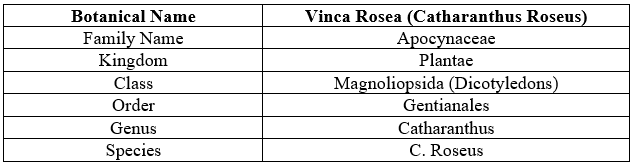
The lovely flowering perennial herb Catharanthus roseus is a year-round decorative plant. We call it Madagascar periwinkle. This plant is grown in a warm climate and is known to produce terpenoids, specifically indole alkaloids. In addition to being high in alkaloids, it also contains significant amounts of organic acids, phenolic compounds, and amino acids with pharmacological value throughout. Traditionally, this herbal plant is a boon to provide preventive action for many deadly health problems being confronted by humans by their direct or indirect usage in skin disease, high blood pressure, rheumatism, menstrual disorders, indigestion etc. Traditional medicine has traditionally used vinca rosea, especially for the treatment of diabetes. Researchers found that the plant contains alkaloids that have anti-cancer potential in the 1950s. Vinblastine, which was first used to treat Hodgkin's disease, was the first alkaloid to be identified. Vinblastine and vincristine, two significant alkaloids derived from C. roseus, have demonstrated encouraging results against a range of cancers, including leukaemia and Hodgkin's lymphoma. Vinblastine prevents microtubules from developing during cell division, which disrupts the cell cycle.
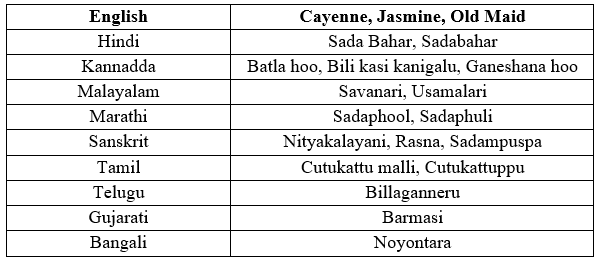
Catharanthus roseus (Vinca rosea), Geographical, Pharmacological, Anticancer
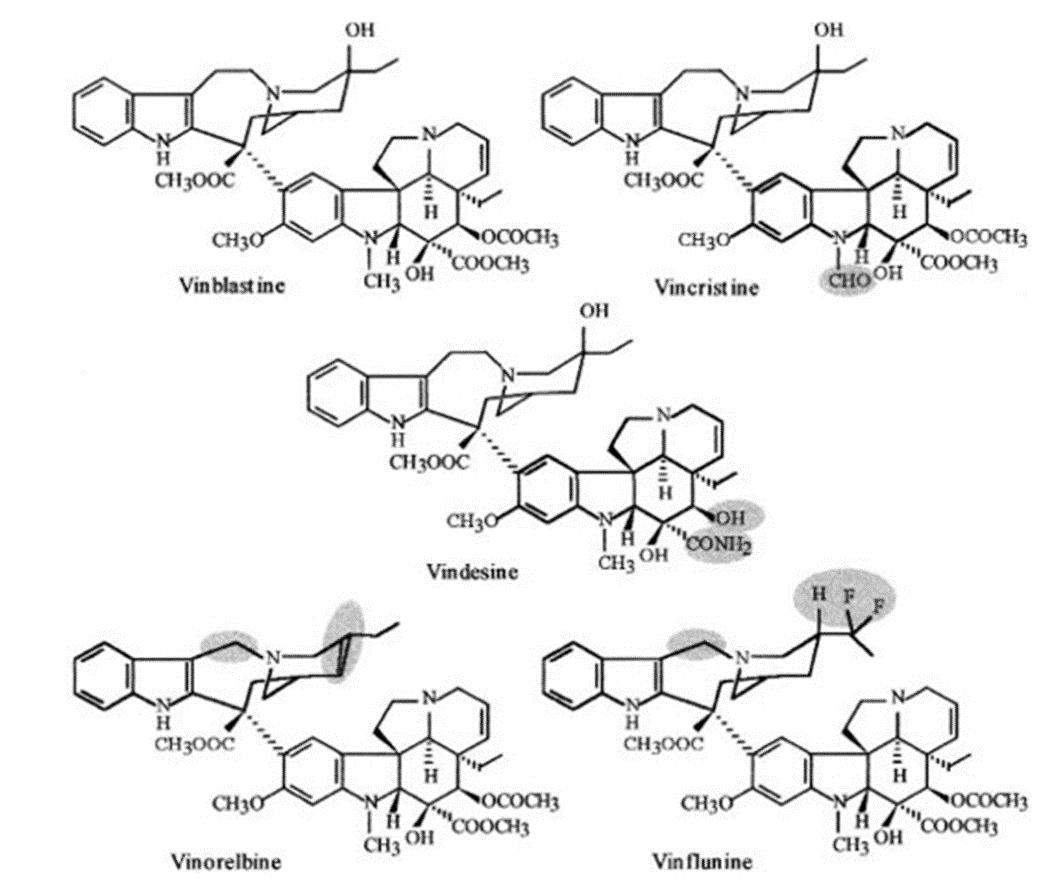
Vincristine: Like vinblastine, vincristine is a potent microtubule inhibitor that exhibits significant anticancer properties. It disrupts the process of mitosis, halting cell division and triggering programmed cell death in cancer cells. Vincristine is frequently prescribed for the management of hematological malignancies, such as acute lymphoblastic leukemia and Hodgkin's lymphoma.
Vinflunine: Vinflunine is a recently developed vinca alkaloid that demonstrates impressive antitumor properties by interfering with the dynamics of microtubules and impeding the growth of cells. It has demonstrated potential in the treatment of advanced urothelial carcinoma, providing a viable therapeutic choice for individuals with metastatic bladder cancer.
