Herbal tooth powder Nature Secret is a natural alternative to commercial toothpastes and is made from a combination of organic herbs and minerals. This powder is formulated to promote oral health by preventing and combating common oral problems such as plaque, bad breath, and tooth decay. The herbal ingredients in Nature Secret work to strengthen the teeth and gums, reduce inflammation, and improve overall oral hygiene. Some of the key ingredients in this tooth powder include neem, clove and turmeric, which have been used for centuries for their powerful antibacterial, antifungal, and anti-inflammatory properties garlic can effectively clear away infections and restore the teeth and gums to their optimal health. By using herbal tooth powder Nature Secret, individuals can achieve optimal oral health without exposing themselves to harmful chemicals commonly found in commercial toothpaste
Toothpowder, Anti-Microbial activity, Ash Value
Taking care of your hygiene is crucial to look good, smell nice, and feel confident. Herbal tooth powders, made from various colorful ingredients, are easily accessible in a wide range. Many studies on factory tools in medicine lack information about what active ingredients they contain and how much. These tools can come in either crystal-like or non-crystal forms. They are seen as the oldest and simplest way to take medicine. 1Toothpaste helps keep your mouth clean and healthy. It works by scrubbing away plaque and food particles from your teeth, preventing problems like cavities, gum disease, and stained teeth. More and more people are realizing the benefits of herbal toothpaste. However, because herbal products can vary in their ingredients and quality, it's important to regulate and ensure they are pure. Herbal toothpaste comes in a variety of options with different natural ingredients. Modern trends focusing on these aspects help standardize products like sauces and their formulations. People trust herbal-based products, such as toothpowders, because they are considered safe, effective, and less harmful 2. The calcium and trace minerals help to restore dental enamel, while the herbs have antibacterial properties and encourage gum blood flow. For its superior quality and longer shelf life, herbal tooth powder is well regarded. The use of powdered substances such as charcoal, brick, salt for cleaning teeth has been historically widespread in India, particularly in rural areas 3 .Plaque is yellowish -white sticky film forms on teeth. When bacteria in the mouth mix with sugary or starchy foods. Tooth brushing and flossing get rid of plaque. If the plaque is not removed, it hardens into tartar. Plaque can lead to cavities, gingivitis and tooth loss. Regular dental checkups remove plaque and protect teeth. The food adheres to the teeth and action of bacteria on the food particles leads to the formation of plaque. Abrasives should clean the teeth but should not damage the enamel or gum4. These are mostly formulated in powder form. Tooth decay is dissolution or erosion of enamel. The food and carbohydrate residue in the mouth undergoes fermentation by bacteria or enzymes, producing lactic acid. The enamel dissolves in this lactic acid and leads to tooth decay.5 Streptococcus mutants are considered as the main species involved in the development of dental caries.6
ANATOMY OF A TOOTH
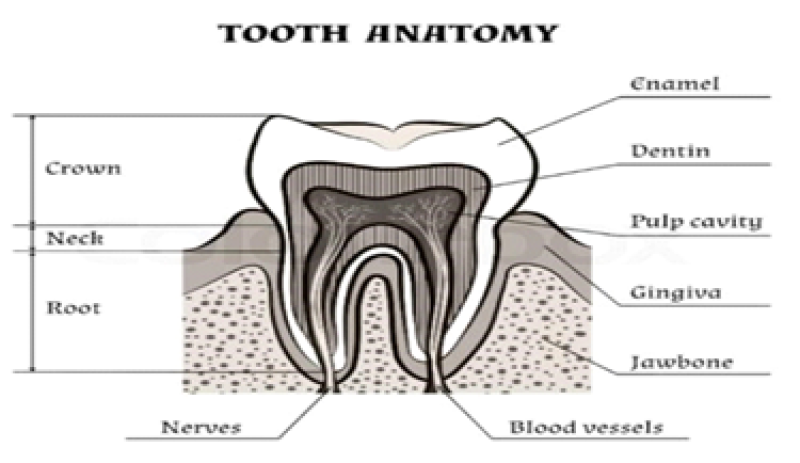
Fig No. 1 Tooth Anatomy
ENAMEL
The tough, shiny, white outer surface of the tooth.
DENTIN
The hard but porous tissue located under both the enamel and cementum of the tooth.
PULP:
The soft center of the tooth and contain blood vessels & nerves.
CROWN:-
The visible part of a tooth.
GUMS:
The soft tissue that surrounds the base of the tooth.
ROOT:-
The anchor of a tooth that extends into jawbone.
CEMENTUM:-
A layer of tough ,yellowish, bone-like tissue that covers the root of the tooth
- Characteristics of Toothpowder
- It should be finely powdered.
- It should have cleansing action.
- Abrasiveness of tooth powder help in remove of surface stains
- It should possess good flavor
- Helps in refreshing teeth
- It provides healthier gums
- It provides polishing effect
- It shows binder property especially in toothpaste
- It provides surfactant activity.
- It shows humectant activity
- It provides foaming effect.7
- Types of Toothpowders

