Abstract
Within the Caesalpiniaceae family, Caesalpinia bonducella (L.) Fleming (Syn. Caesalpinia bonduc (L.) Roxb, Syn. Caesalpinia cristaLinn.) is a prickly shrub that is found all over the world, but is most commonly found in tropical regions of India, Sri Lanka, and the Andaman and Nicobar Islands. The plant is a very significant medicinal plant that is used in traditional medicine since all portions of it have therapeutic qualities. Anxiolytic, antinociceptive, antidiarrheal, antidiabetic, adaptogenic, anthelmintic, antiestrogenic, anti-inflammatory, antimalarial, antimicrobial, antifungal, antispasmodic, antioxidant, antiproliferative, antipsoriatic, antitumor, larvacidal, muscle contractile, hepatoprotective, anticonvulsant, and antifilarial properties have all been reported associated with the plant. Alkaloids, flavonoids, glycosides, saponins, tannins, and triterpenoids have all been found in Caesalpinia bonducella seeds according to phytochemical study.
Keywords
Caesalpinia bonducella, Karanjwa, Fever nut, Unani medicine, Traditional medicine
Introduction
The use of medicinal plants as a possible source of therapeutic help has grown in importance in the global health system for both people and animals, not only in cases of illness but also as a resource for preserving good health. Nonetheless, it is important to understand which components of the medicinal plant are in charge of its therapeutic effects. Consequently, in order to employ it therapeutically, it becomes necessary to extract, isolate, and identify the phytoconstituent in question. Solvents are primarily used in the extraction of plant drugs. Traditionally, extraction techniques such as maceration, percolation, digestion, decoction, and hot continuous extraction have been employed. Worldwide interest in plant research has grown recently, and a substantial amount of data has accumulated to demonstrate the enormous potential of medicinal plants utilized in a variety of traditional systems. The public's interest in the usage of herbal treatments is growing at the moment. Moreover, plant extract was the source of many western pharmaceuticals. Numerous herbs are mostly utilized to treat conditions related to the central nervous system, liver, digestive system, and metabolism. They can be helpful as a medication or supplement in the treatment or management of a variety of disorders due to their ability to have a substantial therapeutic impact. The biological activity of herbal medicines, medicinal plants, and their extracts and isolated substances have been shown to be diverse. These have been and still are used as dietary supplements or folk medicine for a variety of illnesses. Belonging to the Fabaceae / caesalpiniaceae family, Caesalpinia bonducella (L.) Fleming (Syn. Caesalpinia bonduc (L.) Roxb, Syn. Caesalpinia cristaLinn.) is a prickly shrub that is widely distributed throughout the world, particularly in India, Sri Lanka, and the Andaman and Nicobar Islands. It is particularly found in tropical regions of India [1&2].The plant is a highly useful medicinal plant that is used in traditional medicine since all portions of it have therapeutic qualities [3]. There have been reports of the plant's antifilarial, antinociceptive, antidiarrheal, and anxiolytic properties. The presence of alkaloids, flavonoids, glycosides, saponins, tannins, and triterpenoids has been identified by phytochemical examination of Caesalpinia bonducella seeds [4–5].
PHARMACOGNOSTIC STUDY
A large climber, its branches downy and delicately gray, and it is covered in strong yellow prickles that are both hooked and straight. The stipules are a pair of reduced pinnae at the base of the leaf, each with a long mucronate point. The leaves are bipinnate, 30–60 cm long, and have short, thorny petioles. There are seven pairs of pinnae, and between each pair on the underside are three to eight pairs of leaflets with one or two tiny recurved prickles. has two hooked stipulary spines at the base, each about 5.0–7.5 cm in length. Leaflets: 6–9 pairs, membranous, elliptic to oblong, obtuse, strongly mucronate, glabrous above and somewhat puberulous below; dimensions: 2.0–3.8 cm × 1.3–2.2 cm. Flowers have long peduncles and dense terminal racemes, generally spicate, with supraaxillary racemes that are 15–25 cm long and closely spaced at the top. Bracts are squarrose, linear, acute, and up to 1 cm long. The pedicles are extremely short in the buds and elongate to 5 mm in flowers and 8 mm in fruits. They are brown and fluffy. The calyx is fulvous, hairy, and measures 6 to 8 mm. The lobes are obovate-oblong and obtuse. Petals are yellow and oblanceolate, with declinate filaments that are flattened at the base and long, silky white hairs covering them. Pods were short-stalked, rectangular, and were 5.0–7.5 by around 4.5 cm. They were heavily armed with wiry prickles. The 1-2 oblong, green, up to 1.3 cm long, glossy, firm seeds eventually become gray.They serve as a medium for jewelry. [6,7, 9, 10, 11]

SYNONYMS [7, 8,12]
Hindi name- Sagar Gota ,Kantkarej, Kantikaranja,.
