablet prepared are porous, and low mechanical strength, to increase the mechanical strength binding agents are used such as sucrose, acacia or poly vinyl pyrrolidone. The tablets manufactured in this manner are less compact than compressed conventional tablets.
Sublimation:
The sublimation technique to prepare highly porous compressed tablets is rapidly soluble in mouth because of using volatilized solid ingredients such as camphor, ammonium bicarbonate, naphthalene, urea, urethane etc. The volatile material is removed by the sublimation process, to generate a porous compressed tablet are rapidly dissolved in saliva. Mannitol and camphor are used as material to prepared tablet matrix. Tablets manufactured by this technique usually disintegrate in 10-20 second [17]
Mass-Extrusion:
Mass-extrusion technology involves methanol, water-soluble polyethylene glycol for softening the active blend and expulsion of softened mass through the extruder to get a cylinder of the product into even segments using heated blade to form tablet. The dried cylinders are used to coat granules for masking bitter drugs and achieve taste masking of drug[18].
PATENTED TECHNOLOGIES : [19,20]
Fast-dissolving property of FDTs generally attributes the rapid penetration of water in tablet matrix, resulting in its fast dissolution. Many techniques have been patented by many drug companies based on aspects and different processes. The patent technology has been given to below:
Zydis Technology:
Zydis, the best mouth dissolving tablet preparation was the first marketed new technology tablet. Lyophilizing or freeze-drying technique are used to prepare tablet of drug in a matrix consists of gelatin. The product is very light weight and fragile tablet put into the mouth, the freeze-dried structure disintegrates easily. The zydis products are made to dissolve on tongue in 2-3 sec and also pre gastric absorption avoid first pass metabolism. There are some disadvantage of Zydis technology are very light weight and fragile and formulation has poor stability at higher temperature and humidity.
Durasolv Technology:
Durasolv is Cima’s second generation mouth dissolving tablet formulation. DuraSolv has much higher mechanical strength because tablet was prepared by using Conventional tabletting equipment and has good rigidity. These can be packaged in traditional blisters packaging. One disadvantage of Durosolve is the technology is not Compatible with large dose of active ingredients; because of require high pressure on Compression.
Orasolv Technology:
Orasolv was Cima's first mouth dissolving technology, dispersed in saliva in the aid of almost imperceptible effervescence. Orasolv Technology is matrix system dissolve in less thane one min, by the help of effervescent disintegrating agent. Tablets are made by direct compression technique at low compression force. The major disadvantages of the Orasolv technology are lightly compressed, more brittle tablet in compare with other technology[16].
Flash Dose Technology:
Flash dose technology utilized a unique spinning mechanism to produce floss like cylinder structure, like cotton candy. The crystalline sugar can the incorporate the active drug and compressed in tablet. The tablet has high surface area for dissolution.This technology has been patented by Fuisz and is known as shearforms.
Wow tab Technology:
Wow tab technology is mouth dissolving tablet dissolve quickly on 15 sec or less. The WOW in Wowtab means tablet is to be given "with out water". In this process, combination of low mould ability saccharide’s and high mould ability saccharides’ is used to obtain a rapidly melting strong tablet. In this technology the combination of Sacchariedes are used such as sugar and sugar like-(e.g. mannitol as excipients, also provide adequate hardness with mouth dissolving rate.
Flash tab technology:
Flash tab technology is patented by Prographarm laboratories. In this Tablet preparation micro crystals are formed consists of an active ingredient. Drug microgranules may be prepared by using the conventional techniques like coacervation, micro encapsulation and extrusion spheronisation. All the process utilized conventional tabulating technology[17]
Challenges against FDTs[21]
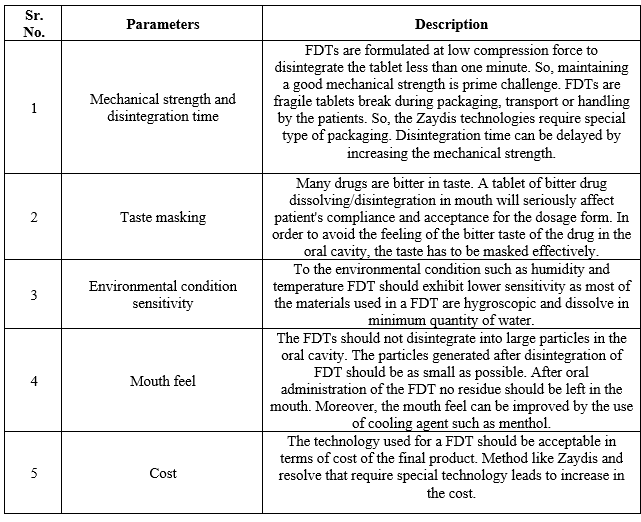
TABLE: 3 Challenges against Fast Dissolving Tablet
Evaluation parameters of FDT[22,23]
Table: 4 Evaluation parameters of Fast dissolving tablet

Marketed Preparation of FDTs[24,25]
Table: 5 Marketed Available Preparation of FDTs

