Abstract
Mouth dissolving films are at the forefront of oral solid dosage forms, offering enhanced comfort and versatility. They outperform fast-dissolving tablets by rapidly dissolving in the mouth with reduced saliva, hence enhancing the effectiveness of the active pharmaceutical ingredient (API). These films are a popular choice among consumers compared to traditional tablets or capsules because they do not require chewing or water for administration. The emerging technology of oral mouth dissolving films demonstrates significant potential due to its capacity to meet diverse requirements. The main goal of this review is to formulate and analyse mouth dissolving film containing fexofenadine hydrochloride. Children have a higher likelihood of experiencing acute rhinitis, hence fexofenadine has a synergistic effect in their treatment. The evaluation criteria include the assessment of organoleptic features, surface characteristics, tensile strength, folding endurance, thickness, drug solubility, percentage of elongation, and drug content determined using estimation techniques.
Keywords
Mouth dissolving film, fexofenadine, solid casting technique,HPMC, oral cavity, anti-histaminics, dysphagia , acute rhinitis, polyethylene glycol (PEG), thin strips,manufacturing.
Introduction
1. Background
In modern pharmaceutical practice, it is required that medications possess aesthetically pleasing shapes. Medications are delivered to the body through various dosage forms like transdermal patches, capsules, suppositories, tablets, parenteral forms, syrups etc. [1] Traditional methods of administering drugs orally often result in rapid and complete release of the medication, which may not be desired due to factors such as the presence of food, stomach acidity, enzymatic breakdown, or changes in gastrointestinal movement, which can limit absorption time. [2-3] Currently, there is significant emphasis on developing drug delivery methods that prioritize sensory appeal and maximize patient acceptance, especially in pediatric and geriatric populations. [4-6]
Initially designed as alternatives to tablets, capsules, and syrups, quick dissolving medicine delivery systems were initially created specifically for patients who are elderly or pediatrics who may suffer through the risk of choking. An important benefit of these devices is their capacity to rapidly dissolve or disintegrate in saliva without the need for additional liquids.[7] Among the various methods to enhance the absorption of hydrophobic pharmaceuticals through the mouth, self-emulsifying drug delivery devices (SEDDs) hold enormous potential. Upon ingestion, these systems disperse in the fluid of the gastrointestinal tract to form drug particles that are either in the form of nano-emulsions or micro-emulsions. By facilitating easier absorption through the lymphatic system, this bypasses the initial metabolism that occurs in the liver. [8-9]
1.1 Mouth Dissolving Films (MDFS)
These are thin polymeric films in the shape of stamps that dissolve quickly in the mouth when placed on the tongue.[10] These films show potential as a dose form, especially for geriatric and pediatric patients who have difficulty swallowing oral medication.[11] Various studies have explored their pharmacological development, including optimizing the formulation, characterizing their properties, assessing their mechanical properties, and successfully masking the taste of the drug incorporated into the film.[12-16] In September 2003, Prestige International Brands introduced Chloraseptic® Relief StripsTM, the first oro-dispersible film product designed to provide relief for sore throats, in the United States. [17] In July 2010, Strativa Pharmaceuticals launched Zuplenz (ondansetron), a film that dissolves in the mouth. Initially approved by the US FDA for prescription use to lower down the symptoms of vomiting and nausea caused due to chemotherapy, this drug holds the distinction of being the first of its kind.[18]
1.2 Features of Mouth Dissolving Films
These films are defined as small, aesthetically pleasing films that are specifically designed for medication distribution. They are approximately the size of a postage stamp. Similar to cotton candy, these films dissolve on the tongue and provide a pleasing texture and satisfactory flavour. These oral films dissolve quickly and smoothly; the film melts within seconds when it comes into touch with the top of the tongue. Unlike pills and other types of oral medication that are released immediately, this method bypasses the initial metabolism in the liver, perhaps enhancing the drug's bioavailability. One of the most significant characteristics of MDFs is their ability to drop no leftover in mouth after use. Moreover, these films must have a low vulnerability to external conditions such as humidity and temperature [19].
1.3 Ideal Requirements
The optimal requirements for Mouth Dissolving Films (MDF) can be summarized as follows:
- MDF should be thin, flexible and stable for efficient manufacturing, packing and handling.
- The film should be portable , non tacky , and stay flat without rolling up.