English name- Nicker seed, nicker nut, bonduc nut, and fever nut
Persian name- Khayahe-i-iblas
Sanskrit name- Kantakikaranja, Kantakini, Karanja, Krakachika, Kuberaksah, Kuberakshi, Kuberaksi, Latakaranja, Prakiriya, Prakirnah, Putikah, Putikaranja, Putikaranjah, Putikaranji, Tinagachhika, Tirini, Valli, Varini, Vitapakaranja
Urdu name- Akitmakit.
Telgu Name: Gaccakayai Mulluthige.
Tamil Name: Kazharchikkaai, Kalachikai, Kalichikai, Kazarci, Kalarci ver, Kalarcik Koluntu, Kalarcip paruppu, Kazharchikkaai.
Kannada name- Gajjiga, Kiri gejjuga, Gajikekayi.
Malayalam name- Ban-karetti, Kaka-moullou, Kazhanji, Kalanci, and Kajanchikkur .
TAXONOMIC CLASSIFICATION
Kingdom : Plantae
Phylum : Magnoliophyta
Division : Magnoliopsida
Class : Angiospermae
Order : Fabales
Family : Fabaceae / Caesalpiniaceae
Genus : Caesalpinia
Species : bonducella
PHARMACOLOGICAL STUDIES
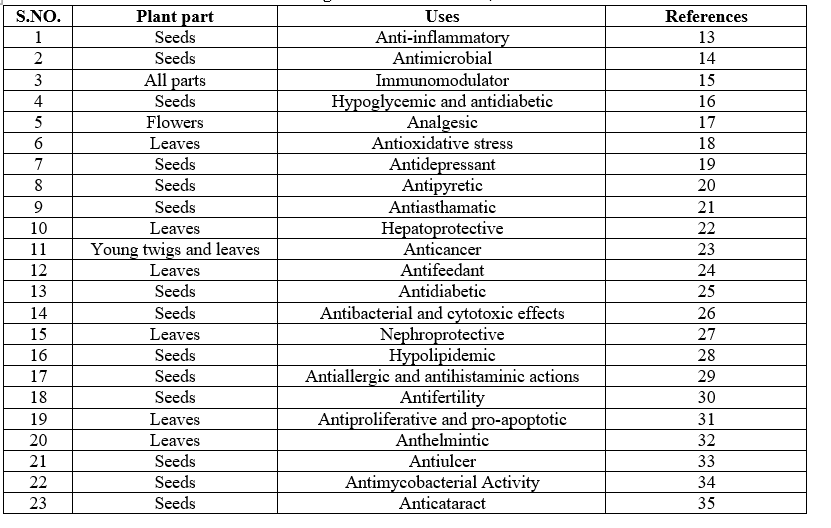
Numerous research investigations on pharmaceuticals were spurred by the presence of diverse phytochemicals in different regions of the plant. However, there are currently insufficient studies and records available about the plant. A plethora of undiscovered phytochemicals with enormous potential to herald new directions and methods in the field of clinical treatments may become apparent with more thorough scientific research. Table No. 1 illustrates how several scientific literature have described the plant's sections as having important characteristics.
