Abstract
Helminthiasis is the intestinal parasitic infection which is caused due to worms like nematodes and platyhelminthes. These organisms spread widely in human beings (host) by feeding on the host's nutrition inside the intestine. This article mainly speaks about the herbal drugs and formulations used for the treatment of helminthic infection.they actively reproduce by feeding on the host tissues including blood. The various worms which cause helminthiasis are Tapeworm, Roundworm and Hookworm. There are different types of herbal formulations in this article which include tablets, syrups, suspensions, some of them are single herbal and others are polyherbal formulations. At present many herbal formulations are widely available in the market due to their less side effects and easy availability of herbs. The herbal plants listed in this article has been reported for anthelmintic activity and details like method of extraction, pathological activity and common uses of herbs namely Punica granatum Linn, Carica papaya Linn, Azadirachta indica, Ziziphus mauritiana, Cissus quadrangularis, Curcuma longa, Zingiber officianale, Ficus indica, Achyranthes aspera, Allium sativum, Cucurbita pepo, Thespesia lampas.
Keywords
Helminthiasis, nematodes, platyhelminthes, parasites, infection, herbal
Introduction
Helminth infections is one of the most common parasitic infections which is affecting a large portion of the human population. In developing countries the parasitic infection causes a larger threat to public health which leads to anemia, eosinophilia, malnutrition and even death if untreated [1]. Males are more prone to helminth infections than that of females. More than 24% of the total population depends on the native frameworks of medication such as Ayurveda, Unani & Sidha in India. Plants with anthelmintic activity were surveyed by Akhtar et al, the survey inferred over 90% of restorative specialists from higher plants. Even today, customary arrangements of medication have been polished in many nations which follow old societies, and major part of their restorative requirements are acquired from plant drugs [2]. Presently the accessibility of allopathic medications isn't adequate for the treatment of helminthiasis of colossal populace and they create opposition or are not powerful. Ingestion of infected food, water, mosquitoes, and flies can all spread helminthiasis. Tropical and subtropical regions, such as sub-Saharan Africa, central and eastern Asia, and the American regions are where it is more common. Hardly any control of parasitic gastroenteritis contaminations is drilled in most conventional creation frameworks (Baker,1995; Chiejina, 1995). Present day veterinary fix is wasteful due to the generally significant expense of anthelmintics, the shortage of current anthelmintic medications, and the detachment of numerous towns as well as the roaming and transhumant custom [3]. Helminths lives in the GI plot of their hosts, and feed off living hosts, taking supplements from host and causing contamination/infections and typically more inclined to kids, soil-communicated schistosomiasis and helminthiasis are the main helminthiases, answerable for disregarded tropical illnesses [4]. There are various drugs to be studied in anthelmintic activity but in this paper we have listed some 20 drugs such as Punica granatum, Carica papaya, Trachyspermum ammi, Azadirachta indica, Ziziphus mauritiana, Cissus quadrangularis etc.. Information about formulation of some plants indigenous (Indian plants), their anthelmintic action and evaluation have been reviewed.
LIST OF HERBS USED AS ANTHELMINTIC:
- Punica granatum :

Punica granatum (Pomegranate) the divine fruit which originated in Iran and then propagated to northern parts of the Himalayas,India which belongs to the family Punicaceae. It is mainly cultivated in arid environments. The principle components of the pomegranate are lignins, punic acid, oleic, linoleic, stearic acid, palmitic, tocopherols, sex steroids, sterols, gallic, ellagic acid, crude fibers, protein, minerals, vitamins, hydroxycinnamic acids sugars, triacylglycerols, polyphenols, and alkaloids. The peel of this fruit shows anthelmintic action hence Pomegranate peel ethanolic extract (PPEE), the extraction was done for three days at room temperature and with sporadic shaking, each 500 g chopped plant material was immersed in 2.5 liters of 90% ethanol in a dark area, then was filtered thrice using Whatman filter paper. The combined filtrate was evaporated at 50°C and lower pressure in a vacuum rotary evaporator to obtain the crude ethanolic extract [5]. Both in vivo and in vitro investigations were conducted on Schistosoma mansoni (S.mansoni) and the anthelmintic effect of Pomegranate (PPEE) against Schistosoma mansoni was evaluated. Punica granatum fruit rind(peel) powder demonstrated impressive efficacy by 85% reduction in gastrointestinal nematodes in sheep. In another study where the sheeps were naturally infected with mixed cestode species showed a significant decrease in ECG when exposed to the same fruit rind powder. The alkaloids and glycosides of P. granatum have demonstrated strong anticestodal activity in goats as well [6]. It can also be used for treatment or prevention of a number of risk factors, such as oxidative stress, hyperglycemia, high blood pressure and high cholesterol levels.
