Abstract
Solid cross-linked porous nanoscale polymeric structures are known as nanosponges. This broad idea includes hydrogels and metal organic frameworks. This manuscript focuses on nanosponges, their types and details related to its crucial type cyclodextrin based nanosponges, their methods of preparation and applications. Cyclodextrins are starch-derived cyclic oligomers of glucose. Cyclodextrins have the rare capacity to form inclusion host-guest complexes with numerous hydrophobic substances due to the unique structure created by the combination of the outward hydrophilicity and the inside hydrophobic surface. These complexes might improve the solubility of the guest molecules and stabilize the molecule without causing any other alterations in their favorable properties. These characteristics along with the flexibility to use various crosslinkers and the high polymeric surface, make these sponges particularly well-suited for a wide variety of applications.
Keywords
Nanosponges, Polymers, Cyclodextrin based Nanosponges, Co-polymer, Cross-linking agents.
Introduction
Innovative medication delivery systems called nanosponges are minuscule sponge-like structures with cavities. These cavities can be filled with drugs and have pores between 1 and 2 nanometers in size.(1) Nanosponges have a sponge-like morphology and are very small in size. These are tiny, mesh- like structures that may enclose a wide range of different substances. They have a demonstrated spherical colloidal nature and are said to have a high capacity for solubilization.(2) Drugs that are poorly soluble in water can be solubilized using nanosponges, which also give extended release and increase drug bioavailability. Due to their internal hydrophobic chambers and exterior hydrophilic branching, nanosponges have unmatched flexibility and can load both hydrophilic and hydrophobic medicinal molecules.(3)
Components of Nanosponges
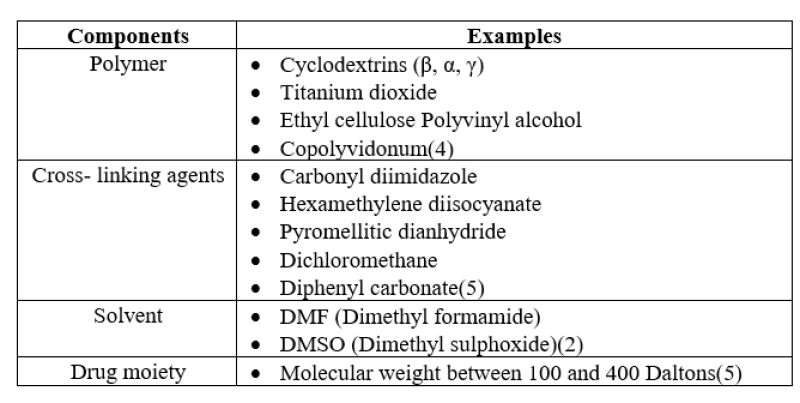
Table1: The major components used in formulation of nanosponges
Types of Nanosponges
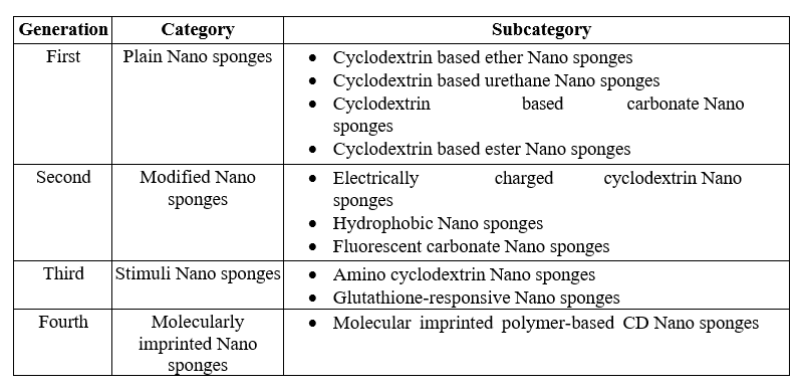
Table2: Categorization of nanosponges into various generations based on their evolution.(6)
- First generation {Plain nanosponges}
Cyclodextrin based ether nanosponges
By reacting CDs with cross-likers containing epoxide groups such as epichlorohydrin, bisphenol A diglycidyl ether, ethylene glycol diglycidyl ether, etc., CD-based ether NSs are frequently created. This particular class of NSs demonstrates strong chemical resistance and variable swelling capabilities.(7)
Cyclodextrin based urethane nanosponges
Diisocyanates are primarily used in the synthesis of urethane (or carbamate) CD-NSs. Their robust structure, great resistance to chemical deterioration and little swelling extent in both aqueous and organic conditions serve as distinguishing features. Li and Ma created the first carbamate CD-NSs which are utilized to remediate wastewater by reacting CD with hexamethylene diisocyanate and toluene-2,4-diisocyanate.(8) These NSs outperformed activated carbons in the elimination of several organic compounds such as p-nitrophenol which was reduced to ppb levels even at low concentrations.(9)
Cyclodextrin based carbonate nanosponges
