Abstract
Multiple emulsions have been proposed for the enhancement of drug bioavailability or as a onset off action for prolonged drug delivery system. Multiple emulsions are often stabilized using a combination of hydrophilic and hydrophobic surfactants. In the present study using W/O/W formulation for prepare of multiple emulsion of ranitidine hydrochloride where analysed the physical parameters and evaluation, during this study most of globular size is ± 5 ?g viscosity is shows the non-Newtonian flow, and the percentage entrapment efficacy is good for drug penetration.
Keywords
span 80, tween 80, liquid paraffin, cmc.
Introduction
Multiple Emulsion: -
Multiple emulsions are defined as emulsions in which both types of emulsions, i.e. water-in-oil (w/o) and oil-in-water (o/w) exist simultaneously. (K,Rajesh) Multiple emulsion of heterogeneous system where one immiscible liquid is dispersed is another in the form of droplets and stabilized. Low Thermodynamic stability. Continuous phase or dispersed phase. Multiple emulsion are complex system and may be called “emulsion of emulsion”, “double or triple emulsions” since the internal phase itself contains dispersed globules which are miscible with the continuous phase based up on the dispersed medium. (S,Pooja I.P 2007)
Ranitidine Hydrochloride: - ranitidine hydrochloride are using for the H2 anti-histaminic. Ranitidine hydrochloride is no anti-androgenic action, less permeability in to the brain does not significantly inhibit hepatic metabolism, over all incidence of side effects is lower. (Triparhi,K.D. Vyas S,P)
Choice of drug: - ranitidine hydrochloride is less toxic as and more effective as compare to other types of anti-histaminic drugs. Ranitidine shows the onset of action for prolonged release.
Types Of Multiple Emulsion: -
O/W/O Emulsion System: -
The O/W/O systems an aqueous (hydrophilic) phase separates internal and external oil phase. In other words, the water-in-oil-water (O/W/O) is a system in which water droplets may be surrounded in oil phase, which is true encloses one or more oil droplets of multiple emulsion. (G, Sumana)
W/O/W Emulsion System: -
The W/O/W systems, an organic (hydrophobic) phase separates internal and external aqueous phases. In other words, water-oil-water (W/O/W) is a system in which oil droplets may be surrounded by an aqueous phase, which is term encloses one or several water droplets. (G, Sumana)
Preparation Of multiple Emulsion by two step method
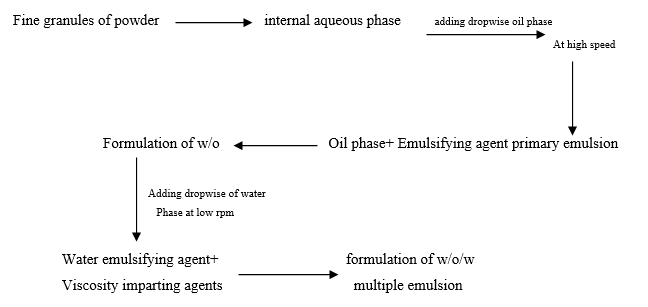
MATERIAL & METHODS
The following chemicals were obtained commercially and were used without further purification. All chemicals used were of the purest grade available the gifted sample of Ranitidine hydrochloride was obtained by PARKBENZ Labourites PVT. Ltd. Mandideep Bhopal, For the preparation of multiple emulsion using span80, tween 80, cmc (carboxy methyl cellulose)
Oil phase :- for the oil phase using (liquid paraffin) as per different concentration for different formulation. Emulsifying agents:- using span 80, span 20. Viscosity imperting agent:- tween 80, cmc
Formulation and Evaluation:-
Three formulation of different W/O/W emulsion were prepared using different ratio of emulsifier and viscosity imparting agent primary and secondary emulsion were prepared as per table no. 01(G,Sumana)
Trial Formulation Of Different Concentration
For Primary Preparation 2000 RPM of Different Formulation for 30 min.