Fig No 2 Types of Tooth Powders
-
- Whitening tooth powder
- Reducing mouth irritation
- Healing gums
- Improving breath
- Polishing teeth
- Making teeth whiter Non-toxic
- Non-irritating effects that last a long time
- Keeping the mouth fresh and clean
- No teeth stains
- Affordability and accessibility
Natural /Organic toothpowder:
-
- Natural tooth powder often contains elements like sea salt, which is an abrasive, natural substances, and some essential oils like peppermint, eucalyptus, and wintergreen.
- Natural toothpaste can also be considered a type of toothpowder, made with natural ingredients.
- Homemade herbal tooth powder can be advantageous as it may be less expensive and allows the maker to know exactly what components are being used.
3. Herbal tooth powder
- Herbal tooth powder is also beneficial for sore or bleeding gums. Ingredients in herbal tooth powder can vary, with white clay, powdered chalk, and baking soda being commonly used.
4. Homemade toothpowder
- These powders can be made at home.
- Homemade herbal tooth powders can be beneficial because they may cost less, and ingredients are free from chemicals produces good effect.
- It involves chewing sticks made out of young woody stem or root pieces.
- It can be easily formulated by using organic neem powder, baking soda, Sea salt, Clove powder or fennel seed powder are weighed and mixed well and applied.8
Benefit of Natural Toothpowder:
Using tooth powder regularly has several benefits, not only for a beautiful smile but also for overall health. The abrasive agents under the applied force scrap off the debris whereas the surfactant helps to dislodge the debris or plaque. In addition, powder contains sweeteners and flavoring agents.9 Inadequate oral hygiene can lead to gum disease and cavities, as well as increasing the risk of more severe problems like heart disease and Alzheimer's disease.

Fig No 3 Healthy teeth
HERBS USED IN FORMULATION
- Neem powder

Fig No. 4 Neem Powder
Synonyms:
Neem Tree, Nimba , Margosa ,Nim tree.
Biological Source :
It consist of dried powder of the leaves the plant Azadirachta Indica.
Family :
Meliaceae.
Plant part used :
Leaves
Chemical constituent:
Nimbin, Nimbidinin, Nimbandiol .
Uses:
- Neem is the Anti-Inflammetry, Antiseptic and highly beneficial.
- This natural neem toothbrush combats teeth and gum diseases, prevents Cavity ,and significantly improves oral health.
- Neem bark is also used in a number of toothpaste and toothpowder and is helping in curing problems related to gingivitis.
- Trikuta powder
Trikatu is the Sanskrit name in which tri means three and katu mean pungent or a herb that accommodates three spices, which are - long pepper (pippali), black papper (kali mirch), dried ginger (sondh). These herbs work in collaboration to stimulate digestive burning. They are categories as demolishing fat, cleansing abdominal glands and dullness of the appetite & indigestion. In Ayurveda trikatu extract used for improving the digestive system. It has antiemetic, carminative, anti-viral, chemo-protective, anti-inflammatory properties.
A. Long pepper (Pippali)

