Abstract
Alzheimer’s disease is an progressive neurological disease and it is a most common form of dementia, affecting more than 20 million people worldwide. AD characterized by progressive deficits in memory and behavioural disturbances. The incident of AD ranges from 1 to 4 percent population per year, rising from its lowest level at ages 65 to 70 years to rates that may approach 6 Percent for those over the years of 85 years. From an many years the medicinal plants have been used in the systems of medicines for the treatment of diseases. AD. There are many categories of Anti-Alzheimer’s drugs available for treatment of Alzheimer’s disease. In the market but due to lack of patient compliance successful outcomes were not observed. Available Anti-AD herbal drugs such as Curcumin, Withania somnifera, Bhrami, Ginkgo biloba, guggul, vincaminor, allium sativum, ginseng, herbs with essential oils, volatile Oils, source and cultivation of the herbs, mechanism of action of the Phytochemicals in the herb responsible for treating AD. In this review we provide a systematic review on the role of medicinal plants and herbal products useful for the treatment of Alzheimer’s Disease, the effect of these herbs on hormones, herb-drug interactions as well as stability-related testing for the herbal pharmaceutical medicines.
Keywords
Alzheimer’s disease (AD), cognitive impairment, Dementia, Herbal medicine, Phytoconstituents, etc.
Introduction
Alzheimer’s is a progressive neurodegenerative disorder caused due to cognitive impairment and Dementia. Alzheimer's disease International (ADI) is the international federation of Alzheimer associations around the world. Alzheimer’s disease has been the most frequent cause of dementia globally and its incidence is increasing owing in part to the globe’s aging population. Dementia affects an estimated 0.7 percent of the world population or 51.6 million individuals. AD was known to occur occasionally in families but was not necessarily thought to be related to the more frequent occurrence of cognition impairment in late life. The latter condition was known as senile dementia Even though the total fatality rate from cardiovascular diseases (CVD) and stroke in the USA is dropping the portion of fatalities linked to AD is growing, rising by 89 percent between 2000 and 2014. Although treatment options for people with Alzheimer's disease are still supportive and can improve memory and alertness, they can also reduce the over all progression of the condition. Several of today’s modern manufactured pharmaceuticals have their origins in the plant world, and herbal remedies led to the main pharmacopeia’s only around two hundred years ago. The specificity of phytoconstituents and extracted chemicals for Brain receptors suggests that herbal medicines may play an essential role in the management of neurological illnesses. Further more, animal and human research have shown a scientific foundation for the use of therapeutic plants. The Allopathic medicine as they overcome the unwanted side effects and improves patient compliance.
What is Alzheimer’s disease?
- Also called: senile dementia.
- Alzheimer’s disease is the most common type of dementia.
- It is a progressive disease beginning with mild memory loss and possibly leading to loss of the ability to carry on a conversation and respond to the environment.
- Alzheimer’s disease involves parts of the brain that control thought, memory, and language.
Who has Alzheimer’s disease?
- In 2020, as many as 5.8 million Americans were living with Alzheimer’s disease.
- Younger people may get Alzheimer’s disease, but it is less common.
- The number of people living with the disease doubles every 5 years beyond age 65.
- This number is projected to nearly triple to 14 million people by 2060.
- Symptoms of the disease can first appear after age 60, and the risk increases with age.
What is known about Alzheimer’s Disease?
- Age is the best known risk factor for Alzheimer’s disease.
- Family history—researchers believe that genetics may play a role in developing Alzheimer’s disease. However, genes do not equal destiny. A healthy lifestyle may help reduce your risk of developing Alzheimer’s disease. Two large, long term studies indicate that adequate physical activity, a nutritious diet, limited alcohol consumption, and not smoking may help people.
- Changes in the brain can begin years before the first symptoms appear.
- Researchers are studying whether education, diet, and environment play a role in developing Alzheimer’s disease.
- There is growing scientific evidence that healthy behaviours, which have been shown to prevent cancer, diabetes, and heart disease, may also reduce risk for subjective cognitive decline.
Symptoms of Alzheimer’s disease:
Memory loss is the key symptom of Alzheimer's disease. Early signs include difficulty remembering recent events or conversations. But memory gets worse and other symptoms develop as the disease progresses.
Memory:
Everyone has memory lapses at times, but the memory loss associated with Alzheimer's disease persists and gets worse.
People with Alzheimer's disease may:
- Repeat statements and questions over and over.
- Forget conversations, appointments or events.
- Misplace items, often putting them in places that don't make sense.
- Get lost in places they used to know well.
- Eventually forget the names of family members and everyday objects
- Have trouble finding the right words for objects, expressing thoughts or taking part in conversations.
Thinking and reasoning:
Alzheimer's disease causes difficulty concentrating and thinking, especially about abstract concepts such as numbers. Doing more than one task at once is especially difficult. It may be challenging to manage finances, balance check books and pay bills on time. Eventually, a person with Alzheimer's disease may be unable to recognize and deal with numbers.
Making judgments and decisions:
Alzheimer's disease causes a decline in the ability to make sensible decisions and judgments in everyday situations. For example, a person may make poor choices in social settings or wear clothes for the wrong type of weather. It may become harder for someone to respond to everyday problems. For example, the person may not know how to handle food burning on the stove or decisions when driving.
Planning and performing familiar tasks:
Routine activities that require completing steps in order become a struggle. This may include planning and cooking a meal or playing a favourite game. Eventually, people with advanced Alzheimer's disease forget how to do basic tasks such as dressing and bathing.
Changes in personality and behaviour:
Brain changes that occur in Alzheimer's disease can affect moods and behaviours. Problems may include the following:
- Depression.
- Loss of interest in activities.
- Social withdrawal.
- Mood swings.
- Distrust in others.
- Anger or aggression.
- Changes in sleeping habits.
- Wandering.
- Loss of inhibitions.
- Delusions, such as believing something has been stolen.
Preserved skills:
Despite major changes to memory and skills, people with Alzheimer's disease are able to hold on to some skills even as symptoms get worse. Preserved skills may include reading or listening to books, telling stories, sharing memories, singing, listening to music, dancing, drawing, or doing crafts. These skills may be preserved longer because they're controlled by parts of the brain affected later in the course of the disease.
Brahmi:



Biological sources:
In a India it is popularly known as Brahmi and can be used for its revitalisingandnootropic properties; it also improves cognition power and intellectual abilities. Bacopamonnieri (B. monniera) is a minor, ever growing creeping herb with a number of branches, leaves are oblong, and flowers can be slight purple or can also be white belonging to Scrophulariaceae.
Chemical constituents:
This plant also contains the alkaloids brahmine, nicotine, and herpestine. Bacopasides I–XII, which are new saponins, have also been discovered.
Uses
- Brahmi Benefits for Brain
- Improves Liver Function
- Powerful Antioxidant Properties
- Manage Anxiety and Stress
- Brahmi Benefits for Skin.
Turmeric:

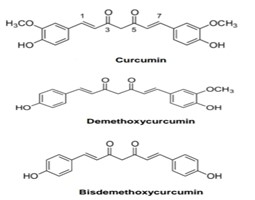
Biological source:
It is derived from the plant's rhizome and is widely used as a food flavouring and colouring agent in India. In South and Southeast Asia, it is grown for commercial purposes.
Chemical constituent:
curcumin (diferuloyl methane), demethoxycurcumin, and bisdemethoxycurcumin, are the majorchemical constituents of turmeric.
Uses:
- It Is an Anti-Inflammatory
- Curcumin May Help Protect Against Heart Disease
- Curcumin May Help Prevent (and Possibly Treat) Certain Types of Cancer
- Curcumin May Help Ease Symptoms of Osteoarthritis
- It May Help Delay or Reverse Alzheimer’s Disease
Shankhpushpi


Biological source:
Convolvulus prostratus (Convolvulus pluricaulis) is an herb found in India and Burma that is used in Ayurveda. The Ayurveda preparation shankapushpi is, according to most sources, identical with Convolvulus prostratus, but some say shankapushpi is instead Clitoriaternatea.
Chemical constituent:
It contains Alkaloids that is shankhpushpine and convolamine, volatile oils, favanoid-kampferol, amino acids, fatty acids, scopoletin, and beta-sitosterol that is SethiyaNKare the main chemical components
Uses:
- It reduces the levels of thyroid hormones in case of stress.
- It Improves skin health.
- Shankhpushpi is one of the best brain tonics which has a protective effect on memory and cognition.
- This herb also reduces cholesterol and helps manage blood pressure.
- For hyperthyroidism
Drumstick Tree