- Carica papaya Linn:

Carica papaya plant Originated in tropical America, it was introduced in India during the 16th century. It belongs to the family Caricaceae. The young leaves of Carica papaya contains several flavonoids such as kaempferol and myricetin, phenolic compounds such as chlorogenic acid, caffeic acid, ferulic acid and benzyl glucosinolate, alkaloids such as carpaine, pseudocarpaine dehydrocarpaine I and II as well as cyanogenic compounds that are found in the leaves [7]. The aqueous extract of Carica papaya seeds (Caricaceae) was assessed for their anthelmintic properties against nematodes Ascaris lumbricoides and Ascardia galli (roundworm). Inhibition of parasitic worms along with eosinophils destroyed their structural proteins [8]. The high efficacy of Carica papaya has also been well-established in Heligmosomoides polygyrus (Nematospiroides dubius) infections in experiments are prevented by papaya latex as reported by Satria et al. The isothiocyanate benzyl was obtained from Carica papaya seed and applied as an anthelmintic treatment for Caenorhabditis elegans. The extract demonstrated that they inhibit the infectious larvae of T. Colubriformis. Carica papaya contains cysteine proteinases which show anthelmintic properties. It is also known that this substance has healing properties such as reducing inflammation, lowering blood sugar levels, preventing fertility, supporting liver health and promoting wound healing. Additionally, studies have shown that it may also have benefits for controlling blood pressure and fighting tumours.
- Azadirachta indica:

Azadirachta indica (neem) is indigenous to sections of Southern-east Asia and the Indian subcontinent. It belongs to the family Meliaceae. It contains phytoconstituents such as isoprenoids, which include limonoids, azadirone, diterpenoids, triterpenoids, gedunin, non-isoprenoids like sulphurous compounds, amino acids, polysaccharides, flavonoids, glycosides, coumarins and tannins. Aqueous extract of neem demonstrated a dose-dependent anthelmintic activity with larger potency against roundworms even at the lowest concentration (10 mg/ml) [9]. Various investigation on this plant had demonstrated for their efficacy against a wide range of parasites including helminths protozoa and ectoparasites like Triatoma infestans, H.contortus, Rhipicephalus microplus and Trichomonas vaginalis [10]. Azadirachta indica is toxic to organisms such as Trypanosma, Salmonella and Plasmodium species. It acts against L.acuminata as well as Fasciola gigantica larvae. By using azadirachtin at a concentration of 1?rived from seeds of Azadirachta indica showed an inhibition of 68.3% against the Haemonchus contortus larval hatching. Neem leaves have various uses such as treating skin conditions, malaria, fever, diabetes and heartburn . In addition, the leaves can be used as a diuretic, for headaches and heartburn.
- Ziziphus mauritiana:
Ziziphus mauritiana (Indian Jujube) is a prickly evergreen shrub that can grow upto 15 meters tall and belongs to the family Rhamnaceae. It consists of ziziphin N, O, P, and Q, polysaccharides, peptides, alkaloids, cyclopeptides, flavonoids, dodeca acetyl prodelphinidin B3, fatty acids and saponins. The ova (eggs) of the nematodes were used for knowing the in vitro ovicidal effects and the egg hatch test by using methanolic extract and aqueous extract of Ziziphus mauritiana. According to the findings, Ziziphus mauritiana exhibited anthelmintic activity with the lethal concentration values 0.1773 and 0.6778 of the aqueous and methanolic extracts respectively. According to results aqueous extract has higher anthelmintic activity than that of methanolic extract [11]. Ziziphus mauritiana is used as anthelmintics, antipyretics and has also been reported for its uses in managing conditions such as nausea, diuretic, scabies, biliousness, heartburn, asthma, stomatitis and typhoid fever.
