Abstract
Psoriasis is a disease characterized by the presence of papules and plaques on the surface of the skin with different morphology, distribution and severity. Psoriasis lesions differ from these other entities and are classically well-circumscribed, circular, red papules or plaques with gray or silvery white dry scales. In addition, lesions are typically distributed symmetrically on the scalp, elbows, knees, lumbosacral region, and body folds. Oral manifestations of psoriasis may involve the oral mucosa or tongue. The dorsal surface of the tongue shows characteristic red spots surrounded by a yellow-white border. The relationship between eye lesions and psoriasis is current knowledge in the literature. Ocular complications along with several extracutaneous manifestations are common complications seen in psoriasis. The pathogenesis of the exact relationship between the two is still controversial. Immunological studies have shown a positive relationship between helper T cells and uveitis. Various signs and symptoms of ocular psoriasis may be overlooked. Thus, a complete understanding of ocular involvement is important for the comprehensive care of patients with psoriasis. Psoriasis can affect almost any part of the body, but ocular complications of psoriasis usually remain clinically inconspicuous. This review highlights the various manifestations of psoriasis with their clinical signs and symptoms.
Keywords
psoriasis, plaque, pustular, multimorbidity, biologic, papules
Introduction
Psoriasis is a lifelong immune-mediated inflammatory skin disease associated with diseases such as psoriatic arthropathy, psychological, cardiovascular and liver diseases. Psoriasis is an immune-mediated inflammatory disease of unknown etiology that may be associated with a defect in keratinocyte proliferation and differentiation associated with infiltration of inflammatory cells, mainly consisting of T-lymphocytes, macrophages, and neutrophils [1]. Psoriasis affects 1–3% of the adult population with various extracutaneous manifestations [2]. Patients affected by psoriasis have ocular manifestations that are characterized by hyperproliferation of keratinocytes with abnormal differentiation together with infiltration of inflammatory cells, especially activated T lymphocytes in the epidermis and papillary part of the dermis [3]. Psoriasis is a skin condition that causes a rash with itchy, scaly patches, most commonly on the knees, elbows, trunk, and scalp.Psoriasis is a common, long-term (chronic) disease that cannot be cured. It can be painful, interfere with sleep and make it difficult to concentrate. The condition tends to go through cycles, flaring up for a few weeks or months and then subsiding for a while. Common triggers in people with a genetic predisposition to psoriasis include infections, cuts or burns, and certain medications. There are treatments available to help manage the symptoms. And you can try lifestyle habits and coping strategies to help you live better with psoriasis.Eye lesions are more common in men and often occur during psoriasis exacerbations. Psoriasis is a common chronic inflammatory skin disease affecting 0.5% to 2% of children and adolescents. The disease affects 4% of all children under the age of 16 with all types of dermatological disorders Common signs and symptoms of psoriasis include:
- A flat rash that varies greatly in appearance from person to person, from dandruff-like patches to large eruptions over large areas of the body
- Rashes that vary in color tend to be shades of purple with gray scales on brown or black skin and pink or red with silver scales on white skin
- Small scales (commonly seen in children)
- Dry, cracked skin that may bleed
- Itching, burning or soreness
Cyclical rashes that appear for several weeks or months and then disappear [4].
Until now, different forms of psoriasis have been known:
- Plaque psoriasis (characterized by dry, scaly patches)
- Pustular psoriasis (contains pus-like fluid, mostly infiltrated with white blood cells)
- Erythrodermic psoriasis (characterized by exfoliation of fine scaly skin with pain and itching)
- Guttal psoriasis (characterized by drops like dots)
- Inverse psoriasis (affects flexural surfaces and is characterized by smooth inflamed lesions)
- Others including psoriasis of the scalp and psoriasis of the nails.
