Abstract
The present study was based on Diabetes, its cure & herbal products available in market. Diabetes mellitus is the most common endocrine disorder, affecting 16 million individuals in the United States and 200 million worldwide. Despite the use of advanced synthetic drugs for the treatment, use of herbal remedies is gaining higher importance because of synthetic drugs have drawbacks and limitations. The herbal drugs with antidiabetic activity are extensively formulated commercially because of easy availability, affordability and less side effects as compared to the synthetic antidiabetic drugs. Antidiabetic herbal formulations (AHF) are considered to be more effective for the management of diabetes. There are around 600 herbal drug manufacturers in India of which almost all manufacturers are developing AHF in addition to others. Till date no article is published to give detailed information of the herbal preparations on diabetes available in market. In this we illustrate about diabetes mellitus and its types, causes, sign and symptoms, complications, pathophysiology, diabetic medication, diabetic treatment, herbal diabetic cure, advantages of herbal medicines over allopathy and herbal formulations. Thus, this review article undertake the attempt for providing updated information on the type of diabetes and herbal formulations which will enhance the existing knowledge of the researchers.
Keywords
Diabetes Mellitus; anti-diabetic herbal formulations; polyherbal formulations.
Introduction
HO defined Diabetes mellitus as a metabolic disorder of multiple etiologies characterized By chronic hyperglycemia with disturbances in carbohydrate, fat and protein metabolism resulting From defects in insulin secretion, insulin action, or both. The effects of diabetes mellitus include Long-term damage, dysfunction and failure of various organs including kidney, nerves, heart and Gastrointestinal tract. It is the most common endocrine disorder world-wide with an incidence Varying between 1 to 8%. The global prevalence of diabetes is estimated to increase, from 4% in 1995to 5.4% by the year 2025.De-spite the advancement in the synthetic antidiabetic drugs in the Recent past; diabetes is still remarkably not cured successfully. A treatment of diabetes is Complicated due to the lack of drugs with safety and efficacy, and is incapable of sustained clinical, Biochemical, and histological cure. On the contrary the herbal drugs have gained wider importance Worldwide, mostly due to higher safety, less number of adverse effects and consistent blood Glucose lowering capacity. In the developed countries, the use of herbal medicine for the sufferers of diabetes is encouraged by the concern about the adverse effects and cost associated with chronic Use of synthetic drug. There are wide ranges of phytoconstituents useful in the treatment of Diabetes. These include alkaloids, glycosides, peptidoglycan, hypoglycan, steroids, guanidine, Glycopeptides, terpenoides, amino acids and inorganic ions. According to ethno botanical survey, There are about 800 plants which possesses antidiabetic potential. (1)
Diabetes Mellitus: Diabetes mellitus is a metabolic disorder in the endocrine system. Diabetes is a chronic disorder in metabolism of carbohydrate, proteins, and fat due to absolute or Relative deficiency of insulin secretion with / without varying degree of insulin resistance. Also, it May be defined as a disease where the body produces little insulin / ceases to produce insulin, or b becomes progressive resistance 6to its actions. Diabetes occurs worldwide and the incidences of both type 1 and type 2 diabetes are rising; it is estimated that, in the year 2000, 171 million people had diabetes, and this is expected to double by 2030.(1)
Classification Of Diabetes Mellitus
- B- cell destruction (Type 1 diabetes -IDDM)
- Immune mediated
- Idiopathy
- Insulin resistance (Type 2 diabetes - NIDDM)
- Genetic defects of P- cell function
- Glucokinase
- Hepatocyte nuclear transcription factor – 4 a
- Insulin promoter factor
- Mitochondrial DNA
- Proinsulin or insulin conversion
- Genetic defects in insulin processing or insulin actions defects in
- Proinsulin conversion
- Insulin gene mutation
- Insulin receptor mutation
- Exocrine pancreatic defects
- Endocrinopathy
- Acromegaly
- Cushing syndrome
- Hyperthyroidism
- Pheochrmocytoma
- Glucocanonama
- Infections
- Cytomegalovirus
- Coxhacivirus
- Glucocorticoid
- Thyroid hormone
- Thiazides
- Phenytoins
- Genetic syndrome associated with diabetes
- Down‘s syndrome
- Kleinfelter‘s syndrome
- Turner‘ s syndrome
10.Gestational diabetes mellitus. (10)
Types Of Diabetes:
There are three main types of diabetes:
Type 1 diabetes: Insulin-dependent diabetes (IDDM;Type I diabeteses one of the most serious Metabolic disorders, It has an autoimmune basis and is characterized by destruction of the Pancreatic beta cells. Genetic and environmental factors play a part and it is no surprise that HLA- DR3 and HLA-DR4 confer susceptibility to Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus. .(1)
Type 2 diabetes:it formerly referred to as non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus, NIDDM for short, and Adult-onset diabetes. Type 2 diabetes mellitus consists of an array of dysfunctions characterized by Hyperglycemia and resulting from the combination of resistance to insulin action, inadequate Insulin secretion, and excessive or inappropriate glucagon secretion. .(1) Gestational diabetes: Gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM) affects^ 7% of all pregnancies and is defined as Carbohydrate intolerance during gestation. It is crucial to detect women with GDM because the Condition can be associated with several maternal and fetal complications, such as macrosomia,birth trauma,hypocalcemia,hypoglycemia,and hyperbilirubinemia in Newborns. .(1)
Causes Of Diabetes:
Multi-fectorial, involving several predisposing conditions and risk factors. In many cases Genetics, habits and environment may all contribute to a person‘s diabetes
- Type 1 Diabetes:
- Type 1 diabetes is believed to be an autoimmune disease. The body’s immune system Specifically attacks the cells in the pancreas that produce insulin.
- Apredisposition to develop Type 1 diabetes may run in families, but genetic causes (a
- Positive family history) are much more common for Type 2 diabetes.
- Environmental factors, including common unavoidable viral infections, may also
Contribute to Type 1 diabetes.
-
- Type 1 diabetes is most common in people of Non-Hispanic, Northern European
- Descent, followed byAlfican Americans, and Hispanic Americans.
Type 1 diabetes is slightly more common in men than in women.
- Type 2 Diabetes:
- High blood pressure
- High blood triglyceride (lat) levels
- Gestational diabetes or giving birth to a baby weighing more than 9 pounds
- High-fat diet
- High alcohol intake
- Sedentary lifestyle
- Obesity or being overweight
- Aging.(1)
Signsand Symptoms:
Early detection and treatment of diabetes can decrease the risk of developing the Complications of diabetes. The following symptoms of diabetes are typical. However, some people
With type 2 diabetes have symptoms so mild that they go unnoticed.
Common Symptoms of Diabetes:
- Feeling very thirsty
- Feeling very hungry - even though you are eating
- Extreme fatigue
- Blurry vision
- Cuts/bruises that are slow to heal
- Weight loss - even though you are eating more (type 1)
Tingling, pain or numbness in the hand/feet (type 2). (1)
Sign & Symptoms of Diabetes smellitus
|
Prediabetes
|
Type 1 diabetes
|
Type 2 diabetes
|
|
No symptoms
|
Increased or extreme thirst
|
Increased thirst
|
|
|
Increased appetite
|
Increased appetite
|
|
|
Increased fatigue
|
Fatigue
|
|
|
Increased or frequent
urination
|
Increased urination
|
|
|
Unusual weight loss
|
Weight loss
|
|
|
Blurred vision
|
Blurred vision
|
|
|
Fruity odour or breath
|
Sores that do not heal
|
|
|
In some cases no symptoms
|
In some cases no symptoms
|
Complications Of Diabetes:
The complications of diabetes mellitus are far less common and less severe in people who have
well controlled blood sugar levels.
- Micro vascular Complications-
- Diabetic Retinopathy
- Diabetic Nephropathy
- Diabetic Neuropathy
- Macro vascular Complications
- Atherosclerosis
- Cardiovascular Disease (CVD)
- Stroke. (1)
Pathophysiology of Diabetes:
Mechanism of insulin release in normal pancreatic beta cells – insulin production is more or Less constant within the beta cells. Its release is triggered by food, chiefly food containing Absorbable glucose. Insulin is the principle hormone that regulates uptake of glucose from the Blood into most cells. Therefore, deficiency of insulin or the insensitivity of its receptors plays a Central role in all forms of diabetes mellitus. Humans are capable of digesting some carbohydrates, in particular those most common in Food; starch, and some disaccharides such as sucrose, are converted within a few hours to simpler Forms, most notably the monosaccharide glucose, the principal carbohydrate energy source used by The body. The rest are passed on for processing by gut flora largely in the colon. Insulin is released Into the blood by beta cells (P-cells), found in the Isletsof Langerhans in the pancreas, in response To rising levels of blood glucose, typically after eating. Insulin is used by about two-thirds of the Body’s cells to absorb glucose from the blood for use as fuel, for conversion to other needed Molecules, or for storage. Insulin is also the principle control signal for conversion of glucose to glycogen for internal Storage in liver and muscle cells. Lowered glucose levels result both in the reduced release of Insulin from the P-cells and in the reverse conversion of glycogen to glucose when glucose levels Fall. This is mainly controlled by the hormone glucagon, which acts in the opposite manner to Insulin. Glucose thus forcibly produced from internal liver cell stores reenters the bloodstream; Muscle cells lack the necessary export mechanism. Normally, liver cells do this when the level of insulin is low. Higher insulin levels increase Some anabolic processes, such as cell growth and duplication, protein synthesis, and fat storage. Insulin is the principal signal in converting many of the bidirectional processes of metabolism from Acatabolic to an anabolic direction, and vice versa. When the glucose concentration in the blood is raised beyond its renal Threshold, reabsorption of glucose in the proximal renal tubuli is incomplete, and part of the Glucose remains in the urine (glycosuria), This increases the osmotic pressure of the urine and Inhibits reabsorption of water by the kidney, resulting in increased urine production Polyuria. (1).
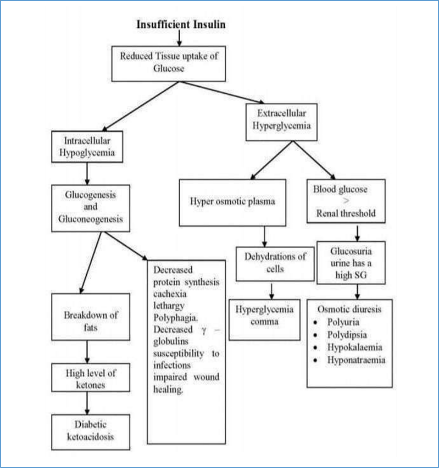
The blood glucose levels of a healthy man are 80mg / dL on fasting and up to 160 mg / dL in The postprandial state. A number of laboratory tests are available to confirm the diagnosis of diabetes.
- Finger Stick Blood glucose.
- Fasting Plasma glucose.
- Oral Glucose Tolerance Test.
- Glycosylated Hemoglobin or. (1)
Chemical Classification of Anti-Diabetics Drugs
|
Drug class
|
|
Agent
|
|
Biguanides
|
|
Metformin
|
|
Sulfonylureas
|
First generation
|
Acetohexamide Chlorpropamide Tolazamide Tolbutamide
|
|
|
Second generation
|
Gliben clamide/ Gliburide Glipizide Glimepiride Glielazide
|
|
Meglitinides
|
|
Repaglinide Nateglinide
|
|
Thiazolidinediones
|
|
Rosiglitazone Pioglitazone
|
|
tt-Glucosidase inhibitors
|
|
Acarbose Miglitol
|
|
Incretin agonists
|
|
Exenatide Liraglutide
|
|
DPP-4 inhibitors
|
|
Sitagliptin Vildagliplin
Saxagliptin
|
https://images.app.goo.gl/L76raS7kyUZeyS£
https://bestdiabetescentre.com/treatment-care-of-diabetes/
Herbal medicine With Anti Diabetic Property.
Fennel:

https:/www.etsv.com/listing/939558144/fennel-seed-foeniculum-vulgare-whle-50g
Synonyms
-
- Fennel fruit
- Fenkel
- Florence fennel
- Sweet fennel
- Wild fennel
- Large fennel. (2)
Biological Source
Fennel consists of the dried ripe fruits of Foeniculum vulgare Miller., belonging to family Umbelliferae(2)
Geographical Source
Fennel is indigenous to Mediterranean countries and Asia; it is largely cultivated in
France, Saxony, Japan, Galicia, Russia, India, and Persia. (2)
Chemical Constituents
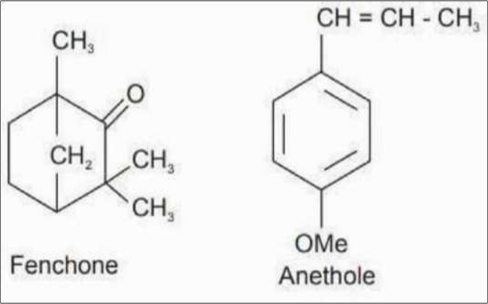
•4 to 5% of volatile oil
•The primary constituents of volatile oil are 50 to 60% of anethole, a phenolic ester; and 18 to
22% of fenchone, a ketone.
•Fenchone is chemically a bicyclic monoterpene which is a colourless liquid and the odour and taste is pungent and camphoraceous. (2)
Uses
Fennel is used as:
-
- stomachic
- Diuretic
- Carminative
- as a digestive
Anethole may have estrogen- like activity and inhibit spasms in smooth muscles. Fennel can increase production of bile, used in the treatment of infant colic, to promote menstrua-tion in women, can increase lactation, act as antipyretic, antimicrobial and antiinflammatory.(2) Antidiabetic Activity of Fennel
Chemical composition was examined inpolar (methanol) and non-polar (hexane) extracts of fennfe seeds using GCM technique. An invitro anti-diabetic and anti- inflammatory assay was observed infennel extract. Astatistical approa was done ch by cluster analysis in fennel seeds.(3)
- Cinnamon:

Synonyms
-
- Cortex cinnamoni
- Ceylon cinnamon
- Saigon cinnamon
- Chinese cassia
- Cinnamomum aromaticum
- Cinnamomum laurus(4)
Biological Source
Cinnamon is the dried inner bark of the coppiced shoots of CinnamomumzeylanicumNees., belonging to family Lauraceae. (4)
Geographical Sources
Cinnamomum zeylanicum is widely cultivated in Ceylon, Java, Sumatra, Westlndies, Brazil, Mauritius Jamaica, and India. (4)
Chemical Constituents
-
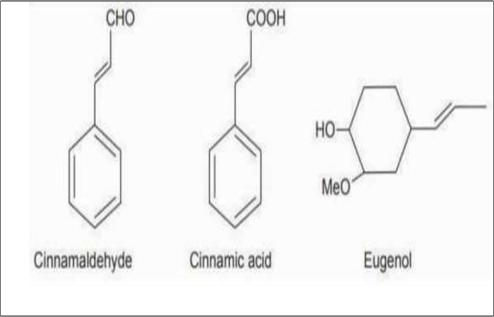
- Cinnamon contains about 10% of volatile oil
- calcium oxalate and sugar
Volatile oil contains 50 to 65% cinnamic aldehyde, along with 5 to 10% eugenol, terpene hydrocarbons and small quantities of ketones and alcohols. (4)
Uses
-
- It is used as an aromatic
- Carminative
- analgesic antiseptic
- antirheumatic
- antispasmodic
- digestive
- expectorant
- stomachic
•It stops vomiting, relieves flatulence and is given with chalk and as astringents for diarrhoea and haemorrhage of the womb.
•It is also used in the treatment of bronchitis, colds, palpitations, nausea, congestion, and liver
problems. (4)

