Abstract
Barleria prionitis Linn. is commonly known as Vajradanti and belongs to family Acanthaceae. This Plant is distributed and found in tropical Asia. This plant carries different medicinal properties such as used in cataract, fever, in cough treatment and to relieve toothache. The aim of this study was to screening different phytochemicals from plant Barleria prionitis Linn and evaluate it. BP leaves extract with petroleum ether, ethyl acetate, methanol and for TLC solvent system used as (Hexane: Chloroform: Acetic Acid: Methanol) and (Hexane: Chloroform: Acetic Acid) with retention coefficient 0.52, 0.66, 0.83, 0.46, 0.76, 0.42. The quantitative Phytochemical tests include protein, glycosides, alkaloids, tannin, Total phenoloic and flavonoid content. The staderdized parameters found after evaluation was Total ash- 6.2 %, Acid insoluble ash 0.90%, Water soluble ash 0.90% and LOD 10%.
Keywords
Phytochemicals screening, TLC, Quantative Phytochemicla test, total Phenolic content, flavonoid content, ash value, acid insoluble ash
Introduction
Barleria prionitis Linn (Acanthaceae) is widely distributed throughout Africa, India, Sri Lanka and tropical Asia. It is commonly known as Vajradanti, the juice of the leaf is used in cataract and fever. The dried bark is used in cough treatment and the leaves chewed to relieve toothache. The paste of the root is applied to disperse boils and glandular swellings. It exhibits several medicinal properties. The leave sare chewed to relieve toothache. Juice of the leaves is used in ulcer and fever. Paste of the roots is applied to disperse boils and glandular swellings. Leaves are also used by some tribal communities for the treatment of piles and to control irritation. Plant is also used in stiffness of limbs, enlargement of scrotum and sciatica. In recent years multiple drug resistance has developed due to indiscriminate use of existing antimicrobial drugs in the treatment of infectious diseases .Barleria prionitis, a perennial, acanthaceous, barbed, bushy medicinal plant, including in Barleria genus containing 300 species is famous for its medicinal value from ancient time.
COLLECTION, IDENTIFICATION & AUTHENTICATION
On the basis of literature survey leaves of Barleria ptionitis Linn. (Acanthaceae) had been selected for present project. Leaves of Barleria prionitis Linn. were collected from from local market of Nanded and identified on the basis of its morphological features with the help of taxonomist. Herbarium of the plant specimen has been given for authentication to Dr. S. S. Bodke (Associate Professor & Head, Department of Botany & Horticulture, Yeshwant College, Nanded) which has been submitted to Nanded Pharmacy College, Nanded with specimen no: H-04/NPC/Pharmacology/2018-19/04 and authenticated as of Barleria ptionitis Linn. Leaves (family: Acanthaceae) Collection, authentication, Identification, processing and storage has been done according to standard procedure for the standard procedure for the plant material (The Indian Pharmacopoeia, 2007).
PROCESSING OF CRUDE DRUG
The collected dried leaves of plant was segregated and pulverized by mechanical grinder and the powder was passed through appropriate sieve and subjected to extraction. Powdered drug is stored in air tight container for further use.
PHARMACOGNOSTIC EVALUATION OF PLANT MATERIAL

Morphological Evaluation of Leaf
Table I : Morphological chacterictics of Barleria prionitis Linn. Leaves

The leaf of Barleia prionitis is dorsiventral, variable in size, 6-9.5cm long, and 2.5-3.5cm wide, spine of leaf mature stem cylindrical with longitudinally arranged, grayish to light brown.
B. Microscopic Characteristics of Leaf

Figure 02: T. S. of Baleria prionitis Linn. leaves
The leaf of Barleria prionitis is dorsiventral, variable in size, 6-9.5 cm long, 2.5 - 3.5 cm wide, spines on leaf mature stem cylindrical with longitudinally arranged, greyish to light brown.


