Abstract
In the present investigation an attempt has been made to study the formulation and evaluation of matrix tablets of Indomethacin using mucilage of hibiscus rosa-sinensis as a release retardant. The mucilage was extracted from the leaves of hibiscus rosa-sinensis using acetone. The matrix tablet were formulated using different concentration (0.15, 0.3 and 0.45) of hibiscus mucilage. The developed formulation of tablets were evaluated for pre-compression and post-compression parameters. The result of precompression parameters like bulk density, tap density, carr’s index and Hausner’s, ratio were found to be within the limits indicating good flow properties of the granules. Swelling index reveals that with increasing mucilage concentration there is increased swelling showing 68% for F3 at the end of 5 hours where as for F1 and F2 it was around 58.3% and 66.66% respectively. In-vitro drug release for F3 formulation was found to be 62.86% at the end of 8 hours. With increase mucilage concentration the drug release from the matrix tablets got retarded. In-vitro drug release data obtained were fitted to various release models access the possible mechanism of the drug release. All the formulation showed matrix (Higuchi Matrix) as a best fit model and the release mechanism was found to be Fickian Diffussion. The matrix tablets of Indomethacin formulated by using Hibiscus mucilage as a release retardant could be employed for retardant drug release. One of the most important (NSAID) non-steroidal anti-inflammatroy drug containing the indol core is represented by the indomethacin. This highly relevant compound has been used for the last 50 years with excellent pharmacological results. Arthritis is most prevalent disorder and Indomethacin choice of drug for arthritis. Oral route is most preffered route of the drug administration and tablets are more convenient dosage form.
Keywords
Indomethacin, Hibiscus, Rosa- sinensis, Mucilage, Matrix tablets
Introduction
Introduction of matrix tablets as sustained release has given a new breakthrough for novel drug delivery in field of pharmaceutical technology. Sustained release (SR) drug delivery systems are developed to modulate the release of drug, in order to achieve specific clinical objectives that cannot be attained with conventional dosage forms. Possible therapeutic benefits of a properly designed SR dosage form include low cost, simple processing, improved efficacy, reduced adverse events, flexibility in terms of the range of release profiles attainable, increased convenience and patient compliance. Arthritis is a term often used to mean any disorder that affects joint. Symptoms generally include joint pain and stiffness. Different types of arthritis exists (i) rheumatoid arthritis (ii) osteoarthritis, each with different causes including wear and tear, infections and underlying diseases.
Control Drug Delivery is that type of system which release the medicaments from the dosage form at a predetermined specified rate for locally or systemically for a specified period of time. It maintains constant drug level in the blood target tissue usually by releasing the drug in a zero order pattern. Controlled release, prolonged action, sustained release, extended release, depot dosage forms are terms used to identify these drug delivery systems that are designed to achieve prolonged therapeutic effect by continuously releasing medication over an extended period of time after administration of single dose.
TYPES OF ARTHRITIES
There are more than 100 different types of arthritis. Some of the most common types include:
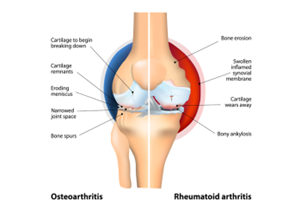
- Osteoarthritis (OA) is a type of degenerative joint disease that results from breakdown of joint cartilage and underlying bone. It is believed to be the fourth leading cause of disability in the world, affecting 1 in 7 adults in the United States alone. The most common symptoms are joint pain and stiffness.
- Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a long-term autoimmune disorder that primarily affects joints. It typically results in warm, swollen, and painful joints. Pain and stiffness often worsen following rest. Most commonly, the wrist and hands are involved, with the same joints typically involved on both sides of the body.
Figure:1 Osteoarthritis and Rheumatoid arthritis
SYMPTOMS AND CAUSES
The most common arthritis symptoms and signs include:
- Joint pain.
- Stiffness or reduced range of motion (how far you can move a joint).
- Swelling (inflammation).
- Skin discoloration.
- Tenderness or sensitivity to touch around a joint.
- A feeling of heat or warmth near your joints
Where you experience symptoms depends on which type of arthritis you have, and which of your joints it affects. Some types of arthritis cause symptoms in waves that come and go called flares or flare-ups. Others make your joints feel painful or stiff all the time, or after being physically activity. The symptoms of a rheumatoid arthritis flare aren’t much different from the symptoms of rheumatoid arthritis. But people with RA have ups and downs. A flare is a time when you have significant symptoms after feeling better for a while. With treatment, you’ll likely have periods of time when you feel better. Then, stress, changes in weather, certain foods or infections trigger a period of increased disease activity. Although you can’t prevent flares altogether, there are steps you can take to help you manage them. It might help to write your symptoms down every day in a journal, along with what’s going on in your life. Share this journal with your rheumatologist, who may help you identify triggers. Then you can work to manage those triggers.