- Cissus quadrangularis:
Cissus quadrangularis is the perennial plant species which is indigenous to Arabian Peninsula, tropical Asia and a large portion of Africa and belongs to the family of Vitaceae. It consists of ?-sitosterol, ?-amyrone, ?-amyrin and flavonoids, the stem of Cissus quadrangularis consists of two asymmetric tetracyclic triterpenoids and two steroidal principles. There is evidence that the tannins may have anthelmintic effects. To assess the in vitro anthelmintic activity on earthworm Pheretima posthuma (Annelida), the alcoholic and aqueous extract of plant Cissus quadrangularis root was done. Cissus quadrangularis stems were washed with tap water, dried, and then ground into a powder. Following that, n-hexane, dichloromethane, ethyl acetate, and methanol were used to extract the powder (246.8 g). After filtering the solutions and eliminating the solvents in a vacuum, the resulting crude extracts were 7.68 g (3.11%, w/w), 4.73 g (1.92%, w/w), 2.71 g (1.09%, w/w), and 14.14 g (5.73%, w/w) of hexane, dichloromethane, ethyl acetate, and methanol, respectively. Dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) was used to dissolve the dried powder of ethyl acetate extract, which was then run through a 0.22 ~M sterile filter. According to studies Schinus molle and Cissus quadrangularis are used in Ethiopia to treat helminthic infections. C.quadrangularis is said to be used in cattle to treat leech infestation, helminthiasis and infestation by ticks and lice [12].
- Curcuma longa:
Curcuma longa Linn is a perennial plant grown in southern parts of Asia, belonging to the family Zingiberaceae. It contains Curcuminoids which make up 3-6% of the polyphenolic compounds in the turmeric rhizome also known as bisdemethoxycurcumin or curcumin demethoxycurcumin [13]. The phytoconstituents were extracted using a Soxhlet apparatus, a 70% ethanolic extract of each plant's rhizomes was obtained from the crude extract. To identify the different active ingredients qualitative testing was done. In a Petri dish the earthworms were sorted into regular groups (Piperazine 20 mg/ml), test groups (10 mg/ml or 20 mg/ml or 50 mg/ml) and control groups (normal saline). The extract demonstrated vermifuge activity and measured paralysis and death times were noted and the effect of the vermicidal activity was observed with respect to change in concentration. Pheretima posthuma (Earthworms) were categorized into test groups, standard groups and control groups of piperazine. The paralysis time of the crude extracts at concentration of 20 mg/ml, 50mg/ml and control group were evaluated. The Curcuma longa ethanolic extract showed both vermicidal and vermifuge activity [14]. Additionally Curcuma longa shows anti-inflammatory, antispasmodic, anti-carcinogenic, anti-parasitic and gastrointestinal effects.
- Zingiber officinale :
The plant Zingiber officinale (ginger) is rhizomatous, the plants have perennial flowers, it belongs to the family Zingiberaceae. Ginger has many active compounds which include volatile oils between 1 and 3% of its weight, while others are non-volatile. These three sesquiterpenes (30–70%) bisabolene, zingiberene, and zingiberol are the main active components of ginger oil. Shogaols and gingerols are two phenolic compounds and major active chemical constituents in ginger [15]. The ethanolic extract of zingiber was evaluated and in vitro anthelmintic activity was determined at the concentration of 50 mg/ml where earthworms were used for observing paralysis and death time. The combined extract of pomegranate (Punica granatum) peel and ginger (Zingiber officinale) bulb were evaluated using in vitro experiments that had antiparasitic properties against Dactylogyrus species. Different dosages of pomegranate peel (50,100,250 and 500 mg/ml) and ginger (10,50,100 and 250 mg/ml) were given to parasites for a predetermined amount of time. The in-vitro cumulative mortality values reached 100?ter the ginger was subjected to 250 mg/ml for 9 minutes, 100 mg/ml, and 50 mg/ml for 5 minutes. After being exposed to 10 mg/ml of ginger for nine minutes the cumulative death rate was 58%, Dactylogyrus species showed resistance to ginger bulb and pomegranate peel solutions based on the concentration of the solution and the length of exposure to some extent [16]. Ginger has been shown to be effective in treating heartburn, nausea and vomiting, analgesic, anti-inflammatory and antipyretic properties . It is effective against Trypanosoma brucei, Giardia lamblia, and Toxoplasma gondii species.
- Ficus indica:
Ficus indica or Ficus benghalensis is indigenous to the Indian Subcontinent and is also referred to as the indian banyan tree. It belongs to the family Moraceae. The plant mainly contains flavonoids, tannins, saponins, alkaloids and terpenoids. The therapeutic action and ecological interactions are facilitated by these constituents. The aqueous extract of Ficus benghalensis roots were done by decoction method and the obtained crude extract underwent qualitative tests to determine the presence of active ingredients. Pheretima posthuma (Indian EarthWorms) were classified into standard categories after being examined using the petri dish method. The root extracts of Ficus benghalensis exhibited strong anthelmintic activity over time and demonstrated vermifuge and vermicidal activity. It works well for diabetes, rheumatism, diarrhoea, dysentery, piles, dental problems and skin sores. It also serves as an immune booster [17].