Biological source:
Moringaoleifera is a fast-growing, drought-resistant tree of the family Moringaceae, native to the Indian subcontinent and used extensively in South and Southeast Asia. It's commonly referred to as a drumstick.
Chemical constituent:
It contains alkaloids, isothiocyanates, tannins, and saponins and polyphenols i.e. flavonoids, chlorogenic acid, glucosinolates, Retinol, and phenolic acids are the main chemical constituents in M. oleifera
Uses:
- Anti-inflammatory properties
- Drumstick leaves are rich in antioxidants
- To treat heart diseases, diabetes, cancer, and Alzheimer’s disease.
- These leaves also contain Quercetin (an antioxidant) that helps lower blood pressure.
- Drumstick leaves are rich in calcium and phosphorus, which are crucial for bone health.
Gotu kala


Biological source:
Centella asiatica, an annual plant belonging to Apiaceae family that is also known as jalbrahmi or mandukparni. It is found throughout India. It bears small oval fruit and possess green leaves with fan like shape and the flowers are white or light purple and can also be pink.It's used to slow down the ageing process, avoid memory problems, and improve memory when combined with milk.
Chemical constituent:
Asiaticosides, madasiatic, asiatic acid, madecassoside, and acid are the chief chemical components of C. asiatica.
Uses:
- It may help boost cognitive function
- It may help treat Alzheimer’s disease
- It may help reduce anxiety and stress
- It may act as an antidepressant
- It may help relieve joint pain.
Morinda citrifolia

Damnacanthal

Scopoletin
Biological source;
It grows in and tolerates a very wide range of soil and environmental and such as those found on coral atolls or basaltic lava flows
Morinda citrifolia is found to be Southeast Asia and Australia.
Chemical constituents;
Scopoletin , Damnacanthal, Morindone, Morindin, lucidin etc.
Uses
- Anti-oxidant
- Repairs broken joints
- Appetite stimulant
- Treats burns, swelling, boils.
- To prepare the health drink
Utrica dioica

3-Hydroxyacetophenone
Biological source;
It is abundant in northern Europe and much of Asia, usually found in the countryside
Chemical constituents;
Phenolic compounds, sterols, fatty acids, alkaloids, terpenoids, flavonoids, and lignans,
Uses;
- Anti- inflammatory
- Anti-oxidant
- Wound healing
- Factures
- Analgesic
- Haematuria.

Commiphora wightii

guggulsterone
Biological source;
Commiphora wightii is sought for its gummy resin which is harvested from the plant's bark through the process of tapping Commiphora wightii, with common names Indian bdellium-tree, gugal, guggul, gugul, or mukul myrrh tree.
Chemical constituents;
Z-guggulsterone , guggulsterol-1 , guggulsterol-II , guggulsterol-III , guggulsterol-IV guggulsterol-V and guggulsterol-VI.
Uses;
- As an Anti-oxidant ( Guggulsterones)
- As astringent , carminative, antiseptic
- Acts as a bitter stomachachic
- Expectorant and Diuretic
- Cardio protective.

Galanthus nivialis

Galantamine
Biological source;
Galanthus nivalis, the snowdrop or common snowdrop, is the best-known and most widespread of the 20 species in its genus, Galanthus
Snowdrops contain also an active lectin or agglutinin named GNA for Galanthus nivalis agglutinin. Potatoes have been genetically modified with the GNA gene.
Chemical constituents;
- Galantamine
- Galanthus
- Galanthus nivalis.
Uses
- Vascular dementia
- Treats dementia in combination with epilepsy
- Anti-depressant
- Treats cognitive impairment due to schizophrenia.

Acorus calamus.