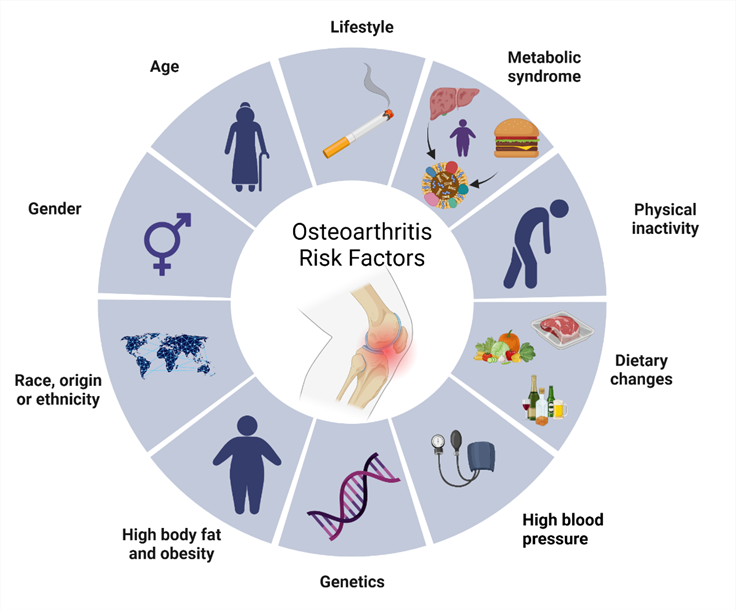
Risk Factors
Anyone can develop arthritis, but some factors may make you more likely to, including:
Tobacco use:
Smoking and using other tobacco products increases your risk.
Family history:
People whose biological family members have arthritis are more likely to develop it.
Activity level:
You might be more likely to have arthritis if you aren’t physically active regularly.
Other health conditions:
Having autoimmune diseases, obesity or any condition that affects your joints increases the chances you’ll develop arthritis.
Some people have a higher arthritis risk, including:
- People older than 50.
- People assigned female at birth (AFAB).
- Athletes, especially those who play contact sports.
People who have physically demanding jobs or do work that puts a lot of stress on their joints (standing, crouching, being on your hands and knees for a long time etc.) arthritis can develop at any age. When it starts depends on which type you have and what’s causing it. In general, osteoarthritis affects adults older than 50. Rheumatoid arthritis usually develops in adults age 30 to 60.
Figure: 2 Risk factor of Osteoarthritis
SUSTAINED RELEASE DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM
A number of terms have been used to describe the oral dosage forms that represent modified release properties; which include delayed release, repeated action, prolonged release, sustained release, extended release and controlled release. Each drug delivery system is focused at eliminating the cyclical changes in plasma drug concentration seen after administration of conventional delivery systems. Modified release dosage forms are designed to provide quick achievement of a drug plasma level that remains constant at a value within the therapeutic range of a drug for a significant period of time or achievement of a plasma concentration of a drug that delivers at a slow rate (i.e. sustained release) that stays within the therapeutic range for a longer period of time. Based on the assumption that a drug, which is to be incorporated into a modified release dosage form, confers upon the body characteristics of a one- compartment open model, then the basic kinetic design of such a product may be assumed to contain two portions, one that provides the initial loading dose, and one that provides the maintenance or sustained dose.
DIFFERENT TYPES OF SUSTAINED RELEASE SYSTEMS:
1. Diffusion sustained system.
i. Reservoir type
ii. Matrix type.
2. Dissolution sustained system.
i. Reservoir type.
ii. Matrix type.
SOLUBILITY ANALYSIS
Table : 1 Data for solubility of drug

METHODOLOGY : Matrix Method
Extraction of mucilage
The fresh leaves of Hibiscus rosa-sinensis were collected and washed repeatedly with water. The leaves were then crushed and then kept for soaking for 5-6 h. The leaves were boiled for 30 min and left to stand for 1 h for complete release of the mucilage. The mucilage was extracted using a muslin cloth bag to remove the marc from the solution. Acetone (three times the volume of the filtrate) was added to precipitate the mucilage. The mucilage was separated, dried in an oven at35C, collected, grounded, passed through sieve no #80 and stored in a desiccator at 35 C and 45% relative humidity till use.
