Abstract
Because the harsh synthetic chemicals and pollution of today's fast-paced lifestyle are detrimental to our health, nature has given us its ageless, notable herbal ingredients. In addition to increasing the risk of skin cancer, UV rays are the primary cause of sunburn. Sunscreen is a topical chemical that shields the skin from UV rays by reflecting or partially absorbing them. The study of phytoconstituents entails figuring out how plants work and then applying that understanding to develop novel pharmaceutical products and their formulations. Among its many benefits are its antibacterial, anti-inflammatory, anti-diabetic, and anti-hypertensive qualities. Plants afflicted with oxidative stress-related illnesses will eventually produce potentially therapeutic secondary metabolites.
sunscreen is a chemical that shields the skin from the sun's UV rays when exposed to it excessively. Due to its capacity to inhibit UV-induced sunburn (known as the sun protection factor, or SPF), sunscreen is used for sun protection.The goal of the current study is to create sunscreen lotion using extracts from bioactive goods that has a broad spectrum of anti-UV radiation efficiency and a lower concentration of chemical UV filters .The extracts such as Citrus sinensis (Orange peel),Aloe vera (Liliaceae),Carrot oil(Daucuscarota),Turmeric(Curcuma Longa).
Keywords
Sunscreen,UV rays ,sunburn,skin,photoprotection
Introduction
Sunscreen is a chemical compound that helps shield the skin from ultraviolet light. Sunburn is caused by UV B radiation, however UV A may cause more skin damage. A sunscreen that blocks both wavebands is ideal. The aim of this study was to develop a topical herbal sunscreen formulation with some fixed oils and a mixture of medicinal herbs. Actinic keratosis, melanoma, and squamous cell carcinoma can all be avoided with regular sunscreen use.[1] Sunscreen chemicals can be either inorganic or organic. Sunscreen products that protect skin from UV radiation by reflecting or absorbing them are also known as sunscreen lotions. The growth in skin cancer instances and the photodamaging effects of UV radiation have led to a surge in the usage of sunblock products, which have shown promising outcomes in symptom reduction.Ingredients in sunscreen should be fully safe, free of chemicals, non-irritating, non-toxic, photostabilized, and capable of protecting skin from the sun.[2] Skin cancer, photoaging, and sunburn are the results of this. Owing to these detrimental effects of UV radiation, sunscreen formulations that boost SPF, cure sunburns and suntans, prevent skin cancer, and slow down skin ageing must be developed. Sunscreen formulation aims to enhance protection against UV range dilation by obstructing them. Flavonoids, phenolic compounds, and herbal oils are essential for UV protection because they possess antioxidant properties and can absorb UV radiation in the UV-A region. Chemicals included in synthetic sunscreens have been linked to dermatitis-like allergic reactions, cell mutation, hormone fluctuations, and DNA damage.[3] Using an aloe vera gel extract can help you physically protect yourself from the sun. It is gentle for the skin and non-greasy. It contains Daucus carota extract.Because it absorbs UVB rays, sunscreens typically incorporate this substance.skin tone uniformity.For this reason, carrot oil may absorb UVB rays. assist in reducing the hyperpigmentation's look.Vitamin C content in citrus sinus powder is very high. Additionally, the synthesis of collagen and elastin enhances the appearance of your skin.[4] You can aid yourself by applying an aloe vera gel extract as a physical sun protection. It is non-greasy and kind to the skin. Daucus carota extract is present.This material is commonly seen in sunscreens because it absorbs UVB radiation.consistency of skin tone.Carrot oil may therefore absorb UVB radiation. help to lessen the appearance of hyperpigmentation.Citrus sinus powder has a very high level of vitamin C. The production of elastin and collagen also improves the appearance of your skin.[5]
Ranges of UV rays

