Abstract
In order to develop a site-specific delivery of NSAID for enhanced gastric retention and controlled release, research in this project is directed at developing floating microspheres. Ideally, most conventional NSAIDs produce a degree of gastrointestinal irritation and are cleared rapidly from the stomach preventing full bioavailability. To address the problem of rapid gastric emptying, floating microspheres have been developed to retain release drugs in stomach for longer periods thereby reducing dosing frequency and improve therapeutic efficacy with decreased side effects. We prepared buoyant microspheres loaded with NSAID using solvent evaporation method employing polymers such HPMC and ethyl celluloseand assessed them for in vitro parameters like particle size, drug entrapment efficiency and release profile. Results showed more than 80% buoyancy for up to 12 hours and controlled drug release profile, suggesting that the system can enhance bioavailability [18], increase patient compliance while reducing gastric irritation associated with NSAIDs therapy.
Keywords
Ketorolac tromethamine, HPMC, CarboPole-930, Aceton.
Introduction
Periodontal disease is a general term which encompasses several pathological conditions affecting the tooth supporting structures. Periodontal diseases include conditions such as chronic periodontitis, aggressive periodontitis, systemic disease-associated periodontitis and necrotizing periodontitis. These conditions are characterized by a destruction of the periodontal ligament, a resorption of the alveolar bone and the migration of the junctional epithelium along the tooth surface. The clinical signs of periodontitis are changes in the morphology of gingival tissues, bleeding upon probing as well as periodontal pocket formation. This pocket provides an ideal environment for the growth and proliferation of anaerobic pathogenic bacteria.The microorganisms colonizing the sub-gingival area represent the principal etiological factor in the development of the inflammation and tissue destruction. Antimicrobial and Anti
inflammatory agents are used to treat periodontal diseases. These agents are associated with drawbacks like short biological half-life and inability of the active product to be retained locally for a sufficient period of time. So, these drawbacks would be markedly reduced by a novel technique, bio adhesive gel incorporated drug loaded microspheres which directly incorporates active agent into the periodontal pocket.
Diseases Of The Periodontium:
The Therapeutic Aspects Diseases of the periodontium (gingivae, cement, alveolar bone and periodontium) are frequent, presenting in children as well as in adults. The etiology of these diseases is complex; clinical manifestations are different making the classification more difficult. One classification, presented in 1999, foremost is based on the etiology of these diseases.
Types Of Microspheres
Floating microspheres
In floating types the bulk density is less than the gastric fluid and so remains buoyant in stomach without affecting gastric emptying rate. The drug is released slowly at the desired rate, if the system is floating on gastric content and increases gastric residence and decreases fluctuation in plasma concentration. Moreover it also reduces chances of striking and dose dumping. One another way is it produces prolonged therapeutic effect and therefore reduces dosing frequencies.
Drug Profile
Ketorolac tromethamine
Chemical Name : (±)-5-benzoyl-2,3-dihydro-1H-pyrrolizine-1-carboxylic acid,2
amino-2-(hydroxymethyl)-1,3-propanediol.
Molecular Formula : C15H13O3.C4H11N03
Type : small molecule
Structure :

A pyrrolizine carboxylic acid derivative structurally related to indomethacin. It is an NSAID and is used principally for its analgesic activity.(from Martin-dale The Extra Pharmacopoeia,32st ed)
Description: It is white to off white, crystalline powder.
