Abstract
India is rightfully called as the botanical garden of world. It is the land of several medicinal plants and herbs that are traditionally used to curve aliments. "The magical plants and indian spice" murraya koenigii has served humankind not only as food enhancer but also serve as village or folk medication to cure many disorders. The whole plant is used as tonic and stomachic properties, curry leaves murraya koenigii is an aromatic tropical and subtropical plant originated from India. The leaves stems barks of this plant are abundant in carbazole alkaloids which having strong pharmacological and biological effects.
Keywords
Curry leaves (Murraya koenigii), Health Benefits, Formulation, Medicinal Properties.
Introduction
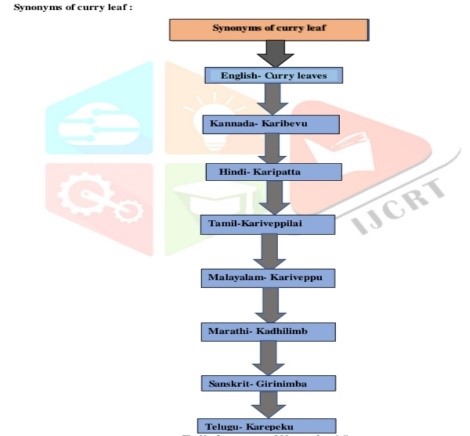
Curry leaf (Murraya koenigii) is a member of the Rutaceae family, which has 150 genera and 1600 species. It has been determined to be native to South Asia, specifically to Bangladesh, India, and Sri Lanka. The first and fourth centuries AD are when Murraya koenigii was first used. The whole plant is thought to be tonic and stomachic and has historical applications . In addition to Karuveppilai in Tamil, Mitha Neem in Hindi, and Surabhinimba in Sanskrit. Due to their compound leaves, curry leaf plants can also be utilised as a hedge and decorative shrub b. The green leaves of M. koenigii are used to treat edema, bruising, piles, diarrhoea, inflammation, itching, and fresh cuts. . The majority of people take herbal medications because they are thought to be safe, efficient, and affordable. Murraya In India, a medicinally significant herb known as koenigii (Curry Leaves/Kadhi Patta/Mitha Nimba/Giri Nimba) is frequently used as a spice, a condiment, and to treat a variety of illnesses. It is a common ingredient in Indian cuisine and is used with assurance in daily cooking because of its delicate flavour. Curry leaves contain a variety of essential nutrients, including nicotinic acid, vitamin B, C, A, and E, antioxidants, plant sterols, glycosides, and flavonoids, as well as carbohydrates, proteins, fibre, calcium, phosphorus, iron, magnesium, and copper. This plant's leaves are commonly used in Indian cuisine, and P-gurjunene, P-caryophyllene, P-elemene, and Ophellandrene2 are the chemical compounds that give them their distinctive aroma.

# Phytochemistry
Alkaloids
Flavonoids
Glycosides
Steroids
Saponins
Resins
Phenol
Tannins
Terpenoid

Formulation of Curry Leaves :-
Curry leaves powder,
Curry leaves shampoos,
Curry leaves tablet,
Curry leaves chutney,
Curry leaves oil.

2. Literature Review
This literature review aims to explore recent advancements in the curry leaves, including discovery of part of plant remedies, scientific validan of traditional Curry leaves and development of curry leaves product.
1) Discovery of part of plant remedies. - studies have identified new herbal remedies with actruttres promising pharmacological Such as anti inflammatory, anti-diabetic, antioxidant., reduce weight properties.
2) Scientific validation of traditional curry leaves :-
- Review, researches have conducted rigorous Studies to evaluate safely and efficacy of traditional curry leaves.
- This validation helps to bridge the gap between traditional and modern medicine providing evidence based support for the use of certain herbal treatments.
3) Development of curry leaves products:-
- Standardization of herbal product is ensure to their quality, safety and efficiency.
- Standardization involves identifying and quantifying the active constituent of herbal medicine, ensuring consistent quality and potency.
3. AIM AND OBJECTIVES
AIM:
The Medicinal Significance of Murraya Koenigii.
Objectives:
1] The objective of this review study is to update information about pharmacognostical,
phytochemical constutuents and pharmacological studies of murraya koenigii.
2] To identify the phytochemical component found in curry leaf product.
3] To evaluate the versatile multi potential medicinal use of murraya koenigii.
4]the review paper focused on different pharmacological ,phytoconstituents,taxonomical classification of this plant.
