Abstract
Oro-dispersible films, often known as oral wafers, are small, thin films coated with drugs whose major goal is to build a novel, fast-dissolving product on this platform to achieve enhanced bioavailability and faster disintegration and dissolution. The model medication for the creation of oral thin films is tadalafil, a phosphodiesters 5 inhibitor(PDE5) used to treat erectile dysfunction. utilizing the solvent casting process using TDP/ODF machine, fast-dissolving oral tadalafil thin films were created utilizing HPMC 15cps as a film-forming polymer, propylene glycol 400 as a plasticizer, SLS as a surfactant, aspartame as a sweetener, and citric acid as a saliva-stimulating agent. The prepared films were then evaluated for physical appearance, surface pH, thickness, weight variation, tensile strength, content uniformity, in vitro disintegration test and in vitro dissolution test,contact angle, wetting time, stability studies, tensile strength, percent elongation,swelling property. From the evaluation studies, all the films were found to show satisfactory results. The film TDF7,containing 47 mg of HPMC 15CPS and10mg of PEG 400, generated by DoE Software with addition of SLS,was found to show more release of drug i.e. 99.99 % at the end of 10 minutes was selected as the best formulation.The film was found to disintegrate in 15 seconds and released 99.99% of drug at the end of 10 minutes.
Keywords
Oro-dispersible film, HPMC, Phosphodiesters 5 inhibitor, Tadalafil, PEG
Introduction
Oral administration of drugs is a highly preferred, economical, and convenient method of medication delivery among other delivery methods. However, certain patients, particularly those in the paediatric and geriatric age groups, experience difficulty swallowing or chewing certain oral solid dosage forms, such as hard gelatin capsules and tablets. They can't take these dose types since they're afraid they'll choke. Fast dissolving drug delivery systems (FDDDS) were developed in a number of ways to get around this. The administration of drugs through the buccal channel is a crucial route. Using the buccal method to give the medicine can help prevent issues such high first-pass metabolism and drug degradation in the gastrointestinal environment. Oral drug delivery system research has resulted in the development of more advanced dosage forms, ranging from straight forward traditional tablets or capsules to modified release tablets or capsules, oral disintegrating tablets, wafer, and the most recent invention of fast dissolving oral thin films. Ultra-thin oral thin films known as "fast dissolving" oral thin films use a hydrophilic polymer, which hydrates or clings quickly to the tongue or buccal canal. Without chewing or drinking, these films breakdown or disintegrate in a matter of seconds to release the active ingredient. Because the mucosa has a highly enriched blood supply, medications are absorbed quickly and become bioavailable instantly. Patient compliance is the reason why oro-dispersible film technology, which is still in its early phases, has a promising future.
Dysphagia, or difficulty swallowing, affects people of all ages, but it is most prevalent among the elderly. It can also occur when taking regular pills and capsules. Numerous illnesses, such as stroke, Parkinson's disease, AIDS, thyroidectomy, head and neck thyroid treatment, and other neurological disorders like cerebral palsy, are linked to dysphagia. Tablet size was the most often voiced concern, followed by form, surface, and flavor. Patients who were traveling and might not have had easy access to water as well as elderly and pediatric patients showed a greater difficulty with swallowing tablets.
Oro-Dispersible Films (ODFs)(12) : Strips known as oro-dispersible films (ODFS) are mostly composed of water-soluble polymers, which dissolve in saliva in less than a minute on average. Although it can sound overwhelming, if you have ever used breath-freshening strips, you have direct familiarity with this technology. One benefit of oro-dispersibe film is that it can be used with elderly patients or people who have trouble swallowing pills or capsules.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Materials: Tadalafil (Yarrow Chem Pvt . Ltd),HPMC 15cps (Medley Pharma Ltd; Andheri) ,Polyethylene Glycol 400 (Jinendra Scientifics, Jalgaon), Citric Acid (Jinendra Scientifics, Jalgaon), Aspartame (Jinendra Scientifics, Jalgaon), SLS (Sodium Lauryl Sulphate) (Jinendra Scientifics, Jalgaon)
Methods: Characterization of Tadalafil:
Solubility of Tadalafil : Tadalafil was freely soluble in PEG400.The solubility was determined by PEG , phosphate buffer pH 6.8 & SLS
Melting Point Determination: The melting point of tadalafil was determined by capillary tube method. Fine powder of the drug was filled into a glass capillary tube which was previously sealed at one end. The capillary tube was placed in digital melting point apparatus and subjected to increasing temperatures. Therefore, the temperature at which tadalafil melts was recorded.