|
Ingredients
|
F1
|
F2
|
F3
|
|
Drug
|
20
|
25
|
30
|
|
Liquid paraffin
|
15
|
18
|
21
|
|
Span 80
|
1.5
|
2
|
2.5
|
|
Water
|
12
|
15
|
18
|
For Secondary Preparation 2000 Rpm Of Different Formulation for 15 min.
|
Primary Emulsion
|
12
|
15
|
18
|
|
Tween 80
|
0.5
|
1.0
|
1.5
|
|
Water
|
30
|
30
|
30
|
|
Cmc
|
2
|
3
|
4
|
|
P value (%)
|
82
|
87
|
90
|
Evaluation:-
(A) Organoleptic evaluation :-
1. General appearance - white or pale yellow crystalline powder
2. Solubility
Freely soluble in water.
Sparingly soluble in anhydrous ethanol
Very slightly soluble in methylene chloride(B.P 2007, USP 2004)
(B)Measurement of globular size:-
Globular size of multiple emulsion was determined by microscopic method size of globular were determined by using tri-ocular microscope firstly the microscope is calibrated using the ocular and stage micrometer.(m, alfred)
Globular size= stage sizeoculer size ×100
×100
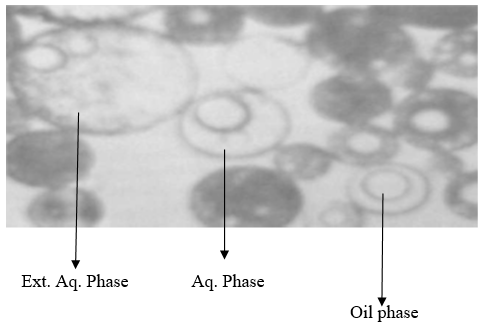
Fig. 1.1 microscopic image of multiple emulsion of w/o/w
For formulation f1
Multiple emulsion was spread the slide by using aqueous and non aqueous dye for the determination of globular
size. Size of 100 globules were measured from different microscopic field.
Table 02. size distribution of globules in formulation f1
|
S. n.
|
Range
|
No. of globules
|
|
1.
|
10-20?m
|
25±4
|
|
2.
|
20-40?m
|
40±2
|
|
3.
|
20-30?m
|
20±2
|
|
4.
|
25-40?m
|
15±3
|
For formulation f2
Multiple emulsion was spread the slide by using aqueous and non-aqueous dye for the determination of globula
size. Size of 100 globules were measured from different microscopic field.
Table 03. size distribution of globules in formulation f2
|
S. n.
|
Range
|
No. of globules
|
|
1.
|
10-20?m
|
40±5
|
|
2.
|
20-40?m
|
25±3
|
|
3.
|
20-30?m
|
20±2
|
|
4.
|
25-40?m
|
15±2
|
For formulation f3
Multiple emulsion was spread the slide by using aqueous and non aqueous dye for the determination of globular
size. Size of 100 globules were measured from different microscopic field.
Table 03. size distribution of globules in formulation f3
|
S. n.
|
Range
|
No. of globules
|
|
1.
|
10-20?m
|
25±4
|
|
2.
|
20-40?m
|
40±3
|
|
3.
|
20-30?m
|
20±2
|
|
4.