- Suitable for mentally disabled patient.
- Should have good taste and comfortable texture.
- No need of water for administration.
- Short disintegration time.
- Low sensitivity to temperature and humidity.
- Offer the benefit of liquid medication in solid form.
- Have smooth and consistent surface.
- Cost effective and easy to create. [20-22]
1.4 Applications Of Mdf In Drug Delivery Systems
- Oro-mucosal drug application: Oral thin-film distribution via buccal, mucosal, and sublingual routes may eventually replace other delivery methods when treating conditions requiring quick drug absorption. This covers treating conditions relating to the central nervous system, pain, allergies, and sleep problems.[23].
- Topical Applications: Topical applications, such as wound care and other therapies, may benefit from the use of soluble films to deliver active chemicals like analgesics or antibacterial agents.
- Gastroprotective Delivery System: An inquiry is now being conducted on dissolvable films as a dosage form for compounds with varied molecular weights, including both water-soluble and poorly soluble substances. These films are designed to be retained in the gastrointestinal tract. The film has the potential to be beneficial in the treatment of gastrointestinal diseases because to its ability to be broken down by the pH levels or enzyme synthesis in the gastrointestinal tract (GIT).
Diagnostic Devices: Oral films can be used as diagnosis of disease as the film is incorporated with sensitizing agents which help to detect the disease.Also may be useful as a controlled release equipment for diagnostic purpose.[24].
2.1 Formulation Consideration:
The drug-loaded MDFs should have an area ranging between 1-20 cm2, allowing for the loading of up to a single dose of 30mg. Those excpients which are used to formulate rapid dissolving oral film should be referred as Generally Regarded As Safe (GRAS listed) so the usage shall be approved in oral thin films. Identifying formulation factors is crucial for defining the mechanical properties of the films.
Quantity Of Ingredients
- The drug (active pharmaceutical ingredient) concentration ranges from 5% to 30%.
- A water-soluble polymer accounts for 45% of the composition.
- Plasticizer concentration ranges from 0 to 20%.
- A saliva stimulating substance with a concentration of 2-6%.
- The surfactant quantity is adjusted as needed.
- The sweetening ingredient has a concentration range of 3-6.
- Flavors, colors, and fillers in quantities as required.
Rapid dissolution , taste masking , mouth feel and taste masking are some characteristics of MDF formulations. All additives used in MDF formulations must be categorised as Generally Recognized as Safe (GRAS) and allowed for use in oral medical dosage forms.
2.1.1 Drug Category
MDF technology offers numerous possibilities for delivering a variety of APIs. However, certain limitations exist, such as the difficulty of incorporating drugs with high doses and considerations regarding the size of the dosage form in films. Mouth-dissolving films can be formulated for various classes of drugs, including anti-asthmatics, antitussives, antihistaminics, antiulcer medications, expectorants, and NSAIDs, among others.
2.1.2 Film Forming Materials
As to enhance the desired mouthfeel, quick disintegration, and mechanical strength in MDFs, hydrophilic polymers may be work as film forming agent. The amount and kind of polymer used in formulations are key factors in determining how resistant the film is. Water-soluble MDFs stick to the mucosa of the buccal cavity and help medicine get into the bloodstream quickly. While there are many other polymers available for making films, gelatin, pullulan, and hypromellose are the most often utilized ones. Typically, the polymer should make up 45% weight percent of the dry film. [25-26].
Desirable characteristics of film forming agents:
- The product must not cause irritation or be harmful.
- The product must have hydrophilic characteristics.
- It is crucial to have exceptional abilities in forming films.
- Excellent spreadability and wettability.
- The polymer should be readily available and cost-effective.
- It is preferable to the product of low molecular weight.
- Polymer should possess a good shelf life period.
- The presence of taste and colour is not required.
- It should not result in the subsequent infections.
Adequate peel, shear, and tensile strengths are required.