4. Plant Description
The plant is grown and distributed all over India. From the Himalayas to Sikkim, Uttarakhand, Garhwal, Bengal, Assam, Western Ghats, and Cochin to Travancore. Seeds are used for propagation, and they germinate well in light shade. in humid forests between 500 and 1600 metres high in Guangdong, South Hainan, South Yunnan (Xishuangbanna), Bhutan, Laos, Nepal, Pakistan, Sri Lanka, Thailand, and Vietnam, for example. The curry leaf, or Murraya koenigii, is a tiny tropical to subtropical tree or shrub that normally reaches heights of 6 to 15 feet. It is famous for its flavorful, aromatic curry leaves, which are a key component of Indian and Asian cuisine. This tree is indigenous to wet forests in Sri Lanka and India. Curry leaves travelled to Malaysia, South Africa, and Reunion Island with South Indian immigration. They are hardly found outside of the Indian zone of influence. Murraya koenigii is an unarmed, semi-deciduous, aromatic shrub or small tree with imparipinnate, glabrous, and highly scented leaves. It has a robust, woody trunk and branches. Herbal tea may be made from curry plant flowers. Fresh leaves from the plant can be picked and used to salads. The plant's essential oil has been used to enhance the flavour of fruits in ice creams, confections, baked products, soft drinks, and chewing gum.
5. Historical Context
It was updated as the word "kari" with its uses in Tamil and Kannada literature. Curry leaf, a term now frequently used to refer to Murraya koenigii, is derived from the Tamil word kari, which means "spiced sauce.". The usage of Murraya koenigii as a vegetable flavouring ingredient is mentioned in early Tamil and Kannada literature. As a culinary flavouring agent, Murraya koenigii is now grown as a cultivated crop in India, Sri Lanka, Southeast Asia, Australia, the Pacific Islands, and Africa.
6. Medicinal Properties Of Curry Leaves
1.Nutritional Benefits
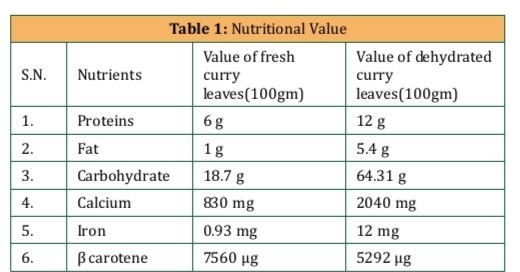
Curry leaves are rich in vitamins A, B, C, and E, as well as essential minerals like calcium and iron. These nutrients contribute to their role in promoting overall health and preventing nutritional deficiencies.
2. Antioxidant and Anti-inflammatory Effects
Scientific studies have shown that curry leaves exhibit significant antioxidant properties. They help neutralize free radicals in the body, potentially reducing oxidative stress and inflammation. This aligns with Ayurvedic principles that advocate for the use of herbs to combat bodily imbalances.
3. Blood Sugar Regulation
Research indicates that curry leaves may aid in regulating blood sugar levels. They contain compounds that enhance insulin sensitivity and could be beneficial for managing diabetes—a condition increasingly prevalent in modern society.
4. Gastrointestinal Health
In Ayurveda, curry leaves are traditionally used to alleviate digestive issues. They are known to stimulate digestive enzymes and promote gut health. Modern research supports these claims by demonstrating their effectiveness in treating gastrointestinal disorders.
7. Uses And Health Benefits
Applications
3.1.1 Traditional Uses: - Curry leaf plant is popular among South Asian Dishes for its peculiar taste and aroma. It has been used as a home remedy since ages. The scented leaves are widely used in flavoring curries to promote appetite and digestion. Leaves are locally used to treat external injuries, burns and remove poison from the bite of poisonous animals and for treating rheumatism. Baked (cooked, crisped) leaves are used to check vomiting. Finely grinded leaves mixed in butter milk have positive effects for stomach upsets and act as laxative when taken in an empty stomach. Fresh leaves juice mixed with lime and sugar is used to treat morning sickness and root juice consumption gives renal pain relief. Stem is used to cleanse teeth that lead to reinforcing the gums. Fruit has anti-astringency properties. Root juice is used in kidney pain. Curry leaf can be used in treating calcium, vitamin deficiencies and anemia. Moreover antitumor, hypoglycemia, anti-hyper-cholesterol emic effects of the plant have been found. Piles, body heat, inflammation and itching are controlled with curry leaves. Traditional Ayurveda includes the use of curry leaf parts as a cure of cough, hypertension, hepatitis, rheumatism and hysteria. Traditionally curry leaves are boiled together with coconut oil until reduction to blanked residue to be used as hair tonic for keeping natural hair tone and invigorating growth of hair.
