Background:
In cognitive impairment (CI), person facing problem in remembering, learning, concentrating and making decisions in everyday life.
Aim:
The present research was focused to evaluate the neuroprotective activity of bexarotene in scopolamine induced Alzheimer’s disease in rat.
Materials and Methods:
The study utilized 36 male Albino Wistar rats, aged 24 months, weighing 150 ± 20 gm (total 6 groups, n = 6 per group). For the oral induction of alzheimer’s, scopolamine was administered at a dosage of 1mg/kg. In group III, Memantine was administered orally dose of 30 mg/kg. at groups IV, V, and VI, Bexarotene was administered orally at doses of 25, 50, and 100 mg/kg, respectively. The statistical significance of the data was determined using Two-way analysis of variance (ANOVA), Bonferroni’s and Tukey’s post-test were used to test the significance of the difference between the variables in various groups.
Results:
The results showed that bexarotene exhibits neuroprotective activity as evidenced by using behavioural models such as radial arm maze and elevated plus maze apparatus. Antioxidant status was determined by level of nitric oxide and and reduced glutathione (GSH) level in plasma of rats.
Conclusions:
The present study showed that the bexarotene stresses its neuroprotective and cognition enhancing property.
Bexarotene, Alzheimer’s disease, Scopolamine, Neuroprotective, ANOVA
Cognition
Cognition refers to "the mental action or process of acquiring knowledge and understanding through thought, experience and the senses". It encompasses many aspects of intellectual functions and processes such as attention, the formation of knowledge, memory and working memory, judgment and evaluation, reasoning, "computation", problem solving and decision making, comprehension and production of language.1
Cognitive Dysfunction / Cognitive Impairment
Mild cognitive impairment (MCI) refers to the transitional state between the cognitive changes of normal aging and very early dementia. MCI has been proposed as a condition of intermediate symptomatology between the cognitive changes of aging and fully developed symptoms of dementia, such as those seen in Alzheimer's disease. Mild cognitive impairment has several types:
- MCI due to Alzheimer’s disease,
- VCI (vascular cognitive impairment)
- MCI due to Parkinson disease
1. Mild Cognitive Impairment Due to Alzheimer’s Disease
There are many terms used to refer to MCI such as benign senescent forgetfulness, age-associated memory impairment, late-life forgetfulness, mild cognitive decline, age-associated cognitive decline, age-related cognitive decline, mild neurocognitive decline, cognitive impairment no dementia, and MCI due to Alzheimer’s disease.

Figure 1. Core clinical criteria of MCI due to Alzheimer’s disease
Amnestic MCI is more common than non-amnestic MCI by a ratio of about 2:1. Non-amnestic MCI may result from normal aging and have reversible causes, or it may be the result of a predementia stage of non-Alzheimer’s disease such as frontotemporal lobar degeneration, dementia with Lewy bodies, Parkinson disease with dementia, vascular dementia, or primary progressive aphasia.2
2. Vascular Cognitive Impairment (VCI)
VCI is a type of MCI that is unlikely to be due to Alzheimer’s disease. It is commonly classified into 2 following:
- Post-stroke related VCI
- Non-stroke related VCI
Vascular cognitive impairment consists of one or more cognitive impairments including executive/attention, memory, language, and visuospatial functions, ranging from MCI to dementia, caused by clinical features of vascular events or evidence of vascular damage found using neuroimaging.3 There are multiple domains of cognitive deficits in cases of VCI that have common presentations with dysexecutive syndrome. Concomitant motor signs with VCI include frontal gait disturbance, lower body Parkinsonism, apathy, depression, urinary incontinence, spasticity, hyper reflexia, and frontal release signs. Majority of VCI would be mixed type, with the most common combined with Alzheimer’s disease. Modification of various vascular risks may potentially reduce the risk of nonamnestic MCI. The pathogenesis of VCI depends on:
-
- Host factors (age, education, genetics, ApoE4 carrier, vascular risk factors, diabetes),
- Vascular causes (atherosclerosis, microvascular diseases, endothelial disorder),
- Additional pathologies (amyloid deposition, cerebral amyloid angiopathy and aging 4
Diagnostic criteria are based on the presence of cognitive deficit and vascular disease plus a clinical decision that the cerebrovascular lesions explain the deficit in the affected patient. There are various modifiable risk factors for VCI, the amelioration of which can decrease the degree of vascular injury.
- Mild Cognitive Impairment in Parkinson Disease
Parkinson disease is the second most common neurodegenerative disorder with progressive loss of dopaminergic neurons of the substantia nigra pars compacta. Mild cognitive impairment in Parkinson disease (PD-MCI) usually takes the form of nonamnestic single-domain MCI and leads to increased healthcare costs, increased fall risk, lower quality of life, and disabilities.
Risk factors for MCI in Parkinson disease are
- Aging
- Severe motor symptoms
- Non-tremor-dominant motor phenotype
- Low education
The prevalence of MCI in Parkinson disease is about 20% to 50%; it varies depending on the population, cognitive domain and utilized definition. The pathophysiology of MCI in Parkinson disease may include synucleinopathy and amyloid deposition, neurochemical dysfunction (acetylcholine and dopamine), synaptic loss, and structural change. These processes are no different from Alzheimer’s disease, as they begin with slowly progressive proteinopathy and progress to cellular dysfunction and, eventually, structural change. Use of the MoCA a screening tool for the diagnosis recommended in PD, as it is validated for both MCI and Parkinson’s disease with dementia.5
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Drug Profile
Name of Drug: Bexarotene

