Abstract
One of the most common and important treatments for cleaning hair is shampooing. Shampoos are primarily used for cleaning hair and the scalp. Nowadays, shampoos are receiving much more attention from consumers compared to soaps. Shampooing is a technique that rinses off the sebum or grease produced by the sebaceous glands, making the hair and scalp dirt and oilfree. In the present scenario, herbal shampoos are considered to perform better and be safer than synthetic shampoos, and they are also gaining more attention from consumers. The main objective of the study was to evaluate synthetic and herbal shampoos. Synthetic shampoos (Dove, Pantene, Clinic Plus, Sun Silk, L'Oréal Paris) and herbal shampoos (Vatika, Kesh King, Chick, Indulekha, Himalaya) were evaluated based on physical appearance, cleansing action, dirt dispersion, wetting action, foaming ability, pH, surface tension, detergency ability, skin sensitization test, eye irritation, and stability studies. The resulting pH of all the formulations was in the range of 7 to 8.5. The evaluation reveals that some have good foaming ability while others do not. Foaming ability should not affect cleansing action. The cleansing action of shampoo should be such that it easily removes grease and dirt from hair. In conclusion, all shampoos are of good quality and can be used safely and effectively by anyone.
Keywords
herbal shampoo, synthetic shampoo, cleansing action, foaming ability
Introduction
In the early days, shampoo was primarily used as an effective cleansing agent for hair and scalp.
However, in the present scenario, shampoos can perform many more functions. Modern shampoos make hair easy to comb, lustrous, radiant, shiny, and smooth. They serve as both cleaning aids and hair care products, effectively removing dirt, oil, environmental pollutants, skin particles, dandruff, and other contaminants from hair. The main focus is on removing unwanted build-up without stripping sebum, thereby making hair manageable. Previously, soap-based shampoos were of special interest, but studies proved that soap did not produce good lather and left an unwanted residual layer on hair that was difficult to rinse off. With advancements in modern shampoo formulations, soap-based shampoos have been replaced by products that offer both cleaning and conditioning capabilities. (1)
Sebum produced on the hair and scalp is excreted from sebaceous glands located within hair follicles. Since sebum cannot be removed by water alone, as oil and water do not mix well, cleansing agents are necessary for its removal. The primary cleansing agents are anionic surfactants with great lathering power that rinse off easily. The most commonly used surfactant is sodium lauryl sulfate, with varying concentrations from brand to brand. Cheaper brands typically have higher concentrations, while more expensive brands have lower concentrations of surfactants. (1,2)
The evaluation of shampoo comprises quality control tests, including visual assessment and physicochemical controls such as pH, density, and viscosity.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Shampoo Selection and Collection: Different marketed synthetic shampoos (Dove Hair Fall Rescue, Sunsilk Black Shine Shampoo, L'Oréal Paris, Pantene, Clinic Plus) and herbal shampoos (Indulekha Bringha Hair Cleanser, Himalaya Hair Fall Control Bhringaraja Shampoo, Kesh King Scalp and Hair Medicine, Chik Protein Solution Thick and Glossy Black Shampoo, Dabur Vatika Health Shampoo) were selected for the study which were collected from the local market of Bhopal, Madhya Pradesh.
Evaluation parameters of shampoo
Different formulations of shampoo were evaluated using various parameters:
- Physical Appearance And Visual Inspection The different formulations were evaluated in terms of their clarity, foam-producing ability, and fluidity. (1)
- Determination of pH The pH of a 10% shampoo solution in distilled water was determined at room temperature (25°C). (1)
- Determination of Percentage of Solid Contents A clean, dry evaporating dish was weighed, and 4 grams of shampoo were added. The dish and shampoo were weighed together. The exact weight of the shampoo was noted before placing the dish on a hot plate until the liquid portion evaporated. The weight of the remaining solids after drying was calculated. (1)
- Dirt Dispersion Two drops of shampoo were added to a large test tube, followed by one drop of ink. The test tube was fitted with a stopcock and shaken ten times. The amount of ink in the foam was estimated and categorized as none, light, moderate, or heavy. (1)
- Wetting Time A canvas disc of 3.5 cm diameter with an average weight of 0.34 g was floated on the surface of a 1% w/v shampoo solution. A stopwatch was started, and the time required for the disc to begin sinking was measured and noted as the wetting time.(1)
- Foam Volume About 20 ml of shampoo solution was taken in a measuring cylinder fitted with a stopcock and shaken for 10 seconds. Foam volume was measured immediately, after 3 minutes, and after 6 minutes.(1)
- Cleansing Action – Five grams of wool yarn were placed in grease, and then placed in 200 ml of water containing 1 gram of shampoo in a flask. The temperature of the water was maintained at 35°C. The flask was shaken for 4 minutes at a rate of 50 times per minute. The solution was then removed, and the sample was taken out, dried, and weighed. The amount of grease removed was calculated using the equation (1):
DP = 100 [1 – T/C] ………………..(1)
DP - % of detergency power
C – weight of sebum in control sample
T – weight of sebum in test sample (3)
- Surface Tension – Measurements were carried out with a 10% shampoo dilution in distilled water at room temperature. Thoroughly clean the stalagmometer using chromic acid and purified water because surface tension is highly affected by grease or other lubricants. The data were calculated using the equation (2):
R2 = [ W3- W1] n1 / [W2-W1] n2 * R1……(2)
W1 = weight of empty beaker
W2 = weight of beaker with distilled water
W3 = weight of beaker with shampoo solution
N1 = number of drops of distilled water
N2 = number of drops of shampoo solution
R1 = Surface tension of distilled water at room temperature
R2 = Surface tension of shampoo solution (3)
- Rheological Evaluation – The viscosity of the shampoo was determined using a Brookfield viscometer set at different spindle speeds from 0.3 to 10 rpm. The viscosity of the shampoos was measured using spindle T95. The temperature and sample container size were kept constant during the study. (1)