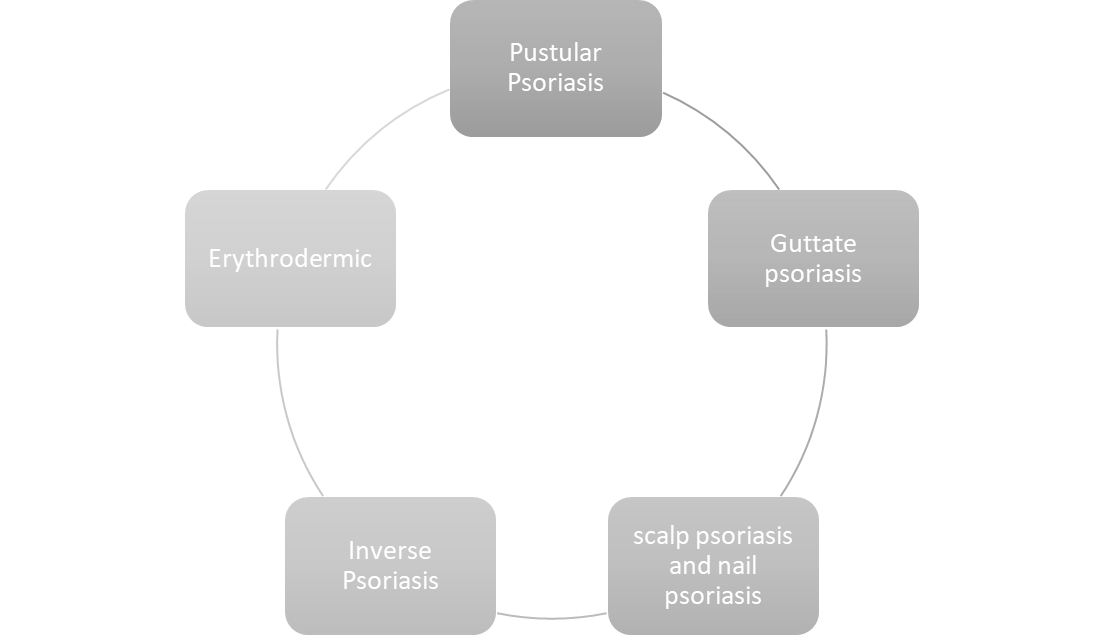
Fig.1: Types of Psoriasis
CLINICAL CLASSIFICATION:
The dermatological manifestations of psoriasis are varied; psoriasis vulgaris is also called plaque type psoriasis and is the most common type.
Psoriasis vulgaris
Psoriasis vulgaris is a chronic skin disease with a waxing and waning course. Abnormally rapid turnover of the epidermis results in the accumulation of thick scales at sites of frequent trauma and irritation. Guttate psoriasis is generally a subacute inflammation following a streptococcal infection. About 90% of psoriasis cases correspond to chronic plaque type psoriasis. The classic clinical manifestations are sharply demarcated, erythematous, pruritic plaques covered with silvery scales. Plaques can coalesce and cover large areas of skin. Common locations include the trunk, extensor surfaces of the limbs, and the scalp [5].
Inverse psoriasis
Inverse psoriasis, also called flexural psoriasis, affects the intertriginous sites and is clinically characterized by mildly erosive erythematous plaques and patches [6].
Guttate Psoriasis
Guttate psoriasis is a variant with acute onset of small erythematous plaques. It usually affects children or adolescents and is often triggered by group A streptococcal infections of the tonsils. About one-third of patients with intestinal psoriasis will develop plaque psoriasis during their adult lives [7]. Pustular psoriasis is characterized by multiple, confluent, sterile pustules. Pustular psoriasis can be localized or generalized. Two distinct localized phenotypes have been described: psoriasis pustulosa palmoplantaris (PPP) and Hallopeau's acrodermatitis continua. Both affect the hands and feet; PPP is limited to the palms and soles and ACS is found more distally on the tips of the fingers and toes and affects the nail apparatus. Generalized pustular psoriasis presents with an acute and rapidly progressive course characterized by diffuse redness and subcorneal pustules and is often accompanied by systemic symptoms [8].