Vindesine: Vindesine is a vinca alkaloid known for its powerful anticancer properties. It functions by attaching to tubulin and preventing the formation of microtubules, leading to the halt of cell division and the induction of programmed cell death in cancer cells. Vindesine is commonly prescribed to treat a range of malignancies, such as lymphoma, lung cancer, and breast cancer (6,7).
Other Alkaloids: Aside from vinca alkaloids, Catharanthus roseus possesses a wide range of alkaloids that may have significant pharmacological properties. Some of the compounds in question are catharanthine, ajmalicine, serpentine, and reserpine, among others. The alkaloids found in this plant are believed to play a role in its medicinal properties, which include potential benefits for hypertension, heart rhythm disorders, and blood sugar regulation. The presence of these potentially active chemical constituents in Catharanthus roseus highlights its importance as a medicinal plant with a wide range of pharmacological activities. Investigation into the isolation, characterization, and therapeutic applications of these compounds is making significant progress, presenting exciting possibilities for the creation of new medications to combat a range of illnesses, with a particular focus on cancer (8).
History
The history of Catharanthus roseus, commonly known as the Madagascar periwinkle, is closely connected to the development of traditional medicine and modern pharmacology. Indigenous cultures in Madagascar have a deep understanding of the plant's medicinal properties and have been using its different parts to effectively treat a diverse array of ailments for generations (9).
- Indigenous Use: The Indigenous Malagasy people were pioneers in recognizing the healing properties of Catharanthus roseus. They utilized extracts from the plant to alleviate symptoms of diabetes, high blood pressure, and malaria. Practitioners of traditional medicine prepared potions using different parts of the Madagascar periwinkle plant, which were then given to individuals seeking relief from a range of ailments.
- European Discovery: The medicinal properties of Catharanthus roseus garnered interest beyond Madagascar in the 19th century when European explorers and botanists came across the plant during expeditions to the island. They studied the way the native people utilized the plant and started investigating its potential in the field of pharmacology.