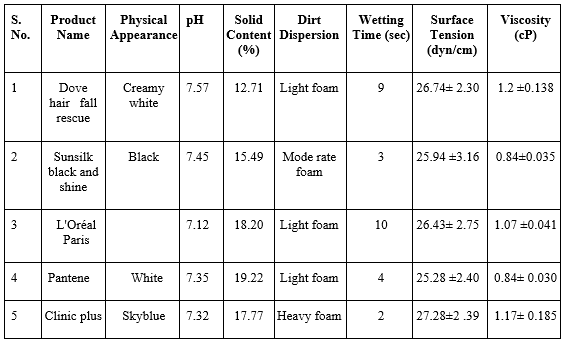
Table 1. Evaluation Parameter Of Synthetic Shampoo
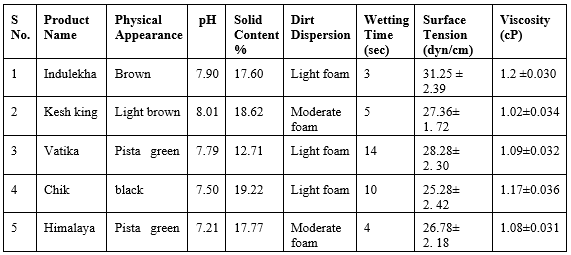
Table 2. Evaluation Parameters Of Herbal Shampoos
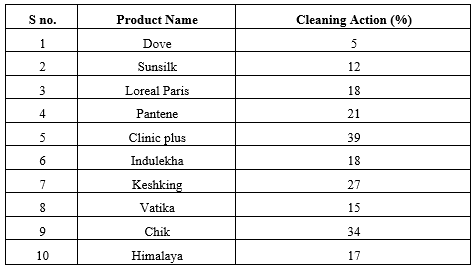
Table 3. Cleansing Action Of Synthetic Shampoos And Herbal Shampoos