|
25-40?m
|
15±2
|
(B) Viscosity:-
The viscosity of the all formulation were determined using brokfield viscometer by using spindal 64. Determination of viscosity of prepared formulation by using different RPM using 64 no. of spindal to determine flow property of multiple emulsion. (vyas s,p & lachman leon)
Compare the viscosity of multiple emulsion (w/o/w) is show in graph
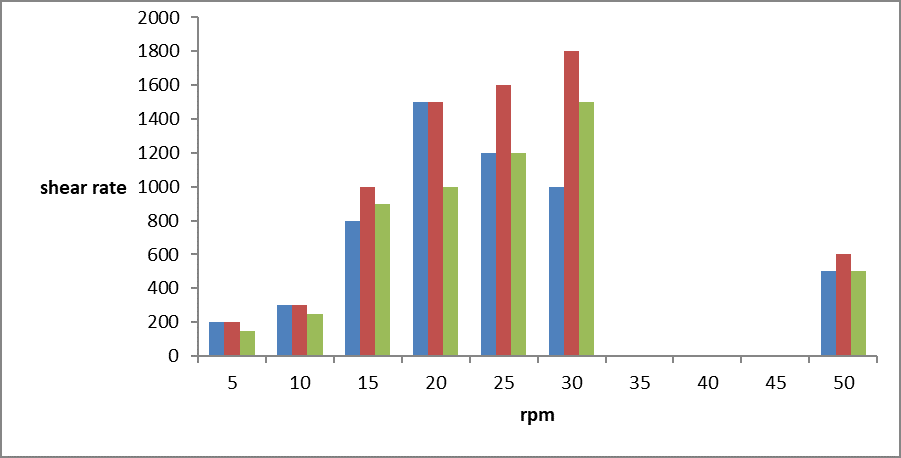
Graph 1. Represent the visosity of different prepared formulation (f1,f2,f3)
(C) Entrapment Efficiency
The Percentage Entrapment Efficiency (?) was determined for the drug content in preparation for the measurement of Percentage Entrapment Efficiency taking freshly prepared W/O/W multiple emulsions different sample (A,B,C) and immediately centrifuged at 4000 rpm for 10 min. Then 1ml of the aqueous phase (the lower layer) was precisely withdrawn through 2 ml hypodermic syringe and diluted properly with phosphate buffer 6.8. The solution was filtered with a Millipore filter (0.22 mm in pore size) and drug content was analyzed on UV spectrophotometer at 247.6 nm. The Encapsulation Efficiency was determined by following equation (lachman, leon)
% Drug Entrapment Efficacy=TOTAL DRUG IN CORPORATED-FREE DRUG TOTAL DRUG×100
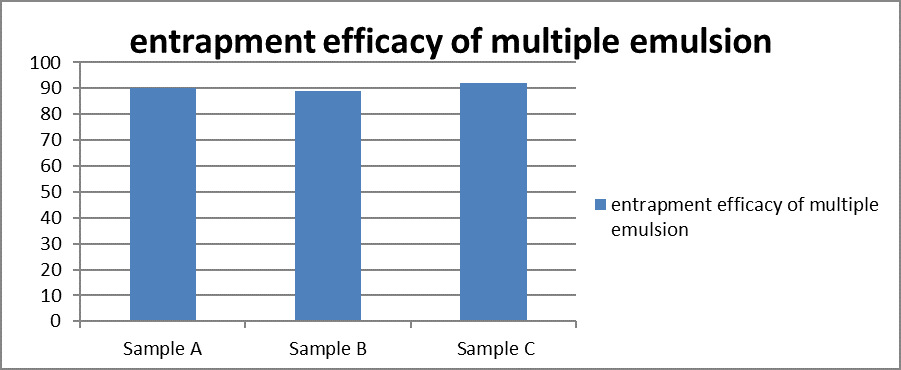
Graph 2. Represent % Entrapment of Drug.