https://www.slideshare.net/sahelichakrabortv6/antidiabetiproperties-of-cinammon
3.Neem:-

https://images.app.goo.gl/UrwfbzQiYdCtzqTJfe
Synonyms
-
- Hin.-Nira, nimb
- Mar. - Limba
- Tam- Vembu(5)
Biological Source:
-
- Neem consists of the fresh or dried leaves and seed oil of Azadirachta indica J. Juss (Melia Indica or M. Azadirachta Linn.).
Family:
Geographical source:
It is found in India, Pakistan, Sri Lanka, Malaya, Indonesia, Japan, Tropical region ofAustralia and Africa. In India, it is found in Uttar Pradesh, Maharashtra, Tamil Nadu, Rajasthan, and M P (5)
Chemical Constituents:
- Leaves:
- Nimbin, 6- desacetylnimbinene.
- Nimbinene, Nimbandiol, nimbolide.
- Quercetin, P-sitosterol,
Ascorbic acid, n-hexacosanol, nonacosane and aminoacid. (5)
Uses:
- Leaves:
- Poultice, applied to boils,
- In worm, jaundice and in skin disease.
- Ulceration of cow-pox.
- Insect-repellent,
- Antiviral and antifungal. (5)
Antidiabetic Activity of Neem
The usage of neem in controlling blood glucose levels has long been in practice inmany countries. Neem leaf extract dilate the blood vessels in diabetic patients and the neem leaves and seed is found to reduce the amount of insulin required to be administered to a diabetic patient. (6)
4. Ginger