Ultraviolet Spectroscopy: The samples were subjected to UV spectrophotometric analysis and were scanned for absorption maxima (? max) in the range of 200 - 400 nm using UV spectrophotometer in an appropriate medium. The obtained data was compared with that of reference values in literature Ultraviolet Spectroscopy: The samples were subjected to UV spectrophotometric analysis and were scanned for absorption maxima (? max) in the range of 200 - 400 nm using UV spectrophotometer in an appropriate medium. The obtained data was compared with that of reference values in literature.
Compatibility Studies: Compatibility of drug and polymers was studied using Fourier Transform Infrared (FTIR) spectroscopy. FTIR Spectrum was recorded between 600-4000 cm-1 using Agilent by KBr Disc method.
Formulation of Placebo Films: Polymers of single or in combination were accurately weighed and dissolved in respective solvent and then casted in a petridish. The films were allowed to dry overnight at room temperature.
Preparation of Oro-Dispersible Film of Tadalafil (By Using TDP/ODF Machine) : Oral fast dissolving film was prepared by solvent casting method.by utilizing 3days procedure.
(Day 1st) Aqueous solution I was prepared by dissolving film forming polymer & Aqueous solution II is prepared by dissolving pure drug (Tadalafil), sweetener(Aspartame) , and plasticizer(PEG400) in specific proportion of distilled water and allowed to stir for 1 h and kept aside for 1 day to remove all the entrapped air bubbles.
(Day 2nd ) Aqueous solution I &II were mixed & stirred for 1h & kept aside for to remove all the entrapped air bubbles.
(Day 3rd) The solutions were cast on TDP/ODF film former machine and dried at 70 ºC. The film was carefully removed from surface of machine and cut according to required size for testing (2 cm length, 2 cm width). The samples were stored in desicator maintained at a temperature of 30ºC and relative humidity 60% ± 5% until further analysis.

Fig : TDP/ODF Machine used for preparation of film
Calculation of Drug Loaded in the Film
- For preparation of 10ml solution for Batch size of 5 films
- Dose Strength of Tadalafil for one film= 10mg
- For total surface area of dragged film by 10 ml solution
- 5 × 10 = 50 mg of drug
DoE model Central Composite design) for Oro-Dispersible Film
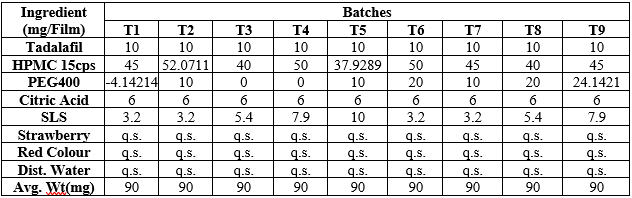
The optimization software Design of Expert (DoE) of version 13 was applied for the maximum possible runs for the development of oral thin film. The Central Composite design was selected for 2 factors (independent factors) predicted 9 possible runs and in actual manner get 5 trial batches.
Composition of Batches by Central Composite Design (TDP1-TDP9)
Evaluation of Fast Dissolving Films: The tadalafil films were evaluated for the following properties:
- General Appearance: This Evaluation were done by visual Perspection .
- Taste
- Odour
- Colour
- Texture
- Surface
- Weight variation: Weight variation were calculated by weighing any five films from the formulation individually on a digital balance and then computed the average weight.
- Thickness: The thickness of film was measured by micrometer screw gauge at different strategic locations. Each film was measured at 5 positions (center and four corners) by digital Vernier caliper and the mean thickness was calculated. This is essential to determine uniformity in the thickness of the film as this is directly related to the accuracy of dose in the film.
