Abstract
Mouth dissolving films (MDFs) represent a significant advancement in drug delivery systems, providing an alternative to conventional tablets and capsules. This review explores the evaluation parameters critical to ensuring the quality, efficacy, and safety of MDFs. These parameters include disintegration time, weight variation, film thickness and uniformity, tensile strength, surface pH, drug content uniformity, and in vitro drug release. The emphasis is on understanding these parameters' roles and the advanced techniques used in their assessment. Regulatory considerations and challenges in formulation are also discussed to provide a comprehensive overview of MDF evaluation in modern pharmaceutics.
Keywords
Mouth dissolving films (MDFs), Oral films, Evaluation parameter
Introduction
The oral route is the most popular and preferred method for administering drugs due to its non-invasive nature, convenience, and high patient compliance. This method involves the intake of drugs through the mouth, leading to systemic absorption primarily via the gastrointestinal tract. Traditional oral dosage forms such as tablets and capsules dominate the market because of their ease of production, accurate dosing, and patient familiarity. However, these conventional forms may not be suitable for all patient groups, particularly those who experience difficulty swallowing (dysphagia), including pediatric, geriatric, and bedridden patients, as well as those with nausea or vomiting tendencies(1).
To address these limitations, recent advancements in drug delivery technology have focused on developing alternative oral dosage forms that can enhance patient compliance and provide a more efficient therapeutic effect(2). Among these innovations are bioadhesive mucosal dosage forms, which include adhesive tablets, gels, patches, and notably, mouth-dissolving films (MDFs)(1) .Mouth-dissolving films (MDFs) are ultra-thin, flexible films designed to rapidly disintegrate and dissolve when placed on the tongue, releasing the active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) directly into the oral cavity. This process facilitates the drug's entry into the systemic circulation primarily through the mucosal lining, bypassing the gastrointestinal tract and the first-pass metabolism by the liver. This results in a quicker onset of action and potentially improved bioavailability of the drug(3) .
MDFs offer several advantages over traditional oral dosage forms. Firstly, their thin and flexible nature makes them easy to administer, without the need for water, making them highly convenient for on-the-go usage. Secondly, the rapid disintegration and dissolution in the oral cavity enhance patient compliance, particularly in populations with swallowing difficulties. Additionally, MDFs provide a precise and consistent dosage form, which is crucial for drugs requiring strict dose control(3) . The ability to bypass the first-pass effect and improve drug bioavailability is another significant advantage, making MDFs an attractive option for drugs with poor oral bioavailability(4).
The development of MDFs leverages several advanced technologies in pharmaceutical manufacturing. Techniques such as solvent casting, hot-melt extrusion, and semisolid casting are employed to produce these films. These methods allow for the incorporation of various APIs, polymers, plasticizers, sweetening agents, and other excipients to tailor the film's properties, including its disintegration time, mechanical strength, and taste(5). Despite their numerous benefits, MDFs present certain formulation and manufacturing challenges. Achieving dose uniformity can be technically demanding due to the film's small size and the need for precise control over the distribution of the API. The hygroscopic nature of many films necessitates special packaging to protect them from moisture, which could otherwise compromise their stability(6)(7) and efficacy. Additionally, incorporating high doses of drugs into the films is limited by the film's capacity, usually restricting the dose to less than 40 mg per 4 cm?2; piece(3) .
MDFs have found applications in various therapeutic areas, including pain management, antihistamines, and antiemetics, among others. Their ability to provide rapid relief makes them particularly useful in acute care settings and for conditions requiring quick therapeutic intervention. The favorable patient acceptance due to their non-invasive and convenient administration further underscores the clinical relevance of MDFs(1) .
In summary, mouth-dissolving films represent a significant innovation in oral drug delivery systems. Their unique properties and advantages over traditional dosage forms address several limitations, particularly for patient populations with specific needs. This review will delve deeper into the various evaluation parameters that ensure the quality, efficacy, and safety of MDFs, providing a comprehensive understanding of this advanced drug delivery system's potential in modern pharmaceutics.