Active carbonyl chemicals including as 1,1'-carbonyldiimidazole, Tri-phosgene, and diphenyl carbonate are used in the synthesis of CD-based carbonate NSs. Short cross-linking bridges decreased swelling ability, strong stability to acidic and mildly alkaline solutions are all characteristics of these NSs.(10) Carbonate NSs exhibit a limited surface area (about 2 m2/g) and a strong attraction for some organic compounds just like urethane NSs do.(11)
Cyclodextrin based ester nanosponges
Ester NS is typically created by combining CDs with dianhydrides or di/ poly carboxylic acids such citric acid, ethylenediamine-tetra acetic dianhydride (EDTA dianhydride), butane tetracarboxylic dianhydride and pyro melic dianhydride.(12)
- Second generation {Modified nanosponges}
The extension of the previously mentioned CD polymers range of application and the emergence of a new generation of NSs were made possible by the incorporation of desired functionalities. There are three ways to introduce certain moieties: Functionalization of an NS after cross-linking but before cross-linking CD functionalization or simultaneous addition of a functionalizing agent and a cross-linking agent step.(13)
- Third generation {Stimuli nanosponges}
Stimuli-sensitive polymers adapt to changes in their environment by changing their structure, permeability or color. The morphology, supramolecular processes and molecular processes that are stimuli sensitive are what enable an organism to perceive a stimulus and respond to it. (14) Stimuli-sensitive nano-carriers are renowned for their potential to boost therapeutic efficiency with a minimum of adverse effects, as well as their controlled target release upon initiation by stimulating signals or particular transport routes.(15)
- Fourth generation {Molecularly imprinted nanosponges}
When a template molecule is present during the synthesis of a polymer, a technique called molecular imprinting can be used to provide three-dimensional polymers molecular recognition properties.(16)
Cyclodextrin-Based Nanosponges
A family of molecular cages known as cyclic 1,4-linked oligosaccharides with hydrophilic exterior surfaces and a lipophilic inside is known as cyclodextrins (CDs). When creating nanosponges, cyclodextrins (CDs) have been the most often used materials.(17,18) Early in the 1950s, physicochemical characteristics of CD were found and ever since, the pharmacological and physicochemical qualities such as stability, solubility and bioavailability of active moieties have then been improved.(19) It has been noted that cyclodextrin complexes made with biocompatible hydrophilic polymers can improve the solubility of encapsulated classes in aqueous conditions.(20) A novel hyper-crosslinked nanostructured material can be created by reacting cyclodextrins with crosslinkers called "nanosponges".(21)
Components of Cyclodextrin Based Nanosponges

Table3: Components of cyclodextrin based nanosponges
Characteristics
- Cross-linked cyclodextrin polymers are known as CD-NS.(24)
- CD-NS are 3-D structures that allow for the selective capture, transport and release of a wide range of chemicals. They can be coupled with several functional groups which enables them to be targeted to various places.(25)
- Highly porous nanoparticles are CD-NS.
- They are capable of forming complexes with many lipophilic and hydrophilic molecule types.(26,27)
- They are biodegradable and safe for biological use.