Instruments Used
|
S. N
|
Name
|
Manufacturer
|
|
01
|
Electronic Weighing Balance
|
Citizen India
|
|
02
|
UV Spectrometer
|
Shimadzu-1700 Japan
|
|
03
|
Melting Point Apparatus
|
Jindal, India
|
|
04
|
Ph Meter
|
M.S. Electronics, India
|
|
05
|
Micro Centrifuge
|
Remi-21c, Japan
|
|
06
|
Vortex Mixture
|
Spinix, Japan
|
|
07
|
Ultra Sonicator
|
Pci, Japan
|
|
08
|
Brookfield Viscometer
|
Japan
|
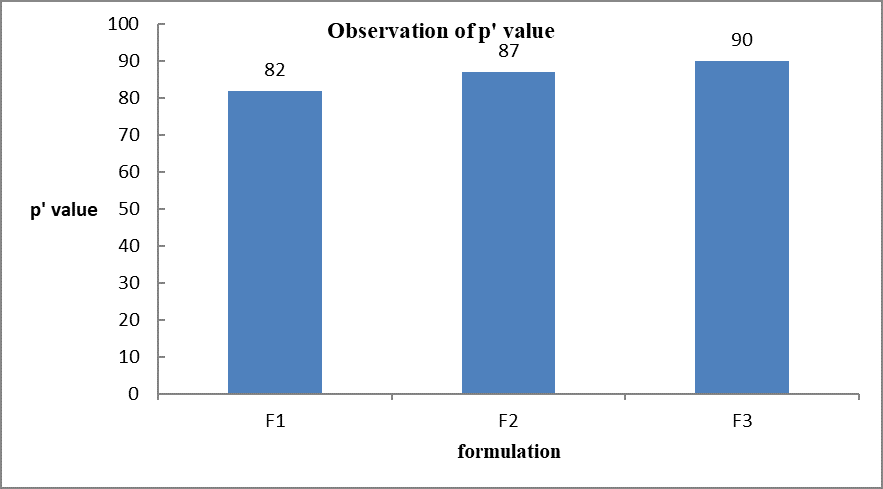
Graph 3.0 Represent the p’value
effect of various viscosity imparting agent on the stability of multiple emulsions.
|
Formulation
|
Viscosity Imparting Agents
|
Conc.
In % W/V
|
Feature
|
P-Value
|
|
S1
|
PVP
|
0.5
|
Unstable
|
Nil
|
|
S2
|
1.0
|
Less viscous
|
64.8
|
|
S3
|
CMC
|
0.5
|
Moderately viscous
|
30.2
|
|
S4
|
1.0
|
More viscous
|
15.6
|
|
S5
|
PEG-20
|
0.5
|
Less viscous
|
59.0
|
|
S6
|
1.0
|
Moderately viscous
|
35.2
|
|
S7
|
HPMC
|
0.5
|
Moderately viscous
|
34
|
|
S8
|
1.0
|
less viscous
|
28
|
RESULT AND DISCUSSION: -
Multiple emulsions are often stabilized using a combination of hydrophilic and hydrophobic surfactants. The ratio of these surfactants is important in achieving stable multiple emulsions. The viscosity of an emulsion can be of crucial importance for the stability of multiple emulsions, specially the viscosity of the external phase.
Melting Point Determination: - Melting point of ranitidine HCL was found at 68-71 ºC.
Determination Of Globular Size Of Prepared Multiple Emulsion: - The globular size of prepared formulation is 5-50?g.
Determination Of Viscosity Of Prepared Multiple Emulsion: -
The viscosity of prepared multiple emulsion of ranitidine hydrochloride is good it will shows non-Newtonian flow.
Determination Of % Entrapment Efficacy: -
The % Entrapment efficacy of prepared formulation is good it’s entrapment efficacy is more then 92%.
REFERENCES
- Rajesh, Kumar., “International Journal of Recent Advances in Pharmaceutical Research” Int J Recent AdvPharm Res, 2012;2(1):9-19
- Pooja, Sonakpuriya., “Formulation And Evaluation Of Multiple Emulsion Of Valsartan” International Journal of Pharm Tech Research, 2013, Vol.5, No.1, page no. 132- 146
- Sherman P. Rheological Properties of Emulsions. In: Becher P. ed. Encyclopedia of Emulsion technology Volume 1: Basic Theory. New York, NY: Marcel Dekker; 1983:215- 248.
- Sumana Ghosh International Journal of Research in Pharmaceutical and Biomedical Sciences, 2012 ISSN: 2229-3701
- Indian Pharmacopoeia. (1996). Controller of publication, Delhi, Vol-I, 436-437.
- Becher, P., (1965). Emulsions, “Theory and Practice (2nd Ed.) Reinhold”, New York, pp.2-149.