Erythrodermic psoriasis is an acute condition in which more than 90% of the total body surface is erythematous and inflamed. Erythroderma can develop in any type of psoriasis and requires emergency treatment [9].
Comorbidities in psoriasis
Psoriasis typically affects the skin, but can also affect the joints and is associated with a number of diseases. Inflammation is not limited to psoriatic skin and has been shown to affect multiple organ systems. Thus, it has been postulated that psoriasis is a systemic entity rather than just a dermatological disease [10]. Coronary plaques are also twice as common in psoriasis patients compared to control subjects. Several large studies have shown a higher prevalence of diabetes and cardiovascular disease in correlation with psoriasis severity [11]. Psoriatic joint inflammation results in psoriatic arthritis (PsA). Cutaneous manifestations generally precede PsA, which shares the inflammatory chronicity of psoriasis and requires systemic therapy due to potential destructive progression. Psoriatic arthritis develops in up to 40% of patients with psoriasis [12]. Approximately 15% of psoriasis patients are thought to have undiagnosed PsA. Clinically, it manifests as dactylitis and enthesitis in oligoarticular or polyarticular patterns. The polyarticular variant is often associated with nail involvement. Nails are specialized dermal appendages that can also be affected by psoriatic inflammation. Nail psoriasis is reported to affect more than half of psoriasis patients and may present as the sole manifestation of psoriasis in 5–10% of patients [13]. In addition to an increased risk of cardiometabolic disease, psoriasis is associated with a higher prevalence of gastrointestinal and chronic kidney disease. Susceptibility loci shared between psoriasis and inflammatory bowel disease support this association, particularly with respect to Crohn's disease[14]. An association with mild liver disease that correlates with imaging studies has been reported. Psoriasis may be a risk factor for CKD and end-stage renal disease, independent of traditional risk factors (demographic, cardiovascular, or drug-related) [15]. Taken together, the various factors contributing to psoriasis as a systemic disease can have a dramatic effect on patients' quality of life and disease burden. The deterioration of the psychological quality of life of psoriasis is comparable to cancer, myocardial infarction and depression [16]. The high burden of disease is thought to be due to disease symptoms, which include pain, pruritus, and bleeding in addition to the aforementioned comorbidities [17]. The impact of psoriasis on psychological and mental health is currently an important factor due to the effects of the disease on social well-being and treatment. Patients with psoriasis have an increased prevalence of depression and anxiety and suicidal ideation. Interestingly, treating psoriasis leads to improvement in anxiety symptoms [18].
TREATMENT OF PSORIASIS:
Psoriasis treatment is divided into five levels. The choice of treatment depends on the severity and response of the individual patient
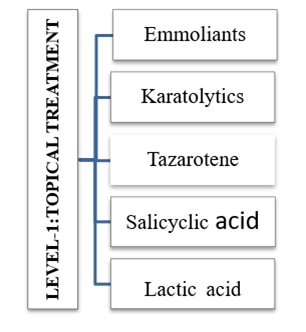
Level 1: Local treatment
Psoriasis treatment aims to stop the rapid growth of skin cells and remove scales. Options include creams and ointments (topical therapy), light therapy (phototherapy), and oral or injectable medications.Which treatment you use depends on how severe your psoriasis is and how it has responded to previous treatments and self-care measures. You may need to try different medications or a combination of treatments before you find an approach that works. Even with successful treatment, the disease usually returns. Emollients (gentle lubricants) should be tried first and then keratolytic lotions. Topical corticosteroids and calcipotriene ointment or cream may be used by internists for psoriasis affecting less than 20% of the body surface area. Most non-dermatologists would probably not use anthralin, crude coal tar, or tazarotene because they are unsightly (messy, uncomfortable to use, and smell bad) and have a high potential for irritation; Coal tar gels, often available over the counter, are more elegant, though less effective. These medications are the most commonly prescribed medications to treat mild to moderate psoriasis. They are available as oils, ointments, creams, lotions, gels, foams, sprays and shampoos. Mild corticosteroid ointments (hydrocortisone) are usually recommended for sensitive areas such as the face or skin folds and for treating large blemishes. Topical corticosteroids can be applied once daily during a flare and every other day or weekend during remission. [19].
