Abstract
Ficus racemosa Linn. (Family: Moraceae), commonly referred to as the gular or cluster fig tree, is a well-known medicinal plant in India. This herb is mentioned in all the ancient writings on Ayurveda, Siddha, Unani, and homeopathy. Bark, roots, leaves, fruits, and latex are among the many plant parts that are used as carminatives, astringents, vermifuges, and anti-dysentery medicines. It is a helpful remedy for eating too much. Menorrhagia, diabetes, leucoderma, hepatoprotection, refrigerant, antioxidant, and antiulcer diseases are all treated with fruit extract. It is given topically to treat skin lesions, fibrositis, lymphadenitis, and sprains to lessen swelling. This study aims to formulate and evaluate the herbal tablets made from Ficus racemosa Linn.bark extract.
Keywords
Ficus racemosa Linn., Moraceae, Pharmacogonstical, Clinical trial, traditional uses
Introduction
Medicinal plants, since times immemorial, have been used in virtually all cultures as a source of medicine. The widespread use of herbal remedies and healthcare preparations, as those described in ancient texts such as the Vedas and the Bible, and obtained from commonly used traditional herbs and medicinal plants, has been traced to the occurrence of natural products with medicinal properties. The use of traditional medicine and medicinal plants in most developing countries, as a normative basis for the maintenance of good health, has also been widely observed. Furthermore, an increasing reliance on the use of medicinal plants in industrialized societies has been traced to the extraction and development of several drugs and chemotherapeutics from these plants as well as from traditionally used rural herbal remedies. The World Health Organization has estimated that 80% of the world’s population use botanical medicine for their primary health care needs. (1) Medicinal plants are an important therapeutic agent for eliminating health- related risks of human being and its witness has been given by their presence in Rigveda and Ayurveda. The rate of prevalence of diseases, as well as discomfort, has increased in the recent era. This situation has to lead the researchers to explore different medicinal as well as herbal plants to eliminate this problem. As per the reports presented by WHO, 80% of the population all over the world implement remedial herbs to heal diseases as the most impor-tant therapy at a basic stage. The use of these medicinal plants having disease curing activity has been widely proposed in most developing countries, on a normal basis these plant sources act as a remedy for health benefits. (2) Medicinal plants, since times immemorial, have been used in virtually all cultures as a source of medicine. The widespread use of herbal remedies and healthcare preparations, as those described in ancient texts such as the Vedas and the Bible, and obtained from commonly used traditional herbs and medicinal plants, has been traced to the occurrence of natural products with medicinal properties (Hoareau & DaSilva, 1999). The use of traditional medicine and medicinal plants in most developing countries, as a normative basis for the maintenance of good health, has also been widely observed (UNESCO, 1996). Furthermore, an increasing reliance on the use of medicinal plants in industrialized societies has been traced to the extraction and development of several drugs and chemotherapeutics from these plants as well as from traditionally used rural herbal remedies. The World Health Organization has estimated that 80% of the world’s population use botanical medicine for their primary health care needs.(3) Solid medicaments may be administered orally as powders, pills, cachets, capsules or tablets. These dosage forms contain a quantity of drug which is given as a single Unit and they are known collectively as solid unit dosage forms, even in the case of Sustained action preparations which, technically, contain the equivalent of several Normal doses of drug The stringent formulation requirements of modern Medicaments, the many advantages of tablet and capsule medication, coupled With expanding health services and the commitment need for large scale Economic manufacture, have led to a steady decline in the prescribing of powders And pills .Tablets and capsules, on the other hand, currently account for well over Two third of the total number and cost of medicines produced all over the world. Tablets are solid dosage form which is the conventional as well as have many reviewed. advantages over other dosage forms. Tablets are the most popular dosage form: about 70% of the total medicines are dispensed in the form of tablet. Tablets had different shapes, sizes, as well as weight depending on medicinal substances and the intended mode of administration. In this paper the some advantages as well as some disadvantages of tablets, the basic ingredients that are commonly found in tablets, methods of tablet preparation and the various types of the tablets are briefly reviewed.(3)
Definition of Tablet
According to the Indian Pharmacopoeia Pharmaceutical tablets are solid, flat or biconvex dishes, unit dosage form, prepared by compressing a drugs or a mixture of drugs, with or without diluents. Tablet is defined as a compressed solid dosage form containing medicaments with or without excipients. They vary in shape and differ greatly in size and weight, depending on amount of medicinal substances and the intended mode of administration.(4,5)
Tablet is defined as a compressed solid dosage form containing medicaments with or without Excipients. Pharmaceutical tablets are solid, flat or biconvex dishes, unit dosage form, prepared by compressing a drug or a mixture of drugs, with or without diluents.(4,5)
Properties(5)
- Should be elegant product having its own identity while being free of defects such as chips, cracks, discoloration and contamination.
