Abstract
Indapamide is a Thiazide- suchlike diuretic medicine used in the treatment of hypertension Since 1977. Class of Thiazide- Suchlike diuretics. It shows great capability to overcome Hypertension as well as Heart failure. Different analytical method used to get to determine a chemical or physical property of a chemical substance, chemical element, or mixture. Even though Indapamide has had the approval for clinical use for more than 30 years now most of the analytical methods for its determination reported in the scientific literature are the ones which utilize different analytical methods. This shows which method and which Solvents are more efficient to determine Indapamide.
Keywords
Indapamide, Hypertension, Thiazide,Diuretic, Analytical Method
Introduction
History of Drug[1-3]
- Indapamide is a thiazide- suchlike diuretic medicine used in the treatment of hypertension, as well as decompensated heart failure. Combination medications with perindopril (an ACE asset antihypertensive) are available. The thiazide- suchlike diuretics (indapamide and chlorthalidone) reduce threat of major cardiovascular events and heart failure in hypertensive cases compared with hydrochlorothiazide with a similar prevalence of adverse events. It was patented in 1968 and approved for medical use in 1977.It is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines.
- It’s Mainly included hypertension and edema due to congestive heart failure. Indapamide has been shown to reduce stroke rates in people with high blood pressure. Studies have shown that the blood pressure lowering goods of indapamide in combination with perindopril reduce the rate of stroke in high threat cases (those with a history of high blood pressure, stroke or type two diabetes). HYVET study showed that indapamide (sustained release), with or without perindopril as antihypertensive treatment in persons 80 times of age or aged with sustained systolic blood pressure of 160 mmHg or advanced, demonstrated significant reduction in all- cause mortality when treated to a target of 150/80 mmHg, but there was set up to be no significant reduction in threat of death from cardiac causes
- Two methodical reviews linked that indapamide with or without perindopril significantly reduced each- beget mortality in youthful- senior cases with a history of stroke, cardiovascular complaint and type 2 diabetes mellitus, when lesser reductions in mean office blood pressure are achieved, significant cardiovascular benefit was only observed when trials including the >75 times old cohort was included.
Class of Drug [4]
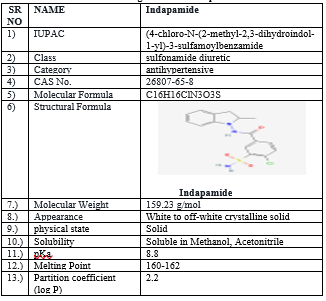
Classified as a sulfonamide diuretic, indapamide is an effective antihypertensive agent and by extension, has shown efficacity in the forestallment of target organ damage. Administration of indapamide produces water and electrolyte loss, with advanced boluses associated with increased diuresis. Drug Profile of Indapamide.
Table 1 Drug Profile of Indapamide
Current Research on Indapamide-
Current exploration on Indapamide- Indapamide (IND) is a medic action to treat high blood pressure that can reduce oxidative stress and ameliorate the survival of whim-whams cells in laboratory studies. IND is presently approved to treat high blood pressure. IND is available in tablet form and is generally taken formerly a day, the most typical cure is 2.5 mg. It's estimated that a cure of 2.5 mg per day will be sufficient to treat oxidative stress in SPMS. IND is generally well permitted.
REVIEW OF LITERATURE
Table 2 UV spectrophotometric method of Indapamide