- Folding Endurance: Folding endurance was determined by- repeated folding of the film at the same place till the film breaks. The number of times the film was folded without breaking & accordingly computed as the folding endurance value.
- Surface pH : The film to be tested placed in petri dish & was moistened with o.5 ml of distilled water & kept for 30 sec. the pH was noted after bringing the electrode of the pH meter in contact with the surface of the formulation & allowing equilibrium for 1 min.
- Wetting Time : A circular single tissue paper was placed in th petridish. 6 ml of 1.1% w/v methylene blue solution was added to the petridish. The film was placed on the surface of tissue paper. The time required for the dye to appear on the surface of the film was noted as the wetting time.
- Moisture Uptake & Moisture Loss : The original weight of the film was determined first and then the film was placed in a desiccator (including calcium carbonate) for three days to determine the percentage moisture loss. The films were removed and weighed again after three days and the moisture loss were calculated using the formula:
A film's percentage moisture uptake was calculated by exposing it to an atmosphere with a relative humidity of 75%RH at room temperature for seven days and then using the following method to calculate the moisture Uptake.
- Disintegration Time: In vitro disintegration time was determined visually in a glass beaker of 25 ml distilled water with swirling every 10 seconds. The disintegration time is the time when the film starts to break or disintegrates.
- Drug Content : Take one film (2×2cm2) & dissolve it in pH 6.8 phosphate buffer in a volumetric flask & make up the volume upto q.s. to 100ml .Withdraw 0.5ml solution from prepared solution & diluted to 10ml with phosphate buffer pH 6.8 measure the absorbance of the solution spectrophotometrically at 290nm
- In Vitro Dissolution Studies :The release rate of Tadalafil oral thin film was determined using United States Pharmacopoeia (USP) dissolution testing apparatus type 2 (paddle method) .The dissolution test was performed using 900 ml of Phosphate buffer pH 6.8, at 37 ± 0.5oC and 50 rpm. In specified time intervals (0, 2, 4, 6, 8, 10 min) an aliquot of 5 ml samples of the solution were withdrawn from the dissolution apparatus and with replacement of fresh fluid to dissolution medium. The samples were filtered through whatmann filter paper of 42 µm. Absorbance of these solutions were measured at ?max 290 nm using a UV/Visible Spectrophotometer (shimadzu-1800). The drug release was plotted against time to determine the release profile of various batches.
- Stability Study) : Stability Studies were carried out as per ICH guidelines Q1A (R2). The optimized formulation was wrapped in aluminum pouch & sealed. It was stored at accelerated (40 ?c ±2 ?c / 75% RH ± 5% RH) conditions for a period of one month. Films were evaluated for weight, folding endurance, disintegration time, drug content and % DR.
- Tensile strength :
Tensile strength is the maximum stress applied to a point at which the strip specimen breaks. It was calculated by the applied load at rupture divided by the cross-sectional area of the strip given in the equation below:
- Percent elongation:
When stress is applied, a strip sample stretches and this is referred to as strain. Strain is basically the deformation of strip divided by original dimension of the sample. Generally elongation of strip increases as the plasticizer content increases.
- Swelling property : Film swelling studies was conducted using simulated saliva solution. Each film sample was weighed and placed in a pre-weighed stainless steel wire mesh. The mesh containing film sample was submerged into 15ml medium in a plastic container. Increase in the weight of the film was determined at preset time interval until a constant weight was observed .The degree of swelling was calculated using parameters
wt-w0/wo,
wt is weight of film at time t, and
wo is weight of film at time zero
RESULTS AND DISCUSSION :
Melting Point Determination :
Melting point of tadalafil was found in the range between 290°C to 295°C. The reported melting point in the range of tadalafil was 290°C to 300°C. Hence, experimental values were in good agreement with official value.
Ultraviolet Spectroscopy: The values of correlation coefficient for the linear regression equation was found to be 0.9974 for phosphate buffer of pH 6.8 indicating a good positive correlation between concentration of tadalafil and the corresponding absorbance values.