Figure 2. Structure of Bexarotene

Mechanism of action
Bexarotene is a retinoid that selectively binds to Retinoid X Receptor (RXR), a compound chemically related to vitamin A that activates RXR receptors found everywhere in the body. It is a synthetic retinoic acid agent with potential antineoplastic, chemopreventive, teratogenic and embryotoxic properties, thereby inducing changes in gene expression that lead to cell differentiation, decreased cell proliferation, apoptosis of some cancer cell types, and tumor regression.
Procurement of experimental animals
The Albino rats (Sprague dawley strain) of age 24 months old, weighing between 150 ± 200gm, were procured from the animal house of Institute of Pharmaceutical Education and Research, Wardha. The animals were housed in the polypropylene cage at a temperature of 20 ± 1ºC with the relative humidity of 50±10% and 12 hour light / dark cycle. Animals were fed with balanced diet and water during the complete experimental period. The experimental protocol was approved by the Institutional Animal Ethics Committee of Institute of Pharmaceutical Education and Research, Wardha (Registration Number 535/PO/ReRcBt/S/02/CPCSEA) on dated 1st Jan 2020 to 5th May 2021 with Protocol No. IAEC/2020-21/02
Experimental Protocol
Groups of animals
The present study conducted using albino wistar rats of either sex. There are six groups. Accordingly the study was assigned and groups were allotted as follows-
Administration Protocol for Scopolamine-induced Learning and Memory Impairment
-
- Group I animals received only vehicle i.e. normal saline solution once daily, per orally.
- Group II Control group received 1mg/kg Scopolamine 30min.prior to behaviour testing by intraperitoneal route
- Group III received standard drug Memantine 30 mg/kg/day by i.p route,
- Group IV, V, VI Test groups received bexarotene 25 mg, 50 mg, 100 mg per kg respectively for 30 days given by p.o route.
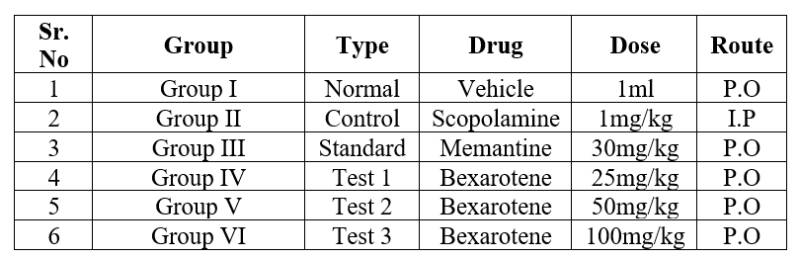
Table No. 1. Groups of animals for Scopolamine-induced Learning and Memory Impairment
Statistical Analysis
Data were analysed using Graph Pad Prism 8.0.1 for Windows (version 10 Pro). Results were expressed as Mean ± SEM. One-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) and Dunnett’s T test were used to test the significance of the difference between the variables in various groups. The P values of less than 0.05 were considered to be statistically significant.
Behavioural Testing
1. Radial Arm Maze
2. Elevated Plus Maze Apparatus