https://www.allrecipes.com/article/whais-ginger
Synonyms
-
- Rhizoma
- zingiberis
- Zingibere.(7)
Biological Source
-
- Ginger consists of the dried rhizomes of the Zingiber officinale Roscoe, belonging to family Zingiberaceae.(7)
Geographical Source
-
- It is mainly cultivated in WestIndies, Nigeria, Jamaica, India, Japan, and Africa.(6)
Chemical Constituents
-
- Ginger contains 1 to 2% volatile oil
- 5 to 8% pungent resinous mass and starch
The volatile oil is responsible for the aromatic odour and the pungency of the drug is due to the yellowish oily body called gingerol which is oodourles (7)
Uses:
-
- Ginger is used as an anti emetic
- positive inotropic
- spasmolytic
- aromatic stimulant
- carminative
- Sore throat, hoarseness, and loss of voice are benefited by chewing a piece of ginger. (7)
Anti-diabetic Activity of Ginger
Ginger has been shown to possess anti-diabetic activity in a variety of studies. Akhani et al.(2004) reported that ginger pre-treatments inhibited the induced hyperglycemia and hypoinsulinemia (10). Other investigators have showed the hypolipidemic effect of ginger (H)(8)
5)Garlic

Synonym
Lehsun (in Hindi) (9)
Biological Source
-
- Bulbs of Allium sativum (9)
Family
Geographical Source
-
-
- Garlic is native to central Asia and is also cultivated in Europe,Africa, USA, India etc.
- It has been a staple food in the Mediterranean region for a long time. (9)
Chemical Constituents
The other Sulphur compounds alliin, allicin, diallyldisulphide etc are also responsible for the pharmacological activities of garlic. (9)
Antidiabetic effect Of Garlic
Garlic has been proposed to reduce blood glucose levels due to the antioxidant S-allyl cysteine sulphoxide present in it. It Increases serum insulin levels by increase in insulin secretion from beta cells as demonstrated in mice. (9)
Uses
-
-
- Wards Off Cough and Cold. Raw garlic has the potential to ward off cough and cold infections.
- Good for Cardiac Health. ...
- Improves Brain Functioning. ...
- Balances Blood Sugar.
- Boosts Immunity....
- Improves Skin Health. ...
- Prevents Cancer and Peptic Ulcer. (10)
6) Aloe

http://images.app.goo.gl/iKWYeSCmCqNRsrHa
Synonym
-
- True Aloe
- Indian Aloe
- Korphad(io)
Biological sources:
-
- The botanical name of aloe is Aloe barbadensis miller.
- The biological source of aloe is dried latex of leaves of it.
- It is also known as curacao aloe, cape aloe and socotrine aloe.
- It belongs to the liliaceae family. (12)
Chemical constituents:
-
- The chief chemical constituent of aloe is aloe-emodin ,which occurs in free form .
They also composed of anthrones and anthranols, which may be present in free or combined form as glycoside.
- It also contain isobarbaloin and resins.
- The active resin present in aloes is also known as aloesin.
- Other chemical constituents are volatile oil to some extent which is responsible of its characteristic odour.
- Gama- coniceine (piperidine) is also present in some species of aloe. It also contain
- amino acids, enzymes, vitamins and minerals. Sugars and hormones and salicylic acid is also present in aloe.
- Steroids are also present in aloe.(12)
Uses:
- It has purgative property.
- It is used to treat painful inflammatory manifestation.
- Aloe gel is used to treat and cure radiation burns to get immediate relief from itching and pains.
- It is usually applied with carminatives.
- It helps to reduce psoriasis and rosacea, warts
•It also helps to reduce ageing and wrinkles.
•It also reduces eczema.
•It helps to improve flexibility.
•It also have bodycell regeneration ability.
•It generate movement of bowel in the condition of constipation.
•Helps to heal insect bites, rashes, sores and fungal infection.
•It is used to treat herpes and urticaria and conjunctivitis.
•It is used to treat vaginal infection and allergic reactions.
•Its boiled juice is used to treat hair fall. (12)
Antidiabetic Activity of Aloe Vera
Previous studies of Aloe vera extract indicate that Aloe can act as a hypoglycemic agent through the potent inhibition of pancreatic amylase activity. This action decreases the breakdown of starch and offers good postprandial glycemic control [13].
7)Pterocarpus