- Achyranthes aspera:
Latjeera Chichira also known as Achyranthes aspera belonging to the family Amaranthaceae. The plant Achyranthes aspera has a high phytochemical content and saponins A and B in their seeds. D-Glucuronic acid was found to be saponin A, and ?-D galactopyranosyl ester of D Glucuronic acid was shown to be saponin B. Oleanolic acid glycosides are found in Achyranthes aspera seeds. Aqueous extract of stem samples were taken at concentrations of 2.5, 5, 10, 20 mg/ml were prepared for the initial assessment of anthelmintic activity [18]. Antiparasitic activity of A.aspera was done using ethyl acetate extracts which showed good activity against the internal parasite Paramphistomum cervi in sheep and the larvae of the cattle Rhipicephalus sanguineus (brown dog tick) and Boophilus ( Rhipicephalus microplus). Some of its important uses include hepatoprotective, anti-allergic, laxative, diuretic, purgative, and antiperiodic effects. This herb has historically been used to treat rheumatism, dropsy, cough, pneumonia, diarrhea, dysentery, ulcers, piles, scabies, snake bites and other skin conditions [19].
- Allium sativum:
The Allium sativum (Garlic) is a species of bulbous member of the Amaryllidaceae family. Garlic constitutes various bioactive substances such as allicin, diallyl trisulfide, diallyl disulfide, diallyl sulfide, ajoene and S-allyl-cysteine. The Soxhlet apparatus was used for obtaining methanolic extract of Allium sativum and on investigation it showed anthelmintic property . Red stomach worms or Haemonchus contortus were grouped into the test, standard and control groups & the crude extracts were used to measure the motility into control groups (normal saline), they showed survival as well as efficacy rise with longer exposure times. Allium sativum functions as an antibacterial agent, nematicide, pesticide and preservative and also shows activity against cancer, hypertension, common cold and red mite [20].
- Cucurbita pepo:
Cucurbita pepo is a warm season annual vegetable vine which is native to South America belonging to the Cucurbitaceae family. The major chemical constituents of the Cucurbita pepo are minerals (like potassium, magnesium and zinc), fiber, proteins, lipids, carbs, vitamins such as A, C and E along with carotenoids and flavonoids, presence of other bioactive substances like cucurbitacins is responsible for their wide pharmacological activity. The fruit of Cucurbita pepo was coarsely pulverized and defatted at 60–80°C using petroleum ether. Hydoalcohol was then extracted using a Soxhlet apparatus and left for approximately 72 hours at 40°C.Following that, Whatman No. 1 filter paper (Whatman Ltd., England) was used to filter the sediment. A rotary vacuum evaporator (Buchan R-V120, Switzerland) was used to further concentrate the fruit extract at 40°C while it was under vacuum. For the next study, the obtained crude extract was weighed. An increase in exposure time showed a significant increase in anthelmintic activity. Even the alcoholic and aqueous extract of seeds of Cucurbita pepo showed potent action against other organisms like Fasciolopsis buski, Hymenolepis diminuta, Moniezia expansa and Ascaris lumbricoides. The most notable component was discovered using aqueous extract, harmless in contrast to ethereal and alcoholic extracts. The ethanol and water extract of Cucurbita pepo seeds exhibited a high degree of anthelmintic effectiveness in mice against Aspiculuris tetraptera. Other uses are lower blood sugar level, worm-borne parasitic infection [21].
- Thespesia lampas:
Thespesia lampas also known as “Hibiscus lampas” is a tall undershrub that grows in the uphill slopes belonging to the family Malvaceae. The presence of active constituents in Thespesia lampas stem was demonstrated which includes 9-tetradecenal, dodecanoic acid, n-hexadecanoic acid and tetradecanoic acid also shows the presence of quercetin and ?-sitosterol. Samples of roots were cleaned, then allowed to air dry at room temperature (RT). After that, a grinder was used to turn the samples into a fine powder. Afterwards, 150 ml of 80% methanol (v/v) and 150 ml of 95% chloroform were used to macerate 15 g of powdered materials. The extract was then dried at 40?C in a water bath, filtered using Whatman® Grade 1 filter paper, and kept at 4°C until needed again. The crude extract of Thespesia lampas displayed good vermicidal & vermifuge activity. The time for mortality and paralysis decreased along with increase in the concentration. Fruits and roots of Thespesia lampas are useful against syphilis and gonorrhea, while leaves are effective against ringworms, inflammation and other skin related disorders [22].