TABLE: 1. Some examples of different polymers
|
Natural polymers
|
Synthetic polymers
|
|
Pullvan
|
HPMC
|
|
Starch
|
Sodium CMC
|
|
Sodium alginate
|
Ethyl cellulose
|
|
Gelatin
|
Polyvinyl alcohol
|
|
Pectin
|
Polyvinyl pyrolidone
|
|
Polymerized resin
|
Polyethylene oxide
|
2.1.3 Salivary Stimulants
Saliva stimulation is improved by these agents, hence accelerating the enzymatic degradation and dissolution of the oral biofilm.These substances enhance the secretion of saliva, which speeds up the decomposition of MDFs when get in contact with saliva.Tartaric acid , malic acid , ascorbic acid and citric acid are some examples.[27]
2.1.4 Plasticiser
Plasticiser is refers to a substance that is added to a material, typically a polymer to increase its durability , flexibility and workability. Typically, these material enhance the physio - mechanical characteristics are improved when plasticizers are employed in films.The quantity of material incorporate is specifically under the range of 0-21% w/w.Tween 80 , triethyl citrate , PEG- 400 and glycerol are some examples of plasticizers employed in the formulations.[28]
2.1.5 Coloring Agent
Pigments are used as colouring agents to imparts colour to the films. Transperancy and the existence of bubbles may be problematic during the formuation phase.In order to address these issues in Modified Drug Delivery , colouring agents are utilised. Titanium dioxide is the main pigment employed in MDFs and various other pharmaceutical formulations. Furthermore, there is a wide variety of colours to choose from, such as natural shades, FD and C colors , and custom Pantone matched tones.[29]
2.1.6 Sweetener
Certain medications may possess an intensely acrid flavour, rendering them unpalatable to ingest. In order to resolve this problem, sweeteners are used into oral films to impart a sweetening effect to the formulation. Some commonly utilized sweeteners are sodium saccharin , alitame , mannitol , apartame and neotame.[30]
2.1.7 Surfactant
Surfactants are essential in pharmaceutical formulations as they are functioning as solublising , dispersing and wetting agents. Surfactants facilitate the quick disintegration of the film, resulting in the fast release of the active component.Oral strips utilize many surfactants , with poloxamer407 being a significant surfactant.Sodium lauryl sulphate is utilize to dissolve , moisten and scatter material.[32]
2.1.8 Flavors
When it comes to therapeutic oral preparations, tastes play a vital role as they have a considerable impact on patients' preferences. The sales of products are greatly influenced by the assortment of flavors they offer. Formulations can incorporate both natural and synthetic flavouring agents. Various plants and their parts can be used as flavouring agents like flower , leaves and fruits, through the use of artificial flavour oils, oleoresins, and extracts. Typically comprising around 10% of the total weight, these flavors can be added to the mixture either individually or in combination. The list of ingredients includes menthol, other mint aromas such as peppermint, sweet mint, spearmint, and wintergreen, as well as cloves, cinnamon,sweets like chocolate or vanilla and for sour taste orange or lemon can be widely used.These ingredients are obtained from water-soluble extracts or essential oils.[33]
2.2 Manufacturing Methods
- Solvent casting is a technique used to create thin films or coatings by dissolving a material in a solvent and then allowing the solvent to evaporate, leaving behind a solid film.
- Semisolid casting refers to a manufacturing process in which a material is partially solid and partially liquid during the casting process.
- Hot melt extrusion is a process used to melt and shape materials.
- Extrusion of solid dispersion
- Rolling
2.2.1 Procedure for the prepration of mouth dissolving film
- Casting Technique of Solvent
Procedure which include the formulation of oral fine strips or coating of material by dissolving the material in a solvent and then cast it into a substrate , technique known as casting method.