https://images.app. goo. gl/BqiBcHNSGt3YmXM¥
Synonym
-
- Bijasal
- Indian kino tree
- Malbar kino. (l4)
Biological Source
It consists of dried juice obtained by making vertical inci-sons to the stem bark of the plant
Pterocarpus marsupium Linn., belonging to family Leguminosae. (14)
Chemical Tests
•When the solution of drug is treated with ferrous sulphate, green colour is produced •
•With alkali (like potassium hydroxide) violet colour is produced.
•With mineral acid, a precipitate is obtained. (14)
Chemical Constituents
•Kino contains about 70-80% of kinotannic acid, kino-red, k-pyrocatechin (catechol),
•resin and gallic acid.
•Kinotannic acid is glucosidal tannin, whereas kino-red is anhydride of kinoin.
•Kinoin is an insoluble phlobaphene and is produced by the action of oxydase enzyme.
•It is darker in colour than kinotannic acid. (14)
Uses
Kino is used as powerful astringent and also in the treatment of diarrhoea and dysentery, passive haemorrhage, toothache, and in diabetes. It is used in dyeing, tanning, and printing. The aqueous infusion of the wood is considered to be of much use in diabetes. The alcoholic, as well as, aqueous extracts of heartwood are known to possess hypoglycaemic action. The cups made of wood are available with Khadi and Gramodyog commission for treatment of diabetes. (14)
Anti-diabetic Activity:
The antidiabetic effect might be due to steviosides counteracting the glucotoxicity in P- cells or also by suppressing the glucagon secretion by a-cell of pancreas; both the mechanisms have been depicted by Shibata et al. and Chen et al. (15)
8) Gymnema:

https://images.app.goo.gl/f4rrXYdsQHn6FBtp8
Synonyms:
-
- Meshashringi
- Gur-mar
- Kavali
- Kalikardori
- Dhuleti(l6)
Biological source:
Extracts from the leaves contain alkaloids, phenols, tannins, flavonoids, and saponin. The hypoglycemic effect of gymnema has been recognized in early animal experiments and
reconfirmed over the last decades.(l6)
Geographical source:
It is distributed through out India in a dry forest up to 600- meterheight.It is found in Banda, Konkan,Western Ghats, and Deccan extending to the part of the northern and western India. It is distributed in Asia, Tropical Africa, Malaysia and Srilanka. It is occasionally cultivated as medicinal plant.(l6)
Chemical constituents
The leaves and extracts contain gymnemic acid, the major bioactive constituents that interact with taste receptors on the tongue to temporarily suppress the taste of sweetness. (16)
Uses
1. Reduction of sugar intake: G. sylvestre extracts taken in the form of lozenges, mouthwash, or tea diminishes the consumption of sweet foods and overall caloric intake. Extracts (formulated as a mintlozenge) reduced the desire for high sugar foods and the pleasant taste of candy. Research also suggests that Gymnema sylvestre extracts reduce cravings for sugar in a double-blind study, participants who received a gymnemic acid lozenge declined candy(before tasting it) more often than the placebo group.
2. Diabetes: Early research suggests when a specific gymnema extract (GS4) is taken orally along with in sulin or diabetes medications, blood sugar reduction in people with type 1or type 2 diabetes is enhanced.
3. Weight loss: In Japan, 50 tons of G. sylvestre leaves are consumed annually for the purpose of weight loss. Early research suggests that taking a specific combination of Gymnema sylvestre extract hydroxycitric acid and niacin bound chromium by mouth for 8 weeks might reduce body weight in people
4. who are overweight or obese.
Antidiabetic activity:-
The first scientific confirmation of its use in human diabetics came almost 80 years ago when it was demonstrated that the leaves of Gymnema sylvestre reduced urine glucose in diabetics22. In 1990 a series of published studies on Gymnema sylvestre extract lifted this herb from interesting to revolutionary. It was shown that the administration of Gymnema sylvestre extract to diabetic animals not only resulted in improved glucose homeostasis, this improvement was accompanied by a regeneration of beta cells in the pancreas21. Studies were conducted on albino rats to establish the antidiabetic activity of Gymnema sylvestre, which was compared with other conventional indigenous oral antidiabetic drugs like Coccinia indica, Pterocarpus marsupium, Momordia charantia. The inhibitory effect was highly significant in Gymnema sylvestre when compared with Pterocarpus marsupium and Momordia charantia 24. Scientific investigation of the biological effect of oral administration of the leaves revealed that Gymnema sylvestre therapy also increased the activities of the enzymes affording the utilisation of glucose by insulin dependent pathways: it controlled phosphorylase levels, gluconeogenic enzymes and sorbitol dehydrogenase. This valuable herb appears to correct the metabolic derangements in diabetic rabbit liver, kidney and muscle25. Gymnema sylvestre extract (400 mg/day) for 18-20 months was observed to reduce blood glucose in 22 noninsulin dependent diabetic patients 26. (17)
- Ajwain

https//www. chandigarhavurvedcentre.com/wp
Synonyms Ajwain Caraway Thymol seed(18) Biological Source
Ajwain is the dried ripe seeds of Trachyspermum ammi(L.) Sprague, belonging to family Apiaceae. (18)
Geographical Source
It is a native of Egypt and grown through out India, Mediterranearagion andin southwest Asian countries suchas Iraq, Iran, Afghanistan, and Pakistan. (18)
Chemical Constituents