Solubility : freely soluble in water and in methyl alcohol ,slightly soluble in alcohol, practically insoluble in acetone
Synonyms:Ketorolac,KetorolacTromethamine,Ketorolaco(Spanish Ketorolacum(Latin)
Excipients Profile
4.2.Carboxy Methyl Cellulose Sodium
Synonyms : Sodium cellulose glycolate, Na CMC, CMC, cellulose gum, sodium CMC;
Chemical names : Sodium salt of carboxymethyl ether of cellulose
Chemical formula :
[C6H7O2(OH)x(OCH2COONa)y]n
Where,
n is the degree of polymerization
x = 1.50 to 2.80
y = 0.2 to 1.50
x + y = 3.0
(y = degree of substitution)
Structural formula:
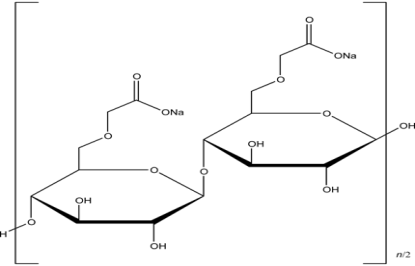
where R = H or CH2COONa
Empirical formula: The USP describes Carboxymethyl cellulose Sodium as the sodium salt of poly carboxymethyl ether of cellulose.
molecular weight: 90,000-7,00,000.
Solubility: practically insoluble in acetone, ethanol (95%), ether , and toluene. Easily
dispersed in water at all temperatures, forming clear, colloidal solutions.
CARBOPOL-934:
Carbopol 934 polymer is a cross-linked polyacrylate polymer. It offers excellent stability at high viscosity and produces thick formulations for opaque gels, emulsions, creams and suspensions. Carbopol 934 polymer has short flow properties in aqueous systems. It contains not less than 56% and not more than 68% of carboxylic acid groups.
Synonyms: Acritamer , acrylic acid polymer
carboxy vinyl polymer.
Non proprietary names : BP carbomer , USP
carbomer.
Chemical name : Carboxyl polymethylene
Empirical formul : ( C3H4O2)X (-C3H5Sucrose)y
Structure :
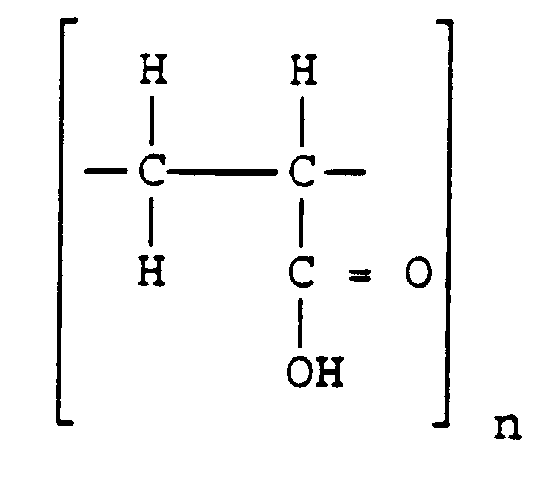
Category : bioadhesive , emulsifying ,
suspending and viscosity enhancing agent , tablet binder and release – modifying agent.
Description : White, fluffy , acidic , hygroscopic powder with a slight characteristic odour.
Solubility : after neutralization with alkali hydroxidres or amines, soluble in water, in ethanol (96%) and in glycerol.
Hydroxy Propyl Methyl
Cellulose:
Chemical name : Cellulose 2 hydroxy propyl
methyl ether.
Synonym : Methyl hydroxyl propyl cellulose
Empirical formula : HPMC is propylene glycol ether of methylcellulose. It contains methoxy (-OCH3) and hydroxyl proxy (-OCH2CHOHCH3) groups confirming to the limits for the types of HPMC.
Molecular weight : 86,000
Functional category : Emulsifying agent, suspending agent and stabilizer in gel and ointments,adhesive in plastic bandages, binder in tablet granulation (2-5%); high viscosity grades are used to retard the release of water soluble drugs.
Description : An odourless, taste less, white or creamy white fibrous or granular powder.
ACETONE
Synonyms : acetonum, dimethylformaldehyde , dimethyl ketone, b- ketopropane, pyroacetic ether
Description : acetone is a colourless volatile , flammable ,transparent liquid with a sweetish odour and pungent sweetish taste.
