Abstract
Aegle Marmeloes is a popular medicinal plants in the Ayurveda and Siddha system of medicine and folk medicine To treat various disease and disorders including Fever The present study was under taken to evaluate the Antipyretic property of Bael leaves on Brewers yeast induced pyrexia in albino ratsIt revels that the ethanolic extract at dose of 200 mg – 1kg body wt C 400 mg- 1kg body weight produced significant .( p< 0.001 )reduction in elevated body temperature in dose depends manner followed by aqueous extract was comparable to that of paracetamol ( 100 mgkg 1- body wt).
Keywords
agele marmmeloes; Ayurveda; folk medicine medicinal use; as a antipyretic drug; ethanolic extraction of bael leaves).
Introduction
The Bael as sacred tree of Hindus They offer it’s leaves to cultivated in India. These plant have medicinal used to treat various disease and disorders In fever management they can be used as herbal formulation In treatment of Fever the various systems like temperature, weekness, fatigue, body pain and other symptoms in Typhoid case Typhoid Fever is acute infection of intestine poor hygiene Habits and poor sanitation condition are responsible for the spread of Typhoid. They can treat by Herbal Medicine. The aim of behind study by using herb remidies they can be easily cure without any contraindications. Its easy to conventional as dose dependent manner this infection are treated with the help of Ayurvedic or folk Medicine.
Aegle Marmeloes (Bael): Kingdom: plantae
Subkingdom: Trachibebionata Order: Sapindales
Family: Rutaceae
Genus: Aegle
Species: MarmeloesIn traditional medicine, A. marmelos are used based on their radio protective antidiabetic, and anticancer activities . The various components of bael are used for its medicinal properties, such as managing asthma, fractures, anemia, wound healing, high blood pressure, jaundice, swollen joints, diarrhoea, and issues with typhoid during pregnancy. The medicinal importance of A. marmelos has been discussed in focusing on each part of the plant.
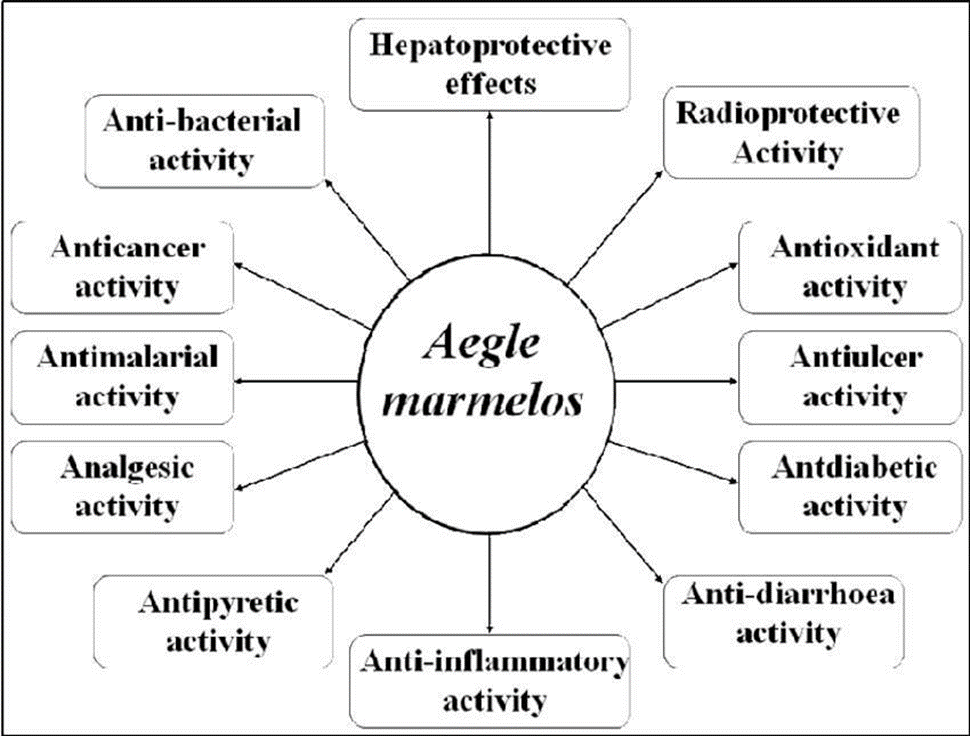
Leaves The leaves are most effective in treating fever, nausea, vomiting, swellings, dysentery, dyspepsia, seminal weakness, and intermittent fever. Bael ptra leaves are used.
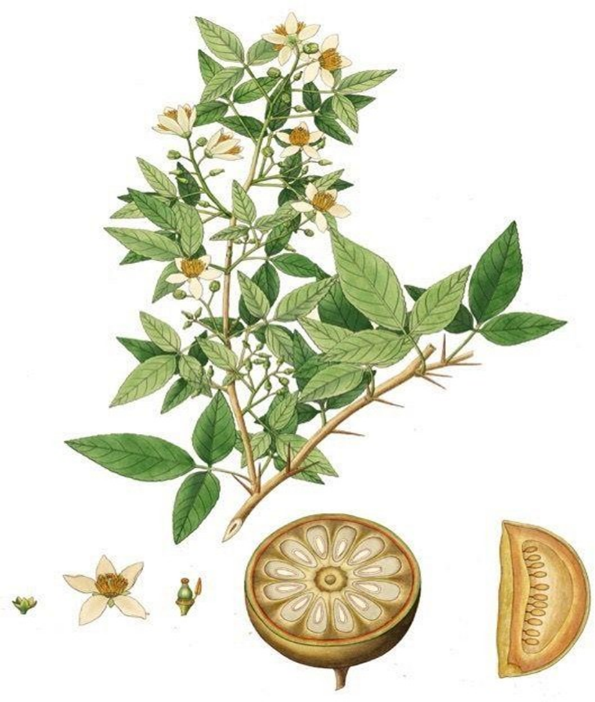