Preparation of matrix tablets
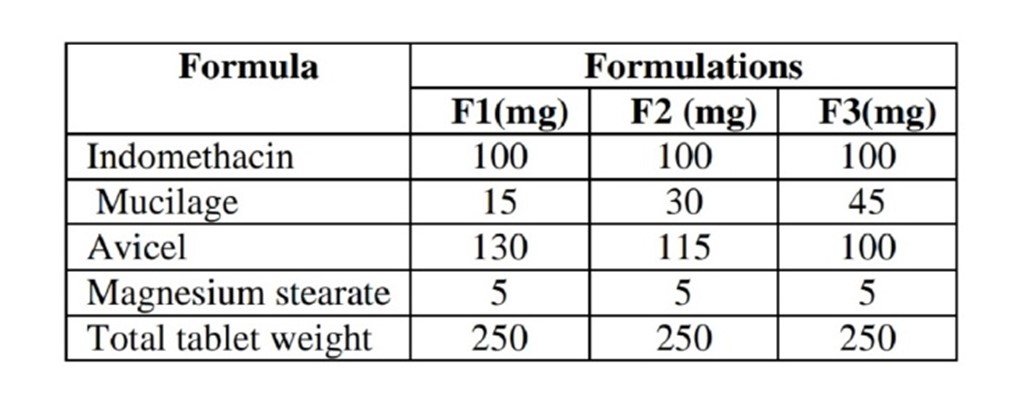
Sustained release matrix tablets of indomethacin with Hibiscus rosa-sinensis leaves mucilage were prepared using different drug: mucilage ratios viz.,1:0.15, 1:0.3 and 1:0.45. (Table1)Hibiscus rosa-sinensis leaves mucilage was used as matrix forming material whilemicrocrystalline cellulose as a diluent and Magnesium stearate as a lubricant. All ingredients were passed through sieve #100, weighed and blended. The granules were prepared by wet granulation technique and compressed by using 6mm flat faced punches in a rotatory tablet punching machine.
Table : 2 Formulation For Matrix Tablets Of Indomethacin Using Mucilage Of Hibiscus Rosa-Sinensis Leaves.
EVALUATION OF TABLET BLEND
Bulk density: Apparent bulk density was determined by placing pre-sieved drug excipient blend in to a graduated cylinder and measuring the volume and weight as it is.The bulk density of a powder is the ratio of the mass of an untapped powder sample and its volume including the contribution of the interparticle void volume. Hence, the bulk density depends on both the density of powder particles and the spatial arrangement of particles in the powder bed. The bulk density is expressed in grams per millilitre (g/mL) although the international unit is kilogram per cubic metre (1 g/mL = 1000 kg/m3) because the measurements are made using cylinders. It may also be expressed in grams per cubic centimetre (g/cm3). The bulking properties of a powder are dependent upon the preparation, treatment and storage of the sample, i.e. how it was handled. The particles can be packed to have a range of bulk densities and, moreover, the slightest disturbance of the powder bed may result in a changed bulk density. Thus, the bulk density of a powder is often very difficult to measure with good reproducibility and, in reporting the results, it is essential to specify how the determination was made.The bulk density of a powder is determined by measuring the volume of a known mass of powder sample, that may have been passed through a sieve into a graduated cylinder, or by measuring the mass of a known volume of powder that has been passed through a volumeter into a cup or a measuring vessel.

EVALUATION OF MATRIX TABLET
Weight variation:
Twenty tablets were randomly selected from each batch individually for the average weight and standard deviation of 20 tablets was calculated as per IP specification for weight variation.
Thickness:
The thickness of the tablet was measured by using screw gauge, Twenty tablet from each batch were randomly selected and thickness were measured.
Hardness:
Hardness was measured using Pfizer hardness tester, tablet from each batch and measured in kg/cm2.
Friability:
Ten tablets were weight and placed in the Roche friabilator and apparatus was rotated at 25 rpm for 4 min. After revolution the tablets were dusted and weighedto check that the variation is less than less than 1%.
Drug content uniformity:
This test is performed by taking twenty tablets randomly, weighed and powdered. A quantity of powdered tablet equal to 250 mg of Indomethacin was dissolved in phosphate buffer pH 7.2 in100ml volumetric flask. The so formed sample was diluted and the absorbance was measured at 265.5 nm using phosphate buffer pH 7.2 as blank and the % drug content was estimated.
Swelling index:
The swelling index of the formulation was carried out by taking one tablet from each batch and placed in a Petridis containing phosphate buffer pH 7.2 At the end of 1h, the tablet was withdrawn, kept on a tissue paper and weighed. The weighing carried out for a period of 5h .