- Should have strength to withstand the rigors of shocks encountered in its production, packaging, shipping and dispensing.
- Should have the physical stability to maintain its physical attributes over time.
- Must be able to release the medicament agent(s) in the body in a predictable and reproducible manner.
- Must have a suitable chemical stability over time so as not to allow alteration of the medicinal agent(s).
Advantages (6)
- They are easy to carry, easy to swallow and they are attractive in appearance.
- Unpleasant taste can be masked by sugar coating and they do not require any measurement of dose.
- Some of the tablets are divided into halves and quarters by drawing lines during manufacturing to facilitate breakage whenever a fractional dose is required.
- An accurate amount of medicament, even if very small, can be incorporated.
- Tablets provide best combined properties of chemical, mechanical and microbiological stability of all the oral dosage forms.
- Since they are generally produced on a large scale, therefore, their cost of production is relatively low, hence economical.
- They are in general the easiest and cheapest to package and ship among all oral dosage forms. Some specialized tablets may be prepared for modified release profile of the drug.
- Product identification is potentially the simplest and cheapest requiring no additional processing steps when employing an embossed or monogrammed punch face.
Disadvantages (6)
- Difficult to swallow in case of children and unconscious patients.
- Drugs with poor wetting, slow dissolution properties, optimum absorption high in GIT
- may be difficult to formulate or manufacture as a tablet that will still provide adequate or full drug bioavailability.
- Bitter testing drugs, drugs with an objectionable odor or drugs that are sensitive to oxygen may require encapsulation or coating.
- In such cases, capsule may offer the best and lowest cost. Some drugs resist compression into dense compacts, owing to amorphous nature, low density character.
Plant profile
Ficus racemosa Linn is a beautiful cluster-fig tree with a curved trunk and a spreading crown. It is not a banyan tree; it does not have aerial roots. The red, stubbly figs in little bunches that grow immediately out of the tree's trunk are the most eye-catching feature of this tree. Those hunting for Ficus racemosa blooms should know that the fig is a component of a tree with hundreds of blossoms. The blossoms are pollinated by extremely little wasps that go through the aperture, looking for a suitable spot to reproduce. Without these pollinators, fig-trees never reproduce by seed.
In response, the blooms provide a safe home and nutrition for the wasps' offspring. Ficus racemosa is a ubiquitous tree in villages, cities, and towns. (7)

Fig 1. Ficus racemosa Linn.(7)
Taxonomic classification
The taxonomical classification has been represented in Fig.2
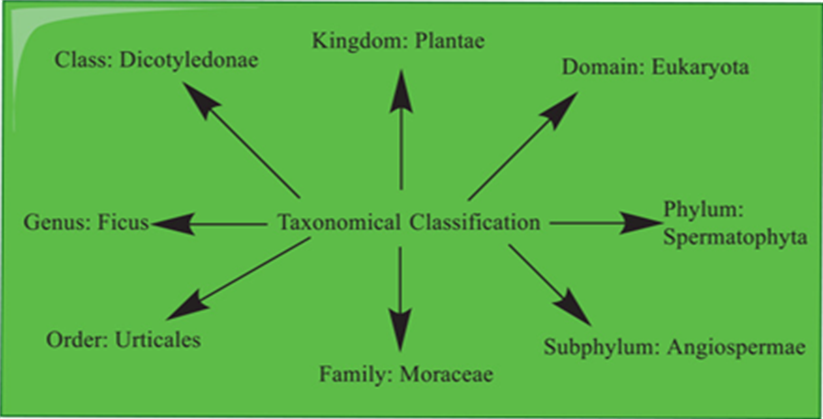
Fig 2. Taxonomical classification of Ficus racemosa.(7)
Ficus racemosa (syn. Ficus glomerata Roxb.) is a species of plant in the family Moraceae. Popularly known as the cluster fig tree, Indian fig tree or gular fig, Udumbara, this is native to Australia, Malaysia, Indo-china and the Indian subcontinent.