Fig No 5 Long Pepper
Synonyms:
Catkins (big), Pippali large.
Biological Source:
This consists of dried fruiting spikes of climbing vine called as piper Longum.
Family:
Piperaceae
Plant part used:
Fruits
Chemical constituents:
Piperin, Volatile oil
Uses:
Long pepper widely used in ayurvedic and unanin medicines, Specially in disease of
URT.
Roots are used for bronchitis, Stomach-ache, Disease of splan and tumours.
B. Black Pepper (Kali Mirch)

Fig No. 6 Black pepper
Synonyms:
Pepper, piper Nigrum, Maricha.
Biological Source:
Pepper is the dried unripe fruit of perennial climbing vine piper nigrum linn.
Family:
Piperaceae
Plant part used:
Fruits
Chemical constituents:
Piperine, starch piperidine, l-phellandrene, caryophylling.
Uses:
- Aromatic, stimulant, stomachin, carminative, condiment, stimulates the taste buds with gastric juice.
- Black pepper as an ingredient in recipes to add flavour and spice to meats,fish vegetables, salad, dressings, soups, stir-fries, pasta, and more.
- High in antioxidants.
- May improve blood sugar control.
C. Dried Ginger (Sunth)

Fig No. 7 Dried Ginger
Synonyms:
Zingiber, Zingiberis, Sunthi.
Biological Source:
Ginger consist of whole or cut, dried scrapped or unscrapped rhizomes of zingiber officinale.
Family:
Zingiberaceae.
Plant part used:
Rhizomes.
Chemical constituents:
Volatile oil, Zingiberene, Curcumene, Resin, Gingerol ,Shogaals, Giggediols.
Uses:
- Aromatic carminative, flavouring agent, motion-in treating sickness.
- It is an effective cure for indigestion, sore throat, cold and cough.
- Ginger has healing properties that boost blood flow, cleanse the bowels and kidneys, eliminate toxins, and nourish the skin
- Babul

Fig No.8 Babul
Synonyms:
Babul, Baboul, Vachellia nilotica.
Biological Source:
Vachellia nilotica, more commonly known as Acacia nilotica, and by the vernacular names of gum Arabic tree, babul, thorn mimosa.
Family:
Fabaceae
Plant part used:
Bark
Chemical constituents:
Methionine, lysine, lupenone, lupeol, Niloticane.
Uses:
- Consuming Babool gum powder along with once a day helps in relieving joint pain due to its analgesic and anti-inflammatory properties.
- Applying a paste of Babool leaf powder and coconut oil helps manage oral problems such as plaque formation and gingivitis due to its antibacterial properties.
- TURMERIC

Fig No.9 Turmeric
Synonyms:
Haldi, turmeric, curcuma, curcuma domestica.
Biological Source:
It consists of dried powder of the plant curcuma longa.
Family:
Zingiberaceae.
Plant part used:
Rhizomes
Chemical constituents:
Curcumin, cureuminoids, Cymene, Tumeron, Isdemethoxy Curcumin, Demethoxy curcumin, Dialy, Heptanoids.
Uses:
- Teeth whitening and reduced risk of gum pain and inflammation.10
- It delays the signs of aging like wrinkles and also possesses other properties like antibacterial, antiseptic, and anti-inflammatory.
- It is the best source of blood purifier. It is effective in treatment of acne due to its antiseptics and antibacterial properties that fight pimples and breakouts to provide your skin.
- It reduced risk of gum disease.
- TULSI