Vinca Alkaloid Discovery: In the 1950s, scientists made a significant discovery regarding the therapeutic potential of Catharanthus roseus. They successfully isolated and identified the first vinca alkaloids, vinblastine and vincristine, from this plant. The discovery of these alkaloids has had a significant impact on the field of cancer chemotherapy, as they have been shown to possess powerful anticancer properties. Their groundbreaking finding represented a breakthrough in the field of medical research, specifically in the realm of treating different types of cancer such as leukemia, lymphoma, and solid tumors (10,11).
Medical Advancements: After the discovery of vinca alkaloids, researchers dedicated significant efforts to understanding how these compounds work, how they are processed in the body, and how they can be used in clinical settings. Vinblastine and vincristine emerged in the 1960s and swiftly became crucial elements of chemotherapy treatments for various types of cancer. Throughout the years, more vinca alkaloids have been discovered and developed for use in cancer therapy, including vinflunine and vindesine.
Pharmaceutical Production: The growing need for vinca alkaloids led to the creation of more effective techniques for extracting and synthesizing them on a large scale. Pharmaceutical companies have set up production facilities to manufacture vinblastine and vincristine, guaranteeing a consistent supply of these crucial anticancer medications for patients across the globe.
Ongoing Research: Despite the extensive research conducted on Catharanthus roseus and vinca alkaloids, there continues to be a strong scientific interest in the plant and its pharmacological constituents. Continual research is being conducted to discover fresh uses for vinca alkaloids, delve into their modes of operation, and create innovative variations that offer improved effectiveness and decreased toxicity.The history of Catharanthus roseus and vinca alkaloids showcases the fascinating convergence of traditional wisdom, botanical exploration, and contemporary pharmaceutical research. Throughout history, the Madagascar periwinkle has made significant contributions to the field of pharmacology and medicine, spanning from ancient practices to modern cancer therapy (12).
Uses
In addition, recent pharmacological research has discovered specific therapeutic applications for the plant's bioactive components, specifically vinca alkaloids. Here are some of the main applications of Catharanthus roseus:
Cancer Treatment: One of the most widely recognized uses of Catharanthus roseus is in the field of cancer therapy. The vinca alkaloids vinblastine and vincristine, derived from the plant, are highly effective cytotoxic agents that disrupt microtubule formation, leading to the inhibition of cell division. They are commonly prescribed for the treatment of different types of cancers, such as leukemia, lymphoma, breast cancer, lung cancer, and bladder cancer. Additionally, the plant contains vinflunine and vindesine, which have demonstrated effectiveness in treating specific forms of cancer (13).
Antidiabetic Activity: There is evidence to suggest that Catharanthus roseus may have potential antidiabetic properties. Compounds derived from the plant have shown promising results in animal studies, suggesting their potential to assist in the management of diabetes by reducing blood sugar levels. Additional research is necessary to better understand the mechanisms behind this activity and assess its potential therapeutic significance in humans.
Traditional Medicine: In traditional medicine systems, Catharanthus roseus has been utilized for centuries to address a wide range of health issues, such as high blood pressure, malaria, and hemorrhages. The plant's leaves, stems, and roots have been traditionally used to treat fever, dysentery, menstrual disorders, and skin infections. Traditional healers in Madagascar and other regions still rely on Catharanthus roseus in their herbal remedies for a range of health issues.
Ornamental Plant: In addition to its medicinal applications, Catharanthus roseus is highly regarded for its aesthetic appeal. The plant's vibrant flowers, available in various shades have made it a popular choice for gardens, parks, and landscaping. Its adaptability to tropical and subtropical climates, along with its extended period of blooming, makes it a desirable choice for outdoor areas (14,15).
Source of Phytochemicals: Catharanthus roseus is an important source of phytochemicals that have potential pharmacological applications. Furthermore, the plant is enriched with various bioactive compounds like flavonoids, terpenoids, and tannins, which are believed to possess antioxidant, antimicrobial, and anti-inflammatory properties. Extensive research is being conducted on these phytochemicals to explore their potential therapeutic benefits in a range of diseases. In general, Catharanthus roseus has a wide range of applications, including cancer treatment, traditional medicine, ornamental horticulture, and phytochemical research. The diverse pharmacological properties of this subject continue to generate interest and exploration in both traditional and modern medical practices (16).