Table no .2 Ranges of UV rays
Ideal properties of herbal sunscreen cream:
? Preferentially absorb light between 280 and 320 nµ.
? Resistance to water
? Be resistant to heat, light, and perspiration.
? The user prefers an odourless environment, however minor odours are acceptable.
? Avoid toxicity, irritation, and sensitization.
? Offers long-lasting sun protection.
? Remains stable while use.
? Does not discolour or absorb quickly.
? Maintain neutrality.
? Be quickly soluble in appropriate vehicles.
- Absorb UV rays that cause sunburn. - Stability in sunlight - Complete skin protection - Safety, effectiveness, chemical inertness, low concentration - No irritation, sensitization, or toxicity - No staining Filtering benefits include UVB and UVA radiation protection, antioxidant and reactive oxygen species scavenging, anti-mutagenicity, and anticancer properties.
?Booster effect.[7]
Merits of herbal sunscreen cream
? Helps prevent sunburn and premature ageing
? Provides immediate sun protection upon application.
? Exposure to direct UV radiation extends its lifespan.
? Ideal for persons with heat-sensitive skin (redness).
• Protects against UVA and UVB rays.
? Easily accessible
? Safe and without adverse effects
? Requires no special equipment to prepare
? Cost-effective
? Ingredients are readily available.
? Use renewable resources.[8]
Mechanism of Photo protection
Sunscreen protects skin from harmful UV rays. Sunscreen has been shown to improve UV protection for the skin. The skin's surface scatters and reflects UV radiation in various ways. Mineral-based inorganic sunscreens function similarly in this manner. They provide solar protection for the skin.UV light absorbs heat energy, limiting its damaging effects and penetration into the skin. This is how most organic sunscreens work.

Fig no.1 : Mechanism of Photoprotection
Plan of work
The botanical garden of Shraddha Institute of Pharmacy in Kondala Zambre and local market
of Washim, where all the herbal ingredients, including Citrus sinensis (orange peel), Aloevera (Liliaceae), Carrot oil (Daucuscarota), and Turmeric powder (Curcuma Longa), were
gathered. Nowadays, practically everyone on the earth uses herbal sunscreen to protect
themselves from the damaging effects of UV radiation from sunlight. Because they have a
superior safety profile and fewer adverse effects, herbal remedies are preferred. The creation
and assessment of herbal sunscreen creams with anti-inflammatory and anti-UV radiation
qualities are the subjects of this study. Plant materials described above were extracted and
used to make creams.
Plant material
Herbal sunscreen creams were prepared by using various plant materials such as Citrus sinensis
(Orange peel),Aloe vera (Liliaceae),Carrot oil(Daucuscarota),Turmeric (Curcuma Longa).
(A) Aloe vera
• Biological source- dried latex of leaves
of it also known as cape aloe .

Fig no. 2 Aloe vera
• Family- liliaceae
• Description Colour- clear to slightly yellow
or translucent gold .
• Odour-similar like rotten garlic or onion
• Taste- Bitter
• Chemical constituents- aloe emodin
• Uses- heals burns and clears acne[10]
(B)Turmeric
• Biological source - It consists of dried rhizomes of Curcuma longa
• Family- Zingiberaceae.

Fig no .3 Turmeric
• Description
• Colour - Yellow
• Odour – Aromatic
• Taste – Bitter
• Chief chemical constituents - Curcumin, Curcuminoids
• Uses -Reduce acne, Glowing skin, Lightens skin[11]
(C) Orange
?Biological source: Citrus sinensis commonly known as orange or sweet orange, is a small
evergreen tree originally domesticated in subtropical Asia.
Family:Rutaceae
?Description
?Colour-Orange to deep orange outside, depending on the harvesting time.
?Odour-tangy
?Taste-: It tastes so sweet and juicy. Skin is aromatic too.
?Chemical constituents-Limonene, Citral
?Uses-An excellent source of vitamin c.

Fig no .4 Orange
?Chemical constituents-Limonene, Citral
?Uses-An excellent source of vitamin c.[12]
(D)carrot
?Biological source :Native from Europe and west and central Asia Daucuscarota
Family:apiaceae
?Description
?Colour: Purple red,orange and white.

