Abstract
The majority of commercial soaps contain chemicals and synthetic components that can be unpleasant or harmful to the skin. Human skin requires specialized therapy for healing, enhanced skin tone, and the look of radiant health.Another potential approach is to use natural herbal soaps. Our study's objective was to create herbal hygienic soap using an antibacterial ingredient and the cold process technology. Herbal soap was prepared using Shikekai, Lemon oil, neem, Ethanol, Glycerin, Steric acid, Soft Paraffin, Ficus religiosa (Active ingredient),and NaOH (lye) and different extracts were included into basic saponification reaction. The herbal formulation was prepared and evaluated for the analysis of pH, moisture content, foaming index, foam retention time, saponification, soluble matter, antimicrobial testing using different concentration of soap solution comparing with standard. The herbal soap has satisfactory antimicrobial results as compared to antibiotic. Moreover, oils used are added to treat various skin infection and for daily usage. Most of the commercial soaps contain chemicals that can be harmful to the skin and using a natural herbal soap can be a good alternative. Herbal soaps are made using natural herbs and ingredients that are healthier and beneficial for the skin and are less likely to cause any damaging effect. Some of the natural soap manufacturers also use aroma therapy and herbal treatments to offer the best skin treatment solution for your skin. Made of rare herbs and 100% natural ingredients, herbal soaps have found to be highly beneficial for the skin. It is generally known that soap is produced by the saponification of a triglyceride (fat or oil). In the process the triglyceride is reacted with a strong alkali such as; potassium or sodium hydroxide to produce glycerol and fatty acids salt.
Keywords
Herbal, Ficus Soap, Cleaning, Religiosa
Introduction
Cosmetics are defined in the Drugs and Cosmetics Act as items intended to be rubbed, poured, sprinkled, or sprayed on, introduced into, or otherwise applied to the human body or any portion thereof for washing, beautifying, encouraging attractiveness, or altering appearance. The cosmetic does not fall under the scope of the drug license. Herbal cosmetics are preparations that contain phytochemicals derived from a variety of botanical sources that influence skin functions while also providing nutrients required for healthy skin or hair. Herbal cosmetics are natural herbs and their products utilized for their aromatic properties in cosmetic preparation.3-5. Herbs and essential oils used in cosmetics cannot claim to have any therapeutic benefit or to penetrate beyond the skin's surface layers, according to the Drug and Cosmetics Act. Herbal soap preparation is a medicine or drug that contains anti-bacterial and anti-fungal chemicals. It mostly uses plant parts such as leaves, stems, roots, and fruits to treat an injury or disease or to promote good health. This preparation has antimicrobial properties and can be applied topically in a variety of forms, including creams, lotion gel, soap, solvent extract, and ointments. Various soap qualities have been utilized to cure a number of skin conditions. The majority of skin infections are caused by fungus, staphylococcus aurous, and streptococcus species.
Discovery of Soap
The Discovery and Art of Soap Making Up to 1660. Soap, defined as the substance produced by the action of a base on fats and oils, has played an essential role in civilization's history, yet its discovery was unintentional, and its utility was only gradually recognized. As a result, following Liebig and others' lead and attempting to analyze prior civilizations based on their knowledge or lack thereof of soap is just impossible. If this were not the case, the Fanti of West Africa and the Gauls of the first century A.D., who appear to have found soap independently, would have advanced further in civilization than the Egyptians or the Greeks, both of whom were unaware of soap. Both the Egyptians and the Greeks were familiar with therapeutic remedies that contained alkalis, tallow, and various vegetable oils, among other components. The Papyrus Ebers describes the use of similar ointments to treat herpes and to remove fat around the eyes25. Many different types of lead plasters were also known. Again, the Berlin Papyrus instructs on preparing an ointment using natron and tallow27, while Hippocrates utilized oil and soda combinations as purgatives26. According to early writings, the Assyrians employed a mixture of castor oil and alkali as a head wash.27 In addition to this knowledge, the production of alkaline lyes from plant ashes was well known to practically all nations from very early times; nonetheless, their usage in the making of soap appears to have occurred at least not until the Christian era.
Herbal Soap.
Herbal soap preparation is a medicine that contains antibacterial, anti-aging, anti-oxidant, and anti-septic characteristics. It mostly uses plant parts such as seeds, rhizomes, nuts, and pulps to treat an injury or disease or to improve health. Herbs are the most commonly used natural items to cure practically all ailments and skin problems due to their great medicinal value, low cost, availability, and compatibility. The herbs used were chandana, nagkeshara, padmak, khus, yashtimadhu, manjistha, sariva, payasya, seta (sweta durva) and lata (shyama durva). These ayurvedic herbs are used to purify blood and eliminate vitiated doshas like (vata, pitta, kapha) from the body as they are mainly responsible for skin disorders and other diseases. The herbs mentioned in khushthagna mahakashaya effective in skin disorders, include khadira, abhaya, amalaki, haridra, bhallataka, saptaparna, karavira, vidanga and jati.
Advantages of herbal soap:
Natural components:
Herbal soaps are prepared with natural plant-based ingredients including essential oils, herbs, and botanical extracts, which are gentler on the skin and less prone to cause irritation or allergies.
Moisturizing properties:
Many herbal soaps include moisturizing components such as shea butter or coconut oil, which help keep the skin hydrated and supple.
Aromatherapy benefits:
Herbal soaps frequently contain essential oils with aromatherapeutic characteristics, which can aid in relaxation, stress alleviation, and overall well-being.
Disadvantages of herbal soap:
Limited availability:
Herbal soaps may not be as readily available as conventional soaps in supermarkets or drugstores, requiring consumers to seek out specialty stores or online retailers.
Cost:
Herbal soaps can be more expensive than regular soaps due to the use of high-quality natural ingredients.
Shorter shelf life:
Because herbal soaps are made with natural ingredients and lack preservatives, they may have a shorter shelf life compared to commercially produced soaps.
Benefits of herbal soap:
Herbal soaps are soap, not detergent bars.
They include no synthetic detergents or foaming ingredients.
Glycerin provides longer-lasting moisture to your hands.
Herbal soap contains natural ingredients, fragrances, and oils that are known for locking in moisture and hydrating the skin.
Because the components are free of chemicals, herbal soap frequently has healing powers.
MATERIAL AND METHOD
All the ingredients are used in this formulation have herbal grade. The ingredients are collected from different sources.Peepal bark,peepal leaves,neem leaves,lemon oil,Shikekai powder,Chandan powder,coconut oil,apricot fruit purchased from the general store.
Ingredients used in formulation of herbal soap & their roles
Table- 1: List of herbal soap ingredients & its role

