Abstract
Mesalazine, also known as mesalamine or 5-aminosalicylic acid (5-ASA), is an anti-inflammatory medication used to manage ulcerative colitis and Crohn's disease. It acts as an antioxidant, trapping free radicals, which can be harmful metabolic by-products. Sulfasalazine is metabolized to sulfapyridine and mesalazine. Cassia fistula, also known as the golden shower tree or Indian laburnum, is a tropical tree native to South Asia and Southeast Asia. Its bright yellow flowers attract pollinators and have been used in traditional medicine for centuries to treat ailments like constipation, skin diseases, and respiratory issues. It contains antioxidant and anti-inflammatory compounds that promote overall health. The study aims to develop a multi-particulate drug delivery system for colonic delivery, offering several advantages over conventional single unit dosage forms. The main advantage is the ability to deliver mesalamine directly to the colon, allowing a higher concentration to reach inflamed areas, leading to improved therapeutic outcomes for patients with inflammatory bowel disease. Synthetic and natural polymers are effective in controlling mesalamine release in the colon, ensuring slow and steady release over an extended period. This formulation also improves patient compliance, reducing dosing frequency and providing a more consistent release profile, leading to better disease management and overall health outcomes. The formulation of colon target matrix tablets of Mesalamine of Optimized Batch (F3) using synthetic and natural polymers offers several key advantages for patients with inflammatory bowel disease, including targeted drug delivery, improved therapeutic outcomes, and enhanced patient compliance. The study's findings suggest that the drug should be subjected to further formulation development.
Keywords
Mesalamine, Mesalazine, Colon Targeted Drug Delivery, Multi-Particulate Drug Delivery, Synthetic and Natural Polymers
Introduction
Mesalazine, also known as mesalamine or 5-aminosalicylic acid (5-ASA), is an anti-inflammatory medication used for managing ulcerative colitis and mild-to-moderate Crohn's disease. It is an amino-salicylate drug with few systemic adverse reactions and has a local effect in the gut. Mesalazine acts as an antioxidant, trapping free radicals, which can be hazardous metabolic by-products. Sulfasalazine is metabolized to sulfapyridine and mesalazine (1). Cassia fistula, also known as the golden shower tree or Indian laburnum, is a tropical tree native to South Asia and Southeast Asia. It is renowned for its ornamental beauty and medicinal properties, with its bright yellow flowers attracting bees, butterflies, and other pollinators. Cassia fistula has been used in traditional medicine for centuries, treating ailments like constipation, skin diseases, and respiratory issues. It contains antioxidant and anti-inflammatory compounds that promote overall health. Despite these, Cassia fistula is a remarkable plant with both aesthetic appeal and medicinal value, making it a valuable addition to any landscape (2,3). Colon Targeted Drug Delivery Systems (CTDDS) are designed for specific site drug delivery, reducing systemic side effects like organ damage, respiratory diseases, and cardiovascular damage. They are used in treating conditions like ulcerative colitis, irritable bowel syndrome, and colorectal cancer. Conventional methods include prodrugs, pH-dependent, time-dependent, matrix-based systems, polysaccharides-derived systems, and bio-adhesive systems (4). Novel approaches include port systems, pulsincap systems, pressure-controlled systems, osmotic controlled systems, CODES, and nanotechnology. A successful colon tissue-targeted drug delivery (CTDD) can target specific colon segments due to different colonic enzymes metabolizing drug carrier linkage. Combining conventional and newer approaches may be the best way to cure colon diseases. Drug molecules are embedded in polymer matrices that can be pH-sensitive or undergo degradation (5). pH-sensitive matrices are prepared to degrade in the colon's basic pH, allowing controlled drug release. pH-dependent matrices, like Eudragit S100, are used due to their affordability and nontoxicity. Kondagogu gum and ghatti gum are natural and biodegradable polymers suitable for colon-targeted drug delivery (6). In this study, the formulation and evaluation of colon target matrix tablets of mesalamine using synthetic and natural polymers offers several key advantages for patients with inflammatory bowel disease. From targeted drug delivery and improved therapeutic outcomes to enhanced patient compliance, this innovative approach has the potential to revolutionize treatment options for individuals suffering from this chronic condition.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Drugs and Chemicals
The list includes Mesalamine from Maan Pharmaceuticals Pvt Ltd., Guar Gum from Strides Arco Labs, Xanthan Gum from Strides Arco Labs, PVP K 30 from Wockhardt Research, Eudragit S100 from Azelis Pvt. Ltd., Talc, Magnesium Stearate and Microcrystalline Cellulose from SD Fine Chem Limited.