3.1.2 Medicinal Uses:- Murraya koenigii is a proven medicinal plant. The plant contains different essential oils particularly ?-pinene (39.93%), sabinene (13.3%) and transcaryophyllene (9.02%) that has been reported to have antibacterial effects against Bacillus subtilis, Proteus vulgaris, Corynebacterium pyogenes. The carbazole alkaloids are present in leaves, fruits, roots and bark of the plant having antidiabetic, anticancer, antibacterial and anti-oxidant properties. N-hexane seeds extract produces three bioactive carbazole alkaloids namely kurryam (I), Koenimbine (II) and koenine(III) out of which I and II compounds has repressive action opposed to castor oil induced diarrhea and PGE2- induced enteropooling in rats. Acetone extraction of fresh leaves contains three bioactive carbazole alkaloids namely mahanine, mahanimbine and marrayanol having astonishing antimicrobial and topoisomerase I and II inhibition activities. Mahanimbine has also been observed to decrease the blood sugar level in Swiss mice. Ether extracts from curry leaves has been observed to decrease the cancer cells in mice. Aqueous extracts of curry plant speeds up the wound healing process. Aqueous extracts contain tannins and carbazole alkaloids that have hepatoprotective activity. Alcohol extracts of stem bark and crude root extract of Murraya koenigii have anti-inflammatory activities. Murraya koenigii alcohol: water (1:1) extract has been found to have the highest antioxidant and free radical scavenging activity.
3.1.3 Industrial Uses:- The essential oils from the plant can be used in sun protection creams and erythema formulations. It can also be used for aromatherapy in the soap and cosmetic industry. Few Industrial products of Curry leaf plant are produced with a volatile oil, crystalline glycoside and murragin obtained from the flowers. The beta carotene, folic acid, riboflavin, calcium and zinc present in curry leaf are useful for oral health and can be during production of mouthwashes. Curry leaf oil (yellow, clear and transparent) is widely exported from India that can be extracted from the seeds of the plant. Stem extract can be used in skin lightening and rough skin improving creams. Petroleum ether extracts and acetone extracts from leaves can be used to prepare larvicide against Aedes aegypti.
Health Benefits:
- Powerful antioxidant:- Curry leaves are rich in plant compounds which are powerful antioxidants.
- Curry leaves are rich in antioxidants, including vitamin C, vitamin A, and flavonoids, which help neutralize free radicals and reduce oxidative stress. Oxidative stress is a condition associated with chronic disease development.
- These compounds keep us healthy and protect us from numerous diseases.They protect us from oxidative damage, preventing diseases of the nervous system, cardiovascular system, kidneys etc.
May reduce the risk of cancer:-
Curry leaves have anti-mutagenic potential. They protect our bodies from different types of cancers. Flavonoids in Curry leaves act as anti-cancer agents. They are effective in inhibiting the growth of breast cancer cells.Curry leaves also protect the body from colon cancers. Curry leaves are also beneficial in protecting our bodies from cervical cancer. In the current study, the highest flavonoid content and anticancer activity against MDA-MB-231 cells were demonstrated for the Kelantan curry leaf suggesting that the high anticancer activity in curry leaf extracts may be attributed to the high concentration of flavonoids such as myricetin, epicatechin, and quercetin.
- Reduces risk of heart diseases:-
Curry leaves protect our hearts by preventing oxidative damage. Consumption of Curry leaves also decreases cholesterol levels. It also reduces the level of triglycerides .Reduction in risk factors thus helps in protecting us from heart diseases. Curry leaves can be beneficial for heart health in a number of ways, including: Lowering cholesterolCurry leaves contain antioxidants that prevent the oxidation of LDL (bad) cholesterol, which can increase HDL (good) cholesterol levels. Regulating blood pressure
Curry leaves contain potassium, which helps to offset the effects of sodium and maintain normal blood pressure levels.
Reducing risk factors
Curry leaves contain compounds like rutin and tannins that have cardio-protective properties.
Reducing insulin resistance
Curry leaves can help regulate blood sugar levels.