Ingredients used in formulation of Soap base and their quantities
Table- 2: List of soap base ingredients& their role
Peepal :-
Synonym-
Peepal, Pipul, Pipar
Scientific name-
Ficus religiosa
Family-
Moraceae
Part typically used: Stem
Color:
Brown
Chemical Constituents:
phenols, tannins, steroids, alkaloids and flavonoids, ?-sitosteryl, n-octacosanol, methyl oleanolate, lanosterol, stigmasterol, lupen-3-one.
Uses:
Shoots are used in treating skin problems. Various parts of the Peepal tree have anti-microbial and anti-inflammatory effects which are helpful in removing many skin-related disorde
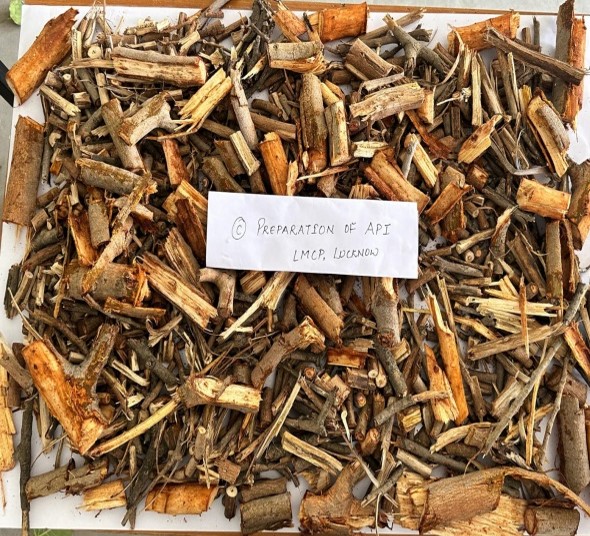