Source of Natural Polymer
The pods of Cassia Fistula were collected in the month of April-May 2023 and identification based on morphological characteristics. They were dried properly in the sunlight for five days, further kept in oven for 2 hours at 45ºC. The dried seeds were grinded in mechanical grinded to get fine powder and store in well closed containers.
Extraction of gum obtained from Cassia Fistula
A 100gm powder was soaked in 500ml distilled water and boiled over a water bath for 30 minutes. It was then diluted with 500ml distilled water in a 1000ml beaker and left overnight. The slurry was collected and diluted with acetone to form creamy brown precipitates. The precipitates were dried on a steel plate/petri plate at 42ºC in a hot air oven for 24 hours. After 24 hours, the powder was powdered using a grinder and passed through a sieve no. 80. The powder was then powdered for purification and stored in a desicator for 48 hours (7).
Preparation of Sodium Carboxy Methyl Gum
This process involves preparing a 45% sodium hydroxide solution, 75% monochloroacetic acid, and Sodium Carboxy Methyl. The mixture is then stirred in hot water and IPA to maintain a liquid state. The reaction mixture is cooled to room temperature, excess alkyl (NaOH) is nitrolized with a glacial acetic acid filter, and 80% of the excess is removed. The slurry is precipitated and washed with 80% methanol three times. The dried product is then filter-dried at 50?, and sumps are dried at 50°C. The sumps are then broken and further dried at 50? for 1 hour.
Preformulation Studies
The study focuses on the characterization and identification of Mesalamine. The drug samples were examined for appearance, color, and odor. The melting point of Mesalamine was determined using the capillary method, where a fine powder of the drug was filled in a glass capillary tube and dipped in liquid paraffin (8). Solubility was also determined in various buffers of different pH values (9). The drug was identified by UV spectroscopy, where a calibration curve was prepared by dissolving 28.20 g of anhydrous disodium hydrogen phosphate and 11.45 g of potassium dihydrogen phosphate monohydrate in 1000 ml of water. The drug was then transferred into a volumetric flask and solved in 15 ml of methanol, resulting in a concentration of 200 µg/ml. The drug was then transferred to another flask and filtered to obtain concentrations of 2,4,6,8,10 µg/ml (10). The infrared spectra of the pure drug were recorded using a Perkin Elmer FT-IR spectrometer, and samples were prepared using the KBr disc method. The study aims to determine the drug-excipients compatibility by FT-IR analysis, as it serves as a pivotal analytical technique for evaluating the interaction between these compounds. The results of the compatibility assessment of Omeprazole with HPMC K100 via FTIR analysis will be elucidated (11).
Formulation and Optimization of Mesalamine Colon Targeted Tablets by Direct Compression Method by using 32 Factorial Design
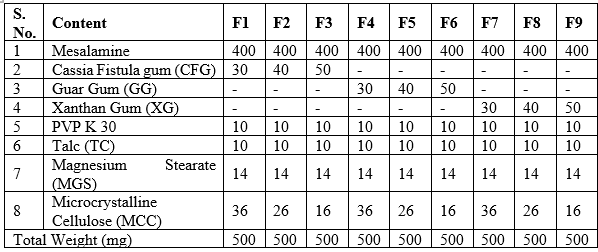
Mesalamine sustain release matrix tablets were prepared by direct compression method according to the formula (Table 1). A total number of four formulations (F1 to F9) of Mesalamine sustain release matrix tablets were prepared using four superdisintegrants namely Calcium Cross linked Isolated Cassia Fistula gum (CFG), Guar Gum (GG) and Xanthan Gum (XG) with three different concentrations (2 %, 3 %, 5 % and 7 %) by using 32 Factorial Design. All the ingredients were passed through mesh no 60 separately and collected. The drug and other excipients were mixed uniformly with gentle triturating using mortar and pestle to get a uniform mixture. Required quantity of superdisintegrants and aspartame were taken for each specified formulation and mixed with the above mixture (12–15). Polymer was dissolved in a solvent, plasticizer added, and talc, titanium dioxide, and color passed through a sieve. The solution was filtered, and tablets were deposited in a coating pan, rotated for five minutes, and dedusted before coating.