Table 3 HPLC Method of Indapamide

Table 4 HPTLC Method of Indapamide

Table 5 LC-MS method of indapamide

Different pie Chart Acoording to Methods and solvents .
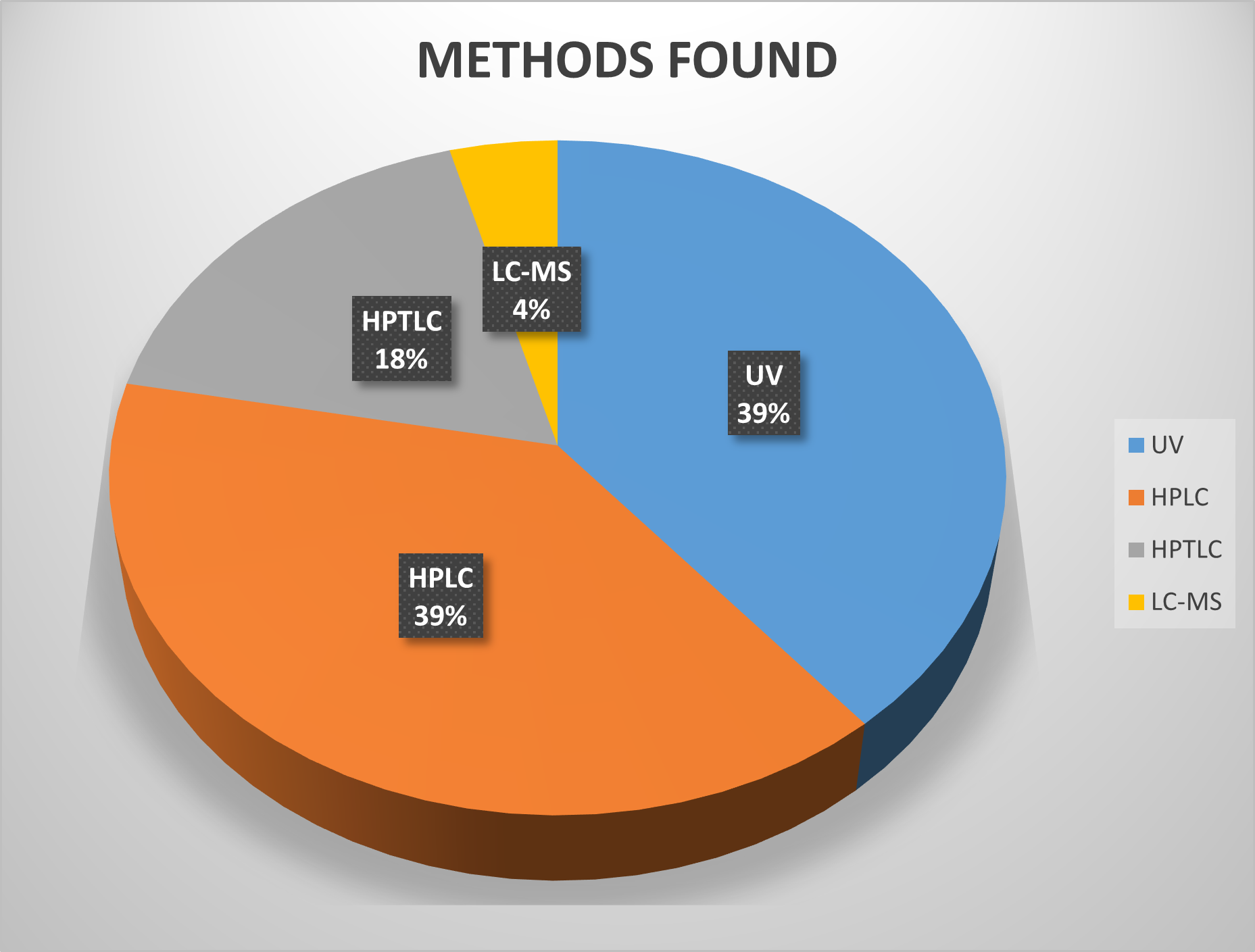
Fig-1 Methos Found for Indapamide