Fig- 1: Ficus Religious Stem & Ficus charcoal powder
Neem :-
Synonym-
Nimba,Aristha,Neem
Scientific name-
Azadirachta indica
Family-
Meliaceae
Part typically used: Leaves
Color:
Green
Chemical Constituents:
Azadirone, Nimbin, Nimbidin, Vanilic acid,Glycosides, B-sitosterol, Nimbectin, Kaempeerol, Quercursertin are present in Neem Leaf.
Uses:
It may have anti-allergenic activity. It may have anti-inflammatory activity. Neem leaves are used to treat head lice, skin diseases, wounds or skin problems.


Fig- 2: Neem leaves & Neem powder
Shikekai :-
Synonym-
Senna occidentalis, Shikekai
Scientific name-
Acacia concinna
Family-
Leguminose
Part Typical used:
Fruits pods
Colour:-
Brown
Chemical Constituents:
Spinasterone , Acacic acid
Uses:
Anti-dandruff detergen. It is amazingly good at cleansing and nourishing skin and hair
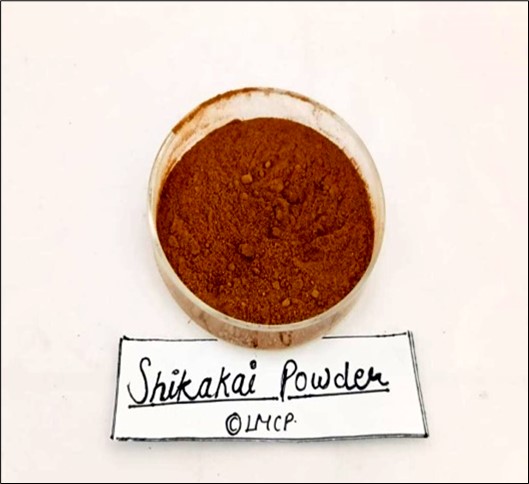


Fig- 3: Shikakai fruit & Shikakai powder
Chandan:
Synonym-
Sandalwood, Chandan
Scientific name-
Santalum album
Family-
Santalaceae
Part partically used:
Wood
Color-
Cream
Chemical Constituents:-
Sandalwood oil contains more than 90% sesquiterpenic alcohols of which 50-60% is the tricyclic ?-santalol. ?-santalol comprises 20-25%.
Uses:-
It has anti-inflammatory properties and calming effect.Deeply Cleanses The Skin By Exfoliating Dirt, Impurities and Clogged Pores.The blend of oils and butters makes the soap super moisturizing.


Fig- 4: Chandan wood & chandan poder
Apricot:
Synonym-
Apricot tree
Scientific name-
Prunus armeniaca L.
Family-
Rosaceae
Part partically used:
Fruit
Color-
Yellowish- orange
Chemical constituent –
Isocitric acid ,succinic acid ,fumaric acid ,shikimic acid.,
Uses-
It is rich in vitamin E and antioxidant properties which keep damage at bay and promote the revival of skin cells.Its rejuvenating and nourishing effects on the skin.


Fig- 5: Apricot fruit
Lemon oil:
Synonym-
Lemon
Scientific name-
Citrus limon
Family-
Rutaceae
Part partically used:
Fruit
Color-
Light-Yellow
Chemical Constituents:-
Citric acid,Ascorbic acid,minerals, flavonoids and essential oils.
Uses:
Contains volatile oil used for aroma, contains Vitamin C, which has antioxidant activity, and antibacterial activity, treat acne.The antiseptic properties of Lemon essential oil in this natural soap relieve oily skin, blemishes, and acne but are surely suitable for normal skin types too.


Fig- 6: Lemon oil
Coconut oil :
Synonym-
coconut, coco, coco-da-bahia
Scientific name-
Cocos nucifera
Family-
Arecaceae
Part partically used:
Fruit
Color-
Light-Yellow
Chemical constituents:
Fatty acids, caprylic acid ,capric acid, lauric acid ,myristic acid, palmitic acid, stearic acid ,oleic acid and linoleic acid.
Uses:
Some oils, such as coconut oil and palm oil, contribute to the hardness and longevity of the soap bar.Coconut oil creates a protective moisturizing shield on the skin.