Table 1: Formulation Design of Mesalamine Sustain Release Matrix Tablets
Evaluation of Mesalamine Sustain Release Matrix Tablets
Pre Compression Evaluation
Key parameters evaluated during pre-compression include bulk density, tapped density, Hausner's ratio, and Carr's index, which provide insights into the flow properties and compressibility of the powder blend. Moisture content and particle size distribution also play a significant role in determining the stability and release profile of omeprazole within floating matrices (16,17).
Post Compression Evaluation
The study focuses on factors such as hardness, friability, disintegration time, and drug release kinetics. Understanding these characteristics is crucial for optimizing tablet performance and ensuring effective therapeutic outcomes. Factors like particle size distribution and moisture content also impact these evaluations. Comprehensive postcompression evaluations are essential for developing effective floating tablets that meet pharmacological standards (18,19).
In vitro dissolution studies
In- vitro drug release studies were carried out by using USP (TDT067) Type II (paddle type) dissolution test apparatus at 50 rpm using pH 6.8 phosphate buffer as dissolution media maintained at the temperature at 37±0.5°C. Samples were withdrawn at specific time intervals and replaced with fresh media and filtered. The amount of drug dissolved was determined by spectrophotometer at 250 nm. The experiments were conducted in triplicate (20).
Kinetic Release Study
To study the release kinetics of In-vitro drug release data of above selected batches were applied to kinetic models such as zero order, first order, Higuchi and Korsmeyer- Peppas (21,22).
Stability Studies
In the present study the stability study was conducted in accordance with ICH guidelines by keeping the sample at 40±2 0C and 75±5 % RH for six months in a stability chamber. The high density Polyethylene bottle is the container closure system used in this study. The selected study intervals were the 1st and 3rd months from the initial time (23).
RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
Preformulation Studies