Determination of Total Ash Content:
2 gm of the air dried crude drug weighed in a tarred silica dish and incinerated at a temperature not exceeding 4500C until free from carbon. After incineration the material was cooled and weighed. The percentage of ash value was calculated with reference to air dried drug.
Determination of Acid Insoluble Ash Value:
2 gm of the air dried crude drug weighed in a tarred silica dish and incinerated at a temperature not exceeding 4500C until free from carbon. After incineration the material was cooled and boiled with 25 ml of 2 M hydrochloric acid for 5 minutes. The insoluble matter was collected in a Gooch crucible or on ash less filter paper. The collected insoluble matter was washed with hot water, ignited and cooled in a desiccators and weighed. The percentage of acid-insoluble ash value was calculated with reference to air dried drug.
Determination of Water Soluble Ash Value:
2 gm of the air dried crude drug weighed in a tarred silica dish and incinerated at a temperature not exceeding 4500C until free from carbon. After incineration the material was cooled and boiled with 25 ml of water for 5 minutes. The insoluble matter was collected in a Gooch crucible or on ash less filter paper. The collected insoluble matter was washed with hot water, ignited and cooled in desiccators and weighed. The percentage of water soluble and water-insoluble ash value was calculated with reference to air dried drug.
Determination of Loss on Drying (LOD):
Glass-stopper shallow weighing bottle was weighed & dried under the same conditions to be employed in the determination; 2 gm of sample was transferred to the bottle. It was covered properly & again weighed. The sample was distributed as evenly as practicable by gentle sidewise shaking to a depth not exceeding 10mm & the loaded bottle was placed in the oven. The stopper was removed and it was also leaved in the chamber. The sample was dried to constant weight. After drying was completed, the bottle with sample was allowed to cool at room temperature in desiccators before weighing. The percentage loss on drying was calculated with reference to the air-dried drug.
EXTRACTION OF PLANT MATERIAL
Selection of Solvent: As per literature review & the nature of phytochemicals present in drug as well as on the basis of their polarity, the solvents were selected for the extraction of the leaves of Barleria prionitis Linn. Like Petroleum-ether (60-800C), ethyl acetate, methanol.
Selection of Extraction method:
According to the literature survey & nature of phytochemicals present in drug, the extraction method was selected. The extraction method selected for extraction from the leaves of Barleria prionitis Linn. Was continuous hot extraction method using soxhlet apparatus. The method was selected for its efficiency. Factors which are considered for selection of extraction method were temperature, time, economy, completion of extraction etc. Out of these temperature is the rate-limiting factor for the extraction method. Constant temperature would increase the efficiency of the extraction by increasing the infusibility of the solvent.
Material used:
Soxhlet apparatus, heating mental, powdered drug, Petroleum-ether (60-800C), ethyl acetate, methanol.

Figure 05: Extraction of Barleria prionitis Linn leaves
Procedure:
Extraction of Barleria prionitis Linn.leaves was carried out by continuous hot extraction method in Soxhlet extractor.

Figure 06: Scheme of Barleria prionitis Linn. Leaves extraction
PHYTOCHEMICAL SCREENING OF PLANT EXTRACTS
Phytochemical Qualitative analysis
Qualitative chemical tests were carried out for all four extracts to identify the presence of various chemical constituents and presented them in table 02.
Table 02 : Phytochemical analysis of Barleria prionitis leaves extracts

In above table + indicates presence & - indicates absence of the phytochemical constituents.
Development of TLC fingerprint:
Development of TLC fingerprints profile of the extracts:
All the extracts of selected plant material were subjected to TLC studies using various solvent systems to determine the presence of various phytoconstituents. The Rf values of observed compounds were noted for all extracts. The characteristic fingerprint of the various chemical constituents in each extract under UV light and after derivatization with suitable reagents was recorded. Preliminary phytochemical screening revealed the presence of carbohydrate, proteins flavonoids, alkaloids, fixed oils, steroid & saponins. Compounds of varying polarity in the extracts well separated using various solvent systems on TLC. Rf value of the separated compounds were recorded and given in Table No. 5 and some images of TLC are given in Fig no.7 (The Indian Pharmacopoeia, 2006)
Total Polyphenolic Content
Procedure: 4 ml of Folin Ciocalteu reagent was mixed with 1 ml of extract solution, this solution mixture was kept on standing for 5 min & then 5 ml of sodium carbonate was added to it. The absorbance of reaction mixture was measured against blank (without extract) at 765 nm using UV-Visible spectrophotometer. Gallic acid was used as standard for determination of total polyphenol content of extract. The calibration curve was drawn using various concentrations of gallic acid (50, 100, 150, 200, 250 µg/ml). The total polyphenol content was expressed as gallic acid equivalent in mg/g of the extract & was calculated by using following equation obtained from standard gallic acid graph ( r2 = 0.9918) (Swamyet al, 2012). Results are given in table.
Absorbance (y) = mx + c
Total Flavonoid Content
Procedure: 1 ml of extract solution was mixed with 4 ml of distilled water & 0.3 ml of NaNo2. After 5 min 0.3 ml of AlCl3& 2 ml of NaOH was added, at last total volume was made up to 10 ml with distilled water. The solution was mixed well & absorbance of the solution mixture was measured at 510 nm against prepared blank (without extract). Rutin was used as standard for determination of total flavonoid content of extracts. The calibration curve was drawn using various concentrations of rutin (100, 200, 300, 400, 500 µg/ml). The total flavonoid content was expressed as rutin equivalent in mg/g of the extract & was calculated by using following equation obtained from standard rutin graph (r2 = 0.9964) (Ekramulhaqueet al, 2011).Results are given in table.
Absorbance (y) = mx + c
Pharmacognostic Evaluation
Physicochemical Parameters:
The powdered drug was evaluated for its physicochemical parameters like total ash values, acid insoluble ash, water soluble ash &loss on drying. All the results are tabulated in following table 03.
Table 03: Physicochemical parameters of Barleria prionitis; Linn. Leaves