PHARMACOLOGICAL ACTIVITIES
Catharanthus roseus, also known as the Madagascar periwinkle, showcases a broad spectrum of pharmacological activities due to its rich variety of bioactive compounds, specifically vinca alkaloids. The plant's pharmacological activities have been extensively researched due to their significant contribution to its medicinal value. Here are some of the main pharmacological activities linked to Catharanthus roseus:
Antidiabetic Activity:
Catharanthus roseus, also known as the Madagascar periwinkle, has demonstrated significant potential in the treatment of diabetes. Numerous studies have highlighted its effectiveness in reducing blood sugar levels. The presence of bioactive compounds, such as alkaloids and flavonoids, in this activity, has been found to have positive effects on glucose metabolism and insulin sensitivity. Here are some important mechanisms that contribute to the antidiabetic activity of Catharanthus roseus:
Insulin Secretion Stimulation: Compounds derived from Catharanthus roseus have been discovered to enhance the production of insulin in pancreatic beta cells. These compounds work to improve blood glucose regulation and enhance glucose utilization by peripheral tissues by enhancing insulin release. This mechanism is especially advantageous for individuals with type 2 diabetes who may experience di?culties with insulin secretion (16).
Glucose Uptake Enhancement: Research has demonstrated that extracts from Catharanthus roseus can enhance glucose uptake in peripheral tissues, including skeletal muscle and adipose tissue. The increased glucose uptake is facilitated by the activation of glucose transporter proteins, like GLUT4, that aid in the cellular absorption of glucose. By enhancing glucose utilization, Catharanthus roseus may potentially contribute to reducing blood glucose levels and enhancing glycemic control in individuals with diabetes.
Glycogen Synthesis Promotion: Glycogen serves as a storage form of glucose in the liver and skeletal muscles, and its synthesis plays a vital role in maintaining blood glucose levels. The compounds found in Catharanthus roseus have been found to have a positive effect on glycogen synthesis in hepatocytes and muscle cells. This leads to increased glucose storage and a reduction in hyperglycemia. This phenomenon plays a role in enhancing glucose regulation in individuals with diabetes.
Antioxidant Activity: The role of oxidative stress in the development and progression of complications related to diabetes is quite significant. Catharanthus roseus is rich in antioxidants like flavonoids and phenolic compounds. These powerful substances help to neutralize harmful free radicals and protect pancreatic beta cells and peripheral tissues from oxidative damage. Through its ability to reduce oxidative stress, Catharanthus roseus has the potential to safeguard beta cell function and insulin sensitivity, which can help refrain from diabetic complications (17,18).
Anti-inflammatory Effects: There is a strong connection between chronic inflammation, insulin resistance, and beta cell dysfunction, which all play a role in the development of type 2 diabetes. Catharanthus roseus demonstrates the ability to reduce inflammation by blocking the production of substances that promote inflammation. Through its anti-inflammatory properties, Catharanthus roseus has the potential to enhance insulin sensitivity and regulate blood sugar levels in individuals with diabetes.
Overall, Catharanthus roseus shows potential as a natural therapeutic agent for managing diabetes, thanks to its diverse antidiabetic properties. Additional research is necessary to uncover the precise bioactive compounds accountable for these effects and to assess their effectiveness and safety in clinical environments. Integrating interventions based on Catharanthus roseus into diabetes management strategies may provide innovative ways to enhance the health outcomes of individuals with diabetes.
Antimicrobial Activity
Catharanthus roseus, also known as the Madagascar periwinkle, has remarkable antimicrobial properties due to its bioactive components, such as alkaloids, flavonoids, and terpenoids. These compounds have shown significant inhibitory effects against a diverse array of microbial pathogens, encompassing bacteria, fungi, and protozoa. Here are some important factors to consider regarding the antimicrobial activity of Catharanthus roseus (19).