Vernacular names:
Hindi : Gular, Umar
Beng : Dumar, Jagya domar
Mar : Umbar
Guj : Umar, Gular
Tel :Atti bodda, paidi, udumbara
Tamil, Kan, Mal : Athi
Oriya : Dimpri(8)
Sans : Udumbarah, Sadaphakh
Assam : Janyedumuru, Yagyadimru
English : Cluster Fig, Country fig(9)
Climate and soil
It is naturally coming up in waste lands and forests. This requires well drained, medium to heavy soil for its successful cultivation. It is also found to be tolerate to lime sulphates and chlorides and can be thus used for planning in industrially polluted sites. However, it is not resistant to carbonates of sodium, potassium. It comes up in all kinds of soil except in water logged and clay types.(9)
Habits and features
Moderate to large sized spreading laticiferous, deciduous tree without much prominent aerial roots. It is an evergreen tree, 15-18 m high, young shoots glabrous.(9)
Leaves
Dark green leaves 7.5-15×3.2-6.3 cm, ovate – oblong (or) elliptic, lanceolate, tapering to a blunt point at the apex, with entire margins glabrous on both surfaces, base acute and rounded 3 nerved, lateral main nerves 4-6 pairs, petioles 1.3-3.8 cm long, glabrous stipules 2 cm long, ovate – lanceolate, scarious, pubescent. Leaves shed by December, replenished by January and April when the tree becomes bare for a short period.(10)
Inflorescence
Hypanthodium- Three kinds of flowers are borne, sterile, male and female flowers together in one receptacle of hypanthodium. The male flowers forming a zone near the mouth, the fertile female flowers forming a layer in the walls of the receptacle and the gall flowers an internal layer. Receptacle short pedunculate on short leafless warted branches which issue from the stem and later branches much contracted at the base when young.(11)
Flowers
Basal bracts 3, ovate-triangular, Male flower sessile, sepals 3-4 membranous, inflated enveloping the 2 elongate ovate anthers, filaments connate. Fertile female flowers sub-sessile, perianth gamophyllous with 4 or 5 long lanceolate teeth enveloping the small minutely tuberculate achene, style sub-terminal, stigma clavate. Gall flowers pedicellate, perianth gamophyllous, irregularly toothed covering only the base of the rough ovoid style, lateral elongate, stigma clavate. have a pleasant odour, resembling that of cider apples. The syconns develops from a hollow, pear-shaped fleshy receptacle which encloses a number of minute male and female flowers. The receptacle grows and becomes fleshy encloses a number of fruits or achene which develop from the female flowers lying within the receptacle.(12)
Bark
The bark is astringent, rusty brown with a firmly smooth and soft surface, thickness from 0.5-2 cm according to the age of the trunk or bark surface with minute separating flakes of whitish tissue, texture homogenous leathery.(12)
Parts used - Root, bark, leaves, fruits, milky juice.(12)
Action
Fruits – Laxative, Improves blood, cooling(12)
Bark leaves and unripe fruits – Astringent, Carminative, Stomachic, Vermicide.(13)
Phytochemicals Aspects
The active phytochemical constituents of Ficus racemosa have been described in Table The structures with their stereochemistry have been noted in Fig.