Fig- 7: Coconut oil
PREPARATION OF HERBAL SOAP
The main goal of present research was to formulate and evaluate the herbal soap which prepared from herbal ingredients.The herbal ingredients chosen for preparation of herbal soap were Ficus religiosa bark charcoal , Azadirachta indica, Citrus limon, Santalum album, Acacia concinna, and Laboratory reagents,etc were used.These ingredients are based on their individual properties. Soap base is used cake formation and remove dirt from the skin.Ficus religiosa bark is used to preventing skin problems.Citrus limon oil is used as antioxidant,skin lightening agent and rice source of Vitamin-c.
PROCEDURE FOR PREPARATION OF SOAP BASE
Soap base is prepared in the two phases.
- Aqueous phase
- Non-aqueous phase (oil phase)
PROCEDURE OF SOAP BASE:
The soap base is prepared to the following steps:-
- Took it coconut oil (75ml) in a 500 ml beaker and put on water bath for 10-15 minutes at 400-450C temperature.(Oil phase)
- In another beaker, took Sodium hydroxide (13.20 gm) dissolved in distilled water (24ml) in 100 ml beaker and mixed properly.Kept a side for 5 minutes.(Aqueous phase)
- After heating the oil phase then oil phase was adding slowly in aqueous phase with continuous stirring on the water bath and maintained the temperature. Avoid the phase separation.
- After mixing the both phases, allowed for cooling and thick texture was formed, Soap base was prepared.



Fig- 8: Prepared liquid soap base
PROCEDURE FOR PREPARATION OF HERBAL SOAP
The herbal soap is prepared to the following steps:-
- Took soap base in a beaker and put on water bath at 400-450C temperature.
- Added all ingredients such as Ficus religiosa bark charcoal, Azadirachta indica powder, Citrus limon oil, Santalum album powder, Acacia concinna powder,Stearic acid, Soft paraffin ,Ethanol,Apricot extract,Sodium lauryl sulphate and Glycerin in soap base. Then, all ingredients were mixed properly on water bath with continuous stirring.
- Prepared soap mixture was filled in clean blank soap mould and after filling the mixture,filled soap mould were put in the refrigerator for 45 minutes.
- After solidification,removed the soap mould and then herbal soap was obtained. Then ,Labeled the herbal soap and submitted.
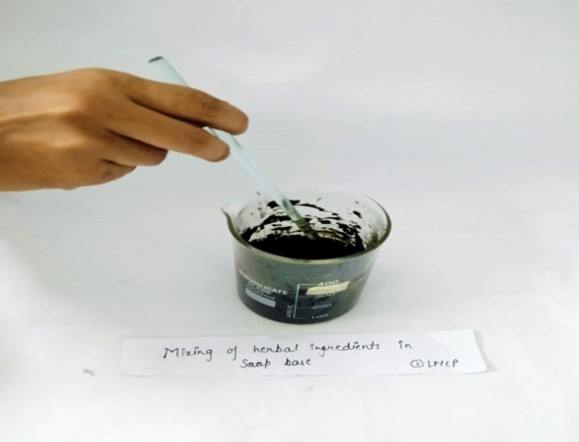
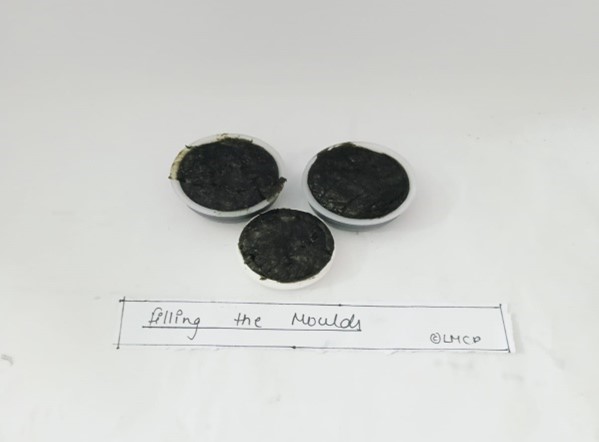