- Even at high temperatures up to 300 degrees Celsius, these are still stable.(28)
- They can exist in both crystalline and Para crystalline forms.(29)
Types of Cyclodextrin Based Nanosponges
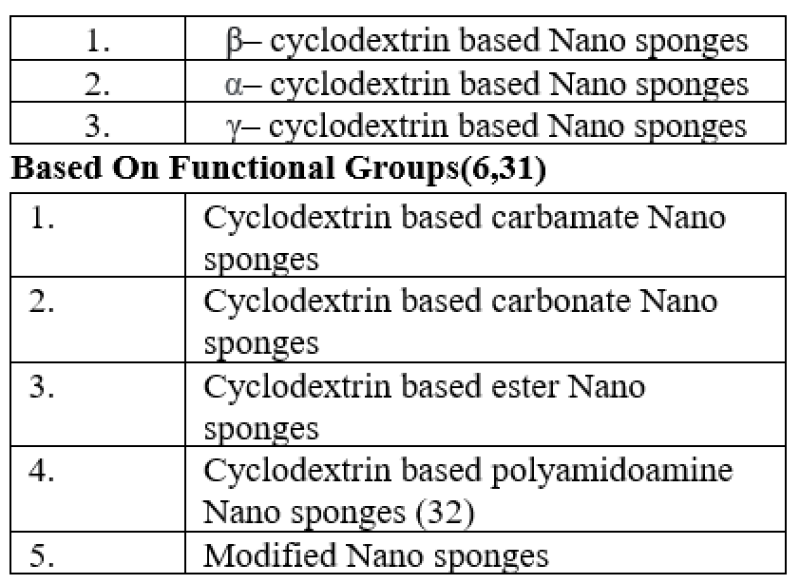
Table4: Classification of cyclodextrin based nanosponges Based On Polymer Used(30)
Based On Functional Groups(6,31)
Methods of Preparation
- Solvent evaporation technique
In the solvent evaporation approach, the fusing step is skipped and the cross-linking agent is instead solubilized using solvents like DMSO or DMF.(33) The polymer is combined with a polar aprotic solvent and the resulting combination is added to a cross-linker solution and refluxed for one to forty-eight hours. The end result is produced by mixing a substantial amount of distilled water with cold solution. Finally, filtration is used to recover the finished product and Soxhlet extraction is used to purify it over an extended period of time.(34) By either a non-inclusional or an inclusional process, spherical, solid nanostructures with high water solubility are produced. High pressure homogenization involves homogenizing prepared nanosponges in water at continuous speed for 10 minutes minimizes the size of NS.(25)
- Ultrasound-assisted technique
In the initial step of ultrasound-assisted manufacturing, cyclodextrins and cross-linking agents are combined without the need of solvents.(35) Anhydrous -CD and DPC are taken in a vial, placed in an ultrasonic bath with water that has been pre-heated to 90°C and then sonicated for five hours. Additionally, the solvent evaporation and melt technique's crystallization and purification procedures are the identical.(36)
- Microwave-assisted technique
Microwave irradiation is the easiest way for synthesizing CDNS and it considerably slows down reaction time. The NS that is produced has more crystallization.(37) Microwave aided manufacturing showed a four-fold reduction in reaction time compared to typical melt technique. The procedure produced crystallinity and a homogenous distribution of the particle size.(38)
- Melt method
In this method, the cross-linking agent is melted with a CD and all of the ingredients are homogenized before being heated at 100°C for five hours while being stirred magnetically. The above matrix is then given time to cool. To get rid of by-products and unreacted components.(6,39)
Drug Loading in Blank Nanosponges
The drug loading capabilities of NS are different for para-crystalline and crystalline forms. When compared to para-crystalline NS, crystalline NS results in a larger drug pay load. Due to the hydrophobic CD channels that are surrounded by hydrophilic nanocavities in the polymeric matrix, these nanosponges have a variety of mesh polarities, enabling strong interactions with drugs of different lipophilicities and structural types.(40,41) The drug or herbal extract is dissolved in ethanol or suitable solvent with uniform agitation for 15 minutes and then keeping the mixture undisturbed for 24 hours. Then the resultant is centrifugated and supernatant of the mixture is lyophilized.(42)
The loading capacity of the nanosponges is calculated using formula(43):
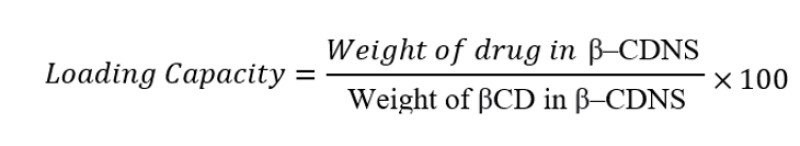
Characteristic Evaluation of Nanosponges
- Production yield
Calculating the initial or beginning weights of raw materials and the end weight of nanosponges will produce the production yield (PY).