Fig No 10 Tulsi
Synonyms:
Tulsi, Holy basil, Padina pavonica.
Biological Source:
It consists of dried powder of the leaves of the plant Ocimumsantum Linn.
Family:
Lamiaceae
Plant part used:
Leaves
Chemical constituents:
Eugenol, Tannin, Vitamin C, Tartaric acid, Volatile oil, Carvacrol, Fixed oil, Alkaloids.
Uses:
- It natural anti-inflammatory and anti-bacteria properties help curb the growth of bacteria in the mouth, further preventing infection.11
- It can also be used by itself to help with mouth ulcers.
- Tulsi helps to reduce inflammation and may be useful in easing stress and lowering blood pressure.
- CAMPHOR

Fig No 11 CAMPHOR
Synonyms:
Turpentine, Rose oil, camphor, resin, menthol.
Biological Source:
Camphor is a solid keton, obtained from the volatile oil of Cinnamomum camphora.
Family:
Lauraceae
Plant part used:
Wood
Chemical constituents:
D-camphor(51.3%), 1,8-cineole, linalool, terpineol.
Uses:
- It is used in many rub-on products to reduce pain related to cold sores, insect stings and bites, minor burns, and haemorrhoids.
- Camphor has a wide variety of topical uses due to its antibacterial, antifungal, and anti-inflammatory properties.
- It can be used to treat skin condition, improve respiratory function, and relieve pain
- CLOVE BUDS:

Fig No 12 clove buds
Synonyms:
Clove tree, Spice tree, Syzygium, Genus syzygium.
Biological Source:
Clove buds is obtained from the dried flower bud of Eugenia caryophyllus.
Family:
Myrtaceae
Plant part used:
Flower buds
Chemical constituents:
Eugenol (76.8%), Caryophyllene, Acetyleugenol, Methyl eugenol, eugenyl acetate (12%).
Uses:
- Clove oil contains the active ingredient eugenol, which is a natural anesthetic.
- Clove oil has been used for easing digestive upset, relieving pain, and helping with respiratory condition.
- It helps numb and reduce pain to ease a toothache.
- Eugenol also has natural anti-inflammatory properties. It may reduce swelling and irritation in the affected area.12
- SENDHA NAMAK

Fig No 13 SENDHA NAMAK
Synonyms:
Halite, Saindhava lavana, Rock salt
Biological Source:
Sendha namak, a type of salt, is formed when salt water from a sea or lake evaporates and leaves behind colourful crystals of sodium chloride.
Chemical constituents:
Sodium chloride, Zinc, iron, Potassium, Magnesium, Calcium.
Uses:
- Rock salt improves digestion and is a natural way to relieve stomach pain.
- It also used to cure stomach infection and aids in deforming as well.
- It helps stabilise blood pressure by maintaining a balance of high and low blood pressure.
- Rock salt provides the entire essential and greatly improves the body immune system.
- Garlic(Allium sativum)