Fig no. 5 Carrot
?Odour :Pungent order
?Taste: earthy or bitter
?Chemical constituents: Moisture
?Uses: Anti-Ageing Properties,Skin Brightening,Natural Moisturisation .[13]
Ingredient and their role
Table no .2 list of ingredients and their role

Instrument
Instruments used for analysis were pH meter , Brookfield viscometer , freezer and UV visible
spectrophotometer ,Hot air oven, Hot plate.
Preparation of herbal extract ( Tumeric powder)
The dry powder of curcuma longa was packaged individually in plastic bags to avoid contamination. After fully extracting the plant material using ethanol, a maceration process was carried out. Ten grams of each powder were weighed using a digital weighing balance. The powder was then macerated for fifteen hours at room temperature with 150 millilitres of 90% ethanol. Filtering was then used to separate the liquid menstruum from the residue. The ethanolic menstruum was therefore collected and subsequently purified in a round-bottom flask for an hour at a constant temperature. The extracts were extracted for one hour, after which they were transferred to a new container and kept cold for further examination and application.[14]
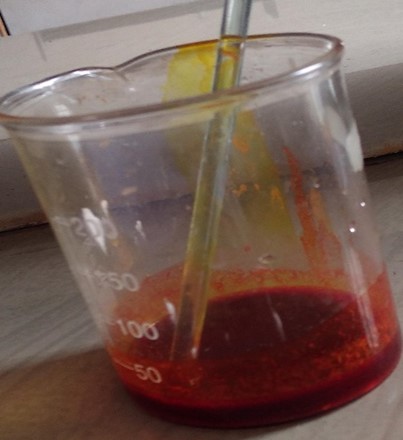
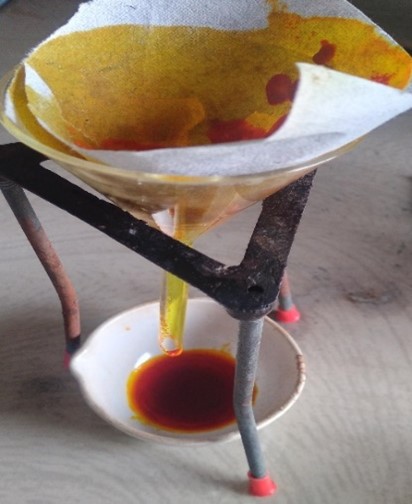


Fig no.6 Extraction of Tumeric powder
Preparation of orange peel powder
Pick up the fresh oranges from the neighbourhood market in Washim. After cleaning, peel the skin and place the peels in a petri dish.Allow the peel to dry after the hot air oven has warmed up to 75 degrees Celsius for 15 minutes. To make orange peel powder, pulverise the peels.[15]

Fig no .7 Preparation of orange peel powder
Preparation of aloevera gel
Pick fresh carrots from the community market in Washim.After washing, peel the skin, grate the carrots, and transfer them to a petri dish.Allow it to dry for fifteen minutes at 75 degrees Celsius in the hot air oven.After coating a container with coconut oil, place the dried Carrot inside and leave it outside in the sun for 48 hours. After that, filter the oil to get the extract out of it.[16]




Fig no .8 Formulation of Aloe vera gel
Formulation of herbal sunscreen cream
Step 1: On a hot plate set at 75 degrees Celsius, the emulsifier (stearic acid) and other oil-
soluble ingredients (cethyl alcohol, almond oil, carrot oil, coconut oil, and vitamin E oil)
were dissolved in the oil phase.