Fig 2- Solvent Used for Indapamide
CONCLUSION
Indapamide is one of the most important Thiazides and even though it received approval for clinical use in the year 1977, just a few analogs of Indapamide have been able to reach the stages of clinical development. The HPLC-based methods coupled with UV are the major analytical techniques available in the literature for the determination of Indapamide in pharmaceuticals as well as in the Development Stages. Most of the methods included in the present review have used HPLC systems coupled with UV detectors. The analytical methods that use mass spectrometers as detectors have emerged in recent years as well as high amount. After the Literature review, we found most of the methods used Methanol and Phosphate Buffer in different ranges.
REFERENCES
- J.Chalmers, et al, “Benefit of treatment based on indapamide mostly combined with perindopril on mortality and cardiovascular outcomes: a pooled analysis of four trials.” Journal of Hypertension.2023,41(3),508-515.
- NICE guideline [NG136] Hypertension in adults: diagnosis and man agreement. National Institute for Health and Care Excellence. https:// www.nice.org.uk/guidance/ng136. Published 28 August 2019. [Accessed 15 October 2022].
- S.Jonathan, et al, “Demonstrating the Benefits of Antihypertensive Nighttime Dosing and Indapamide Usage in Hypertension Management.” Journal of Pharmacy Technology. 2024, 40(1), 10 –14.
- Drug Profile of Indapamide https://go.drugbank.com/drugs/DB00808
- B.Jyoti, et al, “Development of New Spectrophotometric methods for the determination of Indapamide in Bulk and Pharmaceutical formulations.” Int.J. ChemTech Res.2011,3(2),755-760.
- N.K Tarkase, et al, “Development and Validation of UV-Spectrophotometric methods for estimation of Indapamide in bulk and tablet dosage form.” Der Pharma Chemica, 2012, 4 (3), 1128-1132.
- O.B Yalcinkaya, et al, “Solvent effects on UV–Vis and FT IR spectra of indapamide combined with DFT calculations.” Chemical Papers.2020, 74,1103–1111.
- N Fernades, et al, “Dual wavelength and simultaneous equation spectrophotometric methods for estimation of atenolol and indapamide in their combined dosage form.” Int. J. Chem. Sci. 6(1), 2008, 29-35.
- A.Erica, et al, “Development and Validation of a Novel UV Spectrophotometric Method for Simultaneous Analysis of Amlodipine, Indapamide and Perindopril.” Indian J Pharm Sci. 2020,82(5),843-850.
- F Ragisha and K Shilpa, “Development and Validation of UV Spectrophoto metric Methods for Simultaneous Analysis of Amlodipine and Indapamide in Combined Dosage forms.” IJPRA. 2022, 7(4) ,1638-1643.
- K. Modi and N.P Chhagna, “Development and Validation of Spectrophotometric Method for Simultaneous Estimation of Perindopril and Indapamide in Combined Dosage Form by Absorbance Correction Method.” IJPRIF.2010,2(1),411-416.
- P. Seemarini and T. Ashpak, “Development and Validation of UV Spectrophotometric Estimation of Perindopril Erbumine and Indapamide in Bulk and Tablet Dosage by using Area Under Curve Method.” Great Britain Journals Press.2023,23(1),33-39.
- P. Pradnya et al, “Simultaneous Estimation of Indapamide and Atenolol by Two Different Ultraviolet Spectroscopic Methods.” Indian J Pharm Sci .2024, 86(3),896-903.
- S.S Kale, et al, “Two Wavelength Method for Estimation of Indapamide and Perindopril Erbumine in Combined Tablet Dosage Form.” RJPT.2024,1-8.
- T.Jan Hang, et al , “A selective HPLC method for the determination of indapamide in human whole blood: Application to a bioequivalence study in Chinese volunteers.” Journal of Pharmaceutical and Biomedical Analysis.2006, 40 202–205.
- H.K.H Pannu et al, “Validated RP-HPLC Method for the Determination of Indapamide in Bulk and Tablet Dosage Form.” Der Pharma Chemica.2012, 4 (3),996-1002.
- B.Jyoti et al, “Development and Validation of RP-HPLC Method for Quantitative estimation of Indapamide in Bulk and Pharmaceutical dosage forms.” IJPRIF.2011,3(3)1482-1487.
- S.C Heghes, et al, “HPLC-UV determination of indapamide in the presence of its main synthesis and degradation impurities. Method validation.” FARMACIA, 2017,65(5),755-760.
- P.B Deval et al, “Simultaneous Estimation of Amlodipine Besylate and Indapamide in a Pharmaceutical Formulation by a High-Performance Liquid Chromatographic (RP-HPLC) Method.” Sci Pharm. 2012, 80,581–590.
- L Razma ,et al, “A Validated HPLC Method for Simultaneous Determination of Perindopril Arginine, Amlodipine, and Indapamide: Application in Bulk and in Different Pharmaceutical Dosage Forms.” JOAI.2017, 100(4),992-999.
- G. Tulja, et al, “A Validated RP-HPLC Method for Simultaneous Estimation of Atenolol and Indapamide in Pharmaceutical Formulations.” E-Journal of Chemistry. 2011, 8(3), 1238-1245.
- X Gao, et al, “HPLC Determination and Pharmacokinetic Study of Indapamide in Human Whole Blood.” Chromatographia. 2005, 61, 581-585.
- P.S.R.CH.N.P. Varma D, et al, “Validated stability indicating Reverse phase HPLC method for the simultaneous estimation of perindopril and indapamide in pharmaceutical dosage forms.” Int J Pharm. 2013, 3(1), 277-289.
- B.Shiva, et al, “Stability indicating isocratic RP-HPLC method development and validation for indapamide and perindopril erbumine in pure and its combined tablet dosage form.” IJPSR. 2015, 6(8), 3428-3438.
- A.Gindy et al, “Stability-indicating HPLC method for simultaneous determination of captopril, indapamide, and their related compounds.” Journal of Liquid Chromatography & Related Technologies.2024 37,696–712.
- K.Dipen, et al , “Development and validation of HPTLC method for simultaneous estimation of telmisartan and indapamide in pharmaceutical solid dosage form.” J. Chem. Pharm. Res. 2015, 7(11),236-240.
- K.R Gupta, et al, “High Performance Thin Layer Chromatographic Estimation of Atenolol and Indapamide from Pharmaceutical Dosage Form.” Asian J. Chem. 2007,19, (6) ,4183-4187.
- B.Varsha, et al, “Development and validation of stability-indicating HPTLC method for the estimation of perindopril and indapamide.” Int J Pharm Pharm Sci.2014,6(7), 621-625.
- G.V Santosh, et al, “Development and validation of stability indicating HPTLC method for determination of indapamide and amlodipine besylate.” WJPPS.2020,9(8),2082-2092.
- A.K Desai, et al, “HPTLC Method for the Simultaneous Estimation of Amlodipine Besylate and Indapamide in Tablet Formulation.” Asian Journal of Research in Chemistry.2012,5(6),510-514.
- G.A Pinto, et al, “An improved LC-MS/MS method for quantitation of indapamide in whole blood: application for a bioequivalence study.” Biomed. Chromatogr. 2014, 28: 1212–1218.


 Deep Savsani * 1
Deep Savsani * 1
 Mitali Dalwadi 2
Mitali Dalwadi 2






 10.5281/zenodo.13629931
10.5281/zenodo.13629931