Observation and results
A. Determination of Behavioural Parameter
1. Determination of Correct Arm Entries
Correct arm entries determination is required to check the working memory process of experimental animal.
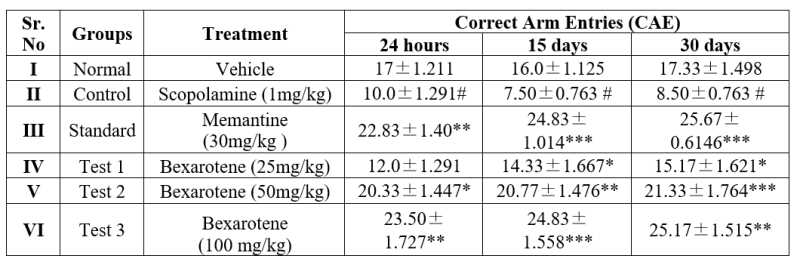
Table 2. Result of effect of Bexarotene on Correct Arm Entries (CAE)
Each group consist of 6 animals (n=6), Values are Mean ± S.E.M. #P< 0>
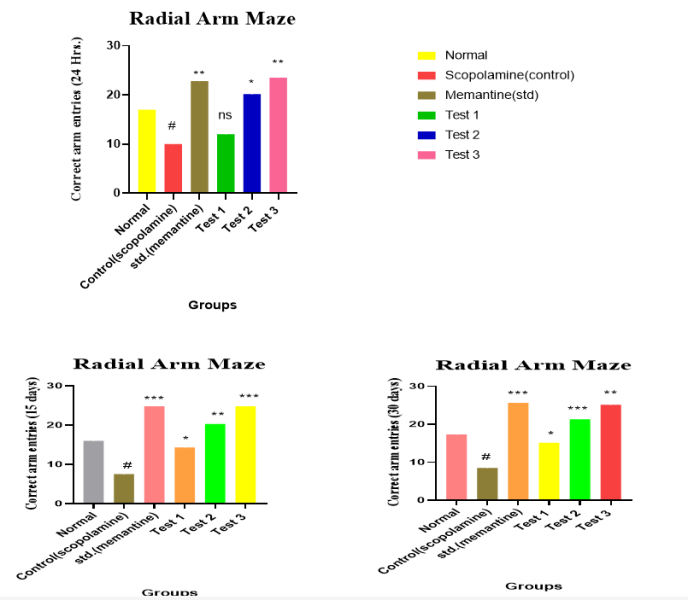
Result and Observation shows that decrease in correct arm entries in animals group II receiving scopolamine. 50mg/kg and 100mg/kg bexarotene receiving group V and VI respectively, significantly increases in correct arm entries after 24 hours, 15 days, 30 days whereas 25mg/kg bexarotene receiving group IV shows little significant change in arm entries values even after 30 days.
2. Determination of Total Number of Errors
Errors are designated as occurring when a rat chooses an unbaited arm (reference memory error) or when a rat returns to a baited arm after obtaining the food reward (working memory error)
Table 3. Result of effect of Bexarotene on Total Number of Error (TNE)
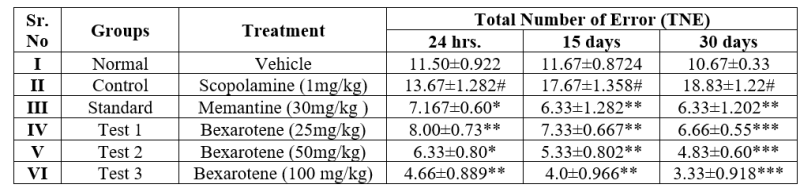
Each group consist of 6 animals (n=6), Values are Mean ± S.E.M. #P< 0>

Figure 4. Observation of effect of bexarotene on Total Number of Error (TNE)
Result and Observation shows that increases total number of error in animals of group II receiving scopolamine. Different doses of bexarotene receiving animals decreases in total number of error after 24 hours, 15 days, 30 days. Bexarotene (100mg/kg) receiving group significantly reduced total number of errors.
3. Determination of Time to Complete Task
Determination of time to complete task gives the idea about improvement in memory performance in experimental animal.
Table 4. Result of effect of Bexarotene on Time to Complete Task (TCT)

Each group consist of 6 animals (n=6), Values are Mean ± S.E.M. #P< 0>

Figure 5 .Observation of Bexarotene on Time to Complete Task (TCT)
Result and Observation shows that increase in time to complete task in animals of group II receiving scopolamine. 100mg/kg bexarotene receiving group VI significantly decreases the time to complete task after 24 hours, 15 days, 30 days whereas 25mg/kg bexarotene receiving group IV shows little decrease in the time to complete task.?
4. Determination of Transfer latency
Shortened transfer latency could be related to memory on the retention phase which gives idea about memory performance in experimental animal.