Structure :
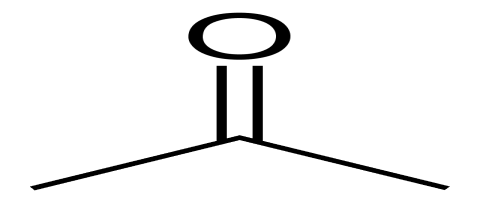
Solubility : it is freely soluble in water an ethanol (95%)
Empirical formula : C3H6O 58.08
MATERIALS AND METHODS
5.1 Materials
Materials used in present study
Table no 5.1: List of ingredients used in the study
|
S. No
|
Name Of The Ingredient
|
Manufacturers
|
|
1.
|
Ketorolac tromethamine
|
Devis laboratories
|
|
2.
|
HPMC
|
Loba chemise laboratory reagents and fine chemicals Ltd,Mumbai.
|
|
3.
|
Carbopol 934
|
Loba chemise laboratory reagents and fine chemicals Ltd,Mumbai.
|
|
4.
|
Acetone
|
Qualigens
|
|
5.
|
Liquid paraffin
|
Qualigens
|
|
6.
|
Ethyl cellulose
|
Qualigens
|
Equipment:
Equipments used in the present study
Table no 5.2 : List of equipments used in the study
|
S.No
|
Model No.
|
Name Of The Instrument
|
Manufacturers
|
|
1.
|
Ll120
|
pH meter
|
Elico pH meter
|
|
2.
|
Alpha-T
|
FT-IR
|
Bruker FT-IR Spectrometer
|
|
3.
|
|
Electron microscope
|
Magnus
|
|
4.
|
UV3000
|
UV-Visible spectroscopy
|
Labindia
|
|
6.
|
2MLH
|
Magnetic stirrer
|
Remi
|
|
7.
|
|
Mechanical stirrer
|
Remi
|
|
8.
|
P1
|
Modified balance
|
Keroy
|
|
9.
|
ELB300
|
Digital weighing balance
|
Shimadzu
|
|
10.
|
KWB220
|
Water bath
|
Remi
|
Formulation Development:
5.3.2.a. Preparation of microspheres by Solvent evaporation method
Floating Microspheres containing the anti-inflammatory drug Ketorolac tromethamine were prepared by a solvent evaporation method (table 5.3). In this technique, drug and polymer (HPMC K4M, Carbopol 940, and Ethyl cellulose in various proportions were dissolved in a 20 ml acetone which was placed in a small beaker with a magnetic bead on the magnetic stirrer at room temperature. The drug-polymer mixture was poured into 30 ml liquid paraffin containing Tween 80 maintained at a temperature of 30-40 °C and subsequently stirred by the stirrer at ranging agitation speed i.e. 1200 rpm (revolution per minute) for 60 min to allow the volatile solvent to evaporate. The microspheres formed were filtered, washed with n-hexane and air-dried for 24 h, and stored in a desiccator
Table 5.3 Formulation table of microspheres
|
S.No
|
Formulation code
|
F1
|
F2
|
F3
|
F4
|
F5
|
F6
|
F7
|
F8
|
F9
|
|
1.
|
Ketorolac tromethamine (mg)
|
40
|
40
|
40
|
40
|
40
|
40
|
40
|
40
|
40
|
|
2.
|
HPMC (mg)
|
-
|
-
|
-
|
-
|
-
|
-
|
100
|
200
|
300
|
|
3.
|
Carbopol 934(mg)
|
100
|
200
|
300
|
-
|
-
|
--
|
-
|
-
|
-
|
|
4.
|
Acetone(ml)
|
20
|
20
|
20
|
20
|
20
|
20
|
20
|
20
|
20
|
|
5.
|
Liquid paraffin(ml)
|
30
|
30
|
30
|
30
|
30
|
30
|
30
|
30
|
30
|
|
6.
|
Ethyl cellulose(mg)
|
-
|
-
|
-
|
100
|
200
|
300
|
-
|
-
|
-
|
5.3.3. Evaluation Of Microspheres:
Micromeritic properties
Bulk density
Bulk density is the ratio of the total mass of the powder to the bulk volume of powder. It is measured by pouring weighted microspheres of about 1g into a measuring cylinder and the bulk volume is noted down.