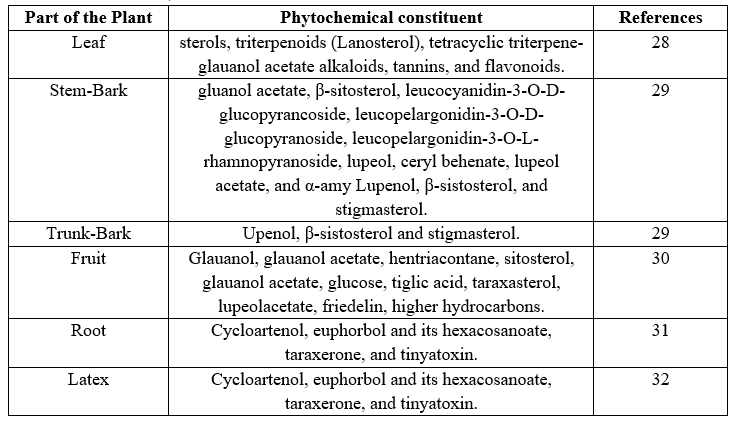
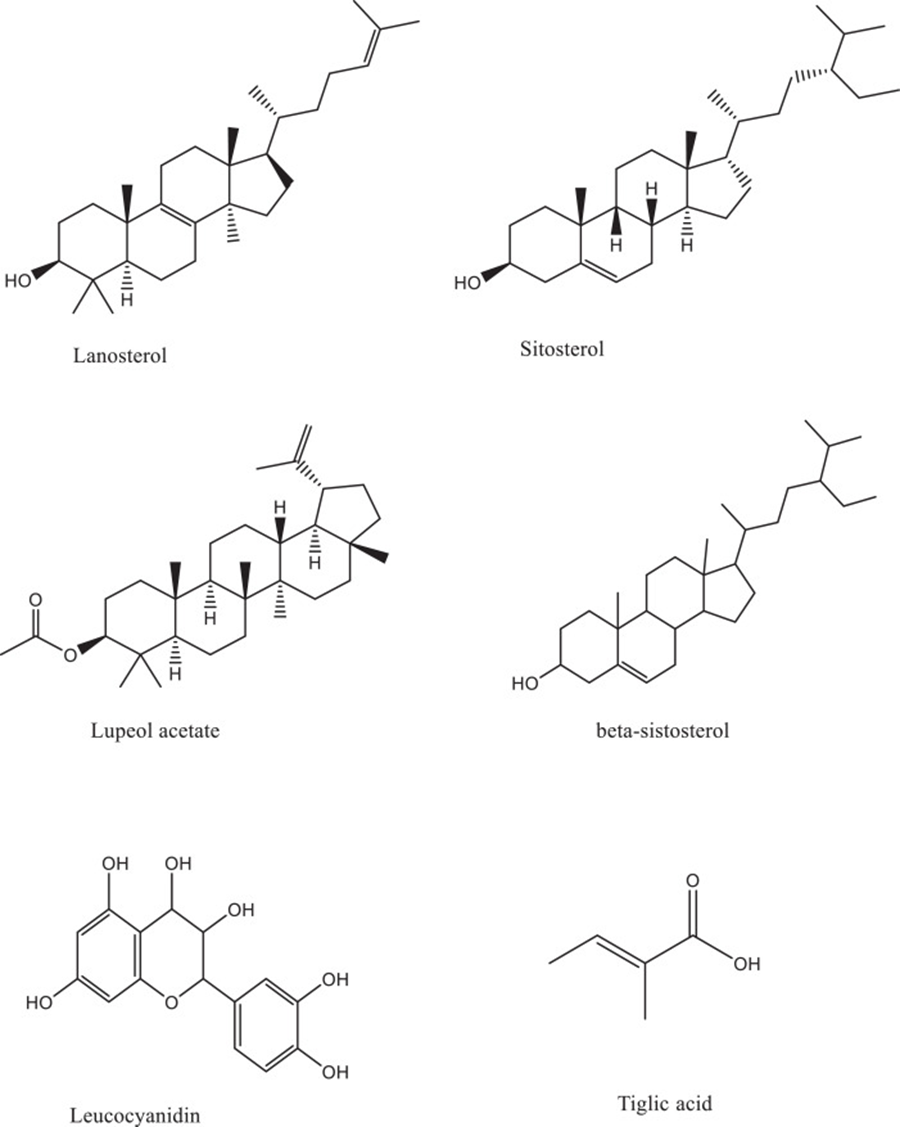
Fig: Chemical structure of the active constituents of Ficus. racemosa.(32)
Medicinal uses
SEED - Powder of the seed mixed with honey is regarded a specific in diabetes, reducing sugar in the urine, thirst and polyuria of diabetes.(13)
LEAVES - Young leaves crushed or reduced to powder or ripe figs mixed with honey or sugar are administered in bilious affections. Decoction prepared with a handful of leaves boiled in four pints of water is given with benefit every morning as a douche in dysmenorrhea.(13)
MILKY JUICE - Milky juice is administered in piles and diarrhoea. Fruit is edible, it is given on aphthous complaints, menorrhagia, haemoptysis with sugar and honey. Fruit when boiled in milk, it is a good remedy for visceral obstructions. In the diarrhoea of the pregnant women, the fruit with honey is given. Fruit and sap extracted from the trunk of the tree are efficacious in diabetes. Fruits are suppressor of pitta and effective in removing srama and sopha. The powder from the roasted fruits form a valuable breakfast food, almost similar to imported grape nuts. Fruits may be dehydrated ground in to flour and taken with milk and sugar or used for preparing cold jelly. Fresh juice of ripe fruit is given as an adjunct or vehicle to a metallic medicine for diabetes and other urinary complaints. Dried fruit one tola with sugar and honey is given in cases of menorrhagia and haemoptysis.(13)
Materials and Methods
Collection and Authentication of plants