Table 5. Result of effect of Bexarotene on transfer latency
Each group consist of 6 animals (n=6), Values are Mean ± S.E.M. #P< 0>

Figure 6. Observation of effect of Bexarotene on Transfer latency (TL)
Result and Observation shows that increase in transfer latency in animals of group II receiving scopolamine. 100mg/kg Bexarotene receiving group VI significantly decreases in transfer latency (TL) after 24 hours, 15 days, 30 days.
B. Biochemical Parameters Estimation
Biochemical tests are mostly applied to samples of serum, plasma and urine where levels of specific chemicals are measured and the results compared with healthy individual. An increase or decrease in any particular component(s) can help to identify a disease process. The diagnosis of Alzheimer disease (AD) requires time consuming and costly procedures. Therefore, biochemical tests can helps in correct diagnosis. Measurement of biochemical markers in blood sample can correlate with the clinical diagnosis. of AD but generally lack sufficient diagnostic accuracy.
1. Determination of Reduced Glutathione
Glutathione is a tripeptide of glutamate, cysteine and glycine found at high concentration in virtually all mammalian tissue. The functionality of glutathione originates from the sulfhydryl (SH) group of the cysteine moiety. This sulfhydryl group is a powerful reducing agent and a strong nucleophile that is able to react with cellular toxicants directly or via the catalysis of the glutathione S-transferase family of enzymes.60 Various animal studies have consistently shown that GSH deficiency in the brain leads to increased OS-associated damage to the brain. Various in-vitroand in vivo studies have evidenced a neuroprotective role of GSH against a wide variety of oxidative insults. Neuronal cells have been shown to be particularly vulnerable to ROS damage due to the reduced GSH content.56
Table 6. Result of effect of Bexarotene on Glutathione level
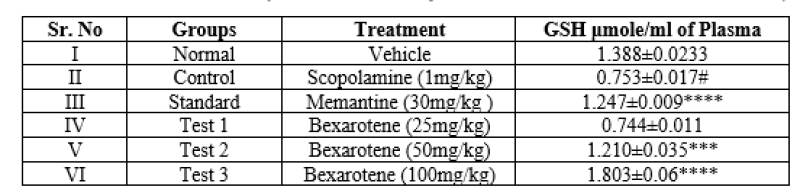
Each group consist of 6 animals (n=6), Values are Mean ± S.E.M. #P< 0>
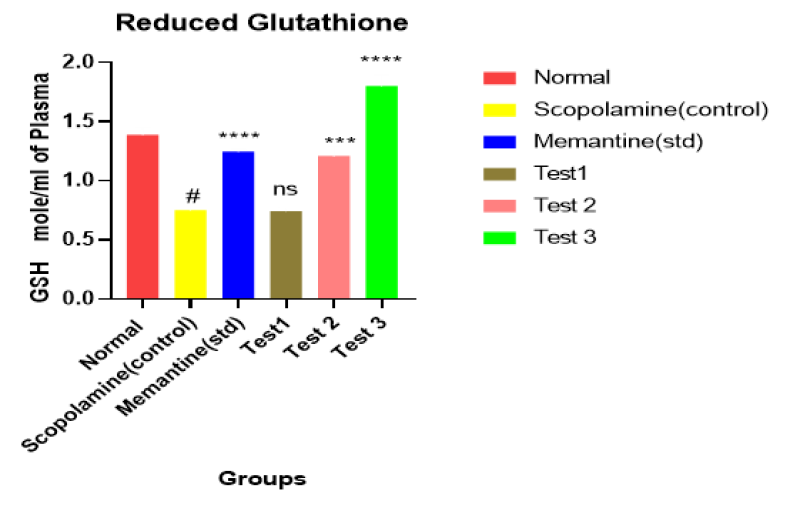
Figure 7. Effect of Bexarotene on reduced glutathione level
Observation and result shows that decrease in glutathione level in animals of group II receiving scopolamine. 25mg/kg bexarotene receiving group IV, less significantly increases whereas 100mg/kg bexarotene receiving group VI respectively, significantly increases the Glutathione level.
2. Determination of Nitric Oxide
There is a functional relationship between the heparan sulfate proteoglycan glypican-1 and the amyloid precursor protein (APP) of Alzheimer’s disease. In rats, embryonic fibroblasts, expression and processing of the APP are required for endosome to nucleus translocation of anhydromannose containing heparan sulfate released from S-nitrosylated glypican-1 by ascorbate induced, nitrosothiol catalyzed deaminative cleavage. In AD rats there is increased processing of the APP to amyloid-? peptides. Simultaneously, there is spontaneous formation of anhydrmannose containing heparan sulfate by an unknown mechanism, anhydromannose-containing heparan sulfate form hypoxia. In hypoxia addition of nitrite to the medium restored anhydromannose-containing heparan sulfate formation. The increased releases of anhydromannose-containing heparan sulfate in hypoxic. Fibroblasts maintain a high level of anhydromannose-containing heparan sulfate production by a stress-activated generation of nitric oxide from endogenous nitrite. This activation is enhanced by hypoxia.55