Fig- 9: Mixing of all ingredients in liquid soap base & Filling the mixture of herbal soap in moulds
EVALUATION PARAMETER OF HERBAL SOAP
The formulated herbal soap were evaluated for color, odour, clearity test, pH test, dirt dispersion, foaming height, foaming ability, skin irritation test, dissolving test, wetting time test, using recommended procedure.
PARAMETERS
- Colour and clarity characterization:
The herbal soap was visualized using a white background for the determination of the colour and see the clarity of the herbal soap.
- Odour:
The odours of herbal soap were evaluated by applying preparation on hand and feel the fragrance of perfume.
- Shape:
The shape of the herbal soap was round and determined by the naked eyes.
- pH test :
First of all prepare 1% of sample (5gm sample/soap in 50ml of Distilled water) for determination of pH and prepared a buffer solution of pH-7. Then the Electrode was immersed in the buffer solution and calibrates the pH meter. After calibrating then measure the pH of the sample solution and record the pH of the sample soluti
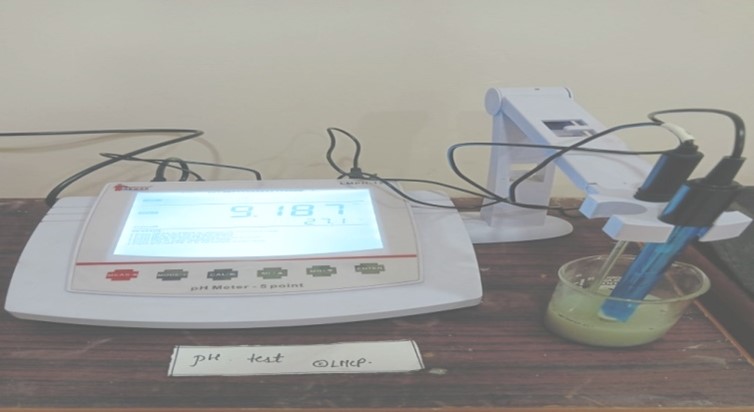

Fig- 10: pH measurement test
-
Dirt dispersion test :
First of all prepare 1% of sample (5gm sample/soap in 50ml of Distilled water) were taken in a measuring cylinder and add 2 drops of ink in the sample. Then the measuring cylinder was covered with hand and shaken 10 times. Sample that because the ink to concentrate in the foam is considered quality. Then identify in water portion the remaining particles of dirt, the portion of ink in the foam was observed.
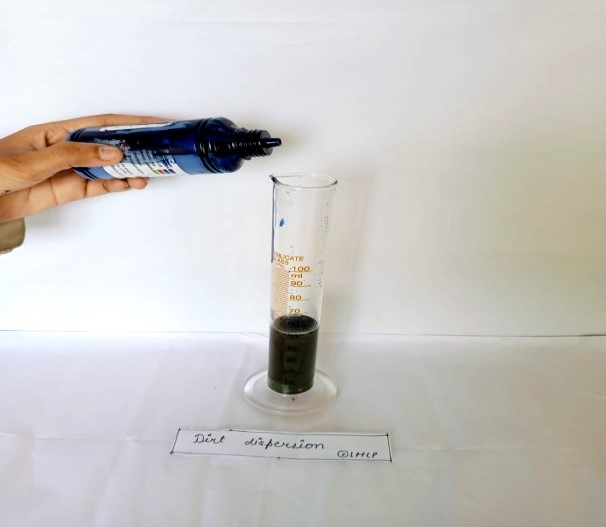
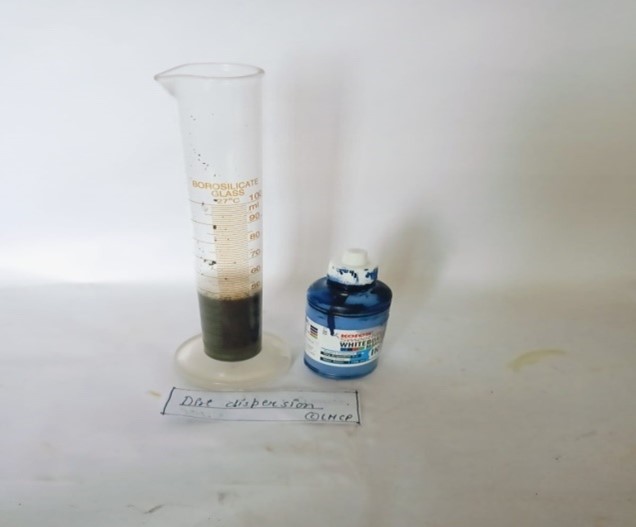