Special Features of Mouth Dissolving Films:
Mouth dissolving films possess several unique attributes that enhance their performance and patient acceptance(3) :
- Thin and elegant appearance
- Flexible and non-intrusive design
- Available in various sizes and shapes
- Rapid disintegration and release of the active ingredient
- Pleasant mouthfeel and acceptable taste
- Leaves no residues in the mouth(8)
Disadvantages:
Despite their benefits, MDFs have some disadvantages that must be addressed during development(3) :
- Technical challenges in achieving dose uniformity
- Hygroscopic nature requiring special packaging
- Limitations on high-dose incorporation (<40>
Formulation Requirements for MDFs:
The formulation of MDFs involves several critical components(5) :
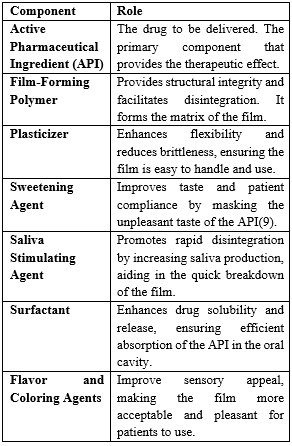
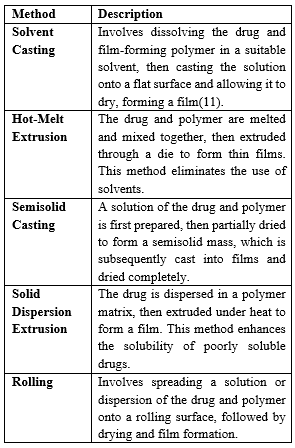
Methods of Preparation of Fast Dissolving Film:
MDFs can be prepared using one or a combination of the following methods(10) :
EVALUATION PARAMETERS FOR MOUTH DISSOLVING FILMS:
Evaluation parameters are crucial for ensuring the quality, efficacy, and safety of MDFs. The following sections detail each parameter and its importance.
- Disintegration Time:
Disintegration time is a critical parameter for mouth dissolving films (MDFs) that measures the duration required for the film to break down upon contact with the oral cavity's saliva. This parameter is essential for ensuring rapid drug release and enhancing patient compliance. Ideally, the disintegration time for MDFs should be within a few seconds to a minute to optimize performance. Quick disintegration facilitates the immediate release of the drug into the saliva, promoting swift absorption through the oral mucosa.
Disintegration time plays a vital role in the effectiveness and acceptability of MDFs. Rapid disintegration is crucial for the prompt release of the active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) into the saliva, ensuring that the drug can be rapidly absorbed through the oral mucosa. This quick onset of action is particularly beneficial for medications requiring immediate relief, such as analgesics and antiemetics. Furthermore, a short disintegration time significantly enhances patient compliance, especially among populations that face challenges with swallowing traditional dosage forms, such as pediatric, geriatric, and dysphagic patients(1) .
Factors Influencing Disintegration Time:
Several factors influence the disintegration time of MDFs, including the composition of the film, the thickness of the film, the presence of disintegrants, and environmental conditions.
- Film Composition: The type and concentration of polymers, plasticizers, and other excipients in the formulation significantly impact the disintegration time. Hydrophilic polymers, for instance, tend to dissolve more rapidly in contact with saliva, aiding quicker disintegration(3) .
- Thickness of the Film: The thickness of the film is directly proportional to the disintegration time. Thicker films generally disintegrate more slowly, so controlling film thickness during manufacturing is critical for achieving the desired disintegration rate(5) .
- Presence of Disintegrants: Incorporating disintegrants into the film formulation can significantly enhance the disintegration process. Disintegrants promote the breakup of the film upon exposure to saliva, thus accelerating the disintegration time(10) .
- Environmental Factors: Storage conditions, such as humidity and temperature, can affect the disintegration time of MDFs. High humidity can increase the film's pliability, potentially altering its disintegration properties(12) .