By employing agitation, this technique facilitates the complete dissolution of hydrophilic polymer such as MCC or HPMC into purified water , which results a clear solution.Each medicine is individually dissolved in water and vigorously stirred to ensure complete solubility. Within the remaining excipients, there are sweeteners, preservatives, and flavorings that have the ability to dissolve in water when placed in a separate container. The polymer solution and excipient solution are combined and then subjected to sonication for a duration of 10 minutes. Combine the pharmaceutical solution with the combination mentioned before and agitate for an additional ten minutes to liberate any trapped air bubbles. Pour the resulting material to the moulds or can use of petri plate and standby it for a day either for air dry or put it in air dry oven for 24 hours at 30?.[34]
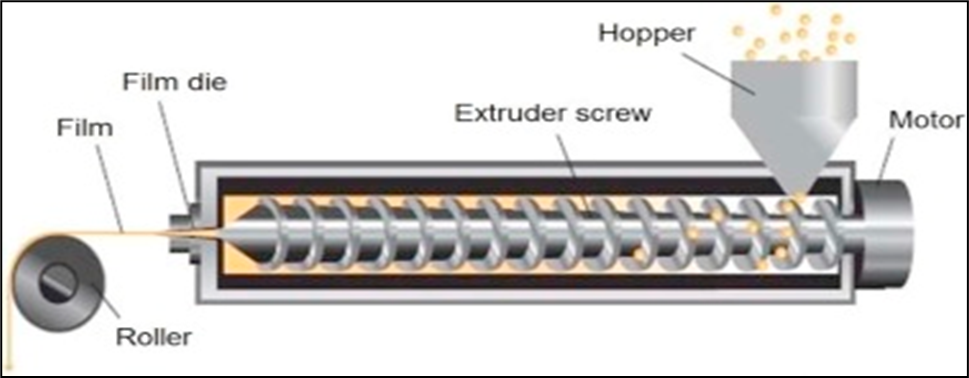
Figure: 1.2 Solvent casting film method used commercially (Image Courtesy: www.particlesciences.com)
(b). By Hot Melt Extrusion
This process shapes polymers by moulding. Both the polymer material and the medication molecules are heated significantly throughout this procedure. These high temperature cause the solid to melt so that it may be shaped and finally forms the film.This method is a solvent free one since it does not call for any solvent system unlike those of solvent casting. This approach cannot be used, though ,if either the polymer or medicament is heat sensitive.[35]
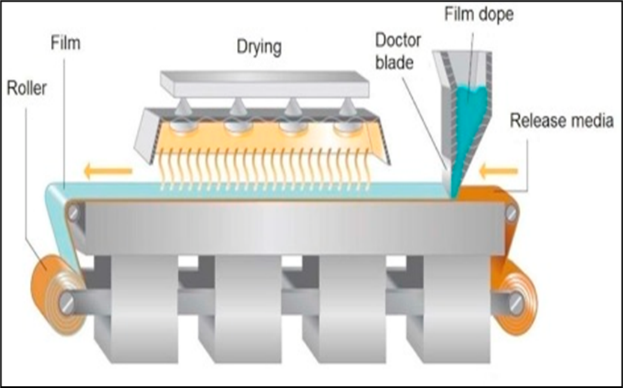
Figure: 1.3 Prepration of film by hot melt extrusion (Image Courtesy: www.particlesciences.com)
- By Solid Dispersion Method
The solid dispersion method is a technique used in pharmaceutical science to enhance the solubility or pharmacological activity of poorly hydrophilic materials.
The formulation procedure involves the collection of suitable active ingredient along with suitable solvent which is non reactive towards them , such as water soluble polymer in powdered form.Now , drugs should be incorporated with appropriate solvent till dissolve , then the mixture is introduced into a polyethylene glycol mixture at temperatures below 70ºC. The solid dispersions that are generated as a result are shaped into films using dies.[36]
- Casting Technique of Semi solid
The semi-solid casting method is a technique used in metal casting where the material being cast is in a partially solid state.
This technique involves the creation of a water-soluble polymeric film, which is subsequently combined to a solution of polymer which is not soluble in acid. Subsequently, a weighed quantity of plasticizer is now incorporated which results in the gel form , then prepare it into a required shape and thickness.Prescribed ratio of hydrophilic polymer to acid insoluble polymer is 4:1.[37]
By Rolling Method
Rolling method involves the use of machinery to cast the films. In this technique the prepared solution of sample containing drug and solvent (majorly water) is poured on the rollers of machine , then some heat applied to dry the film and further the cutting of strips in required dimension will take place. Majorly the solvent used is water or alcohol which can fry easily and ease to obtained the desired product.[38]
2.3 Evaluation Parameters:
2.3.1Thickness Test
The thickness of the oral film was evaluated by digital vernier calliper.One by one the film was measured from the five different angles.Standard deviation and average thickness of one and all formulation will be ascertained.
2.3.2 Weight variation
Average weight of the formulation will be determined by casually select the 3 of them. Cut them at 2×2 cm2 by each sample and weigh separately , then evaluate.[39]
2.3.3 Tack test
Tack is used to denote the tendency of of film to get stick to any paper or foil when pressed within contact. It may also used to evaluate the dryness level of film. [40].