Figure 1. Foaming Capacity Of Synthetic Shampoo

Figure 2. Foaming Capacity Of Herbal Shampoo
RESULT AND DISCUSSION
Different marketed formulations of shampoos were evaluated for their physical appearance visually and consistency. The evaluation studies revealed that all the formulations had a pH range of 7.12-8.01, indicating a neutral pH that influences hair quality and tolerance at the skin and eye levels. Substances that were too alkaline caused the hair cuticle to open, while those that were too acidic caused the cuticle to contract, making it prone to infection; hence, the pH was adjusted to neutral. The viscosity of all the formulations was such that they were easily pourable when shaken due to their pseudoplastic nature, with higher viscosity indicating better shampoo quality. Among synthetic shampoos, Dove exhibited good viscosity, and among herbal shampoos, Indulekha had good viscosity; between Dove and Indulekha, Dove had a higher viscosity value. The foam quality of Chik and Kesh King was found to be high as they produced thick foam among all formulations, shown in graph 1. Shampoos that caused ink to concentrate in the foam were considered of poor quality, as dirt should stay in water, not in foam, to be easily rinsed away and prevent redeposition on the hair. Among synthetic shampoos, Dove, L'Oreal Paris, and Pantene exhibited light foam, while among herbal shampoos, Indulekha, Vatika, and Chick had light foam, indicating good formulations where dirt would not stay in the foam. Shampoos with too many solids can be hard to work into the hair or wash out; Pantene and Chik showed high values of percent solid content, making them easy to wash out. Surface tension measurement was done to assess the cleansing ability of shampoo, where reduced surface tension affected cleansing ability by facilitating the spread of aqueous solution, increasing its wetting ability, or removing environmental dirt from hair by keeping it in suspension. Wetting time for all formulations was found to be within 2-14 seconds, indicating increased wettability with reduced wetting time. Cleansing ability tests were performed on all formulations, with Clinic Plus and Chik showing good cleaning action according to our study.
CONCLUSION
The study aimed to assess the efficiency of marketed synthetic and herbal shampoo products and identify the best formulation available for hair cleaning purposes, considering both effectiveness and potential side effects. Despite herbal shampoos demonstrating better performance and safety profiles, synthetic shampoos remain more popular among consumers in the current scenario. Numerous shampoo products are available in the market, each with its own merits and drawbacks that can be beneficial or harmful to the population. It appears challenging for herbal shampoos to gain widespread popularity unless there is a shift in consumer expectations, emphasizing safety and efficacy. Formulators must take an active role in educating consumers about the potential harmful effects of synthetic detergents and chemical additives in shampoos. Changing consumer perceptions about what constitutes a good shampoo is crucial, and this responsibility primarily rests with the formulators.
REFERENCE
- Deeksha, Rishabha Malviya and Pramod Kumar Sharma, Evaluation of Marketed Shampoo (Synthetic and Natural) for Their Hair Cleansing, Department of Pharmacy, School Of Medical And Allied Sciences Galgotias University, Plot No.2, Global Journal of Pharmacology 8 (4): 490-493, 2014.
- Ashok Kumar1* and Rakesh Roshan Mali2 Evaluation Of Prepared Shampoo Formulations and to compare formulated shampoo with marketed Shampoos3(1), 59-62., 1. Department of Biotechnology, Himachal Institute of Life Sciences, Paonta Sahib, Dist- Sirmour -173025 (HP) INDIA, 2. Dept of Pharmaceutics, Himachal Institute of Pharmacy, Paonta Sahib Dist- Sirmour-173025 (HP) INDIA , Volume 3, Issue 1, July – August 2010; Article 025 ISSN 0976 – 044X.
- Richa madhu sharma*, kinjal shah, janki patel, evaluation of prepared herbal shampoo formulations and to compare formulated shampoo with marketed shampoos , B.Pharmacy College of Rampura, Kakanpur, Godhra, Gujarat 389001, India., Vol 3, Issue 4, 2011 ,ISSN- 0975-1491.
- Sharma, P. P. "Cosmetic Formulation Manufacturing and Quality Control." 3d ed., Vandana Publication, Delhi, 644-647.
- Hadkar, U. B., & Ravinder, R. P. "ijper." (2009) 43: 187-191.
- Gaud, R. S., & Gupta, G. D. "Practical Physical Pharmacy." 1 ed., C.B.S. Publisher and Distributor, New Delhi, 81-105.
- Barel, A. O., Payee, M., & Maibach, H. I. "Handbook of Cosmetic Science and Technology." (2001) 423: 583- 588,773-775.
- International Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences Review and Research." Available online at www.globalresearchonline.net.
- Mainkar, A. R., & Jolly, C. I. "International Journal of Cosmetic Science." (2001) 23(1): 59-62


 Nupoor lokhande *
Nupoor lokhande *








 10.5281/zenodo.11669646
10.5281/zenodo.11669646