UV Estimation of Tadalafil :
Determination of Maxima of Tadalafil
The ultraviolet spectrum was recorded in the range 200 nm to 400 nm, the standard solution (100 µg/ml) of pure drug was prepared in phosphate buffer (pH 6.8) + 1 % sodium lauryl sulphate. From the standard solution 2 to 30µ g/ml dilutions were prepared and 10 µg/ml solution was scanned in the range of 200 nm to 400 nm. The solution showed maximum absorbance at 290 nm. At the ?max of 290 nm tadalafil was estimated using phosphate buffer (pH 6.8) + 1% sodium lauryl sulphate.
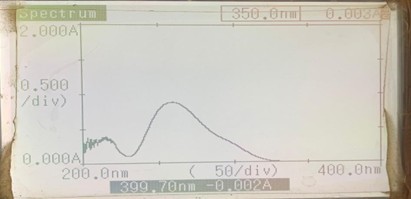
Fig 2 ? max of Tadalafil in Phosphate Buffer pH 6.8
Table 1 Observation Table for Calibration
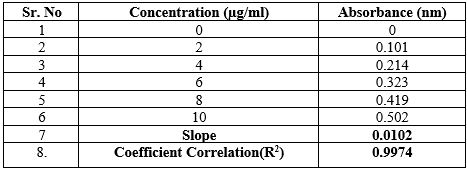
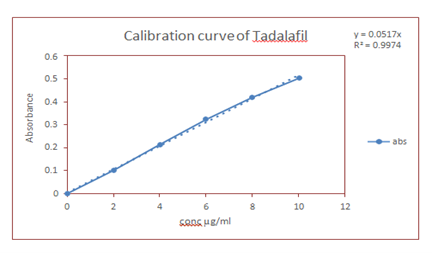
Fig 3 Calibration Curve of Tadalafil in Phosphate Buffer pH 6.8
Compatibility study : The identification of pure sample of tadalafil was carried out with FTIR spectra. The C=C Stretching was available in the range of 1600-1650 cm-1and observed at 1633 cm-1. Whereas (Carbonyl)C=O Stretching predicted in the range of 1650-1750 cm-1and identified at 1690 cm1,Aliphatic C-H Stretching (2850-3000 cm-1) recognized at 2898cm-1 and N-H Stretching (3300-3500 cm-1) at 3451cm-1. The individual peaks of drug and HPMC was clearly reflected in the spectrum, which indicated that tadalafil is compatible with HPMC
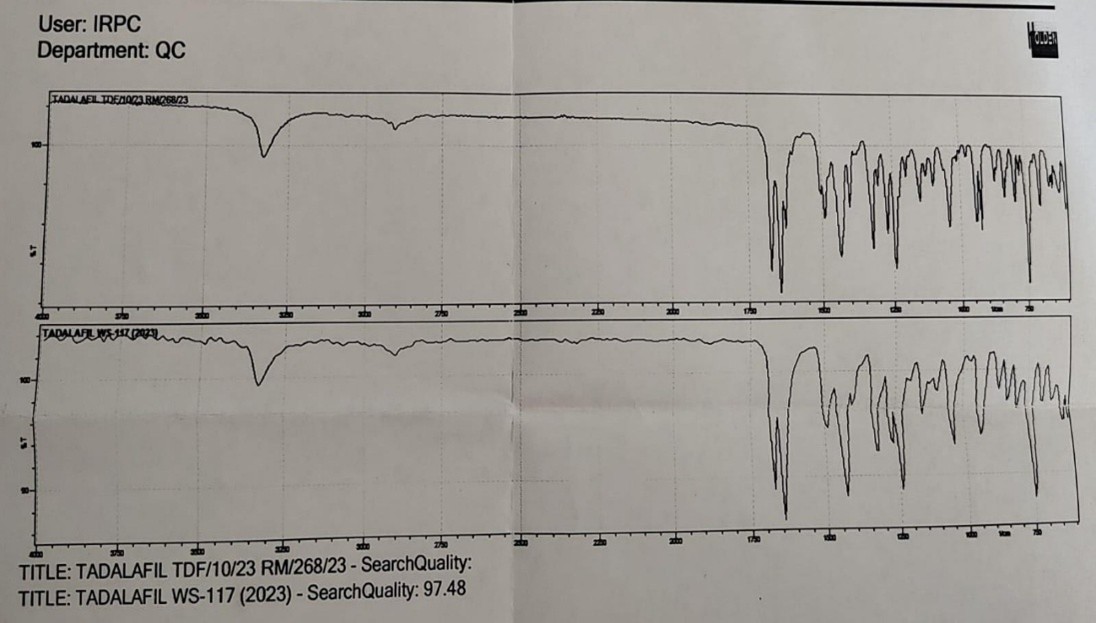
Fig 4 FTIR Spectra of Tadalafil

Fig 6 FTIR Spectra of HPMC 15 CPS
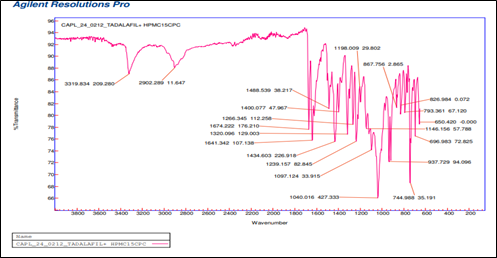
Fig 5 FTIR Spectra of Tadalafil +HPMC 15 CPS
DSC Thermogram
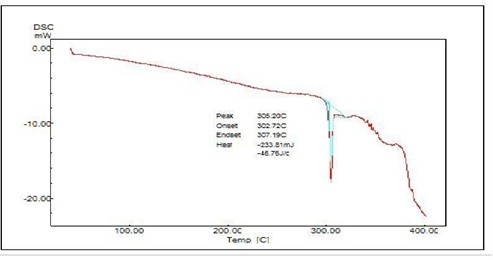
Fig 7 DSC Thermogram of Tadalafil