Testing Disintegration Time:
Disintegration time is typically measured through in vitro tests designed to replicate the conditions of the oral cavity. The MDF is placed in a simulated saliva solution, and the time taken for it to completely disintegrate is recorded. Regulatory guidelines, such as those from the European Pharmacopoeia and the United States Pharmacopeia, provide specific protocols for testing the disintegration time of orodispersible films(13). Regulatory bodies have established standards and guidelines for acceptable disintegration times to ensure the quality and efficacy of MDFs. These standards are essential for ensuring that the films perform consistently and provide the intended therapeutic effect in a timely manner(13) .
- Weight Variation:
Weight variation testing is a fundamental quality control measure for mouth dissolving films (MDFs) that ensures each film unit contains a uniform amount of the active pharmaceutical ingredient (API). This consistency is critical for maintaining dosing accuracy and therapeutic efficacy. By ensuring uniform weight across different units of the film, manufacturers can guarantee that patients receive the correct dose of medication each time.
Weight variation is directly linked to the reliability of dosing in MDFs. Uniformity in weight ensures that each film contains the precise amount of the active ingredient, which is essential for achieving the desired therapeutic effect. Inconsistent weight can lead to significant variations in drug delivery, potentially resulting in under-dosing or overdosing, both of which can compromise the safety and efficacy of the medication(5) . For drugs with a narrow therapeutic index, maintaining weight uniformity is particularly crucial to avoid adverse effects and ensure optimal therapeutic outcomes.
Testing Procedure:
Weight variation testing involves a systematic approach to verify that each unit of the film meets specified criteria. The testing process typically includes the following steps:
- Sample Selection: A random sample of MDF units is selected from a batch to ensure a representative assessment of weight uniformity.
- Weighing: Each selected film unit is individually weighed using a high-precision analytical balance to obtain accurate measurements.
- Data Analysis: The weights of the individual units are compared to the average weight of the sample. The percentage deviation of each unit's weight from the average weight is calculated(14).
- Acceptance Criteria: The calculated weight variation is compared against predefined limits specified in regulatory guidelines or company standards. For example, the United States Pharmacopeia (USP) specifies that for films weighing 300 mg or less, the weight of each film should not deviate by more than 10% from the average weight(5) .
Factors Influencing Weight Variation:
Several factors can influence the weight variation of MDFs, and controlling these factors is essential for ensuring product quality:
- Manufacturing Process: Variations in the casting process, such as differences in the spread of the film-forming solution, can lead to inconsistencies in weight. Ensuring a uniform spread during casting is crucial.
- Film Thickness: Inconsistent film thickness can result in weight differences. Controlling the thickness during the manufacturing process helps in achieving uniform weight.
- Environmental Conditions: Humidity and temperature during manufacturing and storage can affect the film's weight by causing it to gain or lose moisture. Maintaining controlled environmental conditions is essential to minimize these effects.
Quality Control Measures:
Regular weight variation testing during the manufacturing process helps identify and correct any issues that may lead to inconsistencies. Implementing stringent quality control measures ensures that weight variation remains within acceptable limits, thereby maintaining product quality and efficacy. By adhering to these quality control practices, manufacturers can ensure that each MDF unit provides consistent dosing, enhancing therapeutic outcomes and patient safety.
Adhering to regulatory guidelines on weight variation is mandatory for product approval. Regulatory agencies such as the FDA and EMA have set specific limits on acceptable weight variation to ensure product quality and safety. Compliance with these guidelines is essential for the successful market approval and acceptance of MDFs(5) .
- Film Thickness and Uniformity:
Evaluating film thickness and uniformity is a crucial aspect of quality control in the production of mouth dissolving films (MDFs). These parameters are vital for ensuring consistent drug delivery and dissolution properties, which directly impact the therapeutic efficacy and patient compliance of the film.
Uniform film thickness is essential for maintaining consistent drug content across different units of the film. Variations in thickness can lead to significant differences in the amount of active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) present in each film, potentially resulting in variable dosing and therapeutic outcomes. Additionally, thickness uniformity influences the disintegration time of the film; thicker areas may dissolve more slowly, while thinner areas may dissolve more quickly, leading to inconsistent drug release profiles(13) .