Fig- 11: Dirt dispersion test
-
Wetting time test:
First of all a cotton cloth is cut 1 diameter round shape for the determination of wetting time of the sample and then measure wetting time. Then prepare dilute sample 1% solution (5gm sample in 50 ml distilled water) and round shape cotton cloth placed in the sample solution and then start the stopwatch for determination of wetting time. The cloth was floated on the surface of sample solution. After a sometime then the cloth is absorb the sample and sink the cloth in the sample solution. The stopwatch is stop record and note accurately wetting time.

Fig- 12: Wetting time test
-
Skin irritation test:
Prepared herbal soap was applied on the skin for 10 minutes and observed the irritation feeling. No irritation sensation was observed and soap was considered as a, Non-irritation soap.
- Dissolving test:
Take (1gm of sample/soap in 50ml of distilled water) in 100 ml beaker, mix the sample with continuous stirring and observed the sample completely dissolved in water.
- Foaming ability test:
Take 1% of sample (5gm sample/soap in 50ml of Distilled water) were taken in a 100ml measuring cylinder. The measuring cylinder was shaken for 10 times and then, measuring cylinder was allowed to stand for 5 minutes. Then the foam was produced, measured and record it.

Fig- 13: Foaming ability test
10. Foaming height test: Take 1% of sample (5gm sample/soap in 50ml of Distilled water) were taken in a 100ml measuring cylinder. The measuring cylinder was shaken for 10 times and stand till aqueous volume measured up to 50ml and measured the foam height, above the aqueous volume was measured and record it.
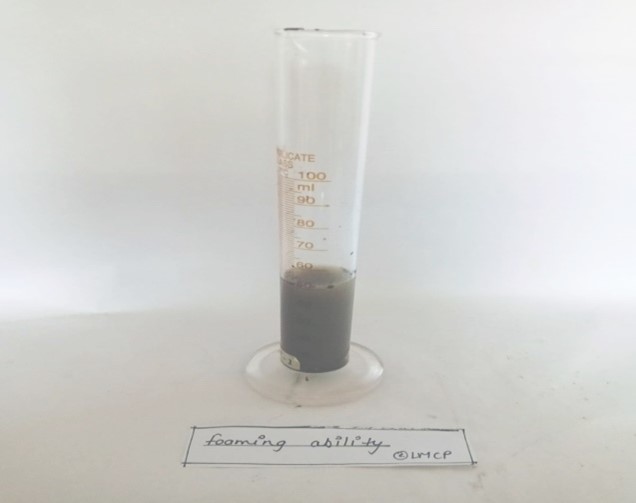
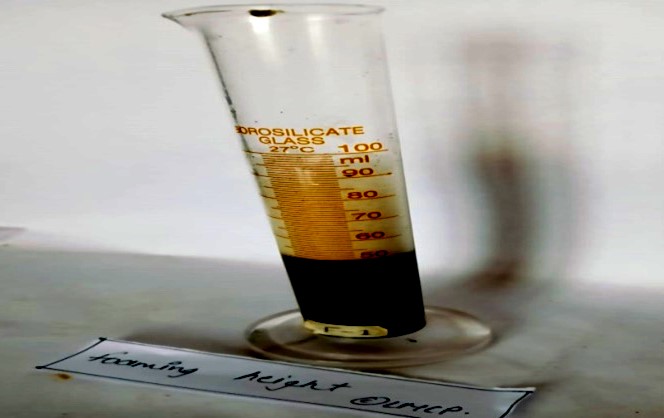