Bark of Ficus racemosa were collected from Tirupati Nagar, Kathora road, Amravati(Maharashtra).The plant was identified and authenticated by Dr. Parul Nandgaonkar of department of Dravyaguna ,P.R.Pote Patil College Of Medical Sciences Ayurved, Amravati, and a voucher sample (code:DGH/24005 dated 05/03/2024) was deposited at the Herbarium of this department. The bark was dried in the sun exposure. Dried bark were powdered in grinder and powder was kept in an airtight container for further study. According to the literarure survey the methanolic extract of bark of Ficus racemosa Linn. Shows significant anti-pyretic activity.
Various excipients are required for the herbal tablet formulation including binders, fillers, dinintegrants, lubricants etc.
Extraction of Plant Material
The dried bark of plant Ficus racemosa Linn were allowed to air dry in a shade under normal environmental conditions for about one week, after that broken in to small pieces with the help of cutter and grinded in a grinder to coarse powder. Coarsely grinded plant parts were extracted in soxhlet apparatus successively with solvents ethanol. Table shows percentage yield of successive extraction.
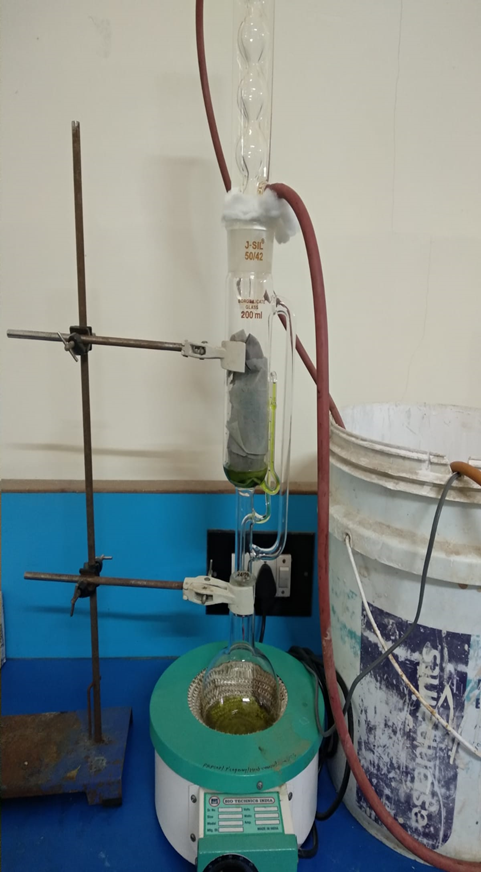

Fig 3. Extraction of Ficus racemosa Linn of bark extract
Taste, sight, smell, touch, and other senses are among the qualities of food, medications, and other substances that are referred to as organoleptic characteristics. These attributes are essential for evaluating the therapeutic efficacy, acceptability, and quality of herbal products.