Antibacterial Activity: Extracts from Catharanthus roseus have shown remarkable antibacterial activity against a range of pathogenic bacteria. Research has indicated that there are inhibitory effects against both Gram-positive bacteria, like Staphylococcus aureus and Bacillus subtilis, and Gram-negative bacteria, such as Escherichia coli and Pseudomonas aeruginosa. The antimicrobial action is due to the alkaloids found in the plant, which disrupt bacterial cell membranes, hinder protein synthesis, and impede bacterial DNA replication.
Antifungal Activity: Extracts from Catharanthus roseus have also shown antifungal properties against various fungal pathogens. They have shown e?cacy against yeasts like Candida albicans, as well as filamentous fungi such as Aspergillus fumigatus and Fusarium solani. The antifungal activity is due to the presence of alkaloids and other secondary metabolites, which disrupt fungal cell membranes, inhibit ergosterol biosynthesis, and interfere with fungal cell wall synthesis.
Antiprotozoal Activity: Compounds derived from Catharanthus roseus have demonstrated e?cacy against various protozoan parasites, such as the Plasmodium species responsible for malaria and the Leishmania species that cause leishmaniasis. These compounds have been found to have a significant impact on the cells of protozoa, disrupting their metabolic processes, ability to reproduce, and overall survival. Catharanthus roseus has shown promising antiprotozoal activity, suggesting its potential as a source for the development of new antiparasitic drugs. Mechanisms of Action: The antimicrobial activity of Catharanthus roseus is achieved through various mechanisms. These include the disruption of microbial cell membranes, inhibition of crucial enzymes and metabolic pathways, and the induction of oxidative stress. Alkaloids like vinblastine and vincristine can attach to microtubules found in bacterial and fungal cells. This attachment disrupts the cells' structural integrity and prevents them from dividing. In addition, the plant contains flavonoids and terpenoids that have antioxidant properties. These properties can help protect against oxidative damage caused by microbes (20,21).
Synergistic Effects: Combining Catharanthus roseus extracts with conventional antimicrobial agents can enhance their effectiveness against drug-resistant pathogens, potentially leading to synergistic effects. This collaboration stems from the harmonious interplay of the mechanisms of action and biochemical interactions between the plant compounds and conventional antibiotics or antifungals. These powerful combinations have the potential to effectively fight against drug-resistant infections and enhance treatment results.
Overall, Catharanthus roseus has demonstrated strong antimicrobial properties against various microorganisms, highlighting its potential as a valuable natural source of antimicrobial agents. The wide range of bioactive compounds found in the plant contribute to its extensive antimicrobial effects, which have potential applications in treating infectious diseases and creating new antimicrobial therapies. Additional research is necessary to better understand the precise ways in which Catharanthus roseus compounds work and to investigate their potential in treating microbial infections.
Wound Healing Property:
Catharanthus roseus, also known as the Madagascar periwinkle, has shown remarkable wound healing properties, making it a valuable natural remedy for a variety of wounds and injuries. The plant's remarkable capacity to enhance wound healing is credited to its abundant phytochemical composition, which encompasses alkaloids, flavonoids, and terpenoids. These compounds possess a wide range of biological activities that support the wound-healing process. Here are some important aspects of Catharanthus roses' wound healing properties (22).
Anti-inflammatory Effects: The role of inflammation in the wound healing process is vital as it helps in the repair and regeneration of tissues. Catharanthus roseus possesses bioactive compounds that possess anti- inflammatory properties, aiding in the reduction of inflammation at the site of the wound. Through the reduction of inflammatory mediators and cytokines, the plant extracts contribute to the creation of an optimal environment for e?cient wound healing.