Testing Techniques:
Several techniques are employed to assess film thickness and uniformity:
- Digital Micrometers: These precision instruments measure the thickness of the film at multiple points to ensure uniformity. Digital micrometers provide accurate and repeatable measurements, making them ideal for quality control purposes(15).
- Optical Microscopes: Optical microscopy allows for the visualization of the film's surface and thickness. By using cross-sectional imaging, manufacturers can observe and measure the film's thickness at various points, ensuring uniform distribution.
- Scanning Electron Microscopes (SEM): SEM provides high-resolution images of the film's surface and cross-section. This technique is particularly useful for detailed analysis of the film's microstructure and thickness. SEM can reveal any irregularities or inconsistencies in the film's formation, which might not be detectable with other methods.
Factors Influencing Film Thickness and Uniformity:
Several factors during the manufacturing process can influence the thickness and uniformity of MDFs:
- Casting Process: The method and equipment used to cast the film-forming solution play a significant role in determining the film's thickness. Ensuring a uniform spread of the solution is crucial for achieving consistent thickness.
- Solution Viscosity: The viscosity of the film-forming solution can affect the final thickness of the film. Higher viscosity solutions tend to produce thicker films, while lower viscosity solutions produce thinner films. Controlling the viscosity is essential for maintaining uniformity.
- Drying Conditions: The conditions under which the film is dried, such as temperature and humidity, can impact its final thickness. Uneven drying can lead to variations in thickness, making it essential to control the drying environment.
- Substrate Surface: The surface on which the film-forming solution is cast can influence the uniformity of the film. A smooth, even substrate helps in achieving a uniform film thickness.
Regular monitoring and control of film thickness and uniformity are essential to ensure the quality and efficacy of MDFs. By employing precise measurement techniques and controlling the manufacturing variables, manufacturers can produce films with consistent thickness, ensuring reliable drug delivery and therapeutic outcomes.
- Surface pH:
Surface pH testing is a critical evaluation parameter for mouth dissolving films (MDFs) that ensures patient safety and comfort during usage. The ideal pH range for MDFs is close to the physiological pH of the oral cavity, which is approximately 6.5 to 7.5. Maintaining this pH range is essential to minimize irritation to the oral mucosa and ensure patient compliance.
The surface pH of the MDF must be within the physiological range to avoid causing any irritation or damage to the oral mucosa. A pH that is too acidic or too basic can lead to discomfort, pain, or even lesions in the mouth, thereby negatively impacting patient compliance and safety(13) .
The pH of the film's surface can influence the stability and efficacy of the drug. Certain drugs may degrade or become less effective if the pH deviates significantly from the neutral range. Ensuring an appropriate surface pH helps maintain the integrity and therapeutic effect of the drug.
Testing Procedure:
Surface pH testing typically involves the following steps:
- Sample Preparation: A specified number of MDF units are selected and slightly moistened with distilled water to create a thin film of water on the surface(16).
- Measurement: The pH is measured using a pH meter with a flat surface electrode, which is gently placed on the surface of the moistened film.
- Data Analysis: The pH readings are recorded, and the average surface pH of the samples is calculated to ensure it falls within the desired range.
Factors Influencing Surface pH:
Several factors can affect the surface pH of MDFs:
- Formulation Ingredients: The type and concentration of excipients, such as polymers, plasticizers, and buffering agents, can influence the surface pH. Selecting excipients that do not alter the pH significantly is crucial.
- Manufacturing Process: The conditions during the manufacturing process, such as the drying temperature and humidity, can impact the final pH of the film. Controlling these parameters is essential to maintain the desired pH range.
- Storage Conditions: Exposure to varying environmental conditions, such as humidity and temperature, during storage can alter the surface pH. Proper packaging and storage conditions are necessary to preserve the film's pH stability.
Regular surface pH testing during the production and storage of MDFs is essential to ensure that the films remain within the safe and effective pH range. Implementing stringent quality control measures helps identify any deviations early in the process, allowing for timely corrections and ensuring the final product meets safety and efficacy standards.