Yield of production = [Actual mass of nanosponges/Theoretical mass (drug + polymer)] × 100
Different batches percentage yields were calculated using weighing the dried nanosponges.(44,45)
- Spectroscopic Technique
- Fourier-transformation infrared spectroscopy
The FTIR spectra of optimized loaded NS and Blank NS were captured and analyzed for potential chemical interactions. The translucent pellets of these samples were generated by mixing these compounds with potassium bromide. FTIR spectra was acquired in the area of 4000–400 cm?1(46)
- RAMAN spectroscopy
- Ultraviolet- visible spectroscopy
- Nuclear magnetic resonance
- Measurement of Zeta-Potential
The stability and durability of the Nanosponges was estimated using a zeta potential study. Zeta potential is a metric for electrostatic charge impact. This fundamental force is what separates nearby particles from one another. Depending on the strength of both forces, the overall effects can be either attraction or repulsion.(47)
- Drug entrapment efficacy
In a volumetric flask, correctly weighed nanosponges (10 mg) were added to 5 ml of methanolic HCl (HCl: Methanol-10:1) to determine the entrapment efficiency. The flask was shaken with a vortex mixer for one minute.(48) The Methanolic HCl was used to create a volume up to 10 ml. After that, the mixture was diluted, filtered and the Spectrometric analysis was used to determine the drug concentration at 295nm.(49)

5. In-vitro drug release-Dissolution Study:
The prepared formulation was subjected to a 12-hour in vitro drug release study utilizing an Electrolab model dissolution tester USP Type-2 apparatus (rotating paddle) set at 100 rpm and a formulation with a temperature of 37±0.5°C was added to the 900ml medium.(50) To maintain a constant volume, 10 ml samples were taken out of the dissolving medium at predetermined intervals and replaced with new medium. Using a UV- visible spectrophotometer, the sample solution's absorbance was measured at 231 nm to determine whether the model drug was present.(51,52)
6. X-Ray Diffraction Technique
7. Porosity or swelling index(53)
8. Differential Scanning Calorimetry
9. Microscopic Technique
10. Photodegradation studies (54)
ROLE IN DRUG DELIVERY
- Targeted and controlled release drug delivery
When drugs are delivered by nanosponges, they are only released at the targeted spot hence preventing their circulation throughout the body.(55)
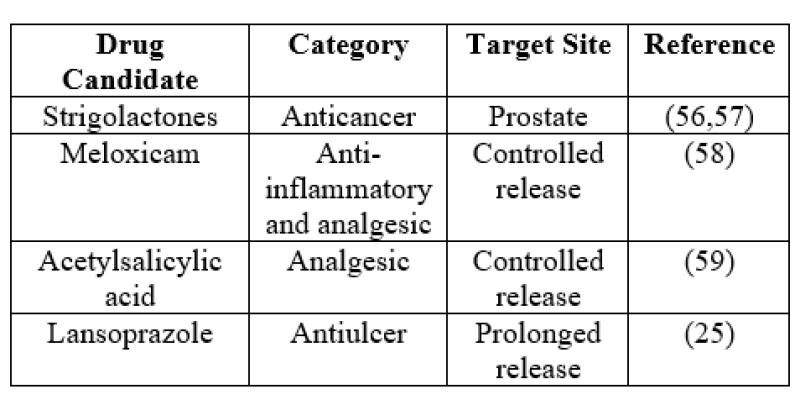
Table5: Various applications of cyclodextrin based nanosponges in targeted and controlled release drug delivery
- Improve stability
Drug compounds that are prone to deterioration when exposed to water, oxygen (air), heat or radiation can be stopped from degrading by using cyclodextrin nanosponges.(60) Nanosponges are being used in numerous studies on these interactions. The nanosponges prevent oxidation, hydrolysis, racemization, polymerization and enzyme hydrolysis from happening to the drug molecules.(61)
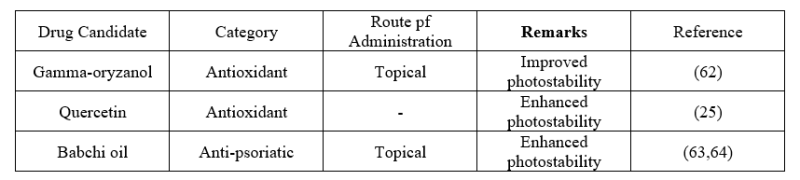
Table6: Various applications of cyclodextrin based nanosponges in improving stability.
