Abstract
Hyperlipidemia is a medical condition that causes an increase in one or more plasma lipid levels including, triglycerides, cholesterol, and phospholipids. The increase in plasma levels can cause various diseases of the cardiovascular system. Cardiovascular diseases include atherosclerosis. Ischemic heart disease, Cardiac arrhythmias, and Heart blockage. Heart blockage due to plaque formation can be treated with various drugs. This article contains an Introduction, type of lipoprotein, classification of Hyperlipidemia, causes, symptoms, Pathophysiology, Diagnosis, Prevention, and Treatment.
Keywords
Hyperlipidemia, Cardiovascular diseases, LDL, VDL, Chylomicrons
Introduction
Hyperlipidemia is the condition in which the elevation of plasma lipids occurs, which can cause various diseases including coronary, cerebrovascular, and peripheral vascular artery diseases. Hyperlipidemia is defined as the condition in which the level of cholesterol and triglycerides increases in the plasma than normal. In the body, the liver produces about 80% of cholesterol but the rest is obtained from the food we eat such as fish, eggs, and meat. Hyperlipidemia is the major cause of various Cardiovascular diseases which shows greater risk factors and causes major issues. Various drugs are used to treat Hyperlipidemia and to reduce cholesterol levels in the plasma which includes statins and fibrates.
Types of Lipoproteins
- High-density lipoproteins (HDL)
- Intermediate-density lipoproteins (IDL)
- Low-density lipoproteins (LDL)
- Very Low-Density Lipoproteins (VLDL)
- Chylomicrons
High-Density Lipoproteins:
HDL is considered a good cholesterol and is synthesized in the liver. It picks up the excess amount of cholesterol from the blood and takes it back to the liver where breakdown happens and removal from the body. An HDL level ranging from 60mg/dL should be considered desirable and protect against heart diseases.
Intermediate Density Lipoprotein (IDL):
After the removal of Triglycerides from VLDL by muscles and Adipose tissues, the IDL particles form which have cholesterol molecules.
Low-Density Lipoprotein:
It is sometimes referred to as bad cholesterol because it makes up most of your body's cholesterol. High levels of LDL cholesterol can cause the risk of Heart disease and strokes.
Very Low-Density lipoprotein:
Very low-density lipoprotein is produced in the liver and released in the bloodstream for supplying fats(triglycerides) to the body tissues.
Chylomicrons:
They are the large triglycerides-rich lipoprotein produced in tight junctions of the cells. They transport dietary triglycerides and cholesterol peripherally.
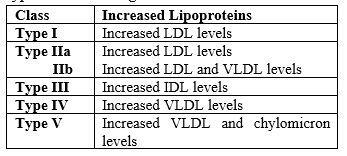
Types of Hyperlipidemia
Various types of Hyperlipidemia include:
Based on lipid types:
Two types:
Hypercholesteremia: It is a medical condition in which is high amount of LDL is found in blood and this can cause various heart diseases.
Hyperlipidemia: it is a condition in which there is a high amount of lipid found in blood and it deposits in blood vessels and restricts the blood flow.
Based on Causing factors:
- Primary Hyperlipidemia (Familial: Hereditary)
It can be caused due to some genetic defects. It can be both monogenic and polygenic. It has various types that cause high-risk factors.
Secondary Hyperlipidemia (Acquired)
It can cause pancreatitis. It is caused by various disorders like Diabetes, glomerular syndrome, Hypothyroidism, and Chronic alcohol intake.
Complications of Hyperlipidemia
There are various complications which include:
- Atherosclerosis
- CAD
- Ischemic Heart Diseases
- Myocardial infarction
- Retinopathy
- Nephropathy
Atherosclerosis:
Hyperlipidemia can cause various cardiovascular diseases. Atherosclerosis is one of the diseases that can be caused by hyperlipidemia. It is the process in which there is accumulation of lipids, cholesterol, and calcium occurs which causes plaque formation on the walls of arteries.
CAD (Coronary Artery Diseases):
It occurs when there is an accumulation of lipids on the walls of arteries and plaques are formed which cause the narrowing of arteries and there is less blood supply, and insufficient oxygen supply occurs in the body.