Antioxidant Activity: The presence of oxidative stress can hinder the wound healing process by inducing harm to cells and prolonging the regeneration of tissues. The compounds found in Catharanthus roseus, such as flavonoids and phenolic compounds, have been shown to have antioxidant properties. These properties help to neutralize free radicals and provide protection against oxidative damage to cells. Through the reduction of oxidative stress, the plant extracts aid in the body's inherent healing processes and promote tissue repair.
Promotion of Collagen Synthesis: Collagen is a vital protein found in the extracellular matrix, which is responsible for supporting tissues and facilitating wound healing. Research has demonstrated that extracts from Catharanthus roseus can effectively enhance collagen synthesis in fibroblasts, which are the primary cells involved in collagen production. Enhanced collagen production expedites the development of granulation tissue and promotes wound contraction, resulting in expedited wound closure and the formation of scars.
Angiogenic Effects: Su?cient blood flow is crucial for ensuring the delivery of oxygen and nutrients to the wound area, which in turn promotes tissue regeneration. The compounds derived from Catharanthus roseus have been discovered to stimulate angiogenesis, which is the process of forming new blood vessels near the site of a wound. This improved blood flow enhances tissue perfusion and speeds up the healing process by supplying the essential resources for cellular proliferation and migration (23).
Antimicrobial Activity: Catharanthus roseus demonstrates antimicrobial properties that aid in the prevention of wound infections and support a sterile wound environment that is favorable for healing. The plant's bioactive compounds have the ability to hinder the growth of harmful bacteria and fungi, which can help lower the chances of wound contamination and potential complications. Through the maintenance of wound cleanliness, extracts from Catharanthus roseus aid in bolstering the body's immune response and promoting unhindered wound healing.
Pain Relief: Catharanthus roseus may also offer pain-relieving effects, helping to ease discomfort and soreness caused by wounds and injuries. Through the modulation of pain perception and the reduction of inflammatory pain mediators, the plant extracts provide symptomatic relief and enhance the overall process of wound healing. Overall, Catharanthus roseus demonstrates a wide range of wound healing properties that can be attributed to its various effects, including anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, collagen-stimulating, angiogenic, antimicrobial, and analgesic effects. The valuable properties of this natural remedy make it highly effective in promoting the healing of different types of wounds, such as cuts, abrasions, burns, and ulcers. Integrating formulations derived from Catharanthus roseus into wound care regimens has the potential to significantly improve the healing process and enhance clinical outcomes for patients with both acute and chronic wounds.
Anti-helminthic Activity:
Catharanthus roseus, also known as the Madagascar periwinkle, has shown promising anti-helminthic properties, which has attracted attention in the field of natural medicine for treating parasitic infections. Although the research on this particular aspect of the plant's pharmacology is still developing, several studies have indicated that compounds in Catharanthus roseus may have the potential to combat helminthic parasites. Here are some important points regarding the anti-helminthic activity of Catharanthus roseus (24).
In vitro Studies: In laboratory studies, extracts from Catharanthus roseus have demonstrated encouraging outcomes in suppressing the growth and reproduction of different helminthic parasites. Various types of parasites can be found in the human body, including intestinal worms and parasitic flatworms. The in vitro findings indicate that Catharanthus roseus may hold promise as a natural treatment for helminthic infections.
Mechanisms of Action: The mechanisms responsible for the anti- helminthic activity of Catharanthus roseus are not yet fully comprehended, but it is thought to involve various pathways. One suggested mechanism involves the disturbance of the parasites' neuromuscular function, resulting in paralysis and subsequent expulsion from the host's body. In addition, specific compounds found in Catharanthus roseus have the potential to disrupt the metabolism, reproduction, or survival mechanisms of parasites, thus enhancing their anti-helminthic effects.
Synergistic Effects: Combining Catharanthus roseus extracts with conventional anti-helminthic drugs may enhance their effectiveness against parasitic infections, potentially leading to synergistic effects. This synergy arises from the complementary mechanisms of action and biochemical interactions between the plant compounds and synthetic anthelmintics. These combination therapies show potential in fighting drug-resistant helminthic parasites and enhancing treatment results for those affected (15,25).