Table-1: Local treatment
Level 2: Phototherapy
All forms of phototherapy are highly effective (80% to 100%) in clearing the skin, but some maintenance is required. Disadvantages are the need for special care, the need to visit the doctor's office two to three times a week, the cost, maintenance therapy, the theoretical short-term risks of sunburn and the long-term risk of skin cancer. In addition to natural sunlight and tanning beds, phototherapy is performed by dermatologists in the office or clinic and is reserved for patients with extensive lesions involving 20% or more of the body surface area. Special equipment and training is required to provide phototherapy. Research shows that different types of phototherapy can effectively treat: Small areas of stubborn psoriasis with thick plaques. Palmoplantar (on the hands and feet) psoriasis that you have had for a long time. Plaque psoriasis that covers a large amount of skin.Phototherapy is a treatment that uses certain types of light. If you are interested in using phototherapy, be sure to ask a dermatologist about this treatment. Dermatologists are the doctors who receive the most training in phototherapy.
This treatment can:
- Slow down fast growing skin cells
- Suppress an overactive immune system
- Reduce inflammation and allow skin to heal
- Reduce or eliminate itching [20].
Table-2: Phototherapy

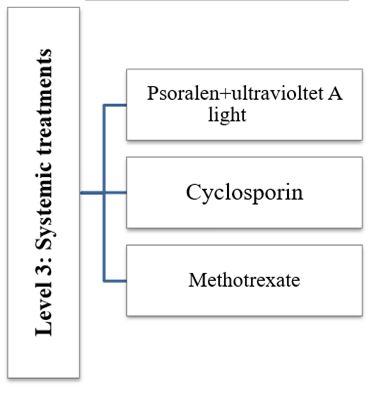
Level 3: Systemic treatment
Systemic treatment is more effective than stage 2 treatment, but is often more expensive and has a greater potential for toxicity. (In general, topical therapies are less toxic than phototherapies, which are less toxic than systemic therapies.) Systemic treatments are generally prescribed only by a dermatologist. Systemic treatments are medications that treat psoriasis from the inside out. They treat the whole body rather than a specific area. A person can take them by mouth or in the form of an injection.Doctors tend to use systemic treatments when people have more severe psoriasis or other related conditions, such as psoriatic arthritis.They may prescribe systemic treatment when the affected area of skin is too large to be treated with topical medications or if the psoriasis plaques do not improve with topical treatment.Systemic treatment may be more effective than topical treatment. They also have more potential side effects and some lower a person's immunity. Although the risk is low, in some cases these treatments can increase the chance of developing an infection or cancer. [21].
Table-3: Systemic treatment
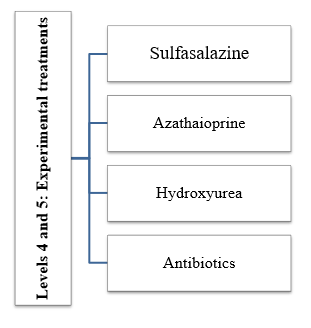
Levels 4 and 5: Experimental treatments
Level 4 and Level 5 treatments are not approved by the US Food and Drug Administration. Level 4 treatment is weakly to moderately effective but less toxic than level 5 treatment, which is reserved for the most severe and resistant cases, including arthropathy. Psoriasis treatment aims to stop the rapid growth of skin cells and remove scales. Options include creams and ointments (topical therapy), light therapy (phototherapy), and oral or injectable medications. Steroid creams or ointments (topical corticosteroids) are commonly used to treat mild to moderate psoriasis on most areas of the body. The treatment works by reducing inflammation. This slows down the production of skin cells and reduces itching. Topical corticosteroids range in strength from mild to very strong. [22].