A SHORT DESCRIPTION ON VARIOUS POLYHERBAL FORMULATIONS :
FORMULATION NUMBER -1
FORMULATION AND EVALUATION OF POLYHERBAL TABLET :
MATERIAL –
Neolamarckaia cadamba leaves and barks of Alstonia scholaris, along with other chemicals including albendazole used were of analytical grade. An Indian earthworm (Eisenia foetida) was used for the anthelmintic assay of formulation.
FORMULATION METHOD OF HERBAL SYRUP –
The leaf part of the plant Neolamarckia cadamba (up to 2kg) was cleaned before formulating and dried under shade, further this material was converted to coarse powder and subjected to maceration separately using 7L of ethanol for 7 days. After 7 days both the extracts were filtered and concentrated using a rotary vacuum evaporator. The obtained residue was stored for the further process. The simple syrup IP was prepared using 66.7g of sucrose; the obtained 1g of each extract was added to this simple syrup IP and dissolved well then made the volume up to 100 ml using distilled water.
Table No. 1- Composition Of Formulation

EVALUATION OF HERBAL SYRUP –
The evaluation of herbal formulation is essential to determine the stability and shelf life of preparation and this can be determined by various physico-chemical parameter such as
- Organoleptic property (colour, odour, taste)
- Viscosity
- pH
- weight /ml
Table No. 2- Evaluation Parameters

The anthelmintic activity was screened using earthworm as experimental animal and albendazole was used as reference standard with different concentration and saline solution (normal saline) was used as control. Later freshly prepared drug solutions and test solutions were used. Neolamarckia cadamba having different concentrations like 50mg/ml, 100mg/ml and 200 mg/ml were taken. Alstonia scholaris having different concentrations like 50mg/ml, 100mg/ml and 200 mg/ml were taken. The formulated herbal syrups having concentrations as 50mg/ml, 100mg/ml and 200 mg/ml were used.
TABLE NO. 3 [23]-

REPORT:
The present investigation of the study on the polyherbal syrup of Neolamarckia cadamba and Alstonia scholaris showed good synergistic and acceptable death and paralysis time on earthworm and has a good efficacy to that of albendazole drug [23].
FORMULATION NUMBER- 2
Evaluation and formulation of anthelmintic activity of Bauhinia variegata
MATERIAL –
Aerial parts of the Bauhinia variegata plant were used for preparation of the formulation. Drugs like albendazole and other chemical reagents of analytical grade were used. Pheretima posthuma (Indian adult earthworm) were used for the evaluation of the formulation.
FORMULATION PREPARATION –
The aerial parts of Bauhinia variegata were shade dried and powdered, it was soaked in rectified spirit for 24 hours later it was refluxed for 3 hours with 2 litres of 95% ethanol. The clear solution was decanted off and the process was repeated thrice and the combined extraction was concentrated to a semisolid consistency, hence total ethanolic extract was collected. The fractionations of ethanolic extract were obtained using solvent in their order of increasing polarity (i.e. ethyl acetate and chloroform). The obtained fractions were concentrated and weighed for further use[24].
PREPARATION OF HERBAL SYRUP-
1 gm of each extract of Bauhinia variegata was mixed in simple syrup IP and this syrup volume was adjusted to 100ml.
TABLE NO.-4-

EVALUATION OF HERBAL SYRUP FORMULATION -
The herbal syrup formulation was evaluated for evaluation parameters like –
- pH
- Viscosity
- Refractive index
- Physical appearance such as colour, odour and taste
- Weight /ml
Even the anthelmintic activity of syrup was evaluated.
TABLE NO. - 5[24]-

REPORT:
The development and formulation of herbal syrup will play an important role in the phytopharmaceutical industry. Therefore anthelmintic activity of herbal syrup shows comparably good effect on earthworms (Pheretima postuma) to that of albendazole [24].
TABLE NO. 6

FORMULATION NO. – 3
FORMULATION AND EVALUATION OF POLYHERBAL SYRUPS BY USING LEAVES EXTRACTS OF Moringa oleifera AND RHIZOMES EXTRACTS OF Curcuma longa –
MATERIAL AND METHOD –
The leaf part of Moringa oleifera plant and rhizomes part of Curcuma longa plant, sucrose, glycerine, propylene glycol, sucralose, menthol, hydroxypropyl cellulose, orange oil, sodium citrate, ethanol [25].
Pheretima postuma was used as an experimental animal to carry-out in-vitro anthelmintic activity.
PREPARATION OF EXTRACT –
The plant material was washed and cleaned thoroughly and shade dried for a week. The dried material is grinded to the coarse powder and stored for further processes. Approximately 200g of powdered plant material and extracted with ethanol at 60-70ºC.