Table 7. Result of effect of Bexarotene on Nitric Oxide (NO) level
Each group consist of 6 animals (n=6), Values are Mean ± S.E.M. #P< 0>
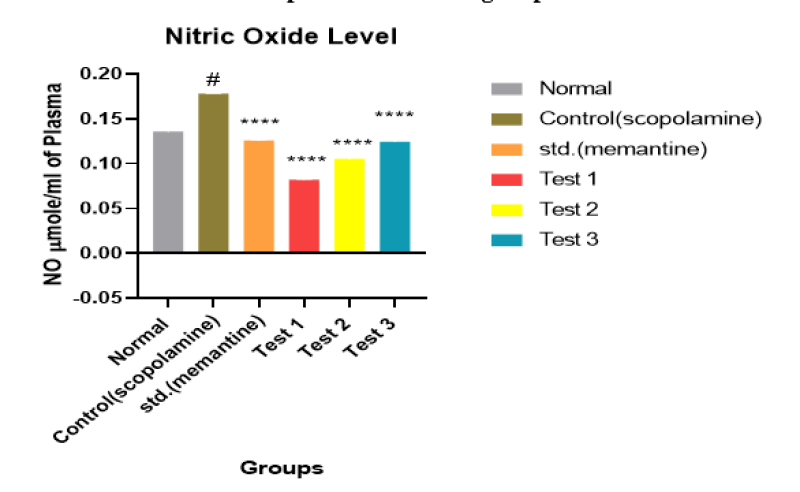
Figure 8. Observation of effect of Bexarotene on Nitric Oxide (NO) level
Observation and result shows that increases in nitric oxide level in animals of group II receiving scopolamine. 100mg/kg bexarotene receiving group VI significantly decreases the nitric oxide level.
3. Determination of Acetylcholinesterase
Directly, and converse to changes in AChE activity has been shown to increase as AD progresses Compared with levels in the brains of healthy control subjects with no psychiatric or
neuropathological abnormalities, AChE has been shown to be 33% lower in the cortex and 38% lower in the hippocampus in AD brain samples.59
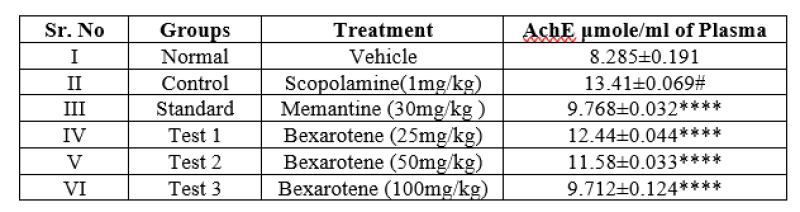
Table 8. Result of effect of Bexarotene on Acetylcholinesterase level
Each group consist of 6 animals (n=6), Values are Mean ± S.E.M. #P< 0>