Bulk density = ????????????????????? ???????? ????????? ????????????????er/tapped
Volume
Tapped density
Tapped density is the ratio of the total mass of the powder to the tapped volume of the powder. Tapped density = ????????????????????? of ????????? ???????????????????????? /???????????????????????? ????????????????????????
Hausner’s ratio
Hausner’s ratio is the ratio of the tapped density
to the bulk density.
Angle of repose45
The angle of repose (?) is used to measure the frictional forces in a loose powder.
? = tan-1h/ r
r = Radius of the heap.
where h = height of the heap
% Compressibility index
The percentage yield of the microspheres was determined by weighing the prepared microspheres of each formulation divided by the total amount of all non-volatile components which were used for the preparation of microspheres.
Carr’s Index = Tapped density?Bulk density Tapped density X 100
Particle size analysis
Particle size analysis of drug-loaded floating microspheres was performed by optical microscopy. Few microspheres were suspended in purified water (10 ml). The sample was placed on a clean glass slide and placed on a mechanical stage of the microscope. The eyepiece of the microscope fitted with a micrometre and the size of the spheres was determined
Drug entrapment efficiency
The amount of drug entrapped was determined by crushing the microspheres in mortar and pestle. 50 mg was used for the evaluation. This was extracted with the aliquots of 0.1N hydrochloric acid (HCl). The extract was transferred to100 ml volumetric flask and the volume was made up with 0.1N HCl (pH-1.2). The solution was filtered and the absorbance was measured spectrophotometrically with suitable dilutions at a particular wavelength against the appropriate blank. The percent drug entrapped was calculated by the formula which is as follows
% Entrapment Efficiency = Practical Drug Content /Theoretical Drug Content X 100
Floating capacity
An in vitro study was carried out to determine floating capacity. 50 mg floating microspheres were placed in simulated gastric fluid (pH 1.2, 100 ml) containing tween 20 (0.02w/v %) and stirred on a magnetic stirrer at 100rpm. After 12h, the layer of buoyant microspheres was separated from the settled microspheres by filtration. Microspheres of both types were collected, dried, and weighed. The buoyancy of microspheres was determined using the following formula
Buoyancy (%) = Wf /Wf+Ws X 100
where, Wf = Weight of floating microsphere
Determination of percentage yield
The prepared microspheres were collected and weighed. The measured weight was divided by the total amount of all non-volatile components, which were used for the preparation of microspheres. The % yield was calculated by following formula
% yield = actual weight/total weight of drug and polymer X 100
Where WRec = Weight of microspheres recovered
Determination of percentage of drug loading
The percentage of Ketorolac tromethamine
loading in microspheres can be estimated using
L=Qm/Wm x100
where, L is the loading (%) of microspheres, Qm is the quantity Ketorolac tromethamine present in Wm of microspheres and Wm is the weight of the microspheres in grams.