Fig 8 Thermogram DSC of Tadalafil
DSC statement:

Table 2 :Evaluation of Batches of ODF of Tadalafil Generated by CCD

Table 3 :Evaluation of Batches of ODF of Tadalafil Generated by CCD

Table 4 :Evaluation of Batches of ODF of Tadalafil Generated by CCD
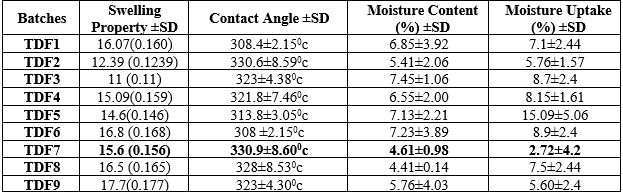
Table 5 : Evaluation of Batches of ODF of Tadalafil Generated by CCD

Table 6 : In-Vitro Diffusion Study of Tadalafil ODF
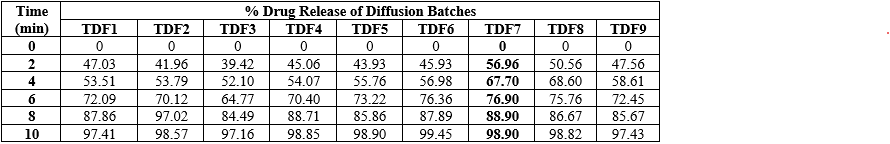
Table 7: In-Vitro Drug Release (Dissolution) of Optimized Batches of Tadalafil ODF Generated by CCD (TDF1-TDF9)


Fig 9 In-vitro Drug Release of Tadalafil (Dissolution)
From the above results of drug loaded mouth dissolving film, it was observed that TDF7 batch showed highest folding endurance which indicates prepared film having good flexibility and the surface pH was found to be 6.8 ± 0.37 which is as same as the pH of oral cavity. The thicknesses of the prepared mouth dissolving films were found to be in the range of 0.50±0.37mm. The TDF7 batch showed 0.50±0.37mm thickness which is higher than other batches. As the concentration of polymer increases, the thickness of the film increases. TDF7 showed better results with % percent elongation and tensile strength among all batches. TDF7 batch showed 114% drug content . and having wetting time 16±1.41which is lesser among all. From the results formulation was selected as the best optimized batch. results with % moisture uptake and moisture content among all batches.& Contact angle better among all batches. TDF7 batch showed 16.5% swelling property from the results formulationTDF7 was selected as the best optimized batch.