- Tensile Strength:
Tensile strength testing evaluates the mechanical strength and durability of the film, which is essential for handling, packaging, and administration without tearing or rupturing. This parameter indicates the film's resistance to breakage under tension, ensuring that the film remains intact during handling and use(17).
Ensuring adequate tensile strength is vital for the mechanical integrity of MDFs. Films with insufficient tensile strength are prone to tearing and breaking during handling, packaging, and administration, which can compromise their effectiveness and usability(18) .
Tensile strength reflects the film's ability to withstand mechanical stress during various stages of its lifecycle, including transportation and storage. Durable films are less likely to be damaged, ensuring consistent performance from production to administration.
Films that tear easily can be difficult for patients to handle, reducing compliance. Strong, durable films improve the patient experience and ensure that the medication can be administered as intended.
Testing Procedure:
Tensile strength is measured using a tensile testing machine, which subjects the film to increasing tension until it breaks. The key parameters measured include:
- Maximum Load: The maximum force the film can withstand before breaking.
- Elongation at Break: The extent to which the film can stretch before it breaks.
- Folding Endurance:
Folding endurance testing assesses the film's ability to withstand repeated folding without breaking, indicating its flexibility and durability. A higher number of folds before failure suggests better quality and handling characteristics(19).
Folding endurance reflects the film's flexibility, which is crucial for its ability to be handled without breaking. Flexible films are easier to use and less likely to be damaged during handling and administration(18) . High folding endurance indicates that the film can withstand repeated mechanical stress, such as folding and bending, without losing its integrity. This is particularly important for ensuring that the film can withstand normal handling without breaking or losing its effectiveness. Films with high folding endurance are more user-friendly, reducing the likelihood of accidental tearing during patient handling and administration, thereby enhancing patient compliance.
Testing Procedure:
Folding endurance is tested by repeatedly folding the film at the same place until it breaks. The number of folds the film can withstand before breaking is recorded, providing a measure of its flexibility and durability.
- Drug Content Uniformity:
Ensuring uniform distribution of the drug within the film is critical for accurate dosing and therapeutic efficacy(20). Analytical techniques such as high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) and UV-Vis spectroscopy are used to assess drug content uniformity. Uniform drug content across the film ensures that each dose is consistent with the intended therapeutic effect.
Uniform drug content ensures that each piece of the film contains the same amount of active ingredient, which is essential for providing consistent and accurate dosing to patients(21) . Inconsistent drug distribution can lead to variations in the therapeutic effect, with some doses being subtherapeutic and others potentially toxic. Ensuring uniformity maintains the intended therapeutic efficacy of the drug. Regulatory guidelines require that dosage forms, including MDFs, meet specific standards for drug content uniformity to ensure safety and efficacy. Adhering to these standards is necessary for product approval and market acceptance.
Testing Procedure:
Drug content uniformity is assessed by analyzing multiple samples from different sections of the film:
- Sample Preparation: Multiple film samples are taken from various parts of the batch.
- Analysis: Each sample is analyzed using HPLC or UV-Vis spectroscopy to determine the amount of active ingredient present.
- Data Analysis: The results are compared to ensure that the drug content in each sample falls within the specified limits, ensuring uniform distribution.
H. In Vitro Drug Release:
In vitro drug release studies are fundamental for evaluating how mouth dissolving films (MDFs) release the active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) once administered. These studies replicate the conditions within the oral cavity to observe the drug's dissolution and diffusion from the film matrix. By providing a detailed understanding of the release kinetics, these tests are crucial for predicting the in vivo performance of the drug. This information helps in fine-tuning the formulation to ensure that the drug is released at a rate and extent that achieves the desired therapeutic effect. Furthermore, consistent in vitro release profiles ensure reliable and reproducible therapeutic outcomes, which are essential for patient compliance and efficacy. In vitro drug release data also support regulatory submissions, demonstrating that the product meets the required standards for drug release and performance(22)(23) .