TABLE NO. -7: FORMULATION OF HERBAL SYRUP [25]
ANTHELMINTIC ACTIVITY OF FORMULATION –
To a beaker add 10 ml of formulation extract and 0.1 N of HCL and diluted with solvent, to this 20 ml of 0.1N HCL and allowed to settle for 2 hours, the solution is then taken and diluted to 900ml by adding phosphate buffer having 6.8 pH. The concentration of solution was formulated to 50mg/ml. From this 10 ml of solution was pipetted and diluted and this was transferred to a petri plate containing Pheretima postuma to determine the anthelmintic activity by calculating paralysis and death time.The anthelmintic activity formulation was compared with marketed ABZ formulation.
TABLE NO.-8
REPORT-
The study concludes that the combination of the formulated extracts Moringa oleifera leaves and Curcuma longa rhizomes showed very good anthelmintic effect. The various concentrations of polyherbal formulation possesses deworming activity, but the polyherbal formulation-02 showed more potent action than that of marketed syrup [25].
FORMULATION NO. – 4
The present study was conducted to analyse the anthelmintic activity of the ethanolic extract of Cinnamomum zeylanicum and its formulation was done.
MATERIALS AND METHODS:
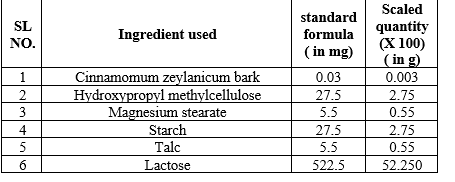
96% ethanol, albendazole, dimethyl sulfoxide, magnesium stearate, Ringers lactate (RL) solution and talc of analytical grades were used. Cinnamomum zeylanicum barks and leaves were washed cleanly and dried at room temperature for 7 days, after the drying process they were powdered separately. The powdered drug was subjected to cold maceration using ethanol (96% w/v) for 72 hours and oven-dried for 5 days at 40ºC.
FORMULATION OF TABLETS:
The tablets were formulated using a wet granulation method. The chemical constituents were weighed accurately and mixed by geometric dilution, talc as well as magnesium stearate were excluded. The wet mass obtained by using distilled water for granulating fluid was screened-out using a mesh size of 2360µm and at 60º C the collected granules were dehydrated by drying to the duration of 60 minutes, they were screened using a 1180 µm mesh. Talc as well as Magnesium stearate were added to the granules before compressing into tablets.
TABLE NO. – 9 Composition of Cinnamomum zeylanicum tablets [26]
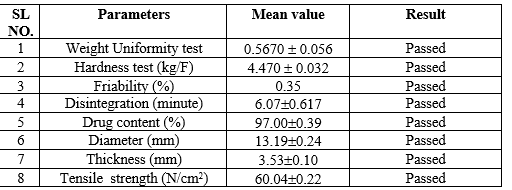
EVALUATION OF TABLETS:
Tablets formulated were evaluated for their weight variation and disintegration tests. Hardness and friability were determined. Dimensional test and their tensile strength for the tablet was done using following formula:
s = 2F/?Dt
where,
s = tensile strength of the tablet
F = force required to break the tablet (in newton)
D = tablet diameter (in cm)
t = tablet thickness (in cm)
IN-VITRO STUDIES –
The extract of Cinnamomum zeylanicum bark and Cinnamomum zeylanicum leaves along with albendazole and ringers lactate were subjected to in- vitro studies using Pheretima postuma in primary assay,
TABLE NO. – 10

REPORT:
This study concludes that the ethanolic extract of leaves and barks of Cinnamomum zeylanicum has anthelmintic activity with bark extract showing highest efficacy against Pheretima posthuma. The ethanolic extract of the bark also showed anthelmintic activity against Haemonchus contortus species and immediate-release tablets were successfully formulated [26].
FORMULATION NO. – 5
PREPARATION AND EVALUATION OF Tagetes erecta EXTRACT LOADED SUSPENSION FOR ANTHELMINTIC ACTIVITY.
The main aim of the study is to formulate stem extract of the Tagetes erecta (American / African variety) suspension and evaluate its anthelmintic property.