Table 1: Pharmacological Studies Of Seeds, Leaves And Flowers
CONCLUSION
C. bonducella is a widely spread shrub with deep roots that is evergreen with a firm, woody stem. This plant's leaves are glossy, ovate-shaped, compound elliptical, and placed alternately on either side of the branches. Several beneficial phytochemicals have been extracted from various sections of this plant, including the seeds, which include caesalpin, ?-caesalpin, and ?-caesalpin, terpenoids, and neutral saponin. Biosterols such as sitosterol, heptocosane noncrystalline, bitter glycoside, bonducin, and neutral saponin are found in kernels; leaves contain pinitol, glucose, calcium, and brazzillin; homoisoflavonoids, 6-Omethylcaesalpinianone, and caesalpinianone are found in bark; roots elaborate cassane furanoditerpene, caesalpinin, bonducellpins A, B, C, D, and diosgenin are found in the roots. These strong, unique phytochemicals exhibit a variety of pharmacological characteristics. The research has reaffirmed that C. bonducella has a variety of active metabolites in different regions that may be used to treat various illnesses. Also, it has been noted that due to the existence of distinct bioactive metabolites, various plant sections exhibit varying pharmacological actions. However, in order to fully investigate all of the opportunities and possibilities the rich plant presents, further scientific study and documentation are needed. This review compiles the data from current pharmacological research studies. The plant exhibited antidiabetic, antioxidant, antihyperlipidemic, antispasmodic, immunomodulator, and antibacterial properties in its seeds, bark, and roots. C. bonducella's flowers have analgesic properties. The leaves of C. bonducella have anti-tumor, anti-ulcer, and antifilarial properties, while the seed kernels have antimalarial properties. There is still need for more investigation even though the plant has a wealth of powerful compounds that make it medicinally rich. This wild plant is abundant in biomarker compounds of medicinal interest and has been demonstrated to have several pharmacological actions; nevertheless, research is still needed to produce formulations for various illnesses and disorders, which might lead to an increase in the plant's economic worth in the future.
REFERENCE
- Asolkar LV, Kakkar KK, and Chakre OJ. Second Suppl. To Glossary of Indian Medicinal Plants with Active Principles, PID-CSIR, New Delhi, 1992: Part 1,150.
- White R. Legume web [Internet]. version 10.01. Cardiff (UK): Cardiff University, School of Computer Sciences. c 2005– [Revised 2005 Nov 1; cited 2008 Sep 23]. Available from: http://www.ildis.org/Legumeweb
- Kirtikar KR, Basu BD. Indian medicinal plants. 2nd ed. Dehradun: International Book Distributors; 1988: 839-902.
- Gaur RL, Sahoo MK, Dixit S, Fatma N, Rastogi S, Kulshreshtha DK, Chatterjee RK, Murthy PK. Indian J Med Res 2008; 128: 65–70.
- Gupta AK, Sharma M, Tandon N. Quality standards of Indian medicinal plants. Vol–2. New Delhi: Indian Council of Medical Research. 2005: 25-33.
- Handa SS. and Kaul MK., Supplement to Cultivation and Utilization of Medicinal Plants, RRL, Jammu-Tawi, 1996: 727-737.
- Kirtikar KR, Basu BD, Indian Medicinal Plants, 2nd ed, BSMP Singh and Periodical Experts, New Delhi, 1975: 2, 842.
- The Wealth Of India, Raw material, Ca-Ci, Revised Ed, Publication and Information Directorate, CSIR, New Delhi, 1992; 3: 6-8.
- Kapoor LD. Hand of Ayurvedic Medicinal Plants, CRC Press 88.
- Elizabeth M. Williamson Major Herbs of Ayurveda, Churchill 83-86.
- Sharma BM and Singh P. J. Res. Indian Med 1972; 7: 8 .
- Kapoor LD. Hand of Ayurvedic Medicinal Plants, CRC Press 87.
- Jagdale RA, Somkuwar AP, Bhoye SK, Sarode KG and Limsay RP. In vivo anti-inflammatory activity and GC-MS analysis of hydroethanolic extract of Caesalpinia bonducella seeds. J of Pharmacog and Phyto. 8(3), 2019, 929-934.
- Reichal C, Prathiba, Vishnpriya V, Ponnulakshmi R, Gayathri R, Madhan K, Shyamala B, Manikannan, M and Selvaraj J. Studies on antimicrobial activity of Caesalpinia bonducella seed ethanolic extract on selected human oral pathogens. Drug Invention Today. 12(4), 2019, 806-808.
- Fouzia K, Nida D, Mehreen L, Muhammad Y, Zulfiqar A and Ahmed M. Immunomodulatory activities of extracts of Caesalpinia pulcherrima. Journal of Herbs, Spices & Medicinal Plants. 24(3), 2018, 245-256.