Phytochemical Composition: Catharanthus roseus possesses a wide range of bioactive compounds, such as alkaloids, flavonoids, terpenoids, and phenolic compounds. These compounds are believed to play a role in its anti-helminthic activity. Out of all these compounds, vinca alkaloids like vinblastine and vincristine have caught the attention of researchers because of their unique pharmacological properties. However, more research is needed to determine their exact role in anti-helminthic activity. Ultimately, further investigation is necessary to completely understand the anti- helminthic properties of Catharanthus roseus and how it works. However, initial findings indicate that it may hold promise as a natural solution for combating parasitic infections. Additional investigation into the phytochemical composition and pharmacological effects of the plant could potentially result in the creation of innovative anti-helminthic treatments derived from Catharanthus roseus (26).
Memory Enhancement Activity:
Although the Madagascar periwinkle, scientifically known as Catharanthus roseus, is not typically linked to improving memory, its cognitive advantages have sparked academic curiosity in recent times. Studies indicate that specific compounds discovered in Catharanthus roseus may possess neuroprotective qualities and could potentially aid in improving memory. Here are some important points about the memory enhancement activity of Catharanthus roseus:
Neuroprotective Effects: Compounds found in Catharanthus roseus, including alkaloids and flavonoids, have demonstrated neuroprotective properties in preclinical studies. These compounds have shown promising results in safeguarding neurons against oxidative stress, inflammation, and neurotoxicity, all of which are linked to cognitive decline and memory impairment. Preserving neuronal function and integrity, Catharanthus roseus may indirectly contribute to supporting cognitive function and memory retention (27).
Enhancement of Neurotransmission: Several alkaloids discovered in Catharanthus roseus, such as vincristine and vinblastine, have been the subject of research regarding their impact on neurotransmission. Although primarily recognized for their anti-cancer effects, these alkaloids have demonstrated the ability to influence neurotransmitter systems in the brain, specifically acetylcholine and dopamine, which play crucial roles in cognitive functions such as learning and memory. Through the enhancement of neurotransmission, compounds found in Catharanthus roseus have the potential to enhance cognitive function and improve memory performance.
Antioxidant Activity: Age-related cognitive decline and neurodegenerative disorders like Alzheimer's disease are often associated with oxidative stress. Catharanthus roseus possesses powerful antioxidants that effectively combat free radicals, thereby minimizing oxidative harm to brain cells. Through its ability to shield neurons from oxidative stress, the plant has the potential to safeguard cognitive function and hinder memory decline linked to aging and neurodegeneration.
Anti-inflammatory Properties: Long-term inflammation in the brain can lead to problems with thinking and memory. The presence of flavonoids and other bioactive compounds in Catharanthus roseus contributes to its anti-inflammatory properties, which aid in the reduction of neuroinflammation and neurodegeneration. Through the modulation of certain pathways in the brain, Catharanthus roseus has the potential to contribute to cognitive well-being and enhance memory capabilities.
Animal Studies: Although there is limited research on humans, studies conducted on animals have yielded some evidence that suggests the potential memory-enhancing effects of Catharanthus roseus. Studies involving the use of Catharanthus roseus extracts or isolated compounds on rodent models have demonstrated significant enhancements in memory-related tasks, including spatial learning and memory retention. These findings indicate the possible cognitive advantages of Catharanthus roseus, although additional research is required to validate these effects in humans. Ultimately, further investigation is needed to completely understand the memory-boosting effects of Catharanthus roseus and the mechanisms behind it. However, initial findings indicate its promising potential as a natural cognitive enhancer. The potential of Catharanthus roseus compounds in supporting cognitive function and memory retention is worth exploring due to their neuroprotective, antioxidant, and anti-inflammatory properties (28).