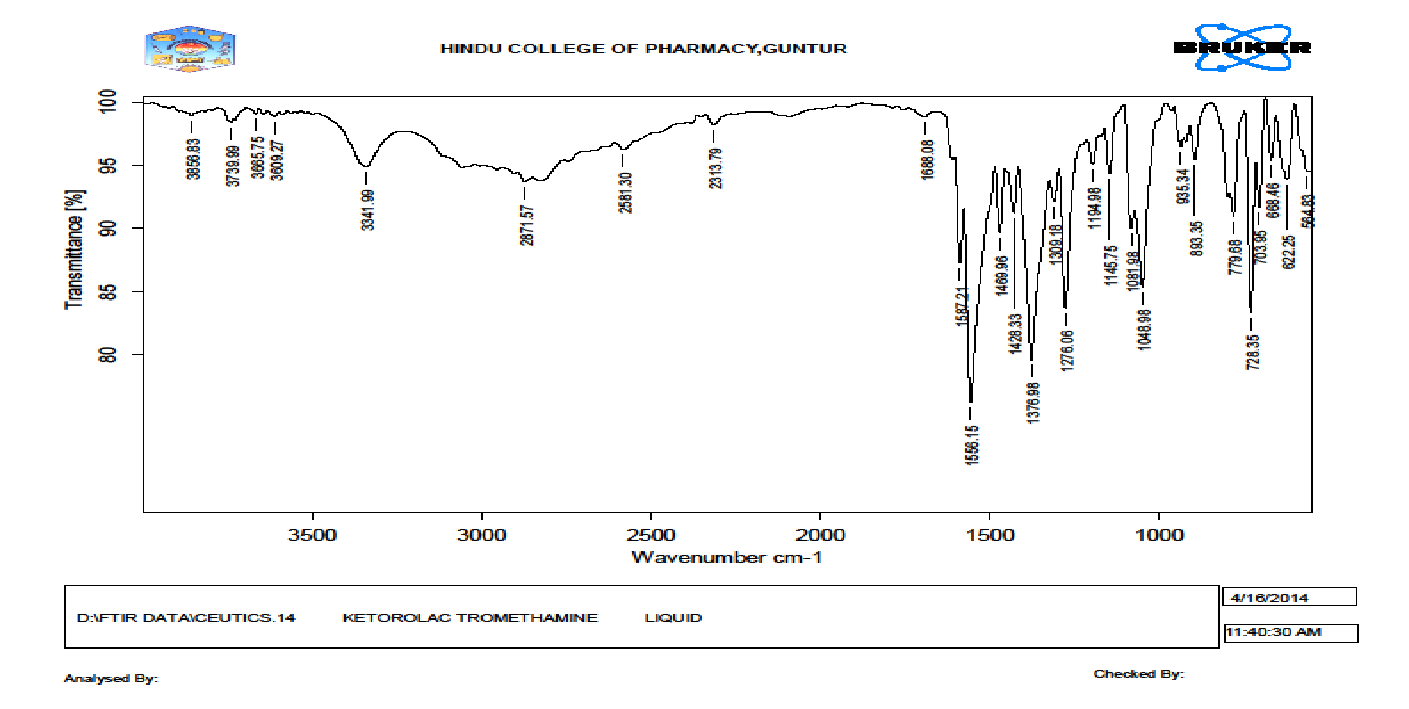
Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy
Drug polymer interactions were studied by FTIR spectroscopy. The spectra were recorded for pure drug and drug loaded microspheres using FTIR. A pellet of approximately 1 mm diameter of drug was prepared by compressing 3-5 mg of the drug with 100-150 mg of potassium bromide in KBr press (Model M-15, Techno Search Instruments). The pellet was mounted in IR compartment and scanned between wave number 4000 – 400 cm-1 using a Shimadzu Model 8400 FTIR.
In vitro drug release studies
An in vitro drug release studies were carried out in USP type II (Paddle type) dissolution apparatus using simulated gastric fluid (pH-1.2) as dissolution medium under sink conditions. Accurately weighed samples of floating microspheres were introduced into 900 ml of dissolution medium maintained at 37±0.5 °C with paddle rotating at 100rpm. The adequate samples were withdrawn at the interval of 1 hour and the same volume of fresh medium was refilled to maintain sink condition. After suitable dilutions, the samples were analysed
spectrophotometrically at a specific wavelength. Dissolution data was analysed for calculating the amount of drug release and percentage cumulative drug release at different time intervals.
Drug content determination
Drug content was determined using UV-Spectrophotometer. Drugloaded microspheres were crushed and 100 mg was suspended in 100 ml 0.1N HCl solution. This suspended solution was kept for 24h. It was stirred for 5 min and filtered. Ciprofloxacin content in the filtrate was determined spectrophotometrically at 275 nm using a regression derived from the standard curve .