Fig no.9 Preparation of oil phase
Step 2: Preservatives and other water-soluble components (methylparaben, glycerol,
starch,triethanolamine, extract) were dissolved in the aqueous phase and mixed and a sufficient
quantity of water was added to the mixture on a hot plate at 75 0

Fig no .10 Preparation of water phase
Step 3: Following the mixing of the two phases, stirring was done continuously until a
homogenous result was achieved.Creams were used for additional analysis after being put
into a different glass container.
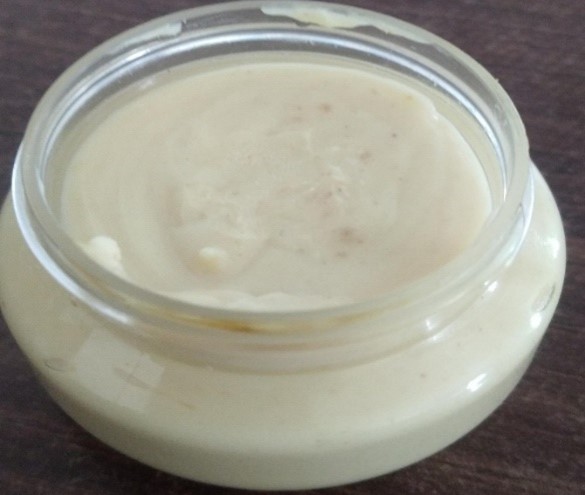