STABILITY STUDY
I) Accelerated Stability Study
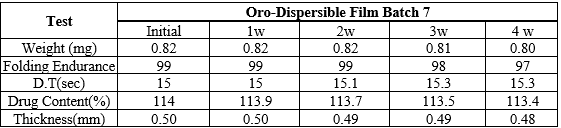
Stability studies were carried out for 30 days at 400c and 75 % RH. The films were observed for any change in parameters like physical changes, folding endurance, disintegration time, percentage drug content, percentage drug release and other parameters also. ODFs of Tadalafil were found to be physically and chemically stable and showed no significant change in terms of physical characteristics, formulation TDF7 was stable and retained their original properties with minor differences in drug content, %DR and other parameter which are in acceptable limits.
Stability Study of Optimized Batch of Tadalafil ODF
Data Analysis of DoE
The general central composite design was applied to optimize the ODF of taste masked Tadalafil. The response surface methodology analyzed data clearly indicate that the %DR, DT, values were mainly depending upon the selected independent variables. The regression equations for the responses fitted in linear model were generated. ANOVA was used to identify the significant effect. Obtained value of F is larger than critical F-value, the result was found to be significant at that level of probability <0>
Final equation in terms of coded form
% DR= +97.33+(-0.1768)+1.35
Final equation in terms of coded form-
DT= +15.33+(-0.02112)+0.3143
Response 1 Dissolution

Response 2 Disintegration
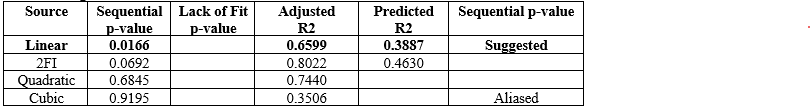
Table 8 : Fit Summary for Dissolution & Diffusion
Table 9 :Result of Analysis of Variance for Batches by CCD of Tadalafil ODF

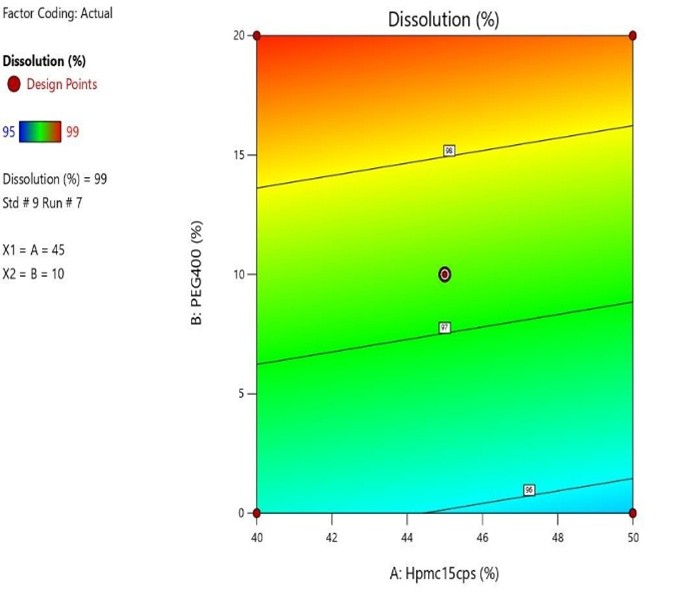
Fig 10 : Response Surface Contour Graph Showing the Influence of HPMC (X1) and PEG 400 on % Drug Release (Y)
|
|
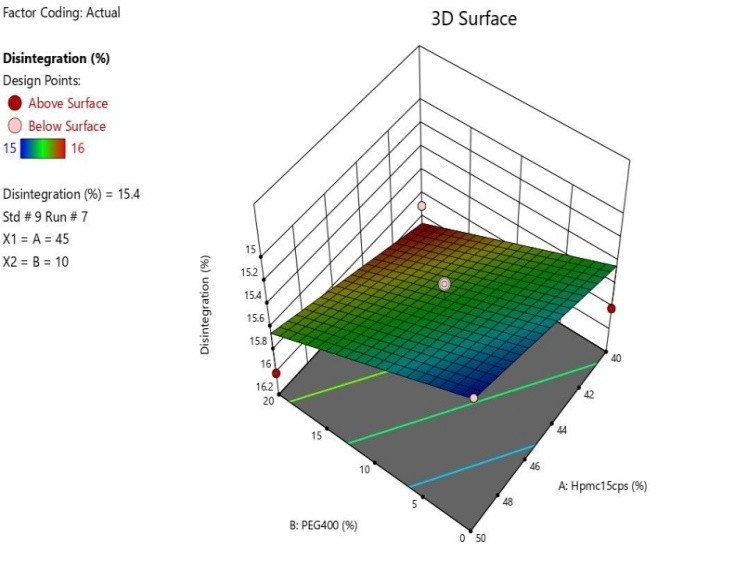