Ischemic Heart Disease (IHD):
Ischemia is defined as inadequate blood supply to the body organ due to plaques that block the blood vessels. Ischemic heart disease is also called CHD (Coronary Heart disease). Due to less blood supply stroke can occur.
Myocardial Infraction (MI):
MI is a medical condition where the heart muscle begins to die due to less blood supply to the heart. It can be a life-threatening emergency.
Other Complications include:
- Peripheral artery disease
- Microvascular disease
- Sudden cardiac arrest
- Carotid artery disease
Causes of Hyperlipidemia
- Dairy Products
- Obesity
- High Fat Intake
- Alcohol
- Smoking
- Genetic or Inheritance
- Several drugs include corticosteroids, estrogens, and beta blockers.
Symptoms of Hyperlipidemia:
- Chest Pain
- High rate of Obesity
- Increased Glucose levels
- High Cholesterol levels
- Blood vessels blockage
- Pancreas, liver and spleen swelling
Pathophysiology of Hyperlipidemia:
Hyperlipidemia is generally elevated LDL levels. Its elevation can cause an increased concentration of lipids and fats in the blood. It can cause endothelial damage and plaque formation on the artery walls. These formed plaques can cause the narrowing of arteries and less blood supply.
Diagnosis:
Diagnosis of Hyperlipidemia occurs through blood tests, by checking blood cholesterol levels. Hyperlipidemia can be diagnosed by regular checkups of LDL, HDL, VLDL, and triglyceride levels in the blood.
Prevention and Treatment of Hyperlipidemia
Prevention
- Maintain weight and cholesterol intake.
- Ensure proper diet and Physical exercises.
- Ensure to take food with high soluble fiber such as oats, beans, and fruits.
Lifestyle Modifications to Prefer for Lowering the Cholesterol Level;
-
- Proper diet
- Eating healthy meals
- Having non oily foods
- Eat plenty of fruits
- Regular exercise and yoga
Treatment
- Lifestyle Changes
- Ayurvedic changes
- Using Home Medications such as turmeric, coconut oil, fish oil, Indian gooseberry, soybean
- Using Medicinal Plants to lower Hyperlipidemia
Pharmacological Treatment
There are various drugs present on the market that reduce Hyperlipidemia which include statins, Fibrates, Niacin, and plant sterols.
Fibrates:
Fibrates include clofibrate, fenofibrate shows lipid-lowering activities, reduces LDL levels, and thus HDL levels increase moderately. It shows a slower reduction in coronary atherosclerosis.
Statins (HMG- CoA reductase Inhibitors)
Statins include atorvastatin, Fluvastatin, Lovastatin, Pravastatin lowers the cholesterol levels of the body. Statins lower the LDL levels by inhibiting the HMG-CoA reductase enzyme activity which leads to results in a decrease in Hepatic cholesterol content.
Niacin (Nicotinic acid Derivatives)
It works by lowering both cholesterol and triglyceride concentrations in plasma. It also increases High-Density Lipoprotein (HDL) lipoprotein.
Side effects of Antihyperlipidemic
Nausea and vomiting, joint pain, Severe headache, vision problems, Swelling of arms and legs, black stool, bleeding, muscle pain.
Recent Invention Drugs for Hyperlipidemia
In a few years there have been many cases of Hyperlipidemia noticed which leads to various cardiovascular diseases, recent advancement shows the new drug discovery for lipid lowering and preventing cardiovascular diseases. Drugs such as Bempedoic acid, Inclisiran, Evinacumab, and Pemafibrate work well in lowering the lipid level and inhibiting cholesterol synthesis.
CONCLUSION
From the above study, the hyperlipidemia condition shows a greater risk factor for cardiovascular diseases. Hyperlipidemia can be treated by recent drugs, proper diet regular exercise, and yoga. Diet maintenance can help to reduce early Hyperlipidemia conditions.