plant Have been claim to used treatment of Inflammation, Haypogylacemia, febrifuge, hepatitis analgesic the roots and the bark of the tree are used in the treatment of fever making by the decoction of them thus effort has been to evaluate antipyretic activity of aegle Marmeloes and betal leaf plant.
?Objective: -
1.To scientifically evaluate the antipyretic potential of aegle marmeols and it’s bioactive compound.
2.To assess it’s potential as a natural and safe alternative for fever management .
?Aim: -
1.The specific aim behind these topic is to development and phytophramaceutical which creat natural , safe C effective dose of antipyretic product from betel and bilva leaves plant .
2.To identify and quantity bioactive compound : Isolate and characterization phytochemicals responsible for antipyretic activity
3.To evaluate antipyretic activity : Cox 1 inhibition ,cox2 5- Cox inhibition
4.To assess in vivo antipyretic efficacy: evaluate fever reduction in animal model ( e.g Yeast- induced fever)
5.To investigate efficacy safety and toxicity.
?Plane of wrok :- Material needed
•Aegle Marmelos powder
•Ethanol (95%)
•Soxhelated apparatus
•Round Bottom Flask
•Condenser
•Filter paper
•Evaporator
Experimental Methodology
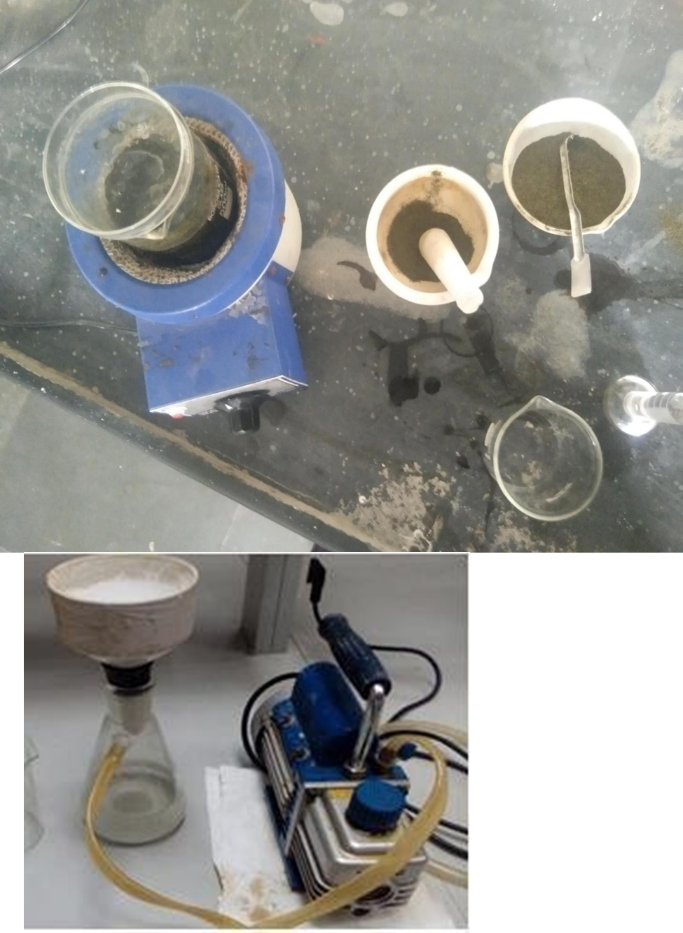
1.Sample preparation : weigh accurate 100 g of Aegle Marmelos powder.
2.Soxhlet Extraction : place the Powder in a soxhlet thimble and extract with 500 ml of ethanol (95%) for 6 to 8 hour .
3.Cold maceration : alternatively mix 100 g Powder with 500 ml ethanol in a container . Seal and keep at room temperature for 24 hour.
4 Filtration : Filter the extract using filter paper
6.Evaporation : concentrate the extract using evaporator to remove excess ethanol
7.Drying : Dry the extract for removed all excess moisture content
8.Yield Calculation : calculate the yield of the extract based on initial weight of the powder
G. Storage : stored at airtight container in a refrigerator.
? experimental Design And Methodology :
•Animal models
Animal models such as rat and mice were use to investigate the antipyretic potential of aegle Marmeloe
•Drug Administration
Different doses of the extracts were administered to the animals to Observe their effects on body temperature.
•Data Analysis
The data obtained from the experiments was analyzed to assess the efficacy and safety of Aegle marmeloes as an antipyretic agent.