I. Advanced Evaluation Techniques:
Advanced evaluation techniques such as texture analysis, surface morphology analysis, and in vitro permeation studies offer a comprehensive understanding of the mechanical properties, surface characteristics, and drug permeability of mouth dissolving films (MDFs). Texture analysis measures parameters like hardness, adhesiveness, and cohesiveness, which are critical for patient acceptance and handling. Surface morphology analysis, often performed using scanning electron microscopy (SEM)(24), provides detailed images of the film's surface, revealing information about the film's uniformity and potential defects. In vitro permeation studies simulate the drug's absorption through the oral mucosa, providing valuable data on the film's effectiveness in delivering the drug across the mucosal barrier. These advanced techniques not only ensure the optimization of the film formulation but also help in maintaining high product quality, thus enhancing the overall efficacy and safety of MDFs(25) .
J. Regulatory Considerations:
Regulatory considerations are paramount in the development and commercialization of mouth dissolving films (MDFs). Compliance with regulatory guidelines ensures that the products meet the necessary safety, efficacy, and quality standards(26). Regulatory bodies such as the FDA and EMA have established comprehensive guidelines that cover various aspects of MDF development, including ingredient safety assessments, quality control measures, labeling requirements, and packaging standards. These guidelines also mandate bioequivalence and bioavailability studies to demonstrate that the MDFs perform consistently and predictably in delivering the drug. Additionally, post-market surveillance is required to monitor the product's performance once it is available to the public, ensuring ongoing safety and efficacy. Adhering to these regulatory requirements is essential for gaining approval and market acceptance, thereby ensuring that patients receive safe and effective treatments(27) .
CHALLENGES IN FORMULATING FAST DISSOLVING ORAL FILM
Several challenges in developing MDFs need to be addressed to enhance their efficacy and patient compliance. These include(28):
- Insolubility of Drugs: Overcoming poor solubility of certain drugs.
- Taste Masking: Masking the taste of bitter and unpleasant drugs.
- Drying Time: Reducing the drying time of films during manufacturing.
- High Dose Incorporation: Incorporating higher doses within the limited film area.
- Co-administration of Drugs: Developing films capable of delivering multiple drugs simultaneously.
- Stability: Ensuring stability against humidity and temperature.
- Packaging: Requiring special packaging for protection and stability.
- Dose Uniformity: Achieving uniform drug distribution within the film .
CONCLUSION
Mouth dissolving films (MDFs) represent a significant advancement in oral drug delivery systems, offering numerous benefits over traditional dosage forms, particularly for patients with swallowing difficulties. The comprehensive evaluation of MDFs through various parameters ensures their quality, efficacy, and safety. Disintegration time, weight variation, film thickness and uniformity, surface pH, tensile strength, folding endurance, drug content uniformity, and in vitro drug release are crucial metrics that must be rigorously tested and controlled. Advanced evaluation techniques further enhance our understanding of the mechanical properties, surface characteristics, and drug permeability of these films, leading to optimized formulations.
Moreover, adherence to regulatory guidelines is essential for the approval and market acceptance of MDFs, ensuring they meet the highest standards of safety and effectiveness. The challenges in developing MDFs, such as achieving dose uniformity, optimizing disintegration time, and ensuring stability, require innovative solutions and meticulous quality control.
Overall, the continuous research and development in the field of MDFs hold great promise for improving patient compliance and therapeutic outcomes. By addressing the various formulation and evaluation challenges, MDFs can be further refined and widely adopted, benefiting both patients and healthcare providers.