2.3.4 Tensile strength
Tensile strength is explained as the utmost load each film formulation can withstand till breaking. Its SI unit is Pascal.The equation which express is that tensile strength is the ratio of force to area.[41].
2.3.5 Percent elongation
The measurement of the increase in length expressed as a percentage, and it is the sign of ductility of material. It may define as the the stretching or elongation of film when definite amount of stress is applied to the film.The ductility of polymers is determined by utilising a texture analyzer.Ductile material shows usually more than 5% of stretch and brittle have less than 5%.
2.3.6 Measurement of pH of surface
By putting the film in a petri dish, this test was assessed. After that, 2 ml of phosphate buffer were added to wet it, and it was left for 30 seconds. Following one minute of equilibration and contact between sample and the electrode of pH meter and the pH was measured. For each formulation, the mean of the three results was calculated.[42-43].
2.3.7 Content Uniformity
Various pharmacopoeias provide standardized test procedures to precisely determine the composition of a drug. Twenty samples undergo analytical methods.The results of assay performed is used to evaluate the active content in the formulation.It may also help to analyse that the concentration of active ingredient in different formulations of same batches are in accuracy or not .The content homogeneity is a measure used to assess the drug concentration in specific films.[44-45].
2.3.8 Disintegration time
To evaluate the disintegration time of the film , strip measuring of 2×2 cm2 was placed in a petri plate with 2 ml of phosphate buffer having pH of 6.8. Using a 10-second swirl, the medium was kept somewhat agitated. Noted was the amount of time needed for the film to completely dissolve. At the time when the strip begin to dissolve is noted as disintegration time. Triple testing was used for every measurement, and average results were given.
(a) Slide frame method
Film is taken and a single distilled water drop is poured on it, which is securely attached to slide frames placed on a Petri plate. The film's disintegration is observed to occur over a period of time. [46-47].
(b)Petri Dish Method
The film is immersed in 2 millilitres of distilled water within a Petri dish. The disintegration time of the film refers to the duration it takes for the film to completely dissolve. [48].
2.3.9 In vitro dissolution test
Film dissolution studies are carried out using standard dissolution apparatus. It works mainly by basket or paddle process.Majorly , the pH buffer of 6.8 is used to evaluate the samples and regulate the temperature ranges to 37 ± 0.5? and the speed of paddle or basket is adjusted at different RPMs.The resulting solution is then taken as sample and analyse using UV spectrophotometer. [49-50].
CONCLUSION
In recent times, pharmaceutical companies have widely adopted Mouth Dissolving Films,a viable and readily acceptable dosage form..Orally dissolving mouth films are a type of medicine delivery technology that rapidly show dissolution in the oral cavity with instance of seconds, without the need for water. The oral dissolving films include unique properties that make them a beneficial delivery form for patients who have difficulty swallowing pills and capsules, such as geriatric, paediatric, or dysphasic individuals. These qualities may include rapid dissolution and disintegration, preferential by patients ease to administer and the rapid onset of action.Moreover, this technology serves as a valuable instrument for pharmaceutical enterprises to enhance the longevity of existing goods and manage product life cycles.As a result Mouth Dissolving Films shows as an promising and beneficial dosage form for every kind and age group of consumer.Our study tries to compile and consolidate the existing knowledge of MDF Formulations.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT
I heartily present deepest appreciation and regards to Ms. Neha Sodiyal, “Assistant Professor”,Department of Pharmacy (SDBIT), Dehradun, for providing proper guidance for selection of the topic , synopsis preparation, research work and thesis submission.It is her constant and insightful suggestions which enabled me to overcome the obstacles in path. I an thankful to Dr. Shivanand Patil, Director, SDBIT Dehradun for giving me the guidance and cooperation. Further I am thankful to faculty members, classmates and teachers for their valuable time and support. Thanks to my respectable parents, my siblings and all my friends for everything they have done while making this project.
REFERENCES
- Mahato RI, Narang AS.Pharmaceutical Dosage Forms and Drug Delivery. Drug delivery systems2011;2: 217–34.
- Reddy PD, Swarnalatha D. Recent advances in novel drug delivery systems. Int J Pharm Technol Res 2010;3:2025–7.
- Rastogi S, Vaya N, Mishra B et al Osmotic pump: A novel concept in rate controlled oral drug delivery. East Pharm 1995;38:79–89.