Fig 11 : 3D Response Surface Graph Showing the Influence of HPMC (X1) and PEG 400 on % Drug Release (Y)
|
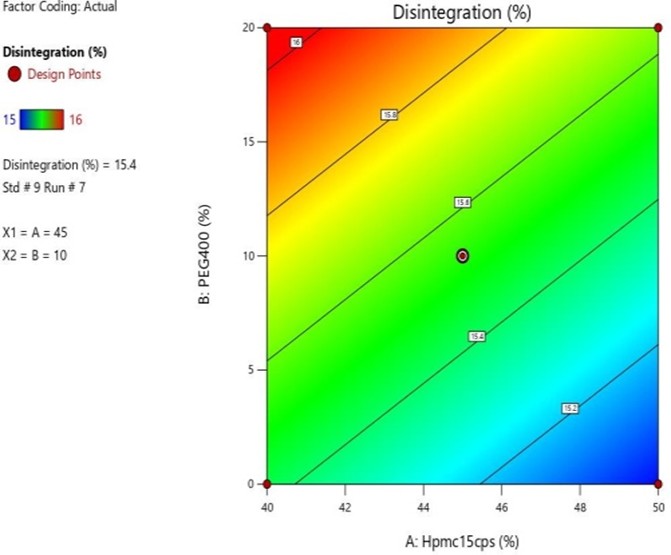
Fig 13 :3D Response Surface Graph Showing the Influence of HPMC (X1) and PEG 400 on% Drug Release(Y)
|
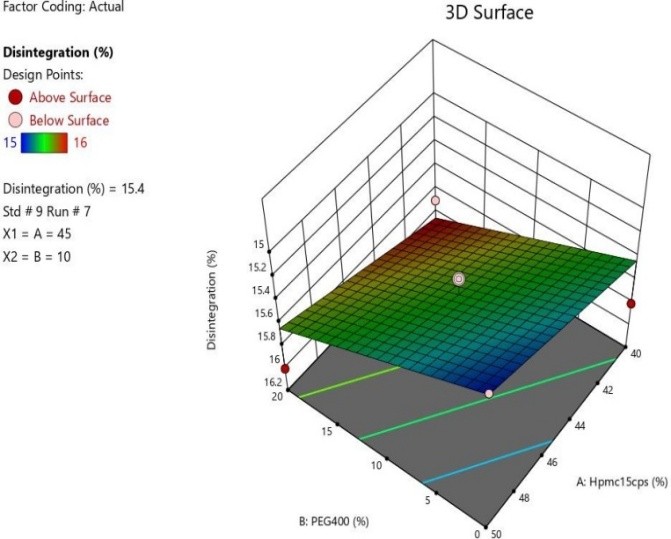
Fig 12: Response Surface Contour Graph Showing the Influence of HPMC (X1) and PEG 400 on% Drug Release (Y)
|
CONCLUSION
Tadalafil matched the standard value as per COA in terms of color, odor, and taste. Tadalafil's melting point was likewise determined by DSC and digital melting point apparatus to be within range, at 290-2950C. With the aid of a UV visible spectrophotometer, the wavelength of Tadalafil was determined to be 290 nm. The concentration and absorbance relationship was shown by the calibration curve showed lining. In the 5–30 µg/ml range, it complies with Beers and Lamberts law. The value of the correlation coefficient was 0.9977.Relationships are indicated by a positive or negative correlation between two variables. When the obtained Tadalafil FTIR spectrum was compared to the standard, the peaks of the functional groups discovered in the obtained spectrum were found to be matched those found in the standard IR spectrum, indicating that the medication was pure and confirmed to be Tadalafil. The results of Batch 7 were the best of all the concentrations provided by CCD; the drug release percentage was determined to be 99.99%, and the disintegration time was discovered to be 15 seconds. 10% of PEG 400 and 45% of HPMC were utilized as the independent variables. It was discovered that the whole drug quantity from the TDP7 formulation diffused entirely in 10 minutes, which is necessary for a quicker beginning of action.