Table-4: Experimental treatments
PATHOGENECIS
Various mechanisms are believed to be involved in the pathogenesis of psoriasis:
- T cell function
- The role of the dendritic cell
- Hyperproliferation of keratinocytes
- Angiogenesis
- Cytokine mediators
- Reduced apoptosis
- Genetic factors
- The role of oxidants and antioxidants in psoriasis
1. T cell function
T lymphocytes consist of a functionally distinct population of helper T cells and cytolytic T cells. The main function of T cells is to recognize processed peptide antigens that are attached to proteins encoded by MHC class II genes. Therefore, to activate T cells, they need APCs to process and present peptide fragments on the surface of APC cells. T cells secrete various lymphokines. T cells can also inhibit immune responses; in this role they are known as suppressor T cells. Different cell membrane proteins are expressed by different T cell populations. Most helper T cells show CD4 positivity, while cytolytic and suppressor cells are CD8 positive. T cell activation requires three steps: a. Binding b. Antigen-specific activation (signal 1) c. Non-antigen-specific cell-cell interaction (signal 2) [23].
Fig-2: Disease Mechanism of psoriasis
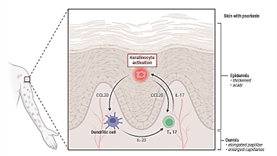
2. The role of dendritic cells
Dendritic cells serve as a major class of antigen-presenting cells that are found in increased numbers in psoriatic skin lesions.[13] Langerhans cells are a type of immature dendritic cell (iDC) found in normal epidermis and can also be found in psoriatic lesions.[14] iDCs are derived from blood monocytes or other myeloid precursors and have an immunostimulatory role. These iDCs are further stimulated to become mature DCs (mDCs). Psoriasis lesions show a marked increase in dermal DCs. XIIIa and CD11c are expressed by myeloid DCs or iDCs, and CD83 and DC-LAMP proteins are positive on mDCs [24].
3. Hyperproliferation of keratinocytes
The skin provides a protective mechanism through its multi-layered structure. The skin consists of five layers, stratum basale, stratum spinosum, stratum granulosum, stratum lucidium and stratum corneum. Keratinocytes are mainly formed in the stratum basale and then migrate to the stratum corneum. As the cells move towards the surface, their organelles disappear and are filled with keratin. The top layer of keratin provides a protective function. Under normal conditions, the epidermal cell cycle is completed in about four weeks. But in psoriatic skin, the epidermal cell cycle is accelerated. Cell division in the basal layer occurs every 1.5 days, and the migration of keratinocytes into the stratum corneum occurs within approximately 4 days. This results in keratinocyte hyperproliferation [25].
4. Angiogenesis
Keratinocytes produce proangiogenic cytokines (VEGF, IL-8), but the exact mechanism of angiogenesis in psoriasis is still unknown. In psoriasis, endothelial cells swell and become activated, these activated endothelial cells migrate, sprout, and lay down a basement membrane with pericytes as structural support for the formation of new vascular networks. This results in an expansion of the intercellular spaces and therefore the dermal blood vessels expand. thereby facilitating the migration of leukocytes into the skin [26].
5. Cytokine mediators
In psoriasis, cytokine production results in epidermal hyperproliferation, vascular dilation, and dermal inflammation. Cytokines implicated in the development of psoriasis include granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor (GMCSF), epithelial growth factor (EGF), IL-8, IL-12, IL-1, IL-6, IFN-?, and TNF- ?. These cytokines result in keratinocyte proliferation, neutrophil migration, potentiation of Th1-type responses, angiogenesis, upregulation of adhesion molecules, and epidermal hyperplasia [27].
6. Reduced apoptosis
To maintain a constant epidermal thickness, keratinocyte proliferation in the normal epidermis is regulated by apoptotic cell death. The epidermal hyperplasia characteristic of psoriasis is thought to be caused by overexpression of P53, and these proliferating cells typically express Bcl-2, which protects them from apoptotic stimuli, whereas terminally differentiated cells lose Bcl-2 expression [28].