In-Vitro dissolution Study:
The study was carried out in 900 ml of phosphate buffer pH 7.2 at 75 Rpm, which was maintained at 37oC ±0.5oC using the USP apparatus type II (ElectrolabDisso 8000).5 ml samples were withdrawn at regular intervals of 1 hr and the absorbance was measured at 265.5nm using Shimadzu UV spectrophotometer 1700. Sink condition was maintained by replacing with fresh buffer medium. The dissolution study was carried out for 8 hrs followed by mathematical treatment of the solved dissolution data.
RESULT AND DISCUSSION
The extracted mucilage of Hibiscus rosa-sinensis was studied for the desired physical properties and results are shown in Table 3. Matrix tablet each containing 100 mg of Indomethacin were prepared using dried mucilage of Hibiscus rosa-sinensis leaves in various ratio of 1:0.15, 1:0.3, 1:0.45 (drug: mucilage).
Table: 3 Flow properties of dried Hibiscus rosa-sinensis leave mucilage
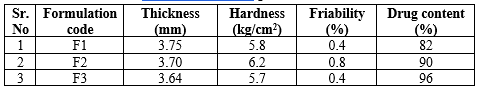
The pre-compression parameters of granules analysis likebulk density, tapped density, Carr’s index, Hausner’s ratio and results are shown in Table 4. The bulk density and tapped density ranged from 0.92 to 0.45 g/ml and 1.3 to 1.05 g/ml. Carr’s index and Hausner’s ratio ranges from0.58 to 0.33 and 2.4 to 1.5 respectively indicating good flowability of granules. Post compression parameters like thickness, hardness, friability and drug content are shown in Table 5. Hardness and friability ranged from 5.8 to 6.8 kg/cm2 and 0.8 to 0.4%. Drug content was ranging from 82% to 96%.
Table: 4 Pre-compression parameters of the granules
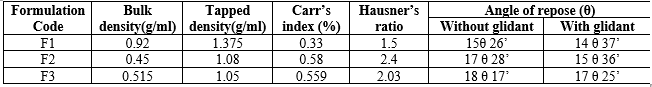
Table: 5 Post-compression parameters of tablets
CONCLUSION
The study deals with the investigation of release retardant effect of Hibiscus rosa-sinensis mucilage when formulated as a matrix tablet. The mucilage exhibited an appreciable physicochemical properties and suited best for the development of sustained release tablets as indicated by the drug release studies. This can be used as a potential natural source over the synthetic release retardant. Hence, Hibiscus rosa-sinensis could be employed as a release rate retardant for sustaining the drug release from the formulation. Thus, Matrix tablets of indomethacin formulated by using Hibiscus mucilage as a release retardant could be employed for retardant drug release. One of the most important (NSAID) non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug-containing the indol core is represented by the indomethacin. This highly relevant compound has been used for the last 50 years with excellent pharmacological results. Arthritis is most prevalent disorder and Indomethacin is choice of drug for arthritis. Oral route is most preferred route of drug administration and tablets are the more convenient dosage form.
REFERENCE
- Kathane Sudhir, dr. Rathore shrute, Chandrakarshashikanttosmulation and Evaluation of indomethacin sa SR Tabled by Using Natural Polymers, Journal of Pharmaceutical Dosage forms & Technology Vol. 16, 2024; (1)
- Khan, A.; Qayum, M.; Ahmad, L.; Khan, S.A.; Abbas, M. Optimization of diluents on the basis of SeDeM-ODT expert system for formulation development of ODTs of glimepiride. Adv. Powder Technol. 2022, 33, 103389.
- Patil, M.B.; Avish, D.M.; Jayshree, S.B. Formulation and Evaluation of Sustained Release Bilayer Matrix Tablet of Glimepiride and Metformin Hydrochloride. Asian J. Res. Pharm. Sci. 2021, 11.
- Won Dong Han ,Heejun Park, Eun-Sol Ha, Hwan-Ho Kim, Sun Woo Jang, Min-Soo Kim, Optimization of bilayer tablet manufacturing process for fixed dose combination of sustained release high-dose drug and immediate release low-dose drug based on quality by design,International Journal of Pharmaceutics 605, 2021, 565
- Niguse, B.; Gebre-Mariam, T.; Belete, A. Design, development and optimization of sustained release floating, bio-adhesive and swellable matrix tablet of ranitidine hydrochloride. PLOSONE 2021, 16, e0253391.
- Md. Khalid Anwar ,Essam A. Ali, Muzaffar Iqbal, Mohammed Muqtader Ahmed, Mohammed F. Al dawsariAhmed Al Saqr,Mohd Nazam Ansari ,M. Ali Aboudzadeh, Development of Sustained Release Baricitinib Loaded Lipid- Polymer Hybrid Nanoparticles with Improved Oral Bioavailability, Department of Pharmaceutics, College of Pharmacy, Prince Sattam Bin Abdulaziz University, Al-Kharj 11942, Saudi Arabia 2021, 33-45.