Preformulation is a crucial process in determining the physical and chemical properties of a drug, which are crucial for its stability and effectiveness in dosage form formulation. A systematic preformulation study was conducted using the standard procedures of Indian Pharmacopoeia and British Pharmacopoeia, involving drug identification, melting point analysis, and compatibility studies with selected polymers. The study used a capillary method to determine the melting point of the drug sample which was found to be 290°C, also the majority of the drug was partitioned towards the organic phase with a partition coeficient of 3.19, indicating lipophilic nature. This information is essential for validating formulation design and determining molecular alteration needs (Table 2).
Table 2: Observed organoleptic properties of drug sample
Determination of Absorption Maxima of Mesalamine and Calibration curve of Mesalamine
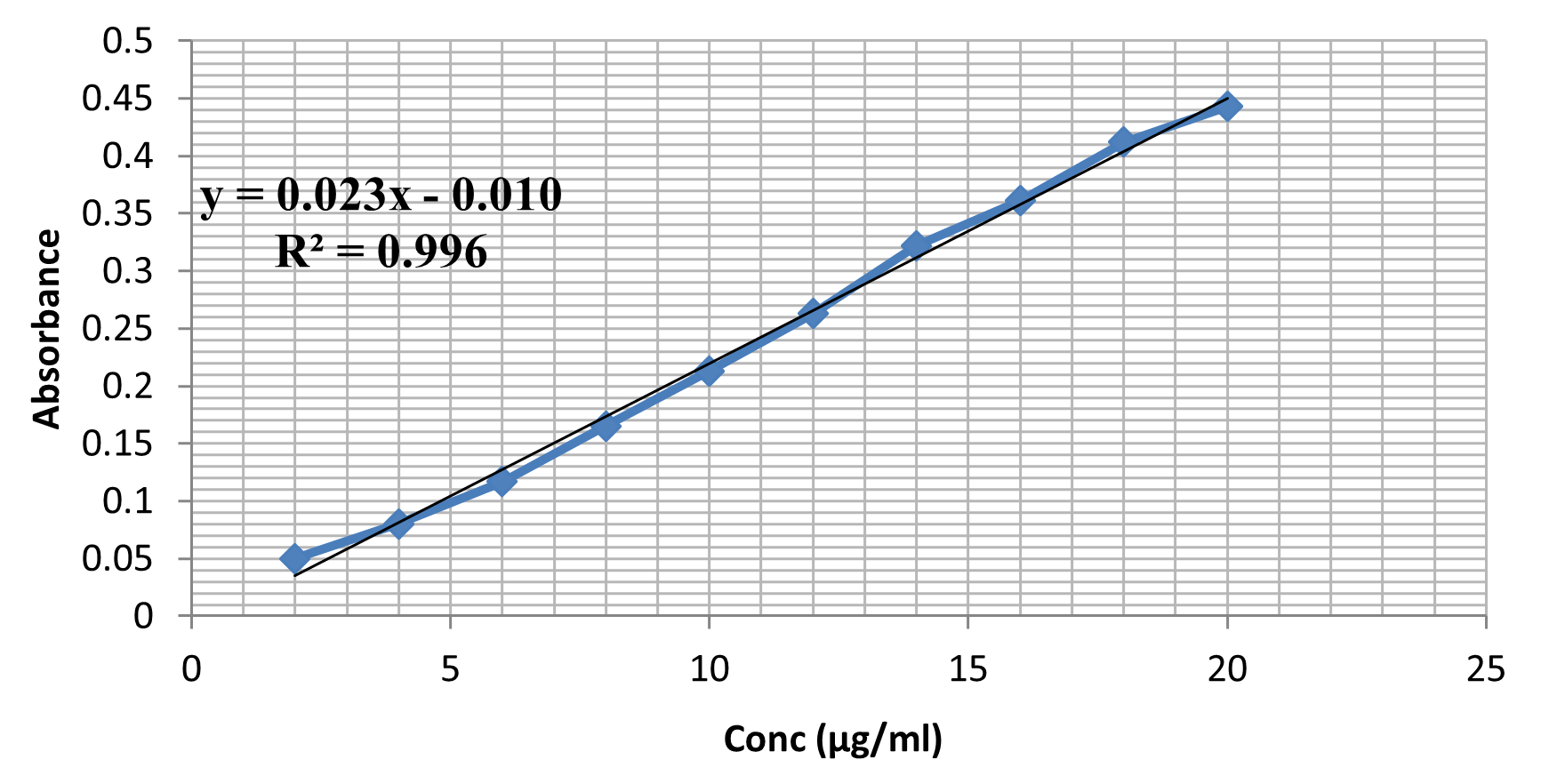
UV absorption spectroscopy is a crucial method for identifying impurities in organic molecules and determining absorbance at specific wavelengths. It is essential for qualitative drug identification due to the presence of additional peaks due to sample impurities. A standard solution of 100?g/ml was prepared with SIF (pH-6.8) and UV scanning was performed between 200-400 nm. The maximum absorption wavelength was found to be 330 nm (Figure 1), and a calibration curve was constructed at 330 nm in pH 6.8 phosphate buffer, showing a regression coefficient of 0.996 (Figure 2).
Figure 1: UV Scan of Mesalamine for Determination of Absorption Maxima
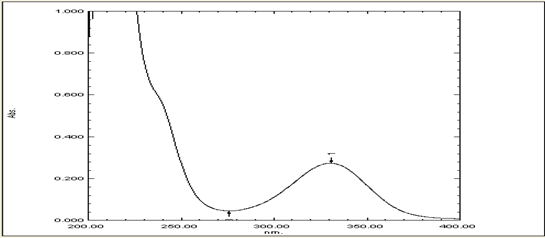
Figure 2: Calibration curve of Mesalamine in pH 6.8 phosphate buffer
FTIR Spectral Assessment of the Mesalamine and Mesalamine-Natural Polymer compatibility
FT-IR is used to identify unknown materials, determine sample quality or consistency, and determine the amount of components in a mixture. A powdered drug was analyzed using potassium bromide powder from 400-4000cm-1. The FT-IR spectra were used for qualitative drug sample identification. The physicochemical compatibility between mesalamine and Natural Polymer was determined by recording the FTIR profile of physical mixtures. A pellet of pure drug and a physical mixture of drug and polymers were prepared using potassium bromide (Figure 3 and 4).