CONCLUSION
Psoriasis is clearly a systemic inflammatory disease with many complications, especially metabolic syndrome. CVD was found to be the most important among them. Therefore, dermatologists should work with cardiologists to clarify the condition of psoriatic patients. However, because it is difficult to perform a thorough cardiovascular evaluation in all patients with psoriasis, clinicians require an understanding of which patients are more likely to develop complications, particularly CVD. Although some biologics have been found to be effective in treating CVD, we need to continue to collect long-term case data.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
I would like to express my special appreciation and thanks to my advisor Mr.Satpal Singh you have been a tremendous mentor for me. I would like to thank you for encouraging my research and for allowing me to grow as a research scientist. Your advice on both research as well as on my career have been invaluable. I also want to thank you for letting my defense be an enjoyable moment, and for your brilliant comments and suggestions, thanks to you. A special thanks to my family. Words can not express how grateful I am to my mother, and father for all of the sacrifices that you’ve made on my behalf. Your prayer for me was what sustained me thus far. Finally I thank my God, my good Father, for letting me through all the difficulties. I have experienced Your guidance day by day. You are the one who let me finish my degree. I will keep on trusting You for my future. Thank you, Lord.
REFERENCES
- Talaee R, Hajheydari Z, Moghaddam AY, Moraveji SA, Ravandi BF. Prevalence of oral mucosal lesions and their association with severity of psoriasis among psoriatic patients
- referred to dermatology clinic: A cross-sectional study in Kashan/Iran Open Access Maced J Med Sci. 2017;(5):978–82.
- Kolli SR, Boda N, Reddy EA. Ocular menifestation in psoriasis Natl J Med Dent Res. 2016;(4):101–4.
- Zohreh H, Leila S, Soheila S. Management of psoriasis in children: A narrative review J Pediatr Rev. 2015;(3):131-139
- Campanati A, Neri P, Giuliodori K, Arapi I, Carbonari G, Borioni E, et al Psoriasis beyond the skin surface: A pilot study on the ocular involvement Int Ophthalmol. 2015;(35):331–40
- Ortonne J., Chimenti S., Luger T., Puig L., Reid F., Trueb R.M. Scalp psoriasis: European consensus on grading and treatment algorithm. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2009;(23):1435–1444.
- Nestle F.O., Kaplan D.H., Barker J. Psoriasis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2009;(361):496–509.
- Ko H.C., Jwa S.W., Song M., Kim M.B., Kwon K.S. Clinical course of guttate psoriasis: Long-term follow-up study. J. Dermatol. 2010;(37):894–899.
- Navarini A.A., Burden A.D., Capon F., Mrowietz U., Puig L., Koks S., Kingo K., Smith C., Barker J.N., Network E. European consensus statement on phenotypes of pustular psoriasis. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2017;(31):1792–1799.
- Sommer D.M., Jenisch S., Suchan M., Christophers E., Weichenthal M. Increased prevalence of the metabolic syndrome in patients with moderate to severe psoriasis. Arch. Dermatol. Res. 2006;(298):321–328.
- Gerdes S., Mrowietz U., Boehncke W.H. Comorbidity in psoriasis. Hautarzt. 2016;(67):438–444.
- Ahlehoff O., Gislason G.H., Charlot M., Jorgensen C.H., Lindhardsen J., Olesen J.B., Abildstrom S.Z., Skov L., Torp-Pedersen C., Hansen P.R. Psoriasis is associated with clinically significant cardiovascular risk: A danish nationwide cohort study. J. Intern. Med. 2011;(270):147–157.
- Ogdie A., Langan S., Love T., Haynes K., Shin D., Seminara N., Mehta N.N., Troxel A., Choi H., Gelfand J.M. Prevalence and treatment patterns of psoriatic arthritis in th UK. Rheumatology. 2013;(52):568–575.