MATERIALS –
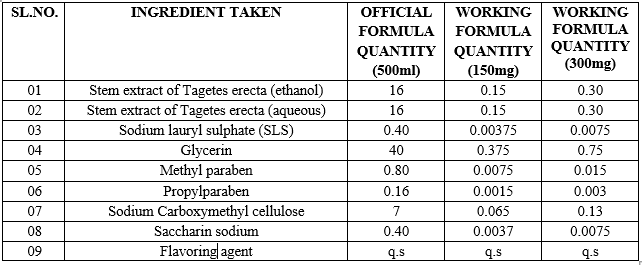
Fresh stems of Tagetes erecta, other components like glycerine, sodium lauryl sulphate, albendazole, methyl and propyl paraben [27].
METHOD-
Extract preparation –
The fresh stem parts of Tagetes erecta plant wer
‘4th dried in shade and grinded until fine powder was obtained. Later the extraction on the powder was carried out by maceration method for 14 days with 95% of 250 ml of ethanol and water. Thus, the obtained extract of respective solvents was filtered and evaporated using a heating mantle. Later using ethanolic and aqueous extract a greenish brown sticky substance was obtained that was refrigerated for later formulating into suspension.
Formulation of suspension –
The formulation of suspension was prepared by using the ingredients from the table below. Both extracts were triturated to fine particles and to this other constituent such as SLS, Na CMC, glycerine, preservative and flavouring agents were accurately weighed and added to the formulation.
TABLE NO.-11

EVALUATION OF FORMULATED HERBAL SUSPENSION–
The formulated suspension was evaluated by such as
- Sedimentation volume
- Viscosity
- Particle size
- pH
Anthelmintic activity of formulation was evaluated by in-vitro method using Pheretima posthuma where both ethanolic as well as aqueous extract were placed in separate petri dish
with earthworms and allowed to show its activity. The paralysis and death time was observed and noted by their change in motility along with change in body colour (fading off colour).
The evaluation was carried out for stability studies and the data is given in table below-
???????REPORT –
This study confirms the anthelmintic activity Tagetes erecta was seen by paralysis time and death time of earthworm. The ethanolic extract of this drug sample showed a potent anthelmintic effect than the standard reference drug albendazole.
CONCLUSION :
Herbal plants were used from ancient times and even in the present modern era they play a major role in the field of medicine. At the same time development in the phytopharmaceutical research field is swiftly shifting hence efforts are made to recognize the capability of these herbal plants for their potent activity against infection-causing parasites in the human gastro-intestinal tract. Yet further exploration for similar plants are required to reduce the side effects of synthetically prepared anthelmintic drugs. As indigenous herbal plants are abundantly available, economically feasible along with less side effects.The enlisted herbal plants in this review article explains their efficiency and when they are prepared in interpreted methods showing prominent anthelmintic activity when compared to present available marketed formulations.
REFERENCES :
- Nirala RK, Raj P, Anjana K, Mandal KG. Medicinal plants and its activity against helminth: A review. Journal of Pharmacognosy and Phytochemistry. 2019;8(5):2348-55.
- Wagh Jyoti G, Mittal A, Lunked A, Veerkar Prachi V, Kumari R, Pathak D, Verma B. Preparation and Evaluation of Polyherbal Syrup Containing Extracts of leaves of Moringa Oleifera and the rhizomes of Curcuma longa Linn.
- Sharma Sandeep Kumar, Gupta Jeetendra Kumar, Gautam Namratal, Varshney Venu. Preliminary anthelmintic studies on the two varieties of Punica granatum fruit extracts. Int. Res. J. Pharm. 2015; 6(2):114-117.
- Manjusa A, Pradeep K. Herbal anthelmintic agents: a narrative review. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine. 2022 Aug 8;42(4):641.
- Hassan NM, Sedky D, El-Aziz TA, Shalaby HA, Abou-Zeina HA. Anthelmintic potency and curative effect of pomegranate peels ethanolic extract against Haemonchus contortus infection in goats.
- Patel DA, Patel UL, Shah PB, Kadikar HK. Anthelmintic evaluation of formulated polyherbal syrup Dardona Z. Literature Review: Punica granatum (pomegranate) with an emphasis on its anti-parasitic activity. GSC Biological and Pharmaceutical Sciences. 2023;23(2):100-14.
- Yogiraj V, Goyal PK, Chauhan CS, Goyal A, Vyas B. Carica papaya Linn: an overview. International journal of herbal medicine. 2014 Nov;2(5):01-8.
- Mali RG, Mehta AA. A review on anthelmintic plants.
- Savitha R. A Review on Anthelmintic Potential of Siddha Herbal Formulation Pirandai Kudineer.
- Batool S, Munir F, Sindhu ZU, Abbas RZ, Aslam B, Khan MK, Imran M, Aslam MA, Ahmad M, Chaudhary MK. In vitro anthelmintic activity of Azadirachta indica (Neem) and Melia azedarach (Bakain) essential oils and their silver nanoparticles against Haemonchus contortus.