The Organoleptic properties are crucial for customer acceptance and safety in addition to guaranteeing the effectiveness and purity of herbal products.
Bulk density and tap density
Important factors in the formulation and quality assurance of herbal tablets include bulk and tapped density. The mass of a powder divided by its volume when loosely packed is known as bulk density, and it represents the initial state of the powder prior to any compaction or compression. Conversely, tapered density is the mass of the powder divided by volume following normal tapping or vibration treatment, which compacts the powder and lowers its volume. comprehension the powder's flow characteristics and its capacity to form a tablet requires a comprehension of these metrics. Consistent tablet weight and active ingredient distribution depend on adequate flowability and uniform packing, which are often indicated by high bulk and tapped densities. The measured difference between these densities.
Compressibility
Herbal product compressibility is a crucial factor in product development and quality assurance, especially when it comes to tablets or powders. It is essential to the creation of tablets and describes a powder's capacity to reduce in volume when subjected to pressure.
Development of Formulation(14,15)
All ready standardized methanolic bark extract from Ficus racemosa Linn were used to prepared granules by wet granulation technique as follows:
- Following the addition of lactose to absorb moisture, the precisely weighed extract amounts were put through sieve number 60.
- Add enough isopropyl alcohol to the mixture together with weighed amounts of the excipients (Starch, PVPK-30, Sodium methyl paraben, and Sodium propyl paraben) to create dough mass.
- The wet mass was passed through sieve no.12.
- Granules were dried for 30 minutes at 50–55 °C in an oven.
- Dried granules were passed from sieve no. 20.
- Then granules were mixed with Lubricants (Talc, Magnesium stearate & Sodium starch glyconate).
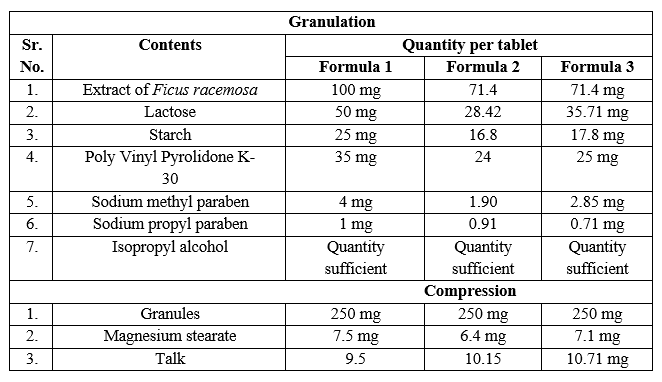
Table:1 Formula for Tablet The granules are prepared by the formula for 250 mg.
- The granules developed in this study were evaluated to ensure, that they meet the specified formulation criteria. (e.g.practicle size, dissolution rate,stability,etc,).
- Based on the results obtained from the tests it is confirmed that the granules prepared according to the formula 3 (table no.1) comply with the formulation.
- 40 tablets for 250 mg were prepared.
Compression Process:
The formulation consisted of methanolic extract of bark of ficus racemosa Linn. in defined properties. Wet granulation was performed Magnesium stearate was used as a lubricant. Tablets were compressed with a target weight of 250 mg each.
Evaluation of Tablet Formulation(15)
Tablets prepared by compression method were evaluated for General Appearance, Weight Variation, Thickness of Tablet, Hardness of Tablet, Friability, Disintegration time, dissolution test as per IP.
1.General Appearance:
Consumer acceptability, lot-to-lot uniformity control, and tablet-to-tablet uniformity are all dependent on a tablet's overall look, identity, and general elegance. Measurements of size, form, color, taste, odor, and other elements are all part of controlling overall appearance.
2.Size & Shape:
Tablets can be made in virtually any shape, although the requirements of patients and tableting machines mean that most are round, oval, or capsule-shaped.Different shapes tablets have a diverse range of sizes but generally size of tablets is in the range of about 1mm to 22 mm. FDA has recommended that size of tablet should not be more than 22 mm.Size of tablet impacts the passage of tablets through pharynx. Large sized tablets get lodged in the esophagus resulting in the dissolution of drug in esophagus which causes injury to esophagus, pain, and ulceration.