In Vivo Antipyretic Activity
Fever was induced in animal models using methods such as injection of pyrogens.
The extract was administered orally or intravenously to the animals after fever induction.
Body temperature was monitored regularly using rectal thermometers or other Methods.
The ability of the extract to reduce fever was assessed by comparing temperature changes in treated animals with control groups.
In vitro Antipyretic Activity of Aegle Marmelos extract
Evaluation Test
|
Sr No.
|
Parameters
|
Results
|
|
1.
|
Color
|
Blackish green
|
|
2.
|
Odure
|
Aromatic
|
|
3.
|
Teste
|
Slightly bitt
|
|
4.
|
Angle of repose
|
35
|
|
5.
|
Bulk density
|
0.28
|
|
6.
|
Tapped density
|
0.37
|
|
7.
|
Hausners ratio
|
1.27
|
|
8.
|
Carr’s index
|
21.73
|
|
9.
|
PH
|
6.8
|
|
10.
|
Stability
|
Stable
|
?Phytochemical Screening
The chemical constituents of the Ethanolic extract of Aegle marmelos (EACL) and aqueous extract of Aegle marmelos leaves (AACL) were identified by qualitative analysis and confirmed by thin layer chromatography for the presence of flavonoids, tannins, steroids and saponins.
Animal used :
Wistar albino rats (150 ±20 g) were used for the antipyretic study. Albino mice weights about 25±5 g were used for the acute toxicity studies of the crude extracts. Institution Animal Ethics Committee has approved the project (919/ac/08/CPCSEA). The animals were kept in departmental animal house in well cross ventilated room at 27±20C, relative humidity 44–56% and light and dark cycles of 10 and 14 h respectively for 1 week before and during the experiments. Animals were provided with standard diet (Lipton, India) and the food was withdrawn 18–24 h before the start of the experiment.
Acute toxicity study:
The acute toxicity of the extracts was determined in albino mice, maintained under standard conditions. The animals were fasted overnight prior to the experiment. Fixed dose (OCED Guideline No. 420) method of CPCSEA was adopted for toxicity studies.
Induction of yeast-induced pyrexia
Rats were divided into five groups of six rats each. The normal body temperature of each rat was measured rectally at predetermined intervals and recorded. Hyperexia was induced in rats by 20 ml/kg administration of 20 % aqueous suspension of brewer’s yeast subcutaneously. The animals were then fasted for the duration of study (approx 24 hrs), but water was made available ad libitum. Control body temperature was taken 24h after the injection to determine the pyretic response to the yeast. Body temperature was taken 1h
prior to drug administration in fevered animal served as pre drug control. Extracts were given in dose 200 mg kg-1 body wt. and 400 mg kg-1 body wt., orally. Paracetamol was
?Formulation Development and Characterization

Capsule Formulation
Capsules were developed for convenient and accurate oral administration of the extract.
Collect and dry the herbs: Collect fresh herbs, clean them, and dry them at room temperature or in a hot air oven.
Grind the herbs: Grind the dried herbs into a fine powder. Mix with excipients: Mix the dried extracts with excipients like lactose, Avicel, or maltodextrin.
Form the granule mass: Mix the dried extracts and excipients to form a granule mass. Fill the capsule: Use a capsule filling machine to fill the capsule shell with the granule mass.

CONCLUSION: -
- Aegle Marmeloes and piper Betel Leaf posses a potent antipyretic propertie.
- The combination of both extract results in enhanced efficacy , B ioavailability , exhibit synargestic effect.
- The development of formulation offers a promising natural alternatives to conventional antipyretics.
Further Research
- Future research should focus on clinical trials to confirm the efficacy andsafety of Aegle marmeloes as an antipyretic agent in human
- Investigate the mechanism of action of Aegle marmeloes extract reducing Fever including the involvement of cytokines , prostaglandin and inflammatory madiators
- Standardization and to quality control to develop and measure the ensure the consistency and purity of Aegle Marmeloes extract.
- Established of antipyretic activity identification of Bioactive compound which is responsible for antipyretic potential of aegle Marmeloes extract.
REFRENCES
- Indian Herbal Pharmacopoeias ( 2002 , 2007 ,2014 ,2022 )
- Orient J Chem 2011;27(1). Available from: http://www.orientjchem.org/?p=24837
- “ Aegle Marmeloes : A medicinal plant by S.K. Sharma , springer 2019.
- “ Phytochemistry and phramcology of Aegle Marmeloes by R. K. Singh, Academic press 2020.
- National Institute of Pharmaceutical Education and Research( NIPER
- )India conduct study in aegle Marmeloes and piper Betel Leaf phytochemistry and pharmacology.
- Charaka Samhita ( 400 CE ) , Ashtanga Haridayam(600CE) :
- Including Aegle Marmeloes as “ Bllva and recommend its use in treating Fever , diarrhea respiratory disorderss
- Sushruta Samhita ( 600 CE ) : Described Piper Betel Leaf is a folk Medicine..


 Vaishnavi Changade*
Vaishnavi Changade*







 10.5281/zenodo.14887531
10.5281/zenodo.14887531