- Xu, Q.; Yang, N.; Feng, S.; Guo, J.; Liu, Q.B.; Hu, M. Cost-effectiveness analysis of combining traditional Chinese medicine in the treatment of hypertension: Compound Apocynum tablets combined with Nifedipine sustained-release tablets vs Nifedipine sustained-release tablets alone. BMC Complement. Med. Ther. 2020, 20, 1-10.
- Nehad K. Abed, Ali Rasool M. Albakaa, Dina Saleem M. Ameen, Zainab A. Jabbar, Amany S. Younis, Development of pharmaceutical chemistry college of pharmacy university of Mustansiriyah, Iraq, 2020 (2).
- Khan, A.; Qayum, M.; Ahmad, L.; Khan, S.A.; Abbas, M. Optimization of diluents on the basis of SeDeM-ODT expert system for formulation development of ODTs of glimepiride. Adv. Powder Technol. 2022, 33, 103389.
- Patil, Amit B., Do Jair Vikas, Gowda D.V., Betala Shweta, Formulation and Evaluation of Sustained Release Matrix Tablets of Indomethacin by Wet granulation method, World Journal of pharmaceutical Research., Vol.8 (0) 2019: (2-3) DOI: 10.20959/wjpr20197-15140.
- Gunda, R.K.; Manchineni, P.R. Formulation Development and Evaluation of Rosuvastatin Sustained Release Tablets. J. Pharm. Ther. 2019, 5, 238-247.
- Abbas Nasir, Sarwarkomal, Hussain Amjad, Irfan Muhammad, Mehmood rabiya , Muhammad Sohail Arshad and Shah Pervaiz Akhtar, FORMULATION AND EVALUATION OF INDOMETHACIN LOADED NANOSPONGES FOR ORAL DELIVERY Acta Poloniae Pharmaceutica ñ Drug Research, Vol. 75 No. 5 pp. 1201ñ1213, 2018 DOI:10.32383/appdr/86683.
- Kalla KuntaaV.R.,Tiwaria R., Sarabua Sandeep, Bandaria Suresh, Michael A., Effect of formulation and process variables on lipid based sustained release tablets viacontinuous twin screw granulation: A comparative study, published by Elsevier. This manuscript is made available under the Elsevier user licence 2018, 57-83.
- Zhe-Peng Liu, Yao-Yao Zhang, Deng-Guang Yu, Di Wu, Hao-Lin Li, Fabrication of sustained-release zein nanoparticles via modified coaxial electrospraying, Chemical Engineering Journal 2018. 363- 378.
- Patel Sunita, Bajpai Jaya , Saini Rajesh, Bajpai AK, Somen Acharya, Sustained release of pesticide (Cypermethrin) from nanocarriers: an effective technique for environmental and crop protection, Process safety and environmental protection 117,2018, 315-325,
- Gadhe, S. Formulation and evaluation of bilayer tablets of NSAID as an immediate release layer and sustained release layer. World J. Pharm. Res. 2017, 66, 952-961.
- Islam MR, al Mamun ME, Moghal MM. Release Modification of Indomethacin Controlled Release Press Coated Tablets. Bangladesh Pharmaceutical Journal, 2016 Aug 12; 19(2): 219-25.
- Guerra-Ponce WL, Gracia-Vásquez SL, González-Barranco P, Camacho-Mora IA, Gracia-Vásquez YA, Orozco-Beltrán E, Felton LA. In vitro evaluation of sustained released matrix tablets containing ibuprofen: a model poorly water-soluble drug. Brazilian Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences, 2016 Dec; 52(4): 751-9.
- F. Ramazani, C.F. Van Nostrum, G. Storm, F. Kiessling, T. Lammers, W.E. Hennink, R.J. Kok, Locoregional cancer therapy using polymer-based drug depots, Drug Discover Today 21 (2016) 640-647.
- Q. Hu, W. Sun, Y. Lu, H.N. Bomba, Y. Ye, T. Jiang, A.J. Isaacson, Z. Gu, Tumormicroenvironment-medicated construction and deconstruction of extracellular drug-delivery depots, Nano Lett. 16 (2016) 1118-1126.


 Manisha Karsh *
Manisha Karsh *
 Rajesh Kumar Chandra
Rajesh Kumar Chandra







 10.5281/zenodo.11500312
10.5281/zenodo.11500312