Evaluation Parameters:
Precompression Evaluation of powder blended characteristics of tablet formulation
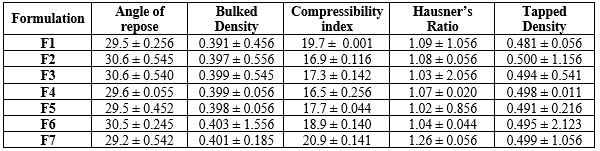
The optimal drug release kinetics in tablet formulations are influenced by factors such as particle size distribution, flow properties, blend uniformity, and compressibility. A narrow particle size distribution ensures uniform blending and prevents segregation during compression, resulting in a more consistent drug release profile. Poor flow properties can lead to uneven distribution of active ingredients, causing variability in drug release rates. Therefore, evaluating powder blended characteristics is crucial for achieving consistent and reliable matrix tablet formulations. The product has a Carr Index of 11.2 to 15.7, indicating free flow, and a Hausner grain ratio of 1.02 - 1.18. Physical tests of many blends comply with standards (Table 3).
Table 3: Physical properties of powder blends of single unit tablet formulations
Postcompression Evaluation of powder blended characteristics of tablet formulation
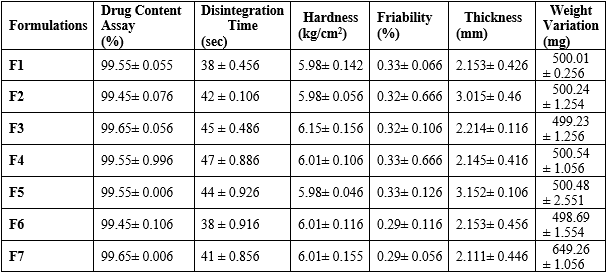
Postcompression evaluation is a crucial process in determining the quality and performance of tablet formulations. It involves assessing parameters like hardness, friability, disintegration time, and drug release profile to determine the tablet's performance. Hardness measures the mechanical strength of a tablet, while friability measures its tendency to break or chip under stress. A low friability value indicates good tablet integrity. Disintegration time determines the rate and extent of drug release, which directly impacts the therapeutic efficacy of a tablet formulation. The drug release profile is the most crucial parameter in postcompression evaluation, as it directly impacts the therapeutic efficacy of a tablet formulation. The physical examination results of the formula are within limits and meet standard requirements. The tablets weigh between 647.62 mg and 650.23 mg, with an average drug content of 99.72% (Table 4).
Table 4: Postcompression Evaluation of powder blended characteristics of tablet formulation
Optimization of the Coded values for sustained release tablets containing Mesalamine 32 Factorial Design
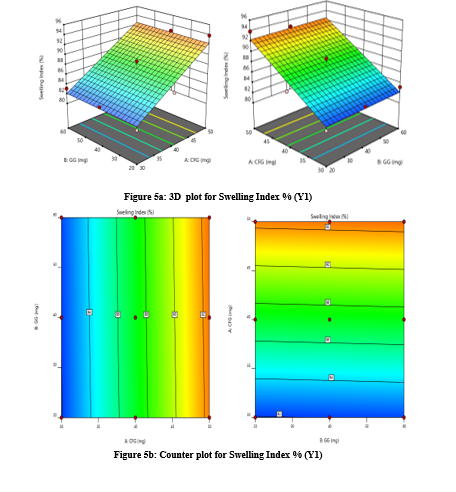
The study focuses on optimizing coded values for sustained release tablets containing Mesalamine, an anti-inflammatory agent used in treating ulcerative colitis. It uses a 32 factorial design to evaluate the effects of multiple formulation variables on desired release characteristics. The study systematically varied polymer concentration and excipient ratio, allowing for comprehensive analysis of their interactions and effects on drug release kinetics. This method minimizes resource expenditure and maximizes data output, ensuring consistent therapeutic doses and reducing potential side effects (Figure 5 and 6).