Ajowan contains an essential oil (2-3.5%), protein (17.1%), and fat (21.8%). Ajowan oil is a colourless or brownish yellow liquid possessing a characteristic odour of thymol and a sharp taste. The principal constituents^ the oil are phenol, mainly thymol (35 - 60%), caracole, p- cymene, y- terpinene, a-, and p-pinenes and dipentene. The fatty oil is composed of palmitic, petroselinic, oleic, linoleic, and 5,6-octadecanoic acids. (18)
Uses:-
Ajwain is widely used as a spice in curries; in pickles, certain types of biscuits, confectionery, and in beverages. It is valued for its antispasmodic, stimulant, tonic, and carminative properties. It is given in flatulence, atonic dyspepsia, diarrhoea, and cholera. It is used most frequently in con-junction with asafoetida, myrobalans and rocksalt. Ajowan is also effective in relaxed sore throat and in bronchitis, and often constitutes an ingredient of cough mixture. Ajwain oil is used as an antiseptic, aromatic, carminative, for perfuming disinfectant soaps, and as an insecticide. The oil is useful as an expectorant in emphysema, bronchial pneumonia and some other respiratory ailments. (18)
Health Benefits of Ajwain Water
- Helps in Digestion
- Improves Respiratory Health
- AntiBacterial and Anti-Fungal
- Helps regulate the Menstrual Cycle

10) Turmeric

Synonyms
Saffron Indian; haldi (Hindi); Curcuma; Rhizoma ctnumae. (19)
Biological Source
Turmeric is the dried rhizome of Curcuma longa Linn. (syn. C.domestica Valeton)., belonging to
family Zingiberaceae. (19)
Geographical Source
The plantis a nativeto southern Asia andis cultivated extensivelyn temperate regions. It is grownon a larger scalein India, China, East Indies, Pakistan, and Malaya. (19)
Chemical Constituent
Turmeric contains yellow colouring matter calledas curcuminoids (5%) and essential oil (6%). The chief constituentof the colouring matteris curcumin I (60%) in addition with small quantities of curcumin III, curcumin II and dihydrocurcumin. The volatile oil contains mono- and sesquiterpenes like zingiberene (25%), a-phellandrene, sabinene, turmerone, arturmerone, borneol, and cineole. Choleretic action of the essential oilis attributed to p-tolylmethylcarbinol. The volatile 0il also contains a- andp-pinene, camphene, limonene, terpinene, terpinolene, caryophyllene, linalool, isoborneol, camphor, eugenol, curdione, curzerenone, curlone, AR- curcumenes,p- curcumene,y-curcumene.a- andp turmerones, and curzerenone(19)