Fig- 14: Foaming height test
RESULT & DISCUSSION
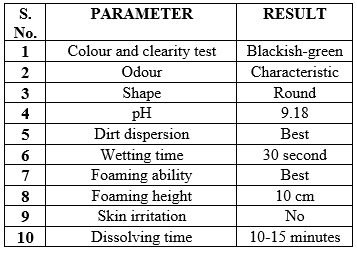
Various types of herbal ingredients were used in the formulation of herbal soap that contains herbal ingredients such as, Ficus religiosa, neem powder, shikakai powder, chandan powder, apricot extract. Ficus religiosa used for the anti-microbial, anti-bacterial property and it is a rich source of Vitamin-k, tainen and Phaetosteroline. Lemon oil contains Vitamin-c and showing anti-oxidant property. Neem powder used as a anti-fungal agent and treatment of acnes. Apricot extract is rich in vitamin E and antioxidant properties which keep damage at bay and promote the revival of skin cells. Its rejuvenating and nourishing effects on the skin. Chandan powder used for the removing of tanning from skin and pigmentations. Shikakai powder may help to remove dead skin cells and give skin a natural glow, may have anti-dandruff potential and anti-hair fall potential. The herbal soap was evaluated to the various parameters such as, organoleptic parameter, pH test, foaming ability and foaming height test, skin irritation, dirt dispersion test, wetting time test and dissolving test. The effect of different herbal ingredients in the formulation was investigated.
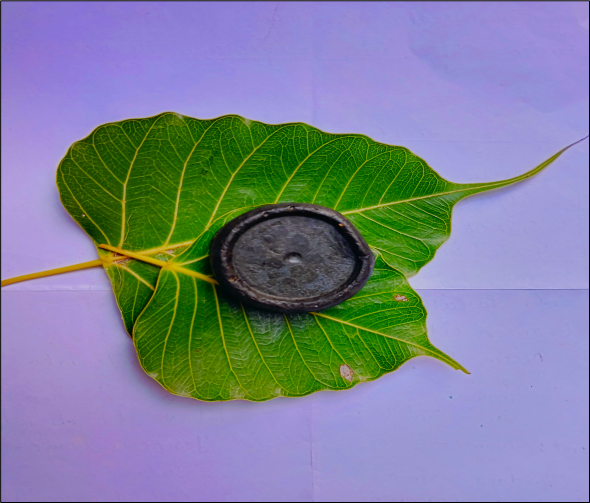
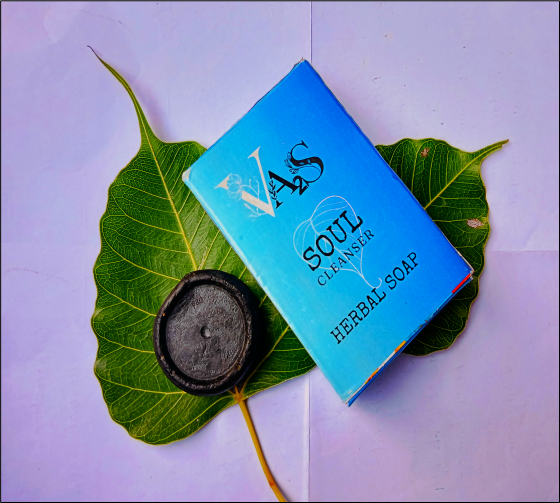