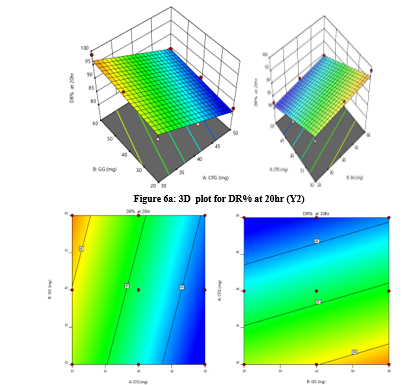
In vitro drug release kinetics studies
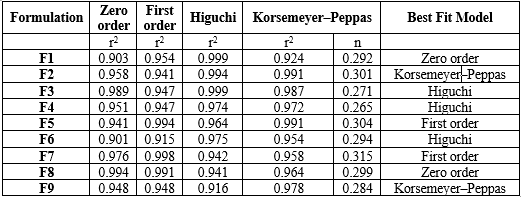
The study analyzed the drug release profiles of nine different formulations using pH 6.8 phosphate buffer. The results showed that the concentration of superdisintegrant increased the disintegration time of the tablets. The F3 formulation with the highest concentration of superdisintegrant and sublimating agent showed enhanced drug release in 20 hours compared to other formulations (Table 5). The study examined the kinetics of Mesalamine sustain release matrix tablet tablets using various diffusion models. The results showed that drug release follows a specific order, with Higuchi, Korsemeyer-Peppas, zero order, and first order being the most common. The Higuchi release kinetics showed a higher correlation, suggesting diffusion as a prominent mechanism of drug release. The correlation coefficients ranged from 0.845 to 0.995 for zero order, 0.864 to 0.998 for first order, and 0.265 to 0.315 for Korsemeyer Peppas (Table 6). For formulation F3, data was best explained by Higuchi equation, as the plots showed the highest linearity (r2=0.998). Higuchi's model defines the release of drugs from an insoluble matrix as a square root of a time-dependent process based on Fickian diffusion.
?
Table 5: In vitro drug release studies of Mesalamine
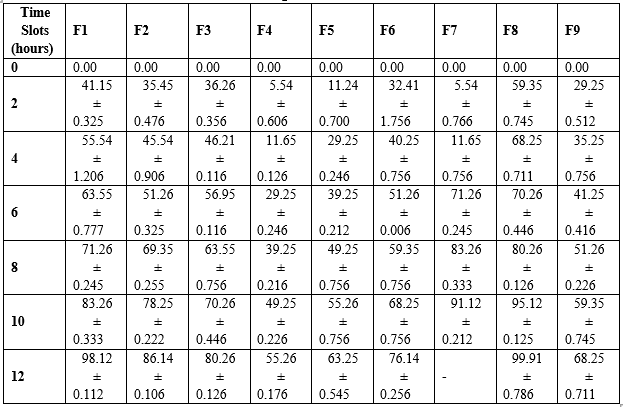
Table 6: In vitro Release Kinetic models for Mesalamine Colon Targeted Tablets of Formulations (F1 to F9)
Stability Studies
Stability Study of Optimized Batch (F3) is shown in Table 7. As per the data, it was concluded that tablet dosage form was stable enough till 6 months under the accelerated conditions as per the ICH.
CONCLUSION:
The study aims to develop a multi-particulate drug delivery system for colonic delivery using synthetic and natural polymers. The drug sample was authenticated and the absorption maxima were found to be 330 nm in different solvents. UV spectroscopy was used to prepare standard curves of mesalamine in phosphate buffer (pH 6.8), and compatibility studies were performed using UV visible spectroscopy and FTIR analysis. The drug was found to be compatible with selected polymers, and further formulation development is needed. The main advantage is the ability to deliver mesalamine directly to the colon, allowing a higher concentration to reach inflamed areas, leading to improved therapeutic outcomes for patients with inflammatory bowel disease. Synthetic and natural polymers are effective in controlling mesalamine release, improving patient compliance, reducing dosing frequency, and providing a more consistent release profile. Statistical techniques like ANOVA can be used to analyze findings, ensuring uniform therapeutic dosages and minimizing adverse effects. In conclusion, the formulation of colon target matrix tablets of Mesalamine of Optimized Batch (F3) using synthetic and natural polymers offers several key advantages for patients with inflammatory bowel disease, including targeted drug delivery, improved therapeutic outcomes, and enhanced patient compliance.
REFERENCE :
- Sehgal P, Colombel J, Aboubakr A, Narula N. Systematic review: safety of mesalazine in ulcerative colitis. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2018;47(12):1597–609.
- Hanif MA, Bhatti HN, Nadeem R, Zia KM, Ali MA. Cassia fistula (Golden Shower): A multipurpose ornamental tree. Floric Ornam Biotechnol. 2007;1(1):21–6.
- Bhandari SS, Khurana K, Balyan A, Kabra MP, Negi K. A review on Cassia fistula. Asian J Pharm Res Dev. 2013;217–9.
- Gupta A, Mittal A, Gupta AK. Colon targeted drug delivery systems–a review. Asian J Pharm Res. 2011;1(2):25–33.
- Naeem M, Awan UA, Subhan F, Cao J, Hlaing SP, Lee J, et al. Advances in colon-targeted nano-drug delivery systems: challenges and solutions. Arch Pharm Res. 2020;43(1):153–69.