FUTURE SCOPE
The future of mouth dissolving films (MDFs) in pharmaceutical sciences is promising, with several avenues for further research and development. Innovations in formulation technologies, such as nanotechnology and microencapsulation, could enhance the bioavailability and stability of active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs) in MDFs. Additionally, exploring biodegradable and naturally derived polymers can provide more sustainable and patient-friendly alternatives. Advanced manufacturing techniques, including 3D printing, hold potential for creating highly precise and customizable MDFs tailored to individual patient needs. Research into taste-masking agents and flavor enhancers can further improve patient compliance, especially in pediatric and geriatric populations. The integration of smart drug delivery systems, such as stimuli-responsive films that release drugs in response to specific physiological conditions, represents an exciting frontier. Furthermore, expanding the application of MDFs to deliver a wider range of therapeutics, including biologics and vaccines, can broaden their impact in medical treatment. Collaborative efforts between academia, industry, and regulatory bodies will be crucial in overcoming existing challenges and ensuring that MDFs meet the stringent requirements for safety, efficacy, and quality. Continuous advancements in this field will likely lead to the development of next-generation MDFs, offering superior therapeutic benefits and patient experiences.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT
The authors acknowledge the support from Lokmanya Tilak Institute of Pharmacy, Kharghar, Navi Mumbai, Maharashtra, India.
REFERENCE
- Fast Dissolving Oral Thin Films: An Effective Dosage Form for Quick Releases [Internet]. Available from: www.globalresearchonline.net
- Shariff ZB, Dahmash DT, Kirby DJ, Missaghi S, Rajabi-Siahboomi A, Maidment ID. Does the Formulation of Oral Solid Dosage Forms Affect Acceptance and Adherence in Older Patients? A Mixed Methods Systematic Review. J Am Med Dir Assoc. 2020 Aug 1;21(8):1015-1023.e8.
- Thakur N, Bansal M, Sharma N, Yadav G, Khare P. Overview “A Novel Approach of Fast Dissolving Films and Their Patients.” Adv Biol Res (Rennes). 2013;7(2):50–8.
- Naiem Raza S, Husain Kar A, Umair Wani T, Ahmad Khan N. Formulation And Evaluation Of Mouth Dissolving Films Of Losartan Potassium Using 3 2 Factorial Design. Int J Pharm Sci Res [Internet]. 2019;10(3):1402. Available from: http://dx.doi.org/10.13040/IJPSR.0975-8232.10
- Reyad-ul-ferdous M, Shamim Shahjahan D, Munirul Islam Tanvir M, Sumi S, Nazmul Alam M, Irfan Amin Chowdury M, et al. Effective Development And Evaluation Of Oral Thin Film Of Etoricoxib. World Journal of Pharmaceutical Research World Journal of Pharmaceutical Research SJIF Impact Factor 5 [Internet]. 2015;4(9):257–72. Available from: www.wjpr.net
- Waterman KC. Understanding and Predicting Pharmaceutical Product Shelf-Life. Handbook of Stability Testing in Pharmaceutical Development: Regulations, Methodologies, and Best Practices [Internet]. 2009 [cited 2024 Jun 7];9780387856278:115–35. Available from: https://link.springer.com/chapter/10.1007/978-0-387-85627-8_6
- Huynh-Ba K. Handbook of stability testing in pharmaceutical development: Regulations, methodologies, and best practices. Handbook of Stability Testing in Pharmaceutical Development: Regulations, Methodologies, and Best Practices. Springer New York; 2009. 1–389 p.
- Panchal MS, Patel H, Bagada A. Formulation and Evaluation of Mouth Dissolving Film of Ropinirole Hydrochloride by Using Pullulan Polymers. Available from: www.ijpras.com
- Sohi H, Sultana Y, Khar RK. Taste masking technologies in oral pharmaceuticals: Recent developments and approaches. Vol. 30, Drug Development and Industrial Pharmacy. 2004. p. 429–48.
- Calixto JB. Efficacy, safety, quality control, marketing and regulatory guidelines for herbal medicines (phytotherapeutic agents). Vol. 33, Brazilian Journal of Medical and Biological Research. 2000.
- Jassim ZE, Mohammed MF, Sadeq ZA. Formulation and evaluation of fast dissolving film of lornoxicam. Asian Journal of Pharmaceutical and Clinical Research. 2018 Sep 1;11(9):217–23.
- Ylilammi M, Ranta-aho T. Optical determination of the film thicknesses in multilayer thin film structures. Thin Solid Films. 1993 Sep 10;232(1):56–62.