- Helps in the management of diabetes:
Consumption of Curry leaves helps in the management of diabetes and its related complications. Curry leaves were found to be highly effective in reducing blood glucose levels. Curry leaves are rich in fibre which slows down digestion, thus preventing sudden spikes in blood sugar levels in our blood. They also boost the activity of insulin, further helping patients with diabetes. The curry-leaf tree, Murraya koenigii, contains a variety of chemical constituents that may help with diabetes, including alkaloids, phenols, saponins, flavonoids, tannins, and cardiac glycosides:
Alkaloids: These are the primary components of the plant's compounds and may play a role in antidiabetic properties. Biguanide related compounds (BRCs): Curry leaves are rich in BRCs, which may help with diabetes. Phenols, saponins, flavonoids, tannins, and cardiac glycosides: These secondary metabolites may help with diabetes by decreasing oxidative stress.
5. Analgesic:- Curry leaves were found to be useful in relieving pain and used traditionally as an analgesic (pain reliever).
6. Heals wounds:- Curry leaves can even be applied topically! Apply curry leaves paste on wounds, mild burns or rashes to help heal them. Curry leaves have antiseptic properties that can even protect the wounded area of the skin from infections Curry leaves (Kadi Patta) can help heal wounds because they have anti-inflammatory, disinfectant, and antioxidant properties: Wound contraction: Curry leaves help wounds contract and reduce in size.
Anti-inflammatory: Curry leaves can help fight inflammatory cells.
Antiseptic: Curry leaves have antiseptic properties that can treat skin eruptions, burns, bruises, and bee stings.
Antioxidant: Curry leaves contain antioxidants that can help protect skin from oxidative damage.
Bioactive compounds: Curry leaves contain bioactive compounds that can promote skin rejuvenation.
7. Excellent for our hair:- Curry leaves when boiled with coconut oil makes an excellent hair tonic that prevents greying and stimulates hair growth.They strengthen our hair and prevent hair loss. They are also helpful in preventing dandruff and dry scalp. Curry leaves may help with hair growth because they contain nutrients that can strengthen hair, nourish the scalp, and improve the health of the scalp:
Protein and beta-carotene: These nutrients can strengthen hair from the roots.
Iron and other vitamins: These nutrients nourish the scalp, which can stimulate hair growth and prevent breakage and loss.
Amino acids: These nutrients protect, nourish, and moisturize the scalp.
Vitamin B: This nutrient revitalizes hair strands and restores hair health.
Antioxidants: These nutrients neutralize free radicals and keep hair healthy and strong.
Minerals: Curry leaves contain minerals like selenium, zinc, iodine, and iron that can delay the onset of gray hair.


8.control side effect :- curry leaves can control the side effects.
9.improve vision:- Curry leaves are rich in carotenoid-containing vitamin A, thereby reducing the possibility of damage to the cornea. The deficiency of vitamin A can cause eye disorders, including night blindness, vision loss, and cloud formation. Thus, the leaves keep the retina safe and protect against loss
10. For Mouth ulcer and Weight loss .
Curry leaf powder mixed with honey can be applied to tongue and inside the mouth to help heal mouth ulcer.
Improving digestion, and reducing cholesterol may help with weight management.
11. Degenerative brain disease:-
Curry leaves may potentially be beneficial for protecting the mind against degenerative brain diseases like Alzheimer's and dementia.
12.Symptoms of diarrhea:- Curry leaves or Kadi patta helps in curing diarrhoea
A component called carbazole alkaloids present in curry leaves have anti-diarrheal properties that significantly control castor oil-induced diarrhea.
13. Treatement of morning sickness:- Curry leaves may help with morning sickness because they have several properties that can help with digestion, blood sugar, and inflammation:
Hydration: Curry leaves contain water-soluble vitamins that may help with hydration.
Aroma: The aroma of curry leaves may have a calming effect that can help reduce nausea and discomfort.
14.Used in insect repellent:- Curry leaves can be used as an insect repellent because they contain chemical compounds that have insect-repelling properties
Neplanocin A: The main constituent of the most larvicidal curry tree leaf extract.
Caryophyllene, ?-guaiene, and ?-phellandrene: The main chemical compounds in curry leaf essential oil.
Oxygenated monoterpenes: These compounds have antioxidant, antibacterial, and insect-repelling properties.

8. Future Prospective
- Exploration of Active Compounds: -Further research is needed to isolate and study the active compounds in curry leaves that contribute to their medicinal properties. This could lead to new therapeutic applications.
- Cultural Significance:- Understanding the historical context of curry leaves within Ayurvedic practices can enhance appreciation for traditional knowledge systems and their relevance today.
- Health benefit:- The curry are useful in many longer time diseases. So the small leaves of curry leaves save humans Life.