- Aswar P and Kuchekar B. Assessment of hypoglycemic and antidiabetic effects of Caesalpinia bonducella (L.) Roxb. seeds in alloxan induced diabetic rat and its phytochemical, microscopic, biochemical and histopathological evaluation. Asian J of Plant Sci and Res. 1(3), 2011, 91-102.
- Aruna D, Tandan S, Dinesh Kumar, Shailesh P, Dudhgaonkar and Lal J. Analgesic activity of Caesalpinia bonducella flower extract. Pharma Bio. 46(11), 2008, 668-672.
- Bharath KP, Ponnu LR, Selvaraj J, Shyamaladevi B, Madhan K, Vishnupriya V, Manikkanan M and kumar S. Antioxidative stress potentials of Caesalpinia bonducella in cardiac tissue of nicotine-induced experimental rats. Drug Invention Today. 12(3), 2019, 402- 406.
- Sarma P, Borah M and Das S. Evaluation of the protective effect of ethanolic extract of seed kernel of Caesalpinia bonducella Flem (EECB) on forced swimming-induced chronic fatigue syndrome in mice. Phcog Res. 11, 2019, 254-259.
- Shukla S, Mehta and Archana. In vivo anti-inflammatory, analgesic and antipyretic activities of a medicinal plant Caesalpinia bonducella. F. Pak J of Pharma Sci. 28, 2015, 1517-1521.
- Khandagale PD and Puri AV. Evaluation of antiasthmatic activity of Caesalpinia bonducella [L.] Roxb. seed. J of Drug Delivery and Thera. 9(2), 2019, 144-149.
- Sumalatha, Bhat S, Kumar MR, Kumar N, Padma, Pai D, Ranganath SK and Choudhary S. Caesalpinia bonducella Linn extracts exhibit hepatoprotective effect on HepG2 cells against paracetamol by Up-regulating glutathione related genes. J of Krishna Ins of Med Sci. 8(2), 2019, 1-12.
- Nonso F, Ogunlana O, Ogunlana OE, Isewon I and Oyelade J. Potential anti-cancer flavonoids isolated from Caesalpinia bonducella young twigs and leaves. Mole Dock and In Silico studies Bioinfor and Bio Insights. 13, 2019, 1-16.
- Backiyaraj M, Elumalai A, Kasinathan Dhamodaran, Mathivanan T, Krishnappa, Kaliyamoorthy and Elumalai K. Bioefficacy of Caesalpinia bonducella extracts against tobacco cutworm, Helicoverpa armigera (Hub.) (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae). J of Coastal Life Medi. 3(5), 2015, 382-388.
- Dwitasari O, Sasongko D, Seno H and Safithri M. Identification of bioactive compounds and ?-glucosidase inhibition activity of Caesalpinia bonducella seed extract. In vitro Current Biochemistry. 4(3), 2017, 1-9.
- Sundar JS, Christobel RJ, Selvi NK, Abirami MP and Dr. Samuel S. Efficient green synthesis of silver nanoparticles from Caesalpinia bonducella seeds and its antibacterial and cytotoxic effects an in vitro study. Pharma Inno J. 7(11), 2018, 95-102.
- Bharath KP, kumar S, Kayalvizhi E, Ponnu LR, Selvaraj J, Vishnupriya V, Shyamaladevi B and Madhan K. A study on the nephro protective effect of Caesalpinia bonducella on nicotine-induced rats. Drug Invention Today. 10, 2018, 3512-3519.
- Sarma G and Das S. The hypolipidemic activity of ethanolic extract of seed kernel of Caesalpinia bonducella fleming on serum lipids and atherogenesis in albino rats fed with high fat diet. Int J of Basic & Clinical Pharmaco. 7(2), 2018, 266-272.
- Vikhe S & Nirmal S. Antiallergic and antihistaminic actions of Ceasalpinia bonducella seed possible role in treatment of asthma. J of Ethno. 216, 2018, 251–258.
- Tripathy B, Swain NS, Panda MK, Pradhan RN, Acharya UR. Antispermatogenic effects of seed extract of Caesalpinia bonducella in Swiss mice. Int J of Biosciences. 12(4), 2018, 23-34.