- Bala R, Khanna S, Pawar P, Arora S. Orally dissolving strips: A new approach to oral drug delivery system. Int J Pharm Investig. 2013;3(2):67.
- Talele Swati G HY ,Bakliwal AA ,Chaudhari GN. Formulation and Evaluation of mouth Dissolving Film of Almotriptan Malate. Available from: www.jpbs-online.com
- Nitesh J, Ranjan M. Comparative Physical and Chemical Stability Studies of Orlistat Liposomal Drug Delivery Systems. Vol. 12, Asian Journal of Pharmaceutics.
- Tomar A, Sharma K, Chauhan NS, Mittal A, Bajaj U. Formulation and Evaluation of Fast Dissolving Oral Film of Dicyclomine as potential route of Buccal Delivery “Formulation and Evaluation of Fast Dissolving Oral Film of Dicyclomine as potential route of Buccal Delivery” Int [Internet]. Vol. 4, J. Drug Dev. & Res. Available from: http://www.ijddr.in
- Senthilkumar K, Vijaya C. Formulation Development of Mouth Dissolving Film of Etoricoxib for Pain Management. Advances in Pharmaceutics. 2015 Jan 26;2015:1–11.
- Parthasarathi Keshavarao K, Mudit D, Anis S, Mangla SN, Ajay K, Kulkarni PK. Formulation And Evaluation Of Mouth Dissolving Film Containing Rofecoxib [Internet]. Vol. 2, IRJP. 2011. Available from: http://www.irjponline.com
- Perumal VA, Govender T, Lutchman D, Mackraj I. Investigating a new approach to film casting for enhanced drug content uniformity in polymeric films. Drug Dev Ind Pharm. 2008 Oct;34(10):1036–47.
- Berman J, Planchard JA. Blend Uniformity and Unit Dose Sampling. Drug Dev Ind Pharm. 1995;21(11):1257–83.
- Dave V, Haware R, Sangave N, Sayles M, Popielarczyk M. Drug-Excipient Compatibility Studies in Formulation Development: Current Trends and Techniques. American Association of Pharmaceutical Scientists (AAPS) Formulation Design and Development (FDD) Section Newsletter [Internet]. 2015 Jan 1 [cited 2024 Jun 7]; Available from: https://fisherpub.sjf.edu/pharmacy_facpub/212
- Govender S, Pillay V, Chetty DJ, Essack SY, Dangor CM, Govender T. Optimisation and characterisation of bioadhesive controlled release tetracycline microspheres. Int J Pharm. 2005 Dec 8;306(1–2):24–40.
- Kumirska J, Czerwicka M, Kaczy?ski Z, Bychowska A, Brzozowski K, Thöming J, et al. Application of spectroscopic methods for structural analysis of chitin and chitosan. Vol. 8, Marine Drugs. MDPI AG; 2010. p. 1567–636.
- Furlanetto S, Cirri M, Maestrelli F, Corti G, Mura P. Study of formulation variables influencing the drug release rate from matrix tablets by experimental design. European Journal of Pharmaceutics and Biopharmaceutics. 2006 Jan;62(1):77–84.
- Sankeshwari S, Gangadharappa H V., Asha Spandana KM, Eliyas A, Thirumaleshwar S, HARSHA Vardhan PV. A Review On The Solid Oral Dosage Form For Pediatrics, Regulatory Aspects, Challenges Involved During The Formulation, And Toxicity Of The Excipients Used In Pediatric Formulation. Vol. 15, International Journal of Applied Pharmaceutics. Innovare Academics Sciences Pvt. Ltd; 2023. p. 12–27.
- Advances in Delivery Science and Technology [Internet]. Available from: http://www.springer.com/series/8875
- Galgatte U. Challenges in formulation development of fast dissolving oral film [Internet]. 2013. Available from: www.iajpr.com.


 Avinash Bichave*
Avinash Bichave*
 Somesh Phate
Somesh Phate


 10.5281/zenodo.12623624
10.5281/zenodo.12623624