3. Enhanced solubility
Poor solubility of BCS (Biopharmaceutical Classification System) class II medications possesses a challenge in their preparation.(65) However, these medications can be more effectively integrated into cyclodextrin nanosponges. By increasing their wetting and solubility in water, these nanocarriers increase their aqueous solubility through the formation of inclusion complexes.

Table7: Various applications of cyclodextrin based nanosponges in enhancing solubility:
- Oral drug delivery
An established route of administration with good patient compliance is oral medication delivery. Due to poor solubility, ineffective intestinal permeability, and pre-systemic activation, delivering molecules via oral route presents difficulties. Nanosponges made from cyclodextrin have shown promise as oral delivery without sacrificing any safety concerns.(69)
- Topical drug delivery
For topical drug delivery, nanosponges may be included in creams and gels. Although they haven't been extensively studied, nanosponges could be a very effective method for treating skin conditions. If successfully entrapped, nanosponges enhanced drug delivery via topical gel in addition to drug targeting.(70,71)
- Pulmonary drug delivery
The pulmonary route is a substitute for parenteral drug delivery but the drug has to be in the form of aerosol to be delivered by this route. The advantage of the nanosponges is their lower interparticle forces of attraction and improved flow properties. Additionally, they have a small, thin and low bulk density. Their increased deposition in the lower pulmonary area is the result of their dynamic diameter.(72)
CONCLUSION
Nanosponges are innovative crosslinked carriers which are used to deliver variety of drugs to targeted sites and plays vital role in increasing their bioavailability. Drugs that are either lipophilic or hydrophilic can be incorporated into the nanosponges which release them in a regulated and predictable way at the target location. It can be modulated by adjusting the polymer to water ratio, the release rate, particle size, and cross-linker. Nanosponges permit the insoluble medications and safeguard the active components from controlled physicochemical deterioration. Due to their diminutive size and spherical shaping, they can be created in a variety of ways or dose types/ forms like aerosol, topical, parenteral, capsules and pills. Cyclodextrin nanosponges are a rapidly growing area of nanotechnology with numerous uses in medicine delivery, research and targeting among other elements due to their distinct size-dependent characteristics and porous nature. They offer the potential to create novel therapeutic approaches. Their capacity to seize drugs and exercise control releasing features provide a novel method of medication delivery that raises the level of the drug targeting. Consequently, cyclodextrin nanosponges hold out a lot of hope for achieving the site-specific and regulated delivery objectives which can also provide fresh viewpoints in the near future in the treatment of difficult disorders.