EXTRACTION OF BARLERIA PRIONITIS; LEAVES
Table 04: Physical properties of Barleria prionitis; Linn.Leaves extracts

PHYTOCHEMICAL SCREENING OF PLANT EXTRACTS
TLC Finger printing


Total Polyphenolic content
Table 06: Calibration Curve of Gallic acid



Figure 08 : Calibration Curve

Table 07 : Total Polyphenolic content of Barleria prionitis; Linn.leaves extracts

Fig no 09 : Total Phenolic content in diffrent solvents
After subjecting extracts which showed positive tests for polyphenols to the total polyphenolic content, the Petroleum ether showed (60-800C) 39.5 mg/g & ethyl acetate extract of BPL showed maximum content of polyphenols i.e. 63.75 of GAE. Methanolicic extracts contains 59 mg/g of polyphenols.
Total Flavonoid content

Table 08 : Calibration Curve of Rutin


Figure 10 : Calibration Curve Rutin
Table 09 : Total Flavonoid content of Barleria prionitis; Linn. Leaves extract
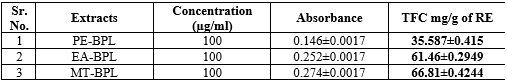

Fig no 11 : Total Flavonoid content in diffrent solvents
RESULT AND DISCUSSION
The BP leaves powder crude drug was evaluated thoroughly and standardization parameters found that total ash 6.2%, acid insoluble ash 0.90 % and LOD 10%. Leaves extract performed in petroleum ether, Ethyl acetate and Methanol. The respective extract obtained from different solvents, where analyzed by photochemical screening test and result was found to be presence of photochemical i.e., alkaloids, flavonoid and glycosides. found. The TLC fingerprinting shows different chromatogram using different solvent systems which have effective retention coefficient 0.52, 0.66, 0.83, 0.46, 0.76, 0.42. The total phenolic content shows absorbance on the UV spectrophotometer 39.5± 0.4330, 63.75± 0.4330, 59± 0.4330 using Gallic acid as standard and total flavonoid content 35.587±0.415, 61.46±0.2949, 66.81±0.4244 Rutin as standard.
REFERENCE
- Egon S: Thin layer chromatography. Springer International Edition, Heideiberg, 2nd edition 2004.
- H. Gerhard Vogel: Drug discovery & evaluation. Pharmacological assays, II edition 2002.
- Barar F. S. K : Essentials of Pharmacotherapeutics. S. Chand and Company Ltd, 2000.
- K. R. Khandelwal: Practical Pharmacognosy. Nirali Prakashan, Twentieth Edition2010.
- Chavan C. B , Shinde U. V , Hogade M, Bhinge S: Screening of in-vitro antibacterial assay of Barleria prionitis Linn. J, Herbal Med Toxicol (2010), 197-200.
- Khare CP: Indian Medicinal Plants: An Illustrated Dictionary, Springer Science 1st ed. 2007.
- Aneja KR, Joshi, Sharma C: Potency of Barleria Prionitis L. bark extracts against oral diseases causing strains of bacteria and fungi of clinical origin, New York Science Journal (2010),3: 5-12.
- Chetan C, Suraj M, Maheshwari C, Arhuland A, Priyanka P: Screening of antioxidant activity and phenolic content of whole plant of Barleria prionitis Linn, Int J. Research Ayurveda pharm (2011), 2: 1313-1319.
- Gangopadhyay A, Manalkar J, Ghosh A, Pramanic G, Karmakar Sujit: Comparative antibacterial study of Barleria prionitis Linn. Leaf extracts, International journal of pharmaceutical and biological archives ( 2012),3: 2391-93.
- Sawarkar HA, Kashyap PP, Panday AK, Singh MK, Kaur CD: Antimicrobial and cytotoxic activities of Barleria prionitis and Barleria grandiflora: a comparative study, Bangladesh Journal of pharmacology(2016), 11: 802-809.


 Shrinivas Sarje *
Shrinivas Sarje *






















 10.5281/zenodo.13972678
10.5281/zenodo.13972678