- Bhushan SY, Sambhaji SP, Anant RP, Mahadik KR et al New drug delivery system for elderly. Indian Drugs 2003;37:312–18.
- Bradoo R, Shahani S, Poojary S, Deewan B, Sudarshan S et al Fast dissolving drug delivery systems. JAMA India2011;4:27–31.
- Wadhwani A, Prabhu NB, Nandkarni MA, Amin PD et al Consumer friendly mucolytic formulations. Indian J Pharm Sci 2004;7:506–7.
- Akhtar N. Vesicles: a recently developed Novel carrier for Enhanced Topical Drug delivery. Curr Drug Deliv 2014;11(1):87–97.
- Heer D., Aggarwal G., Kumar S.L.H. et al Recent trends of fast dissolving drug delivery system - an overview of formulation technology. Pharmacophore2013; 4(1):1–9.
- Mahapatra A.K., Murthy P.N., Swadeep B., Swain R.P. et al Self-emulsifying drug delivery systems (SEDDS): an update from formulation development to therapeutic strategies. Int J PharmTech Res 2014;6(2):546–568.
- Slavkova M, Breitkreutz J. Orodispersible drug formulations for children and elderly. Eur J Pharm Sci 2015;75:2–9.
- 11.Hoffmann EM, Breitenbach A, Breitkreutz J. et al Advances in orodispersible films for drug delivery. Expert Opin Drug Deliv 2011;8:299–316.
- Preis M, Woertz C, Kleinebudde P, Breitkreutz J. et al Oromucosal film preparations: classification and characterization methods . Expert Opin Drug Deliv 2013;10:1303–17.
- Borges AF, Silva C, Coelho JF, Simões S. et al Oral films: Current status and future perspectives: I - Galenical development and quality attributes. J Control Release 2015;206:1–19.
- Brniak W, Ma?lak E, Jachowicz R. et al Orodispersible films and tablets with prednisolone microparticles. Eur J Pharm Sci 2015;75:81–90.
- Visser JC, Dohmen WM, Hinrichs WL, et al.Quality by design approach for optimizing the formulation and physical properties of extemporaneously prepared orodispersible films. Int J Pharm 2015a;485:70–6.
- Visser JC, Woerdenbag HJ, Crediet S, et al. Orodispersible films in individualized pharmacotherapy: the development of a formulation for pharmacy preparations. Int J Pharm 2015b;478:155–63.
- Chemical Market Reporter Fuisz sign deal for drug delivery. Chem Mark Report 1998;253(3):17.
- http://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/1941 80.php. 8. Patel R, P.
- Dixit RP, Puthli SP.“Oral strip technology: Overview and future potential”. Journal of Controlled Release. 139: 94– 97.Available at (http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jconrel.2009.06.01 4).
- Hoffmann, E.M., Breitenbach, A., Breitkreutz.et al Advances In Orodispersible Films for Drug Delivery.Expet.Opin. Drug Delivery 2011;8:300.
- Prasanna. Desu, B.Brahmaiah, A.Nagalakshmi, K.Neelima, Sreekanth Nama, Chandu Baburao. et al An Overview on Rapid Dissolving Films. Asian J. Pharm. Res 2013;3(1): 15-23.
- Shinde R B, Phoke S V, Sarda R R1, Chaudhari P M, P V Kasture. et al Fast Dissolving Film: Current Status And Approaches. Inventi Impact: NDDS 2013;3(1): 3-11.
- Brown D.Orally disintegrating tablets- taste over speed. Drug Deliv Technol 2003;3:58- 61.
- Zerbe H, Guo J.Water soluble films for oral administration with instant wettability 1997; US Patent 5948430, Sep 7.
- Aggarwal J., Singh G., Saini S., Rana A. C et al .Fast Dissolving Films: A Novel Approach To Oral Drug Delivery. Int. Res. J. Of Pharm 2011; 2 (12): 69-74.
- Dixit RP, Puthli SP.Oral strip technology: Overview and future potential. J Control Release 2009;139:94–107.
- Bhyan B, Jangra S, Kaur M, Singh H. et al Review Article Orally fast dissolving films: Innovations in formulation and technology 2015;9(2):50–7.
- Pattewar SV, Kasture SB, Pande VV, Sharma SK. et al A New Self Microemulsifying Mouth Dissolving Film 2016;50(3):191–9.