- Prakash SP, Balaji KS, Lakshmi GM, Chandrashekara KT, Jayarama S. Methanol extract of Caesalpinia bonducella induces apoptosis via up-regulation of bax and activation of PARP in Ehrlich ascites tumor cells. Med Aromat Plants. 5, 2016, 273.
- Gogoi S, Yadav AK. In vitro and in vivo anthelmintic effects of Caesalpinia bonducella (L.) Roxb. leaf extract on Hymenolepis diminuta (Cestoda) and Syphacia obvelata (Nematoda). J of Intercultural Ethno. 5(4), 2016, 427-433.
- Sawian O, Girish N, Zambare, Arulmozhi S and Deepali A. Bansode Effect of Caesalpinia bonducella extract in pylorus ligation induced ulcers in wistar rats. Scholars Research Library Der Pharmacia Lettre. 8 (4), 2016, 191-197.
- Sonvane SM, Deshpande AN, Shaikh RA, Gadgul AB, Choutmahal SA and Bhosale PV. Evaluation of IN-VITRO antimycobacterial activity of Caesalpinia bonducella seed coat extracts. International Journal of Pharma Research & Review. 5(10), 2016, 7-11.
- Kurmi P, Konwar M and Das S. In-vitro Anticataract activity of ethanolic extract of seed kernel of Caesalpinia bonducella (l.) Fleming on goat lens. Pharma Science Monitor. 6(1), 2015.
- Billah MM, IslamR, Khatun H, Parvin S, Islam E, Islam SE and Ali. Antibacterial, antidiarrhoeal, and cytotoxic activities of methanol extract and its fractions of Caesalpinia bonducella (L.) Roxb leaves. BMC Complementary and Alternative Medi. 13, 2013, 101.
- Gaur M, Sahoo S, Fatma N, Rastogi S, Kulshreshtha DK, Chatterjee RK & Murthy PK. Antifilarial activity of Caesalpinia bonducella against experimental filarial infections. Indian J Medi Res. 2008, 65- 70.
- Datte J, Traore A, Offoumou M & Ziegler A. Effects of leaf extract of Caesalpinia bonducella (Caesalpiniaceae) on the contractile activity of uterine smooth muscle of pregnant rats. J of Ethno, 60(2), 1998, 149-155.
- Khan, Ullah H , Ali, Khan I, Ullah A, Naz R and Gilani and Hassan A. Antibacterial, antifungal, antispasmodic and Ca antagonist effects of Caesalpinia bonducella, Natural Product Research. 25(4), 2019, 444- 449.
- Salunke KR, Nazeer R, Ahmed, Marigoudar SR and lilaram. Effect of graded doses of Caesalpinia bonducella seed extract on ovary and uterus in albino rats. J Basic Clin Physiol Pharmacol. 22(1-2), 2017, 49-53.
- Khedkar A, Mandavkar YD, Shinde G, Khalure P and Dere P. Diuretic effect of Caesalpinia bonducella in rats. Bangladesh J Pharmacol. 6, 2011, 61-63.
- Gupta M, Mazumder UK, Kumar RS, kumar TS and Vamsi ML. Antitumor activity and antioxidant status of Caesalpinia bonducella against ehrlich ascites carcinoma in swiss albino mice. J of Pharmacological Sci. 94, 2017, 177-184.
- Ali A, Rao NV, Shalam M, Gouda TS, Babu J, kumar SS. Anxiolytic activity of seed extract of Caesalpinia Bonducella (Roxb) in laboratory animals. Internet J of Pharmacology. 5(2), 2017.
- Ali A, Rao V, Nimmagadda, Hussain, Shalam, Gouda T and Shantakumar SM. Anticonvulsive effect of seed extract of Caesalpinia bonducella (Roxb.). Iranian Journal of Pharmacology and Therapeutics. 8(2), 2019, 51-55.


 Lilachand Bhaidas Patil*
Lilachand Bhaidas Patil*
 Khushal Kalyan Chaudhari
Khushal Kalyan Chaudhari
 Mayur Sharad Patel
Mayur Sharad Patel
 Nandini Arun Marathe
Nandini Arun Marathe


 10.5281/zenodo.14000383
10.5281/zenodo.14000383