Fig No. 14 GARLIC (Allium Sativum)
Synonyms-
Seasoning, Flavorer, Seasoner, Allium Sativum, Garlic clove.
Biological sources:
Garlic (Allium sativum L. family Liliaceae) is originally from Asia but it is also cultivated in China, North Africa (Egypt), Europe and Mexico.
FAMILY:
Amaryllidaceae
Part of plant :-
The garlic plant's bulb is the most commonly used part of the plant.
chemical constituent :
Allicin ,Alliin, Ajoene, Sulphides, Polysulfides, Organosulfides, Organosulfur Compound, Vitamins and Minerals , Enzymes ,Amino Acids
USES:
- Garlic supplements, such as garlic capsules or garlic oil, are available in health food stores. These can provide a concentrated dose of garlic's active compounds. Follow the recommended dosage on the product label, and consult a healthcare professional for guidance.13
- Garlic Tea: You can make garlic tea by steeping crushed or minced garlic cloves in hot water.
- This can be used for respiratory issues or as a general health tonic.
- Garlic can be used topically for skin conditions. Crush a garlic clove and apply it to the affected area, but be cautious as it can cause skin irritation in some people.
HISTORY
Since 5000 BC, the Egyptians made a tooth powder, which consisted of powdered ashes of ox hooves, myrrh, powdered and burnt eggshells, and pumice. The Greeks, and then the Romans, improved the recipes by adding abrasives such as crushed bones and oyster shells Toothpowder provide cleanliness and Polishness in teeth enamel to prevent dental caries. Historically used by Romans to clean and whiten teeth, to fix them when loose and to prevent toothache. They usually made toothpowder with bones, hoofs and horns of certain animals like oyster, crabs and eggshells after previously burnt and reduced to fine powder Ancient Indian medicine has used the neem tree and its products to create toothbrushes and similar products for millennia Teeth can have problems like plaque, cavities (caries), and pyorrhea. Taking good care of your teeth is important to prevent decay and gum diseases. In places like the Indian subcontinent, many people rely on traditional methods to treat toothaches, cavities, and other tooth-related issues. The mouth naturally has bacteria, but most of them are harmless under normal conditions. Around 1000 AD, Ancient Persia started to take note of vigorous abrasives’ side effects. They opted instead for somewhat softer materials, like hartshorn, charred gypsum, herbs, honey, and minerals. The Persians also focused on strengthening teeth, compiling recipes that featured lead and powdered flintstone, among other things. In politically precarious 18th-century England, tooth powder recipes remained stable. Before long, though, the English thought to introduce a powerful, beloved British standby: toast. They would grind toast and use the abrasive powder to scrub their teeth. This provided an affordable, albeit humble, option. Years later, dentists and doctors collaborated and dentifrice made its official appearance in England. This powder was made up of cuttlefish, brick dust, and crushed dishware. Baking soda and sugar were often added as well. Toward the 19th century, manufacturers threw in borax powder to achieve a pleasant foaming effect. Poverty-stricken Brits moved on from toast, using straight baking soda to clean their teeth.
LITRATURE SURVEY :
- Sharat Asokan et al [2019]14 :
To evaluate antibacterial, antifungal, antioxidant properties of custom-made natural tooth powder and the effectiveness of custom-made natural tooth powder on the oral hygiene status of children. Antibacterial and antifungal properties were determined by agar diffusion method against Streptococcus mutans, Candida albicans and antioxidant properties were determined by DPPH (2,2-diphenyl-1-picryl-hydrazyl-hydrate) assay. Clinical trial included 60 children aged 8 to 11 years.
- Nandini Bushan Patil et al [2013]15 :
Dentifrices are products that are primarily used to maintain oral hygiene, including breath freshness and tooth decay prevention. Throughout the day, oral hygiene can be kept up by using a variety of dentifrices made from both herbal and artificial substances. This research was done to create a tooth powder that can be used to maintain good oral hygiene and to combat the negative effects of the synthetic components used to create traditional tooth powder.
- Kannan Krishnamurthi et al [2015]16:
The oral hygiene is of utmost importance in healthcare system as it is not only related with health as a whole but it is also linked with physical appearance and societal communication senses, as well as bad breath and other oral problems play adverse effect on personality and self-confidence. The tooth pastes and tooth powders available in the market may have harmful ingredients, many statutory warnings related with cautious use of it are being floated in social media.
- Chandrashekar Janakiram et al [2018]17:
A clinical equipoise exists between the plaque reducing effi cacies of two of the most commonly used dentifrices in India. This study compared the plaque removal effi cacy of a commercially available tooth powder with commercially available toothpaste in young adult. Methods: This was an investigator-blinded randomized controlled clinical trial with crossover design conducted among 89 young adults aged 18 - 25 years. Interventions were a commercially available tooth powder and toothpaste. Plaque scores were measured at baseline, after 24 hours and seven days.
- Megha Gupta et al [2004]18:
A well-known herbal toothpowder was evaluated & standardized for its Piperine contents. Methods-The formulation was subjected for physical constants like Moisture content, Ash value, and Extractive values in various solvents including Petroleum ether, Ethanol and Water. Thin layer chromatography and spectroscopic studies was carried out for the qualitative analysis of Piperine content. Results & Conclusion _Present study reveals the presence of Piperine in toothpowder. As the present scenario is moving towards the herbal medicines, these evaluation parameters will further help to set up a standard validation process for herbal formulations
MATERIAL AND METHOD:
For the development of the herbal tooth powder, we gathered all the required drugs from the nearby market. We chose ten crucial components for our tooth powder, including Neem, Trikutu, Babul, garlic , turmeric ,clove budes ,tulsi, Clove oils, Sendha namak, Camphor, stevia leaf . We passed all the herbal substances through a mesh size of 75 before mixing them in a homogeneous way to create the tooth powder.19