Uses
Turmeric is used as aromatic, antiinflammatory, stomachic, uretic, andyne for billiary calculus, stimulant, tonic, carminative, blood purifier, antiperiodic, alterative, spice, colouring agent for ointments and a common household remedy for cold and cough. Externally, it is used in the form of a cream to improve complexion. Dye-stuff act as a cholagogue causing the contraction of the gall bladder. Curcumin has choleretic and cholagogue action and is used in liver diseases. Curcuminoids have antiphlogistic activity which is due to inhibition of leukotriene biosynthesis. ar-Turmerone has antisnake venom activity and blocks the haemorrhagic effect of venom. (19)
Formulation Of Herbal antidiabetic Powder
- Cinnamon:
- Collection: Collected from market in the form of raw material i.e. bark of cinnamon
- Authentication: Chemical test:On addition of a drop of ferric chloride solution to a drop of volatile oil, a pale green colour is produced. With ferric chloride, cinnamic aldehyde give brown colour and eugenol gives blue colour, resulting in the formation of pale green colour.
- Processing: as it collected from market in the form of bark .processing done with the help of mortar and pestle resulted in powder form.
- Method: Trituration
- Fennel:
- Collection : Collected from market in the form of raw material i.e. fruit of fennel
- Authentication: Dilute 2 mL of Formalin with 10 mL of water in a test tube, and add 1 mL of silver nitrate-ammonia TS: a gray precipitate is produced, or a silver mirror is formed on the wall of the test tube.
- Processing: as it collected from market in the form of fruit .processing done with the help of mortar and pestle resulted in powder form.
- Method: Trituration
- Neem :
- Collection : Collected from naturally from neem tree in the form of leaves .
- Authentication: Test for Terpenoids (Salkowski Test): 0.2 g crude drug extract was mixed with 2ml of chloroform (CHCl3) and 3 ml of concentrated H2SO4 was carefully added to form a layer Formation of reddish brown color interface. presence of terpenoids confirmed
- Processing: As it collected from naturally in the form of leaves .processing done with the
help of mortar and pestle resulted in powder form.
-
- Sandalwood (Pterocarpus):
- Collection: Collected from market in the form of powder
- Authentication: Chemical Tests: When the solution of drug is treated with ferrous sulphate, green colour is produced.
5) Turmeric and Ajwain:
It is used as preservative in the formulation . Bothof them having antidiabetic activity also.
Collection: collected from market in the form of powder.
CONCLUSION
The aim of the present study is to give complete information about diabetes and herbal polyherbal formulation available in market for diabetes that are alternative to synthetic medicines. Herbal medication of diabetes is much better than allopathy. The research revealed that the selected herbal medicines had significant potential as potential anti-diabetes drug alternatives. Furthermore, each of these herbs has an original mechanism of action for lowering blood sugar. This is owing to the fundamental fact that each herb’s power to work is strongly impacted by the presence of different active compounds. Several plants will decrease blood glucose levels following 4, 3, 2 or 1 mechanism of actions. Aloe vera have a minimum of 3 mechanisms of action such as increased GLP 1 secretion and inhibition amylase, glucosidase, and SGLT 2. Prepared herbal antidiabetic powder formulation needs to be further evaluated as in vivo and in vitro study for checking combined effect of antidiabetic drugs and exact pharmacological action, to determine stability and expiry date of antidiabetic drugs.
REFERENCES
- Maninder Kaur 2 Vandana Valecha,Diabetes and Antidiabetic Herbal Formulations: An Alternative to Allopathy,European Journal of Medicine, 2014, Vol.(6), ? 4
- https://www.pharmacy180.com/article/fennel-240/
- Nisha Mehta, Garima Tamta, Vivekanand, Indian Journal of Natural Products and Resources(IJNPR)4598 [Formerly Natural Product Radiance (NPR)] 20 March 2023, Vol 14, No 1
- https://www.pharmacy180.com/article/cinnamon-231/
- https://www.vourarticlelibrarv.com/biology/plants/neemsourcesmacroscopical
- https://mkas.iournals.ekb.eg https: //www.pharmacy 180.com/article/ginger-271/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4277626
- https: //pharmaxchange.info/2014/01 /pharmacognosy-and-health benefits of- garlic/
- https://pharmeasy.in/blog/top-10-health-benefits-of-garlic
- https://testbook.com
- https://gpatindia.com/aloe-biological-sources-morphologicalaturesmedicinal-usesandmcqs/
- https://www.hindawi.com
- https://courseware.cutm.ac.in/wp-content/uploads/2022/09/45.-
- R. S. Kujur, Vishakha Singh, Mahendra Ram, Harlokesh Narayan Yadava,1 K. K. Singh,2 Suruchi Kumari, and B. K. Roy,Antidiabetic activity and phytochemical screening of crude extract of Stevia rebaudiana in alloxan-induced diabetic rats, 2010 Jul-Aug; 2(4): 258–263.
- Erik Gylfe es.uu.bcm@eflyg. kire Department of Medical Cell Biology, Uppsala University, BMC Box 571, SE-751 23 Uppsala, Sweden, Glucose control of glucagon secretion—‘There’s brand-new gimmick every year’,Ups J Med Sci. 2016 May; 121(2): 120–132.Published online 2016 Mar 24. doi:10.3109/03009734.2016.1154905
- https://www.researchgate.net/publication/2623789 Gymnemasylv estre a co
- https://courseware.cutm.ac.in/wpcontent/uploads/24
- https: //www.pharmacy 180.com/article/aj o wan
- https://www.pharmacy180.com/article/turmeric-283/


 Prakash Honrao*
Prakash Honrao*
 Shoaeb Mohammad Syed
Shoaeb Mohammad Syed





















 10.5281/zenodo.14583967
10.5281/zenodo.14583967