REFERENCES:
- DiPiro JT, Pharmacotherapy Handbook, Wells BG, Schwinghammer TL, DiPiro CV, Education MH, editors, Appleton and Lange: 2000 Jan
- Goodman LS, Gilman A the Pharmacological Basis of therapeutics. Macmillian. New York. 1970
- Singh R, Nain S. A Mini Review on Hyperlipidemia. Common Clinical Problem. Interv Cardiol J 2018; Vol 4
- DuBroff R, de Lorgeril M. Cholesterol confusion and statin controversy. World J Cardiol. 2015 Jul 26
- Inkeles S, Eisenberg D. Hyperlipidaemia and coronary atherosclerosis: a review. Medicine (Baltimore). 1981 Mar
- Nelson RH. Hyperlipidaemia is a risk factor for cardiovascular disease. Prim Care. 2013 Mar
- Pettersson C. Studies on the atherogenicity of apo-containing lipoproteins in type 2 diabetes. Institute of Medicine. Department of Molecular and Clinical Medicine; 2009 Jan 15.
- Murphy SL, Xu J, Kochanek KD. Deaths: final data for 2010. Natl Vital Stat Rep. 2013 May 8;61(4):1-117. PMID: 24979972.
- Lipid Research Clinics Coronary Primary Prevention Trial. The lipid research clinics coronary primary prevention trial results. American Medical Association; 1984.
- Steinberg D. Thematic review series: the pathogenesis of atherosclerosis. An interpretive history of the cholesterol controversy, part V: the discovery of the statins and the end of the controversy. J Lipid Res. 2006 Jul;47(7):1339-51. doi: 10.1194/jlr.R600009-JLR200. Epub 2006 Apr 3. PMID: 16585781
- Joseph, D. Pharmacotherapy, A pathophysiological approach, 8thedn, The McGraw Hill Companies, Inc. 2011; pp370.
- Tripathi KD. Essentials of Medical Pharmacology. 5 [sup] th ed. New Delhi: Jaypee Brothers Medical Publishers (P) Ltd. 2008:778-9.
- Joseph, D. Pharmacotherapy, A pathophysiological approach, 8thedn, The McGraw Hill Companies, Inc. 2011; pp370.
- Gupta R, Mohan I, Narula J. Trends in Coronary Heart Disease Epidemiology in India. Ann Glob Health. 2016 Mar-Apr;82(2):307- 15. doi: 10.1016/j.aogh.2016.04.002. PMID: 27372534.
- Moynihan R. Surrogates under scrutiny: fallible correlations, fatal consequences. BMJ. 2011 Aug 15;343:d5160. doi: 10.1136/bmj.d5160. PMID: 21844159.
- Abourbih S, Filion KB, Joseph L, Schiffrin EL, Rinfret S, Poirier P, Pilote L, Genest J, Eisenberg MJ. Effect of fibrates on lipid profiles and cardiovascular outcomes: a systematic review. Am J Med. 2009 Oct;122(10):962.e1-8.
- Belay B, Belamarich PF, Tom-Revzon C. The use of statins in pediatrics: knowledge base, limitations, and future directions. Pediatrics. 2007 Feb;119(2):370-80. doi: 10.1542/peds.2006- 0787. PMID: 17272627
- National Cholesterol Education Program. Second Report of the Expert Panel on Detection, Evaluation, and Treatment of High Blood Cholesterol in Adults (Adult Treatment Panel II). Circulation. 1994 Mar;89(3):1333-445. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.89.3.1333. PMID: 8124825.
- Cunningham AB. An investigation of the herbal medicine trade in Natal/KwaZulu. Institute of Natural Resources, University of Natal; 1988
- Gao W, He HW, Wang ZM, Zhao H, Lian XQ, Wang YS, Zhu J, Yan JJ, Zhang DG, Yang ZJ, Wang LS. Plasma levels of lipometabolism-related miR-122 and miR-370 are increased in patients with hyperlipidemia and associated with coronary artery disease. Lipids Health Dis. 2012 May 15;11:55. doi: 10.1186/1476-511X-11-55. PMID: 22587332; PMCID: PMC3439335.


 juhi Tiwari*
juhi Tiwari*

 10.5281/zenodo.11261886
10.5281/zenodo.11261886