- Possibility:- There are possibility to produce biscuits, bites (murukku) and other bread products using curry leaves. Western countries prone to Ayurwedic medicines now days, so it has potential to produce balms, inhalers, oils and etc.
- First Preference – Ayurveda:- Different types of ayurvedic products are available in market such as curry leaves products, aloevera products,neem,tulsi,etc.. So we know that ayurvedic products are less side effects than allopathic products.
9. CONCLUSION
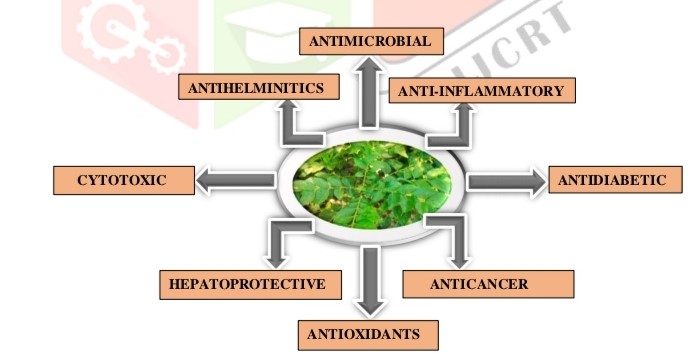
Murraya koenigii is a valuable medicinal plant used globally in different traditional systems of medicine. We attempted to provide morphological, phytochemical, information on M. koenigii in this review. This plant shows antimicrobial, anti-inflammatory, antidiabetic, anticancer, antioxidant, antihelminitics, and hepatoprotective activities.
10. ACKNOWLEDGEMENT
Authors are thankful to the “first and foremost, I would like to praise and thank God, the Almighty, who has granted countless blessings, knowledge, and opportunity to the writer. The Authors are thankful to the Management & Principal of Satyajeet College Of Pharmacy, Mehkar for Providing facilities to carry out the work. The authors are thankful to Project Guide Prof. Vikas K Gawande. The authors are also thankful to Prof. Tejas J. Sharma Providing the ideas about the publication.
REFERENCES
- A REVIEW ARTICLE ON CURRY LEAVE (Murraya koenigii) Arti Bochare, Shankar Aher, Dhanashri Jadhav Matoshri Institute of Pharmacy, Dhanore, yeola (423401) Maharashtra, India. 2023 IJCRT | Volume 11, Issue 1 January 2023 | ISSN: 2320-2882
- A REVIEW ON CURRY LEAVES (MURRAYA KOENIGII): POTENTIAL MEDICINAL PLANT. Laxmikant D Shirole, Sunil M Ahire, Rajesh T Shewale, Assistant prof. Vijay V Pawar2022 IJCRT | Volume 10
- REVIEW ARTICLES Reviews in Food and Agriculture (RFNA)DOI: http://doi.org/10.26480/rfna.01.2021.36.38 CURRY LEAF: A REVIEW Dipika Bhusal and Dhirendra Pratap Thakur Issue 11 November 2022 | ISSN: 2320-2882
- Suman singh, p.k. omre & sandhya madan mohan ,curry leaves- a miracle plant
- Herbal Medicine Advancement: Comprehensive Review Himanshu. G. Bokde?1;, Gopal A. Chavhan?2;, Vinayak A. Katekar?3;, Yashkumar R. Dhole?, Dr SJIF Impact Factor: 7.187 https://zenodo.org/records/10575776.Swati.P.Deshmukh
- B Maheswari Reddy, CK Dhanpal, BVS Lakshmi International Journal of Advances in Pharmacy Medicine.
- Suman Singh, PK More, Sandhya Madan MohanIndian Journal of Scientific Research .46-52, 2014
- Sinha Parul, Akhtar Javed, Batra Neha, Jain Honey, Bhardwaj Anuj Asian Journal of Pharmaceutical Research 2 (2), 51-53, 2012
- Muthulinggam Nishan, Partiban Subramanian Int. J. PharmTech Res 7 (4), 566-572, 2015
- Mylarappa B Ningappa, Ramadas Dinesha, Leela Srinivas Food chemistry 106 (2), 720-728, 2008.


 Sarla Gaikwad*
Sarla Gaikwad*
 Vikas Gawande
Vikas Gawande
 Dr. Shivshankar Mhaske
Dr. Shivshankar Mhaske
 Tejas Sharma
Tejas Sharma










 10.5281/zenodo.14590932
10.5281/zenodo.14590932