- Salomon J., Szepietowski J.C., Proniewicz A. Psoriatic nails: A prospective clinical study. J. Cutan. Med. Surg. 2003;(7):317–321
- Ellinghaus D., Ellinghaus E., Nair R.P., Stuart P.E., Esko T., Metspalu A., Debrus S., Raelson J.V., Tejasvi T., Belouchi M., et al. Combined analysis of genome-wide association studies for crohn disease and psoriasis identifies seven shared susceptibility loci. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2012;(90):636–647.
- Wan J., Wang S., Haynes K., Denburg M.R., Shin D.B., Gelfand J.M. Risk of moderate to advanced kidney disease in patients with psoriasis: Population based cohort study. BMJ. 2013;(347):59-61.
- Szepietowski J.C., Reich A. Pruritus in psoriasis: An update. Eur. J. Pain. 2016;(20):41–46.
- Fleming P., Bai J.W., Pratt M., Sibbald C., Lynde C., Gulliver W.P. The prevalence of anxiety in patients with psoriasis: A systematic review of observational studies and clinical trials. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2017;(31):798–807.
- Sampogna F., Tabolli S., Abeni D. Living with psoriasis: Prevalence of shame, anger, worry, and problems in daily activities and social life. Acta Derm. Venereol. 2012;(92):299–303.
- Henderso n CA, Highe t AS. Acut e psoriasis associate d wit h Lancefiel d grou p C an d grou p G cutaneou s streptococca l Infections . Br J Dermato l 1988, (118):559-562
- Ogdie A., Langan S., Love T., Haynes K., Shin D., Seminara N., Mehta N.N., Troxel A., Choi H., Gelfand J.M. Prevalence and treatment patterns of psoriatic arthritis in the UK. Rheumatology. 2013;(52):568–575.
- Li R., Sun J., Ren L.M., Wang H.Y., Liu W.H., Zhang X.W., Chen S., Mu R., He J., Zhao Y., et al. Epidemiology of eight common rheumatic diseases in china: A large-scale cross-sectional survey in Beijing. Rheumatology. 2012;(51):721–729.
- Carneiro J.N., Paula A.P., Martins G.A. Psoriatic arthritis in patients with psoriasis: Evaluation of clinical and epidemiological features in 133 patients followed at the university hospital of Brasilia. An. Bras. Dermatol. 2012;(87):539–544.
- Abuabara K, Azfar RS, Shin DB, Neimann AL, Troxel AB, Gelfand JM. Cause-specific mortality in patients with severe psoriasis: a population-based cohort study in the U.K. Br J Dermatol. 2010; 163(3): 586–92.
- Ikumi K, Odanaka M, Shime H, et al. Hyperglycemia is associated with psoriatic inflammation in both humans and mice. J Invest Dermatol. 2019; 139(6): 1329–38.
- Brauchli YB, Jick SS, Curtin F, Meier CR. Association between use of thiazolidinediones or other oral antidiabetics and psoriasis: a population based case-control study. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2008; 58(3): 421–9
- Kimball AB, Szapary P, Mrowietz U, et al. Underdiagnosis and undertreatment of cardiovascular risk factors in patients with moderate to severe psoriasis. J Am Acad Derm. 2012; 67(1): 76–85.
- Shih CM, Chen CC, Chu CK, Wang KH, Huang CY, Lee AW. The roles of lipoprotein in psoriasis. Int J Mol Sci. 2020; 21(3): 859.
- Yamazaki F, Takehana K, Tamashima M, Okamoto H. Improvement in abnormal coronary arteries estimated by coronary computed tomography angiography after secukinumab treatment in a Japanese psoriatic patient. J Dermatol. 2019; 46(2): 51–52.


 Shivati manohar*
Shivati manohar*
 Karan Sharma
Karan Sharma






 10.5281/zenodo.11208913
10.5281/zenodo.11208913