Fig- 15: Formulated Herbal Soap (Soul Cleanser)
RESULTS OF EVALUATION PARAMETER OF HERBAL SOAP
Table-3: Evaluation result of herbal soap formulation
CONCLUSION
The investigation of herbal soap was done and it was concluded that the prepared herbal soap shows the best results. Hence, present research shown that the herbal soap possess less / minimal or no side effects and showing a satisfactory results. The various types of herbal ingredients were used in the formulation of herbal soap that contains herbal ingredients such as, Ficus religiosa, neem powder, shikakai powder, chandan powder, apricot extract, etc for skin care or maintain the healthy skin. The herbal soap was evaluated to the various parameters such as, organoleptic parameter, pH test, foaming ability and foaming height test, skin irritation, dirt dispersion test, wetting time test and dissolving test. The effect of different herbal ingredients in the formulation was investigated. The evaluated parameters wre exactly similar to standard parameters. On the basis of evaluation studies the formulations provide excellent foaming property and skin irritation and other parameters was determined by using prepared herbal soap, hence it proven that this herbal soap does not produce any side effects or irritation after applying on the skin. The herbal soap was prepared by using cold process method.
REFERENCES
- Moore Michael, “Herbal Formulas for Clinic and Home”, Bisbee, AZ 85603, 1995.
- There U G, et al. Formulation of Hand Made Soap by using Goat Milk, International Journal for Research in Applied Science & Engineering Technology, 2022; 10(2): 955-960
- Bhupinder Singh Sekhon and Neeraj Choudhary, “An overview of advances in the standardization of herbal drugs”, J Pharm Educ Res., 2011.
- Newman DJ, Cragg GM, “International collaboration in drug discovery and development from natural sources, Pure Applied. Chemistry, 2005.
- Lachman L, Lieberman H, Kanig J, “The Theory and practice of Industrial pharmacy”, 3rd edition Bombay, Varghese publishing House, pg. 1987-457.
- Pawar, et al. Formulation and Evaluation of Polyherbal Soap. Research J. Topical and Cosmetic Sci, 2019; 10(1): 23-28. 18)
- Joshi, et al. Formulation and Evaluation of Herbal Soap, Shampoo andFace Wash Gel, Journal of Plant Resources, 2019; 17(1):112-117.
- Talreja, Shreya & Tiwari, Dr. (2023). Formulation and Evaluation of Herbal Soap By Using Moringa Oleifera As Main Active Constituents. European Chemical Bulletin. 12. 2121-2141.
- Brickell C and Zuk JD. 1997. The American Horticultural Society A-Z Encyclopedia of Garden Plants. DK Publishing, Inc., NY.2019.
- Chandira et al. Formulation and Evaluation of Herbal Soap by using Melt and Pour Method, Indian Journal of Natural Sciences, 2022; 13(72): 44244-44626. 23)
- Rajan, et al. Physio-chemical study of various marketed soap samples: a comparative evaluation, The International journal of analytical and experimental modal analysis, 2021; 13(1): 35-41. 24)
- Haneefa , et al. Formulation and evaluation of medicated soap of Ixora coccinea root extract for dermal infections, J. Pharm. Sci. & Res, 2019; 11(8): 3094-3097.
- Galil J and Eisikowitch D. 1968. On the pollination ecology of Ficus religiosa in Israel. Phytomorphology.18: 356-363.
- Hocking D. 1993. Trees for Drylands. Oxford & IBH Publishing Co. New Delhi.
- Nadel H, Frank JH, and Knight RJ. 1992. Escapees and accomplices: The naturalization of exotic Ficus and their associated faunas in Florida. Florida Entomologist. 75(1): 29-38.
- K. K. Singh, ed. (2009). Neem A Treatise. I.K. International Publishing House, India.
- Paul R., Prasad M., Sah N. K. Anticancer biology of Azadirachta indica L (neem): a mini review. Cancer Biology and Therapy.2011.
- Rutuja RS, Shivsharan U, Shruti AM. Ficus religiosa (Peepal): A Phytochemical and Pharmacological Review.
- Murti K, Lambole V, Gajera V, Panchal M. Exploration of healing promoting potentials of roots of Ficus religiosa.
- Klimek Szczykutowicz M, Szopa A, Ekiert H. Citrus limon (Lemon) phenomenon-a review of the chemistry, pharmacological properties, applications in the modern pharmaceutical, food, and cosmetics industries, and biotechnological studies .Plants 2020
- Khanpara, Komal & J Renuka, V & Harisha, Channappa. (2012). A detailed investigation on shikakai (Acacia concinna Linn.) fruit. J. Curr. Pharm.


 Sadhana Singh*
Sadhana Singh*
 Shashank Tiwari
Shashank Tiwari
 Amisha Kumari
Amisha Kumari
 Abhay Rajvanshi
Abhay Rajvanshi






























 10.5281/zenodo.13731677
10.5281/zenodo.13731677