3. Organoleptic properties:
The freshly peeled and the dried stem barks were spread on a clean dry plastic sheet and investigated different organoleptic features such as condition, thickness, color, odour, taste and fracture by repeated observations using a magnifying glass (where required) and recorded.
4. Hardness:
A tablet needs to be strong enough to endure mechanical shaking during manufacturing, packing, and delivery, as well as resistant to friability. In general, hardness indicates how strong a tablet can be crushed.
5. Weight Variation test (U.S.P.):
20 tablets should be taken and weighed separately. Compute the mean weight and contrast each tablet's weight with the mean. If no more than two tablets deviate from the % restriction and if no tablet varies by more than twice the percentage limit, the tablet passes the U.S.P. test.
5. Disintegration Test (U.S.P.):
The U.S.P. apparatus for testing disintegration consists of six three-inch glass tubes with 10 mesh screens at the bottom end and an open top. One pill is put in each tube to measure the disintegration time, and the basket rack is set up in a 1-liter beaker of water. either simulated intestinal fluid or simulated gastric fluid at 37 ± 20 C so that the tablet stays 2.5 cm below the liquid's surface throughout its upward movement and does not come any closer to the beaker's bottom during its downward movement. Move the tablet-containing basket up and down at a rate of 28 to 32 cycles per minute over a distance of 5 to 6 cm. It is possible to stop the tablets from floating.
6. Dissolution Test
The United States Pharmacopoeia (USP) dissolving apparatus is essential for guaranteeing the effectiveness, safety, and quality of oral dosage forms. In order to predict the release and bioavailability of active pharmaceutical substances, it stimulates gastrointestinal conditions. This helps with formulation development and ensures uniformity between batches.To ensure that products fulfill strict quality control criteria, regulatory approval requires compliance with USP standards or dissolution testing. Dissolve testing also supports comparative evaluations and stability investigations between name-brand and generic drugs, maintaining patient safety and therapeutic dependability.
RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
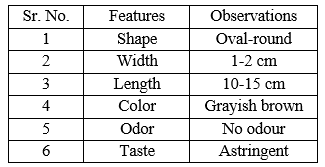
Table no. 2: Organoleptic features of Ficus racemosa Linn. Bark
Precompression Parameters:

Table 3. Precompression parameters
Evaluation of Formulation:
Around 40 tables were prepared and pharmaceutically evaluated. The results observed are as follows:
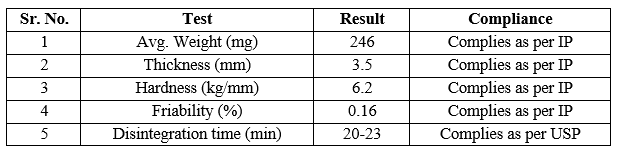
Table 3. Evaluation of Developed Tablet
In vitro dissoultion study:
The in vitro dissolution study was conducted using USP apparatus II (paddle method) in 900 mL of distilled water maintained at 37°C ± 0.5°C. Sampling was performed at predetermined time intervals over a 120-minute period.The in vitro dissolution study was conducted using USP apparatus II Drug release was quantified by measuring the concentration of the dissolution medium using UV Vis spectroscopy.
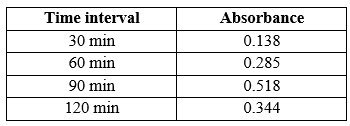
Table 4. In vitro dissoultion study
DISCUSSION
In this article indicates that Ficus racemosa Linn. bark has antipyretic properties in methanolic extract form. Ficus racemosa Linn. were used to prepared granules by wet granulation used to prepared granules by wet granulation.
The formulation consisted of methanolic extract of bark of ficus racemosa Linn. in defined properties wet granulation was performed magnesium stearate was used as lubricant. Tablets were compressed with a target weight of 250 mg each.
Ficus racemosa bark methanolic extracts were used to developed the tablet formulation. Pharmaceutical evaluations were conducted on the generated formulations in terms of general appearance, weight variations, tablet thickness, tablet hardness, friability test, disintegration time and dissolution test stable tablet were developed. The in vitro dissolution study was conducted using USP apparatus II.