Figure 9. Observation of effect of bexarotene on Acetylcholinesterase level
Observation and result shows that increase in acetylcholinesterase level in animals of group II receiving scopolamine. 100mg/kg bexarotene receiving group VI significantly decreases acetylcholinesterase level.
DISCUSSION
Cognition refers to the mental action or process of acquiring knowledge and understanding through thought, experience and the sense. It contains many aspects of intellectual functions and processes such as attention, the formation of knowledge, memory and working memory, judgment and evaluation, reasoning, problem-solving and decision making, comprehension and production of language. Alzheimer's disease is a neurodegenerative disease of the brain and the neuronal degeneration is associated with the formation of senile plaques, neurofibrillary tangles which are composed of amyloid B-peptide (A?). Scopolamine, a muscarinic cholinergic antagonist is widely used in induction of cognitive impairment in experimental animals. After intraperitoneal administration of scopolamine, the cholinergic neurotransmission is blocked, leading to cholinergic dysfunction and impaired cognition in rats. It has been further reported that memory impairment induced by scopolamine in animals is associated with altered brain oxidative stress status. Bexarotene is a retinoid X receptor (RXR) agonist, effectively used for the treatment of cutaneous T cell lymphoma. It is also useful for the reduction of cholesterol, peripheral thyroid hormone metabolism, amyloid plaques and ?-amyloid protein. Bexarotene also reduced the pathological events of ?-amyloid accumulation such as synaptic degeneration, neuronal loss, tau phosphorylation and neuro-inflammation in mice. Radial arm maze (RAM) is a type of model of procedural memory of implicit memory where animal behaviour is influenced by previous experience and classical conditioning is given by positive reinforcement of food. In the course of learning something like a field map of the environment gets established in the rat's brain (spatial memory). The performance of rats in a radial maze task is determined to check spatial working memory processes which critically depend on the functions of the hippocampus. In radial arm maze observation, it is found that bexarotene produces significant improvement in memory performances similar to that of standard drug Memantine. Test drug receiving animals significantly increased the correct arm entries, decreased the number of errors and time to complete task in RAM as compared to scopolamine receiving groups. Additional evidences for the memory enhancing effect of the bexarotene were obtained from the studies on elevated plus mare. In plus maze, rats show natural aversion to open and high spaces and therefore, spend more time in enclosed arms. It is reported that transfer latencies is shortened if animal had previously experienced entering the open arm. The shortened transfer latency could be related to memory to present study the shortened transfer latency was obtained on the retention phase, i.e. on 11 days in treated groups and the effect were statistically significant. Bexarotene significantly decreased (P<0>
CONCLUSION
In cognitive impairment (CI), person facing problem in remembering, learning, concentrating and making decisions in everyday life. Therefore, in the present study, rats with scopolamine induced cognitive impairment were used. After treating with scopolamine, performances on several memory task, decreased number of correct arm entries, increased number of errors, increased time taken to complete task and increased transfer latency in radial am maze and elevated plus maze were determined in animals. Some biochemical parameters were also determined to confirm the activity of drug. Increased Nitric oxide level, reduced glutathione level and increased acetylcholinesterase level were confirmed after induction of cognitive impairment with scopolamine. From the results of present study bexarotene found to be improve memory performance in experimental animals thus it is concluded that Bexarotene act as a protective agent against learning and memory impairment produced by scopolamine as well. So Bexarotene can serve as a drug for Alzheimer’s disease too.
REFERENCES
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cognition
- Petersen RC. Clinical practice. Mild Cognitive Impairment. N Engl J Med. 2011; 364(23):2227-2234.
- Smith E. Vascular cognitive impairment. Continuum (Minneap Minn). 2016;22(2 Dementia):490-509.
- Goldman JG, Litvan I. Mild cognitive impairment in Parkinson’s disease. Minerva Med. 2011; 102(6):441-459.
- Monastero R, Cicero CE, Baschi R, et al. Mild cognitive impairment in Parkinson’s disease: the Parkinson’s Disease Cognitive Study (PACOS). J Neurol. 2018; 265(5):1050-1058.


 Vinay V. Sarode* 1
Vinay V. Sarode* 1
 Sadhana P. Gautam 2
Sadhana P. Gautam 2


















 10.5281/zenodo.10793085
10.5281/zenodo.10793085