Swelling index determination
The swelling index behaviour of the floating microspheres was measured by studying its weight gain. To determine the swelling index the microspheres were kept in the dissolution apparatus using the dissolution medium 0.1N HCl at 37±0.5 °C. After 0.5, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, and 6 h, each microsphere from the dissolution apparatus was withdrawn, blotted with tissue paper to remove the excess water, and weighed on the analytical balance. The experiment was performed in triplicate at each time point. The swelling index was determined by the following formula
Swelling Index = Wet weight of the microspheres?Dry weight of the microspheres / Dry weight of microspheres
RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
The present investigation was carried out on the development and characterization of floating microspheres incorporating ketorolac tromethamine loaded microspheres for periodontal therapy by using different polymers like Ethyl cellulose, HPMC and solvent.
Ketorolac tromethamine pure drug

SUMMARY AND CONCLUSION
- Ketorolac tromethamine is an NSAID used to treat pain and inflammation in the periodontal socket. The bioavailability of Ketorolac tromethamine is less, primarily due to presystemic metabolism and partly due to incomplete absorption.
- Floating microspheres of Ketorolac tromethamine can achieve a prolonged therapeutic effect by a controlled release mechanism of the drug for an extended of period time in the stomach. The floating microsphere increases the gastric residence time as well as bioavailability and decreases the dosing frequency of the drug.
- The main aim and objective of the present study was to formulate and evaluate floating microspheres of Ketorolac tromethamine for periodontal therapy
- In the present study an attempt has been made to develop microspheres with Ketorolac tromethamine using
- HPMCK4M, Carbopol 934, Ethyl cellulose as a polymer
- Based on literature survey various excipients like HPMCK4M, Carbopol 934, Ethyl cellulose used as polymers. Liquid paraffin and Acetone are selected as solvents for preparation of the floating Ketorolac tromethamine loaded microspheres.
- In pre formulation studies, solubility studies were carried out by using distilled water pH 6.8 phosphate buffer and pH 7.4 phosphate buffer. and the solubility was found to be grater in pH 6.8 phosphate buffer.
- The compatability studies were performed for individual drug sample using FTIR spectroscopy. No chemical interactions were observed in the present study.
- Formulation of Ketorolac loaded floated microspheres were done by using polymers like HPMCK4M, Carbopol 934, Ethyl cellulose, and two solvents like liquid paraffin and Acetone by Solvent Evaporation method. F1, F2, F3 Formulations are prepared by using Carbopol934. F4, F5, F6 Formulations are prepared by using Ethyl cellulose. F7, F8, F9 Formulations are prepared by using HPMCK4M as the polymers. Thus, nine formulations of floating
microspheres were prepared.
- The obtained microspheres are evaluated by using various tests like Bulk density, Tapped density, Hausner’s ratio, Angle of repose, % Compressibility index. All the values of the formulations are within the limits.
- The prepared microspheres are evaluated for percentage yield, percent drug loading, particle size, Drug entrapment efficiency, Floating capacity, In -vitro drug release, Drug content determination, Swelling determination.
- F7 formulation was found to be the optimized formulation due to the
controlled release of the drug at the end of 10 h. The release was found to be 90.79±0.89%. The floating microspheres not only increase the bioavailability of the drug it also improves patient compliance.
ACKNOWELEDGEMENT
It gives us an honor to express our deep sense of gratitude and Indebt
Ness to our project guide Mrs. M.S.BHAVANI, M. Pharm,(Ph.D) Assistant
Professor, Department of Pharmaceutics, Hindu College of Pharmacy, Guntur for
his valuable guidance, constant encouragement, every scientific and personal
concern throughout the course of investigation and successful completion of this
work.We wish to extend our sincere thanks to Principal DR. M.V.NAGABHUSHANAM , Hindu college of Pharmacy, Guntur, for his constant support, encouragement enabling us to do a work of this magnitude.