CONCLUSION:
Fast dissolving tablets are innovative dosage forms that have been designed and specifically developed to solve some of the problems encountered with conventional solid dosage forms, i.e. Difficulty swallowing tablets in geriatric and pediatric patients. Fast dissolving tablet dosage forms and their route of administration result in improved efficacy, rapid onset of action, increased bioavailability, and improved patient compliance. fast dissolving tablets, usually designed to rapidly dissolve or disintegrate in saliva in less than 60 seconds (range 5-60 seconds). There is a need to prepare FDTs for mentally ill patients, Bedrested, geriatric, pediatric, patients who may not have access to water, patients who are busy traveling. Considering the many advantages of FDTs, a number of formulations are manufactured in FDT form by most pharmaceutical companies. Through increased patient demand, popularity of this dosage Forms will certainly be expanded in the future.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT:
The authors are thankful to the authorities of Mahakal Institute of Pharmaceutical Studies Ujjain (M.P.) for providing support to India Studies and other essential facilities such as web browsing, library writing and other technical support of a review article.
CONFLICT OF INTEREST STATEMENT:
Author declared no conflict of interest. The author alone is responsible for the content and paper writing.
REFERENCE:
- Chien YW. Novel drug delivery systems. New York – Marcel Dekker Inc., 2nd ed.1992;139-140
- Gajare, G.G., Bakliwal, S.R., Rane, B.R., Gujrathi, N.A., Pawar, S.P., Mouth dissolving tablets: A review, Int J Pharma Res &Deve, 2011, 3(6), 280 – 296 .
- Chang RK, Guo X, Burusid B, Couch R.A review of fast dissolving tablets. Pharm Tech, (North America).June, 2000; 52-58.
- Nautiyal U, Singh R, Singh S, Gopal, Kakar S. Prepared Fast dissolving tablets as a novel boon: a review. Journal of Pharmaceutical, Chemical and Biological Sciences 2014;2:5-26.
- Kuchekar BS, Atul, Badhan C, Mahajan, HS, Mouth dissolving tablets: A novel drug delivery system. Pharma Times. 2003;35:7-9
- Bandari, S., Mittapalli, R.K., Gannu, R., Rao, Y.M., An overview of Orodispersible tablets in Asian J Pharm, 2008,2, 2–11
- Kumari, S., Visht, S., Sharma, P.K., Yadav, R.K., Fast dissolving Drug delivery system : Review Article; J.Pharmacy Research, 2010, 3(6),1444-1449
- Singh S, Virmani T, Virmani R, kumar P, Mahlawat G, Fast dissolving Drug Delivery systems: Formulation, Preparation Techniques and Evaluation; Universal Journal of Pharmaceutical Research 2018; 3(4):56-64
- Erande Ritesh, T. Regupathi , Shaikh Surfraj , Baokar Shrikrishna, Fast Dissolving Tablet an Indo American Journal of Pharmaceutical Research. 2011:1(1);84-91.
- Debjit B., Chiranjib B., Krishnakanth, Pankaj, R.Margret Chandira, Fast Dissolving Tablet: An Overview,J Chemical and Pharma Res,2009, 1(1), 163-177.
- Kaur T, Gupta GD, Gill B, Kumar S. Mouth dissolving tablets: An Overview, International Journal of Current Pharmaceutical Research Vol 3, 2011;1:1-7.
- Khan AB, Tripuraneni A. Fast dissolving tablets; novel approach in drug delivery. Rguhs J Pharm Sci 2014;1:7-16.
- Swarbrik J, Encyclopedia of Pharmaceutical technology, 3rd Edition, London, 2003, 267-273.
- Panigrahi R, Behera S. A Review on Fast Dissolving Tablets. Webmed Central; 2010; 1-15.
- Donald LW. 1st ed. New York: Marcel Dekker Inc; 2005. Handbook of Pharmaceutical Controlled Release Technology; pg 112.
- Lieberman HA, Lachman L, Schwartz JB. 2nd ed. Vol. 3. New York: Marcel Dekker Inc; 2005. Pharmaceutical Dosage Forms: Tablets; p. 187..
- Dalavi A, Mahale A. M. Fast Dissolving Tablet by Sublimation Technique: A Review Journal of Emerging Technologies and Innovative Research (JETIR) 2014;c887-c897.
- Kumar S, Annu K. Fast dissolving tablets: waterless patient compliance dosage form Journal of Drug Delivery & Therapeutics. 2019; 9(1):303-317.
- Kumar V. D, Sharma I, and Sharma V, Review on Fast dissolving tablet technology. Journal of Applied Pharmaceutical Science) ;2011; 01(05) : 50-58.
- Mangal M., Thakur N., Bansal R., Goswami M. Review on fast dissolving tablet technology and approaches for emergency treatment. IJRAP;2012;(3) :377-380.
- Bhandari V, Patel F, Sanghavi K, Chaudhary S, Hiral Shah Ragin, Approaches of taste masking. International Journal of Pharmacy and Integrated Life Sciences; 2013;1(5):48-61
- Ratnaparkhi M. P. Mohanta G. P., Upadhyay L., Review On: Fast Dissolving Tablet; Journal of Pharmacy Research Vol. 2. I ssue 1. January 2009 pg 5-15.
- Siddiqui Nehal Md., Garg G., Sharma Kumar P., Fast Dissolving Tablets: Preparation, Characterization and Evaluation: An Overview; International Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences Review and Research; 2010; 87-96.
- Khanna K, Xavier G, Joshi K. S., Patel A, Khanna S, Goel B, Goel V. Fast Dissolving Tablets- A Novel Approach International Journal of Pharmaceutical Research & Allied Sciences, 2016, 5(2):311-322.
- Masih A, Kumar A, Singh S, Tiwari K. Review of Fast Dissolving Tablets International Journal of Pharmaceutical Research Vol.9, Issue 2, 2017 pg 8-18.


 Afreen Nagori*
Afreen Nagori*
 Akanksha Jagwani
Akanksha Jagwani






 10.5281/zenodo.11186249
10.5281/zenodo.11186249