- Patil P, Shrivastava SK. Fast Dissolving Oral Films : An Innovative Drug Delivery System 2014;3(7):2088–93.
- Bhyan B, Jangra S, Kaur M, Singh H. et al Review Article Orally fast dissolving films: Innovations in formulation and technology 2015;9(2):50–7.
- Thakur N, Bansal M, Sharma N, Yadav G and Khare P. et al “A Novel Approach of Fast Dissolving Films and Their Patients”. Advances in Biological Research 2013;7 (2): 50-58.
- Maheswari K.M.“Development and Evaluation of Mouth Dissolving Films of Amlodipine Besylate for Enhanced Therapeutic Efficacy; Journal of pharmaceutics” 2014.
- Rathi V.“A Brief Review on Oral Film Technology”, International Journal of Research in Ayurveda & Pharmacy 2011; 2(4): 1138- 1147.
- Cilurzo F, Cupone IE, Minghetti P, Buratti S, Selmin F, Gennari CGM, et al Nicotine Fast Dissolving Films Made of Maltodextrins : A Feasibility Study 2010;11(4).
- Rajat P, Ravi S, Pravin S, Darwhekar GN.et al A Review on Mouth Dissolving Film 2019;9(6):206–10
- Upendra CG, Sunil S K, Yuvraj GJ, Praveen DC. et al Investigation of different polymers, plasticizers and superdisintegrating agents alone and in combination for use in the formulation of fast dissolving oral films, Int J Pharm Tech Res 2013;5: 1465-1472.
- Devaraj H, Venkatachalam S, Radhakrishnan A. et al .Research Article A Review on Formulation of Oral Dissolving Film 2018;10(4):151–9.
- Bilal Q, Unhale SS. A review on mouth dissolving films 2020.
- Hariharan M, Bogue A.Orally dissolving film strips (ODFS): the Final evolution of orAlly dissolving dosage forms. Drug Deliv Technol 2009;9(2):24-9.
- Sakellariou P, Rowe R, White E. et al.An evaluation of the interaction And plasticizing efficiency of the polyethylene glycols in ethyl Cellulose and hydroxypropyl methylcellulose films usIng the Torsional braid pendulum. Intj Pharm 1986;31(1-2):55-64.
- Patil PC, Shrivastava SK, Vaidehi S, Ashwini P.et al .Oral Fast Dissolving drug delivery system: A modern approach for patient Compliance. Int J Drug Regulatory Affairs 2014; 2(2):49-60.
- Rekha MR, Sharma CP.Pullulan as a promising biomaterial for Biomedical applications: a perspective. Trends biomaterartif Organs 2007;20(2):116-21.
- U.S. Congress, Office of Technology Assessment, Biopolymers: Making Materials Nature’s Way-Back Ground Paper, OTA-BP-E-102 (Washington, DC: U.S. Government Printing Office, 1993).
- Saini S, Rana AC, Gupta S. et al .Optimization of formulation of fast Dissolving films made ofpullulan polymer. Int J Pharm Sci Rev Res 2011;9(1):127-31.
- laudia, A. R. B.,Bello-Perez, L. A.Gacia, M. A.; Martino, M. N.; Solorza-Feria, J.; Zaritzky, N. E. et al.Carbohyd. Polym 2005;60: 235-244.
- Laohakunjit N, Noomhorm A.Effect of plasticizers on mechanical And barrier properties of rice starch film. Starch/Staerke 2004;56:348–356.
- Wu Y, Weller C, Hamouz F, Cuppett S, Schnepf M. et al Moisture Loss And Lipid Oxidation for Precooked Ground-Beef Patties Packaged in Edible Starch-Alginate -Based Composite Films. Journal of Food Science 2001;66(3):486-493.
- El-Setouhydel-MalAk N.Formulation of a Novel Tianeptine Sodium Orodispersible Film. AAPS pharmscitech 2011; 11(3):1018-1025.
- Kunte S, Tandale P.Fast dissolving strips: A novel approach for The delivery of verapamil. J Pharm Bio Sci 2010;2(4):325-328.
- Ramani C.C., Puranik P.K., Dorl A.K.et al.Study of diabetic acid as Matrix forming material. Int J Pharm 1996;137:11-19.


 Neha sodiyal
Neha sodiyal


 10.5281/zenodo.14547851
10.5281/zenodo.14547851