We take this opportunity to express our sincere thanks to SRI JUPUDI RANGARAJU garu, Chairman, DR. BOGARAJU VIJAYA BHASKAR, vice chairman
and DR. MADHUSUDHANA RAO garu, Secretary & Correspondent, Hindu College
of Pharmacy, Guntur for providing dexterities to carry out this project.
Our sincere thanks to all teaching and non-teaching staff members of
Hindu college of Pharmacy.
Lastly, I bow to my affectionate parents for their love, blessings, which has
sustained me a lot in completing this project work successful.
REFERENCES
- http://www.nidcr.nih.gov/OralHealth/Topics/GumDiseases/PeriodontalGumDisease.htm.
- Palak V Patel, Dhiren J Daslaniya, Upendra L Patel and Ragin R.Shah , Formulation and Evaluation of Bioadhesive Gel Incorporated Amoxicillin Trihydrate Loaded Microspheres for Periodontal Therapy, International Journal Of Pharmaceutical Innovations Volume 3, Issue 3, May ? June 2013.
- Ainamo J, Loe H. (1966). Anatomical characteristics of gingiva. A clinical and microscopic study of the free and attached gingival, J Periodontol 37:5–13.
- H.E. & Listgarten, M.A. (1997). The gingival tissues: the architecture of periodontal protection. Periodontology 2000 13, 91–120.
- www.intechopen.com Gingival Diseases – Their Aetiology, Prevention and Treatment
- Rose, Louis F (2004). Periodontics: Medicine, Surgery and Implants.
- Leon, Lachman, Herbert A. L., Joseph, L. K; “ The Theory And Practice Of Industrial Pharmacy”, pg-412, 428.
- N.K.Jain, Controlled and Novel drug delivery, 04 Edition, 236-237
- Pharmaceutical Technology – II, Zainab Fathima ,2.1- 2.34
- Microencapsulation: a review international journal of pharmaceutical sciences review and research volume 1, issue 2, marches – April 2010.
- http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Coacervate
- Wakode R and Bajaj A. Gelatin microspheres for topical delivery of Vitamin A palmitate. NHSM Journal of Phar
- ‘macy and Healthcare Management 2011; 2 pg.no:61-65.
- Harper, Douglas. "Online Etymology Dictionary: gel". Online Etymology Dictionary. Retrieved 2013-12-09.
- Soppimath, K.S.; Kulkarni, A.R.; Rudzinski, W.E.; Aminabhavi, T.M. Microspheres as floating drug delivery systems to increase gastric retention of drug Drug Metab. Rev, v.33, p.149-160, 2001.
- Gholap, S. B., Bannerjee, S. K., Gaikwad, D. D., Jadhav, S. L., and Thorat, R. M. (2010). ?Hollow Microsphere: A Review? IJPSRR, 1(1), 74-79.
- Somwanshi, S. B., Dolas, R. T., Nikam, V. K., Gaware, V. M., Kotade, K. B., Dhamak, K. B., and Khadse, A. N. (2011). ?Floating Multiparticulate Oral Sustained Release Drug Delivery System. J. Chem. Pharm Res, 3(1), 536-547
- van Esch J., Schoonbeek F., De Loos M., Veen E.M., Kellog R.M., Feringa B.L. (1999) "Low molecular weight gelators for organic solvents", pp. 233–259 in: Ungaro R., Dalcanale E. (eds.) Supramolecular science: where it is and where it is going. Kluwer Academic Publishers, ISBN 079235656X.
- K Karthikeyan1, R Durgadevi1, K Saravanan1, K. Shivsankar1, S. Usha2 and M Saravanan2* Formulation of Bioadhesive Carbomer Gel Incorporating Drug-Loaded Gelatin Microspheres for Periodontal Therapy Tropical Journal


 Muggu Sankara bhavani*
Muggu Sankara bhavani*
 K. ChandraSekhar Gupta
K. ChandraSekhar Gupta






 10.5281/zenodo.14133790
10.5281/zenodo.14133790