- Kita Y, Matsumoto S and Yonezawa D (1978). “Permeation of water through the oil layer in w/o/w type multiple phase emulsions”. Nippon Kagaku Kaishi, pp.11-14.
- Alfred martin, james swarbrick, Arthur cummarta physical pharmacy 3rd edition K.M. Varghese company Indian edition page no.480-482
- Leon lachman, Herbert A. lieberman. The theory and practice of industrial pharmacy, special Indian edition 2009 published by CBS publishers and distributors. page no-529-530 and 513-514.
- K.D Tripathi Essential Of Medical Pharmacology 5th edition 1996 published by Jaypee brothers page no.589-591
- S.P Vyas and R.K Khar targeted and controlled drug delivery novel carrier system published by CBS and publisher and distributors page no.309.
- USP/NF the official compendia of standards Asian edition 2004 page no.1624
- Indian pharmacopoeia 2007 volume 1st government of ministry of health and family welfare published by the Indian pharmacopoeia Ghaziabad page no.151,387,1651,163
- British pharmacopoeia 2009 volume 2nd general notice monograph medicinal and pharmaceutical substances,(j-z) marketed tower 1nine elms lane London SW 85 NQ page no.1765-176
- Gilbert s banker Christopher t Rhodes Morden pharmaceutics 3rd edition revised and expended volume 72 printed by united state of America
- Florence, AT., and Whitehill, D., (1982). “The formulation and stability of multiple emulsions”. J. Pharm. Pharmacol., 34: 687.
- Florence, AT., Whitehill, D.,(1982) “The formulation and stability of multiple emulsion”. Int J Pharm.11:277.
- Florence, AT., Whitehill, D., (1984) “Some features of breakdown in w/o/w multiple emulsions. JGarti N. Progress in stabilization and transport phenomena of double emulsions in food Groves MJ”. “The application of particle characterization methods to submicron dispersion and emulsions”. Chemical Analysis, 73: 43-92.
- Hideaki, Okochia., Masahiro, Nakanob .,(2000) “Advanced Drug Delivery” Reviews 45 : 5–26
- Kawashima Y, Hino T, Takeuchi H and Niwa T (1992). “Stabilization of water/oil/water multiple emulsion withhypertonic inner aqueous phase”, Chem. Parma. Bull., 40: 1240-1246
- Khan, AY.,(2007) “Potentials of Liquid Membrane System”:An overview, Pharmainfo.net. 5
- Kita Y, Matsumoto S and Yonezawa D (1978). “Permeation of water through the oil layer in w/o/w type multiple phase emulsions”. Nippon Kagaku Kaishi, pp.11-14.
- Laetitia O, Monique S, Lev B, Madelein B, Thi-Nhat- Lien D and Jean-Louis G (2003). “Optimization of a thermally reversible w/o/w multiple emulsion for shear-induced drug release”. Int. J. Cont. Release, 88: 401-412.
- Lee JS, Kim JW, Han SH, Chang HS, Kang HH, Lee OS, Oh SG, Suh KD., (2004) The stabilization of l-ascorbicacid in aqueous solution and water-in-oil-inwater double emulsion by controlling pH andelectrolyte concentration, J Cosmet Sci.;55:1.
- Lee, SC., (2004) Comparison of extraction efficiencies of penicillin G at different w/o ratios in theemulsion liquid membrane systems with dilute polymer Solutions. J Membr Sci. 237:225.
- Lee,V.H., and Robinson, J.R.., (1978)Sustained and Controlled Release Drug Delivery System, NewYork, Marcel Dekker.
- M. Sedef Erdal, Ahmet AramanTurkish (2006)J. Pharm. Sci. 3 (2), 105-121.
- Mathiowitz,(1999) “Encyclopedia of Controlled Drug Delivery”, New York, John Wiley & Sons.


 Mohd Sajjad* 1
Mohd Sajjad* 1














 10.5281/zenodo.14067766
10.5281/zenodo.14067766