Fig no.11 final Preparation of sunscreen cream
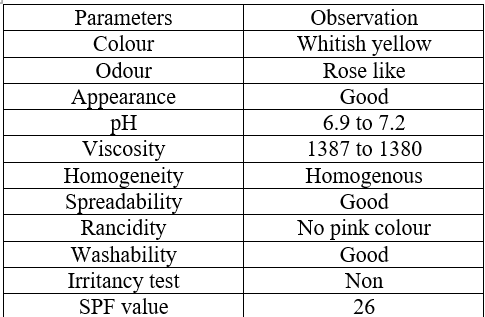
Evaluation of cream:
(1) Physical parameters
(2)pH Determination
(3)Determination of Viscosity
(4)Homogeneity
(5)Spreadability
(6)Rancidity
(7)Washability
(8)Irritancy test
(9)After feel
(10Determination of SPF
Table no.3 Evaluation of cream
CONCLUSION
The effects of UV radiation on skin damage are numerous and unexpected. Sunburn, inflammatory skin conditions, hyperpigmentation, photoaging, and skin cancer are the outcomes. Cosmetics made of herbs can protect skin from the sun's damaging rays without having any negative or comedogenic effects. The primary focus of this review is the scientific basis for the use of herbal remedies in cosmetics. The active components of herbal extracts have a significant UV-blocking capacity. Herbs are more readily available, environmentally friendly, and harmonic than synthetics.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
The authors are very thankful to the president Dr.Ramkrishan shinde Shraddha institute of pharmacy,washim (India) for providing necessary facilities through principal Dr. Swati Deshmukh to complete this work., And special thanks to the author Vinayak.A. katekar for his creative suggestions, helpful discussion, unfailing advice, constant encouragement during this work
Disclosure of conflict of interest
All authors declare that they have on conflict of interest
REFERENCE
- Mishra AK, Chattopadhyay P. Herbal Cosmeceuticals for Photoprotection from Ultraviolet B Radiation: A Review. Tropical Journal of Pharmaceutical Research. 2011; 10 (3): 351-360.
- Skotarczak K, Osmola-Mankowska A, Lodyga M, Polanska A, Mazur M, Adamski Z. Photoprotection: facts and controversies. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2015; 19(1): 98-112. PM
- Neema R, Singh R, Dubey B. Introduction and classification. Text book of cosmetics, CBS Publication and distributors 2009; (1): 82-87.
- Waghmode Monika Vasant, Prof.Khade. P.Dr. HINGANE L.D.Formulation and evaluation of herbal sunscreen cream 2021 IJCRT Volume 9, Issue 12 December 2021 | ISSN: 2320-2882.
- Kaimal S, Abraham A. Sunscreens. Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol. 2011;77(2):238-43.
- Saraf S, Kaur CD. Phytoconstituents as photo protective novel cosmetic formulations. Pharmacogn Rev. 2010; 4(7): 1-11.
- Dutra EA, Oliveira DAGC, Kedor-Hackmann ERM, Santoro MIRM., Determination of sun protection factor (SPF) of sunscreens by ultraviolet spectrophotometry,
- COLIPA method for the in vitro determination of UVA protection provided by sunscreen products Guidelines a, 2007; 2-4.
- Wood C, Murphy E, Sunscreen efficacy, Glob. Cosmet. Ind, 2000, 167: 38-44. 4.
- Wolf R, Wolf D, Morganti P, Ruocco V, Sunscreens, Clinic. Dematol. New York, 2001; 19: 452-459.
- Saraf S, Kaur CD. Phytoconstituents as photo protective novel cosmetic formulations. Pharmacogn Rev. 2010; 4(7): 1-11.
- Amit Roy, Ram Kumar Sahu Formulation and development of herbal sunscreen cream5(1):Jan -June 2014 page 12-14.
- Vaishali Bambal, Neha Wyawahare, Ashish Turaskar and Manisha Mishra (2011) ; Study of sunscreen activity of herbal cream containing flower extract of Nyctanthes Arbortristis and Tagetes Erectal.
- C.K. Kokate, A. P. Purohit ans S. B. Gokhale 2018, Parmacognocy by nirali prakashan 54th edition.
- Butler H (2000) Poucher's perfumes, cosmetics, and soap. quality, stability, and safety assurance. Kluwer Academic Publishers, Dordrecht, pp 507–621
- Abhishek D. Purohit, Rahul A. Bisen, Kajal D.Gajbhiye, Kiran S. Ukey, Aachal H. Baghele, Madhuri I. Sharnagat Formulation and evaluation of sunscreen lotion containing Natural and synthetic agents 2023; Vol. 27 (4): 597-623.
- Sahu RK, Roy A, Kushwah P, Sahu A. Formulation and development of face cream containing natural products. Research Journal of Topical and Cosmetic Science. 2012: 3(1): 16-19.
- Deep C, Saraf (2008) Novel approaches in herbal cosmetics. J Cosmet Dermatol 7:89–9511.
- COLIPA method for the in vitro determination of UVA protection provided by sunscreen products Guidelines, a, 2007, 2-4.
- 22.Parmacognocy and pytochemistry, volume 1, 1st edition, CBS Publishers and Distributors, New Delhi, 2009, page no. 3-4.23.Shanbhag S, Nayak
- Shivraj V. Mane,Devendra L. Visokar S. Yeole, Shrinath S. Waghmare,Harshita S. Waghmode, Shubham R. Khade, Surbhi C. Gupta. ‘‘Formulation Development And Evaluation of Herbal Sunscreen Lotion’’2023,12(Special issue 13), 1-10
- Vaishali Bambal and Manisha Mishra evaluation of in vitro Sunscreen activity OF herbal cream containing extracts of crucuma longa and butter monosperma.
- Bendová H, Akrman J, Krejcí A, Kubác L, Jírová D, Kejlová K, et al. in vitro approaches to evaluation of Sun Protection Factor. Toxicol in vitro 2007;21:1268-75.
- Sayre. R. M, Agin P.P, Levee, G. J, MarloweE. Comparison of in vitro testing of sun screening formulas. Photochemical Photobiological. Oxford . 1979; ver. 29, 559-566.Lin, T. K. , Zhong, L. & Santiago, J. 2017. Anti-inflammatory and skin barrier repair effects of topical application of some plant oils. International Journal of Molecular Sciences 19(1): 70.
- Deore SL, Kombade S, Baviskar BA, Khadabadi SS. Photoprotective antioxidant phytochemicals. International Journal of Phytopharmacy, 2012; 2(3): 72-76.


 Vaishnavi P. Bansod* 1
Vaishnavi P. Bansod* 1
 Vinayak A. Katekar 2
Vinayak A. Katekar 2
 Swati Deshmukh 3
Swati Deshmukh 3

















 10.5281/zenodo.13167007
10.5281/zenodo.13167007