- JASRA K, Singh A, PAINULY N, Singh K. COLON TARGETED DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM: A SYSTEMIC REVIEW. NeuroQuantology. 2022;20(12):84.
- Brummer Y, Cui W, Wang Q. Extraction, purification and physicochemical characterization of fenugreek gum. Food Hydrocoll. 2003;17(3):229–36.
- Hwang K-M, Cho C-H, Lee S-H, Kim J-Y, Park E-S. Preformulation and evaluation of multi-layer tablets. J Pharm Investig. 2024;54(2):161–74.
- Noman MA, Alburyhi MM, El-Shaibany A, Alwesabi NA. Preformulation and Characterization Studies of Pandanus Odoratissimus L Extract Active Ingredient in Treatment of Nocturnal Enuresis. World J Pharm Pharm Sci. 2024;13(2):1603–20.
- Geeta SS, Saroha G, Dolly S, Rana S, Narwal S. Potential of Granisetron Hydrochloride for Transdermal Drug Delivery: Comprehensive Characterization, Preformulation studies and Compatibility Analysis.
- Siregar C, Martono S, Rohman A. Application of Fourier transform infrared (FTIR) spectroscopy coupled with multivariate calibration for quantitative analysis of curcuminoid in tablet dosage form. J Appl Pharm Sci. 2018;8(8):151–6.
- Kumar I, Chaudhary D, Thakur B, Pandit V. Formulation and evaluation of piroxicam fast dissolving tablets using direct compression and sublimation method. J Drug Deliv Ther. 2020;10(3-s):17–25.
- Gashaw S, Getachew A, Mola F. Characterization of Acid Hydrolyzed Taro Boloso?I (Colocasia esculenta Cultivar) Starch as a Diluent in Direct Compression of Tablets. Adv Pharmacol Pharm Sci. 2024;2024(1):6560070.
- Bekaert B, Janssen PHM, Fathollahi S, Vanderroost D, Roelofs T, Dickhoff BHJ, et al. Batch vs. continuous direct compression–a comparison of material processability and final tablet quality. Int J Pharm X. 2024;7:100226.
- Pandey SK, Pudasaini J, Parajuli N, Singh RE, Shah KP, Adhikari A, et al. Formulation and evaluation of floating tablet of nimesulide by direct compression method. Magna Sci Adv Res Rev. 2024;10(1):153–61.
- Cirri M, Rangoni C, Maestrelli F, Corti G, Mura P. Development of fast-dissolving tablets of flurbiprofen-cyclodextrin complexes. Drug Dev Ind Pharm. 2005;31(7):697–707.
- Maheshwari S, Singh A, Varshney AP, Sharma A. Advancing oral drug delivery: The science of fast dissolving tablets (FDTs). Intell Pharm. 2024;
- Rodriguez-Saavedra LR, Alva-Plasencia PM, Curo-Vallejos YF, Saavedra-Suárez SF, Chávez-Abanto LA, Caballero-Aquiño OE, et al. Dissolution kinetics of propranolol hydrochloride 40 mg tablets under biowaiver conditions. J Pharm Pharmacogn Res. 2024;12(5):814–21.
- Modi A, Tayade P. Enhancement of dissolution profile by solid dispersion (kneading) technique. AAPS pharmscitech. 2006;7(3):68.
- Siepmann J, Peppas NA. Modeling of drug release from delivery systems based on hydroxypropyl methylcellulose (HPMC). Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2012;64:163–74.
- Singh S, Dixit Y, KanikaTuli DSMSA. KINETIC STUDIES AND STABILITY ASSESSMENT OF XANTHAN GUM-BASED FLOATING MATRIX TABLETS OF ENALAPRIL MALEATE.
- van der Haven DLH, Jensen R, Mikoroni M, Zafar U, Elliott JA, Fragkopoulos IS. Tablet ejection: A systematic comparison between force, static friction, and kinetic friction. Int J Pharm. 2024;124369.
- Subhramanya ABK, Nayak P, Ramalingappa H, Hemanna HK, Shetty P. ICH Q1 a Stability Testing for New Dosage Form. 2024;


 Ritesh Rana*
Ritesh Rana*










 10.5281/zenodo.13891592
10.5281/zenodo.13891592