Table No.1
How To Prepared :
All these ingredients can be easily found at home Trikuta powder-black pepper, long pepper and ginger powder in equal Quantity
- Take neem , trikuta, babul, garlic, turmeric, tulsi, camphor, clove buds, sendha namak, and stevia leaf then dry them in sunlight
- Grind each ingredient separately to make its fine powder.
- The powdered herbal material were sieved through mesh size 70. 4) Measure each ingredient and mix all ingredients together in the quantity mentioned in the

Fig No. 15 Mix Herbal Powders
EVALUTION PARAMETERS OF HERBAL TOOTH POWDER :
The herbal tooth powder that was prepared underwent an analysis of its different aspects including organoleptic evaluation, physic-chemical evaluation, rheological evaluation, and antimicrobial activity.
- Organoleptic Evaluation
The evaluation of the organoleptic characteristics involved assessing sensory attributes such as colour, Odor, and taste. These characteristics were carefully observed and recorded. Both the raw materials used and the resulting powder were examined separately, considering their organoleptic and morphological properties such as colour, Odor, texture, and appearance.20
Colour :
The color of the tooth powder was visually assessed under normal lighting conditions.
Odour:
The odor of the product was determined by smelling.
Taste:
The taste was evaluated through manual tasting.
- Physio-Chemical Evaluation
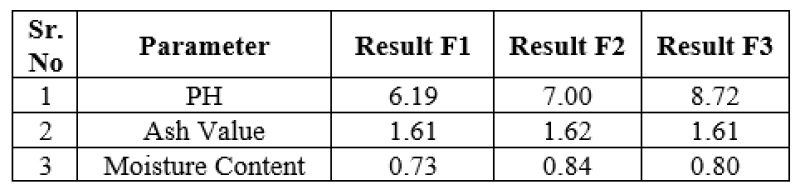
The assessment of the pH, moisture content, ash value, and quantity of inorganic substance in the herbal tooth powder was conducted to assess its physical and chemical characteristics.
pH
The pH of a formulated herbal tooth powder was determined using a pH meter. A 5g sample of the tooth powder was added to a 100ml beaker. Additionally, 10ml of boiled water was added and allowed to cool. The mixture was stirred vigorously to create a suspension, and the pH was measured.21

Fig No. 16 Ph Meter
Moisture Content
Tooth powder (10gm) weighed and dried it in the oven at 105o C then it was cooled. The loss of weight is recorded as percentage moisture content and calculated by the given formula 22. %
Moisture content = Original sample weight?Dry sample weight
Ash Value
Weight approximately 3 grams of the powdered drug in a silica crucible. Incinerate the powdered drug by gradually increasing the heat until the sample is free from carbon, and then allow it to cool in a desiccator. Weigh the resulting ash and calculate the percentage of total ash in contrast to the air-dried sample.

Fig no 17 Ash value
- Rheological Evaluation
Physical parameters such as bulk density, foaming test, and angle of repose were observed and calculated for the formulation.
Bulk Density
The bulk density of the powder is determined by dividing the mass of an untapped powder sample by its volume, including the void volume between particles. It is expressed in grams per milliliter.22
Foam test
The foamability of the product was assessed by taking 2 grams of tooth powder and mixing it with water in a measuring cylinder. The initial volume (v1) was recorded, and then the mixture was shaken ten times. The final volume of foam (v2) was noted23.