- Savitha R. A Review on Anthelmintic Potential of Siddha Herbal Formulation Pirandai Kudineer
- Srisook K, Palachot M, Mongkol N, Srisook E, Sarapusit S. Anti-inflammatory effect of ethyl acetate extract from Cissus quadrangularis Linn may be involved with induction of heme oxygenase-1 and suppression of NF-?B activation. Journal of ethnopharmacology. 2011 Feb 16;133(3):1008-14.
- Niranjan A, Prakash D. Chemical constituents and biological activities of turmeric (Curcuma longa l.)-a review. Journal of Food Science and Technology. 2008 Mar 1;45(2):109.
- Sharma Sandeep Kumar, Gupta Jeetendra Kumar, Gautam Namratal, Varshney Venu. Preliminary anthelmintic studies on the two varieties of Punica granatum fruit extracts. Int. Res. J.Pharm. 2015; 6(2):114-117.
- Bhattarai K, Pokharel B, Maharjan S, Adhikari S. Chemical constituents and biological activities of ginger rhizomes from three different regions of Nepal. J. Nutr. Diet. Probiotics. 2018;1:180005.
- Van QP, Y?lmaz BH, Yavuzcan H. In vitro Antiparasitic Activity of Ginger (Zingiber officinale) Bulb and Pomegranate (Punica granatum) Peel Against Monogenean Fish Parasite., Dactylogyrus sp. Acta Aquatica Turcica. 2021;17(1):56-63.
- Sharma Sandeep Kumar, Gupta Jeetendra Kumar, Gautam Namratal, Varshney Venu. Preliminary anthelmintic studies on the two varieties of Punica granatum fruit extracts. Int. Res. J. Pharm. 2015; 6(2):114-117.
- A Review on Pharmacological Aspects of Achyranthes Aspera.
- Nirala RK, Raj P, Anjana K, Mandal KG. Medicinal plants and its activity against helminth: A review. Journal of Pharmacognosy and Phytochemistry. 2019;8(5):2348-55.
- Sharma Sandeep Kumar, Gupta Jeetendra Kumar, Gautam Namratal, Varshney Venu. Preliminary anthelmintic studies on the two varieties of Punica granatum fruit extracts. Int. Res. J. Pharm. 2015; 6(2):114-117.
- Kanupriya J, Arihara Sivakumar G. Antioxidant potential and Phytochemical analysis of fruit extract of Cucurbita pepo. Int J Curr Res Chem Pharm Sci. 2019;6(3):22-32.
- Singh N, Mansoori A, Jiwani G, Solanke AU, Kumar R, Kumar A. Evaluation of antioxidant and antimicrobial potential of Thespesia lampas root extracts.
- Patel DA, Patel UL, Shah PB, Kadikar HK. Anthelmintic evaluation of formulated polyherbal syrup. International Journal for Pharmaceutical Research Scholars. 2012;1:20-4.
- Lakshmi V.V*, Archana Akhileswaran, Aysha Binsy P, Greeshma Sreenivas, Nafih T and Sudheesh P.S, a study on evaluation of anthelmintic activity of bauhinia variegata.WJPLS 2022, Vol. 8, Issue 6, 158-161
- Wagh Jyoti G, Mittal A, Lunked A, Veerkar Prachi V, Kumari R, Pathak D, Verma B. Preparation and Evaluation of Polyherbal Syrup Containing Extracts of leaves of Moringa Oleifera and the rhizomes of Curcuma longa Linn.
- Entsie P, Owusu F, Boakye-Gyasi ME, Osei YA, Adu F, Bayor MT. Formulation of Cinnamomum zeylanicum immediate release tablets as an anthelmintic. Int J Pharm Sci Res. 2021;12(5):2835-41.
- e Santos PC, Granero FO, Junior JL, Pavarini R, Pavarini GM, Chorilli M, Zambom CR, Silva LP, da Silva RM. Insecticidal activity of Tagetes erecta and Tagetes patula extracts and fractions free and microencapsulated. Biocatalysis and Agricultural Biotechnology. 2022 Oct 1;45:102511.


 Chaithra K*
Chaithra K*
 Varshitha A
Varshitha A
 Vidyashree R
Vidyashree R
 Vinod Kumar B G
Vinod Kumar B G
 Yashaswini M U
Yashaswini M U
 Hardeek G
Hardeek G














 10.5281/zenodo.13862770
10.5281/zenodo.13862770