CONCLUSION:
The literature survey reveals that the methanolic extract of bark of Ficus racemosa Linn. shows anti-pyretic activity. There is enough scope for the development of an effective formulation from the bark extract of Ficus racemosa Linn. for the anti-pyretic activity. Additionally, the formulation and assessment of herbal tablet formulation were the main foci of this work. One of the main conclusions is that the tablet's formulation complied with the required standards. The study was carried out under controlled laboratory conditions, which may not accurately mirror real-world scenarios. Variations in the active components of herbal compounds due to environmental factors are additional limits of this research, despite the encouraging results.
REFERENCE
- Faiyaz Ahmed & Asna Urooj traditional uses, medicinal properties, and phytopharmacology of Ficus_racemosa: A review, Pharmaceutical Biology, (2010) 48:6, 672-681.
- Leon Lachman, Herbert A. Lieberman, Joseph L. Kanig: The theory and Practice of Industrial Pharmacy, Varghese publication house1990; 3 293-373.
- Herbert A. Liberman, Martin M. Rieger and Gilbert S. Banker, pharmaceutical dosage forms: Tablets; (2013);11:34-40
- Faiyaz Ahmed & Asna Urooj traditional uses, medicinal properties, and phytopharmacology of Ficus_racemosa: A review, Pharmaceutical Biology, (2010) 48:6, 672-681.
- C. C Berg, Classification and distribution of Ficus, Experientia, 1989, 45, 605-611.
- Kaur Harbir. International Research Journal of Pharmacy. 2012, 3 (7)..
- Lieberman HA, Rieger MM, Banker GS. “Pharmaceutical Dosage Forms: Disperse System”, vol.3; (2),473-511
- Llamas, K. A. Tropical flowering plants: a guide to identification and cultivation/text and photography by Kirsten Albrecht Llamas, (2003) (4)
- The Wealth of India, Vol- IV, page 35, Publications and information Directorate, CSIR, New Delhi 1988 v6 2018
- Lt.Colonel K.R.Kirthikar B.D.Basu,Indian Medicinal plants-Published by Bishen Singh Mahendra Pal Singh,Dehradun, 2018;110:220-245
- A.C. Dutta, A class book of Botany Published by Oxford University Press, New Delhi,2018;37:70-80
- Chaudhary and Tawar. Pharmacognostic and phytopharmacological overview on Bombax cebia. Systematic Reviews in Pharmacy 2019;10 (1): 20-25
- Vaithyarathnanm K.S.Murugesa Mudaliar, Gunapadam mooligai vaguppu,Published by Dept of Indian medicine and Homeopathy, Ch 2003;106:110- 120
- Karthick Chandra Bose M.B., Pharmacopoeia Indica Published by Bishen Singh Mahendra Pal Singh, Dehradun,1986;6: 96-110
- S. Vedavathy, D.N. Rao Herbal folk medicine of tirumala and tirupati region of Chittoor district, Andhra Pradesh Fitoterapia,1995;32:167-171
- Bhattacharya S, Zaman MK. Pharmacognostical evaluation of Ficus racemosa bark. Intl J Pharm Tech Res. 2009;1:292-8.
- Chaudhary PH, Khadabadi SS. Bombax cebia Linn.: Pharmacognosy, Ethonobotany and Phyto-pharmacology.Pharmacognosy Communications 2012; 2 (3): 2-9
- Kar A, Choudhary BK, Bandyopadhyay NG. Comparative evaluation of hypoglycaemic activity of some Indian medicinal plants in alloxan diabetic rats. Journal of ethnopharmacology. 2003 Jan 1;84:105-8.
- Chaudhary PH. et al. Pharmacognostical and phytochemic al studies on root of Bombax cebia Linn. Journal of Pharmacy and pharmacognosy research 2014; 2(6): 172-182.

 Tejaswi Kohale*
Tejaswi Kohale*
 Gauri Raut
Gauri Raut










 10.5281/zenodo.13132221
10.5281/zenodo.13132221