REFERENCE
- Hema J, Oral Strip Technology: A Review, Indian J Pharm Biol Res, 2, 2014, 130-143.
- Swapnil LP, Paresh R, Mahaparale, Madhavi A, Shivnikar, Shradha S, Tiwari, Ketan V, Pawar, Prashant N, Sane, Fast Dissolving Oral Films: An Innovative Drug Delivery System, IJRRPAS, 2, 482-496.
- Rubia Y, Firoz Y, Chandra Mouli, Vikram A, Mahitha, Aruna U, Preparation and Evaluation of Oral Fast Dissolving Films of Citalopram Hydrobromide, International Journal of Biopharmaceutics, 3, 2012, 103-106.
- Arunachalam M, Karthikeyan S, Ashutosh K, Kishore, Konam P, Hariprasad, Fast Dissolving Drug Delivery System: A Review, Journal of Global Trends In Pharmaceutical Sciences, 1, 2010, 92-110.
- Shubham V, Nitin K, Pramod K S, Buccal Film: An Advance Technology For Oral Drug Delivery, Advan Biol Res, 8, 2014, 260-267.
- Raghavendra R NG, Shravani, Mettu SR, Overview On Buccal Drug Delivery Systems, J Pharm Sci & Res, 5, 2013, 80-88
- Shruti C Prabhu Et.Al ‘A Review On Fast Dissolving Sullingual Films For Systemic Drug Delivery’ Int Jr Ph & Che Sci, 2014, V0l 3 (2) P.No 501 511
- Pawar Rajat, Sharma Ravi, Sharma Pravin, Darwhekar G. N. A Review On Mouth Dissoliving Film.”Journal Of Drug Delivery and Therapeutics”, 2019, Vol.9(6) Pg.No.206-210.
- Saeed Shirazian, Rahamatullah Shaikh Development and Evaluation of Amorphous Oral Thin Films Using Solvent-Free Processes: Comparison Between 3D Printing And Hot-Melt Extrusion Technologies Journal of Pharmaceutics 2021 13(10) 1621.
- Carnaby-Mann, G.; Crary, M. Pill Swallowing by Adults With Dysphagia. Arch. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2005, 131, 970–975.Sanjay Singh . Formulation and In Vitro Evaluation of Mouth Dissolving Films of Amlodipine Besylate (2020) . World Journal Pharmacy and Pharmaceutical Sciences. Vol .9.(6), Page No- 974-997.
- Patel Viralkumar F, Liu Fang, Brown Marc B, "Advances In Oral Transmucosal Drug Deliver, School of Pharmacy, University Of Hertfordshire, Hatfield, UK AL10 9AB Medpharm Limited,Guilford, Surrey, UK GU2 7YN, 3-12


 Yogesh Sonawane*
Yogesh Sonawane*
 M. M. Bari 1
M. M. Bari 1
 S. D. Barhate 2
S. D. Barhate 2
 Reema Jagnit 3
Reema Jagnit 3
 Abhay Sawant 4
Abhay Sawant 4
 Amol Chaudhari 5
Amol Chaudhari 5


























 10.5281/zenodo.13221841
10.5281/zenodo.13221841