Fig no 18-foaming index
Flow Property
A funnel was secured with a clamp and placed above a sheet of graph paper. The distance between the graph paper and the bottom of the funnel was measured. Next, 50 grams of powder were weighed and poured into the funnel, blocking the orifice with a thumb. Once the thumb was removed, the powder flowed down onto the graph paper, forming a cone-shaped pile until the peak touched the bottom of the funnel stem. The angle of repose was calculated using the formula: Tan ? = H/R, where H represents the height of the powder and R is the radius of the graph paper.

Fig No 19 Angle of Repose
- Anti-microbial Activity-
Anti-bacterial activity was determined by agar well diffusion method- 24
Preparation of Agar media :
Suspended 7gm Nutrient agar in a 250ml conical flask and 250ml distilled water was added. Then, it was heated on a hot plate with frequent agitation until it completely dissolved. Then, the media was sterilized in an autoclave at 121ºC for 1 hour.
Agar well diffusion method :
Approximately 25ml of Nutrient agar was poured into a sterile Petri dish and allowed to solidify. 50µl of bacterial inoculums was spread on the solidify nutrient agar media by using the sterile spreader. In these plates, four wells (5mm diameter) were punched into the agar by using a sterile cork borer. Then, the working concentration dilution were prepared and was separately added into wells and allowed to diffuse at room temperature. The plates were incubated for 24hours at 37?C for one day and another day I seen the zone of inhibition.25
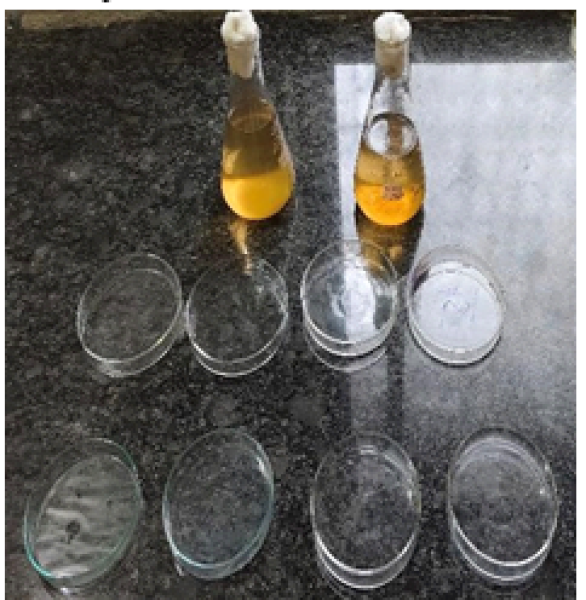

Fig no. 20 Sterile Nutrient Agar medium
RESULT AND DISCUSION
It is often believed that the use of toothpowder has higher benefits in our lifestyle. They can produce good healthcare to teeth. Powders are pharmaceutical solid dosage form encountered in almost every aspect of pharmacy both in industry and practice. They are the mixture of finely divided drugs and chemicals in dry form, meant for internal and external use. Toothpowder undergoes several characteristics like cleansing action, refreshing, foaming and polishing effect etc. Different types of toothpowders are available with different ingredients of preparation like whitening toothpowder, Natural toothpowder and homemade toothpowder. Toothpowder always follows formula with different penetrating agents like abrasives, polishing agents, Flavoring agents Different commercial brands of toothpowder are available in market, when it comes to brands names and manufacturers. So, it helps people to find their characteristic toothpowder for the use. Different evaluation methods including Determination of pH, Foaming Index, Density of powder, Bulk density, Angle of repose. As compare to F1 and F3 result of F2 are better. Because obtain ph and ash value of F2 is better as compare to standard value.


 Prajakta S. Bhasme*
Prajakta S. Bhasme*
 Kishor N Shingnapure
Kishor N Shingnapure
 Abhay V. Pawar
Abhay V. Pawar
 Amol B. Jaybhaye
Amol B. Jaybhaye

























 10.5281/zenodo.10860860
10.5281/zenodo.10860860