Biological source;
Acorus calamus Linn commonly known as “sweet flag” or “calamus”, is a species of semiaquatic, perennial, aromatic herb with creeping rhizomes. The plant is found in the northern temperate and subtropical regions of Asia, North America, and Europe.
Chemical constituents;
asarone, benzen, , trans-?-Ocimene, Isocalamendiol, Methyleugenol, ß-asarone and ?-Pinene etc.
Uses;
- Anti-oxidant
- Insecticidal activity
- relives stomach ache and dysentery
- skin problems
- earache
- remove the smell of tobacco.
REFERENCE:
- Matthews, K. A., Xu, W., Gaglioti, A. H., Holt, J. B., Croft, J. B., Mack, D., & McGuire, L. C. (2018). Racial and ethnic estimates of Alzheimer’s disease and related dementias in the United States (2015–2060) in adults aged? 65 years. Alzheimer’s & Dementia.
- Xu J, Kochanek KD, Sherry L, Murphy BS, Tejada-Vera B. Deaths: final data for 2007. National vital statistics reports; vol. 58, no. 19. Hyattsville, MD: National Center for Health Statistics. 2010.
- Heron M. Deaths: leading causes for 2010. National vital statistics reports; vol. 62, no 6. Hyattsville, MD: National Center for Health Statistics. 2013.
- Hurd MD, Martorell P, Delavande A, Mullen KJ, Langa KM. Monetary costs of dementia in the United States. NEJM. 2013;368(14):1326-34.
- Tejada-Vera B. Mortality from Alzheimer’s disease in the United States: data for 2000 and 2010. NCHS data brief, no 116. Hyattsville, MD: National Center for Health Statistics. 2013.
- James BD. Leurgans SE, Hebert LE, et al. Contribution of Alzheimer disease to mortality in the United States. Neurology. 2014;82:1-6.
- Quiroz YT, Zetterberg H, Reiman EM, Chen Y, Su Y, Fox-Fuller JT, et al. Plasma neurofilament light chain in the presenilin 1 E280A autosomal dominant Alzheimer’s disease kindred: A cross-sectional and longitudinal cohort study. Lancet Neurol. 2020;19(6):513-21. [CrossRef] | [Google Scholar]
- Mohamed T, Shakeri A, Rao PPN. Amyloid cascade in Alzheimer’s disease: recent advances in medicinal chemistry. Eur J Med Chem. 2016;113:258-72. [CrossRef] | [Google Scholar]
- Implications for Behavioral and Social Research of Preclinical Markers of Alzheimer’s Disease and Related Dementias: Proceedings of a Workshop–in Brief 2021
- Mechanisms for Organizational Behavior Change to Address the Needs of People Living with Alzheimer’s Disease and Related Dementias: Proceedings of a Workshop 2022
- Neuroprotective Herbs for the Management of Alzheimer’s Disease Julie Gregory ?1;, Yasaswi Vengalasetti 2, Dale E. Bredesen?3; et al. 2021 Biomolecules
- History and Experience: A Survey of Traditional Chinese Medicine Treatment for Alzheimer’s Disease Ping Liu ?1;, Mei Kong2, Shihe Yuan?3; et al. 2014 Evidence-Based Complementary and Alternative Medicine
- Traditional Oriental Medicines and Alzheimer’s Disease Seong Gak Jeon ?1;, Eun Ji Song 2, Dongje Lee ?3; et al. 2019 Aging and disease
- A Review on Treatment of Alzheimer’s Disease in Traditional Medicine Vs. Modern Science Rashda Khatoon Shaikh ?1;, Vanita G.Kanase 2 2022 Int J Pharma Bio Sci
- Herbal medicine in the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease Shahin Akhondzadeh 1, Seyed Hesameddin Abbasi 2 2006 Am J Alzheimers Dis Other Demen.
- Herbal Therapeutics for Alzheimer’s Disease: Ancient Indian Medicine System from the Modern Viewpoint Shikha Kushwah 1, Neha Maurya 2, Sandeep Kushwaha?3; et al. 2023 CN
- A Systematic Review of Single Chinese Herbs for Alzheimer’s Disease Treatment Li-Chen Fu?1;, Ju-Tzu Li2 2011 Evidence-Based Complementary and Alternative Medicine.
- A Review on Treatment of Alzheimer’s Disease in Traditional Medicine Vs. Modern Science Rashda Khatoon Shaikh ?1;, Vanita G.Kanase 2 2022 Int J Pharma Bio Sci.
- Goswami S, Saoji A, Kumar N, Thawani V, Tiwari M, Thawani M, et al. Effect of Bacopa monnieri on Cognitive functions in Alzheimer’s disease patients. Int J Collab Res Intern Med Public Health. 2011;3(285):93 [CrossRef] | [Google Scholar].
- Herbal medicine in the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease Shahin Akhondzadeh 1, Seyed Hesameddin Abbasi 2 2006 Am J Alzheimers Dis Other Demen.


 Pranav Manik Sonawane *
Pranav Manik Sonawane *
 Saurabh Arjun Khairnar
Saurabh Arjun Khairnar




















 10.5281/zenodo.12560496
10.5281/zenodo.12560496