ANTI-CANCER ACTIVITY (Objective)
Introduction:
Cancer continues to be a significant global cause of death, prompting the need to investigate new treatment methods to fight against this destructive illness. In this context, natural products have become a focal point for researchers due to their potential as anti-cancer agents. They provide a wide range of chemical structures and mechanisms of action, making them a promising area of study. One natural source that has attracted considerable attention is Catharanthus roseus, also known as the Madagascar periwinkle, due to its impressive anti-cancer properties. Hailing from Madagascar, Catharanthus roseus is a member of the Apocynaceae family and boasts a rich heritage of medicinal application in traditional healing customs. Nevertheless, the breakthrough came with the identification of vinca alkaloids, which are powerful cytotoxic compounds extracted from Catharanthus roseus. This propelled the plant to the forefront of cancer treatment. Vinca alkaloids, such as vinblastine and vincristine, have greatly transformed the field of cancer treatment since their discovery in the 1950s. These compounds have proven to be highly effective against a range of cancers, including leukaemia, lymphoma, and solid tumours. This review provides a thorough examination of the anti-cancer activity of Catharanthus roseus. It covers its historical significance, phytochemical composition, mechanisms of action, clinical indications, and prospects in cancer therapy (29,30).
Historical Significance:
The historical importance of Catharanthus roseus in cancer therapy can be traced back to the mid-20th century when vinca alkaloids were initially extracted from this plant. Scientists conducting research on natural products with potential anti-cancer properties made a significant discovery with vinblastine and vincristine, two highly recognized vinca alkaloids. The discovery of vinca alkaloids from Catharanthus roseus was a breakthrough in cancer treatment, introducing a unique category of chemotherapy drugs with distinct ways of working. Vinblastine and vincristine have been discovered to effectively hinder cell division by interfering with the formation of microtubules. This disruption ultimately results in the arrest of mitosis and triggers apoptosis in cancer cells. These significant findings have opened up new possibilities in the clinical application of vinca alkaloids for the treatment of haematological malignancies and solid tumours. Throughout the years, Catharanthus roseus has been a significant subject of cancer research, motivating scientists to uncover its pharmacological activities, enhance drug formulations, and investigate its potential synergistic interactions with other anti-cancer agents (31).
Phytochemical Composition:
Catharanthus roseus is well-known for its intricate phytochemical profile, which includes a wide range of bioactive compounds that have the potential to combat cancer. Catharanthus roseus contains a significant class of compounds known as the vinca alkaloids. This class includes vinblastine, vincristine, vinflunine, and vindesine. The alkaloids found in the plant's leaves have shown remarkable cytotoxic effects on cancer cells. Vinblastine and vincristine have been the subject of extensive research and are commonly utilized in cancer chemotherapy protocols. Aside from vinca alkaloids, Catharanthus roseus also contains various bioactive constituents. such as flavonoids, terpenoids, and phenolic compounds. These additional components could potentially play a role in its anti-cancer properties. Flavonoids like quercetin and kaempferol possess remarkable antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties. These properties are beneficial in mitigating the progression of cancer by effectively reducing oxidative stress and inflammation. The presence of terpenoids in Catharanthus roseus, including diterpenes and triterpenes, has demonstrated cytotoxic properties against cancer cells. This indicates their potential as additional anti-cancer agents. The interplay of these phytochemicals amplifies Catharanthus roseus' anti-cancer properties, highlighting the significance of investigating the plant's comprehensive pharmacological profile in cancer treatment (32).
Mechanisms of Action:
![<span style=]() Vinca Rosea Cancer's Mechanisms of Action..png" height="150" src="https://www.ijpsjournal.com/uploads/createUrl/createUrl-20241006165756-1.png" width="150">
Vinca Rosea Cancer's Mechanisms of Action..png" height="150" src="https://www.ijpsjournal.com/uploads/createUrl/createUrl-20241006165756-1.png" width="150">
Fig.4: Vinca Rosea Cancer's Mechanisms of Action.


 Abdul Hameed* 1
Abdul Hameed* 1


 10.5281/zenodo.13894530
10.5281/zenodo.13894530