ABBREVIATIONS
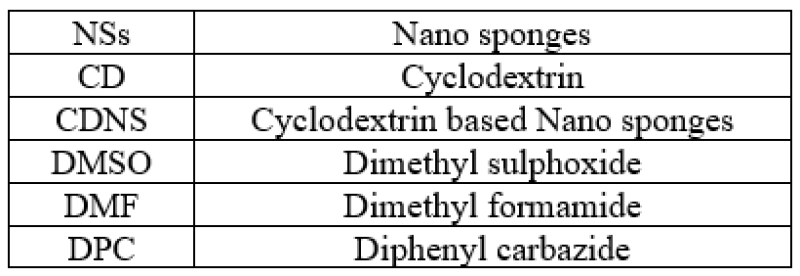
REFERENCES
- Omar SM, Ibrahim F, Ismail A. Formulation and evaluation of cyclodextrin-based nanosponges of griseofulvin as paediatric oral liquid dosage form for enhancing bioavailability and masking bitter taste. Saudi Pharmaceutical Journal. 2020 Mar 1;28(3):349–361.
- Silpa R KKSN. Nanosponges: A targeted drug delivery system and its applications, Department of pharmaceutics. 2019; 07(03):040–047.
- Vij M, Dand N, Kumar L, Wadhwa P, Wani SUD, Mahdi WA, et al. Optimisation of a Greener- Approach for the Synthesis of Cyclodextrin-Based Nanosponges for the Solubility Enhancement of Domperidone, a BCS Class II Drug. Pharmaceuticals. 2023 Apr 1;16(4).
- Khan A, Arshad K, Khan A, Bhargav E, Rajesh Reddy K, Sowmya C. ANTI-CANCER ACTIVITY IN HEPATOCELLULAR CARCINOMA CELL LINE HEPG2 FROM FOLKLORE PLANT View project SOLUBILITY ENHANCEMENT View project Nanosponges: A New Approach for Drug Targetting, 2016;7.
- Ravi SC, Krishnakumar K, Nair SK. Nano sponges: A targeted drug delivery system and its applications. GSC Biological and Pharmaceutical Sciences. 2019 Jun 30;7(3):040–047.
- Bilal J. S, Abhishek S. P, Ankush S. B, Indrayani D. R, Manojkumar M. N. NANOSPONGES: AN EVOLUTIONARY TREND FOR TARGETED DRUG DELIVERY. International Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences and Medicine. 2021 Jun 30;6(6):1–14.
- Alvarez LC, SRTC, LTJJ and C. Method of obtaining hydrogels of cyclodextrins with glycidyl ethers, compositions thus obtained and applications. 2008.
- Li D and MM. Nanosponges: from inclusion chemistry to water purifying technology. Chemtech. 1999;29(5):31–37.
- Li D and MM. Nanosponges for water purification. Clean Products and Processes. 2013:112- 116.
- Caldera F, Tannous M, Cavalli R, Zanetti M, Trotta F. Evolution of Cyclodextrin Nanosponges. Int J Pharm. 2017 Oct;531(2):470–479.
- Trotta F, Cavalli R, Martina K, Biasizzo M, Vitillo J, Bordiga S, et al. Cyclodextrin nanosponges as effective gas carriers. J Incl Phenom Macrocycl Chem. 2011; 71:189–194.
- Ferro M, Anomalous diffusion of Ibuprofen in cyclodextrin nanosponge hydrogels: an HRMAS NMR study. Beilstein J Org Chem. 2014; 10:2715–2723.
- Sabzi NE, Kiasat AR. ?-Cyclodextrin based nanosponge as a biodegradable porous three- dimensional nanocatalyst in the one-pot synthesis of n-containing organic scaffolds. Catal Letters. 2018; 148:2654–2664.
- Caldera F, Tannous M, Cavalli R, Zanetti M, Trotta F. Evolution of cyclodextrin nanosponges. Int J Pharm. 2017;531(2):470–479.
- Lendlein A and S. Stimuli-Sensitive Polymers. Advanced Materials. PV. 2010;3344–3347.
- Sellergren B and ACJ. Molecularly imprinted polymers: A bridge to advanced drug delivery. Advanced Drug Delivery Reviews, 2005; 1733-1741.
- Utzeri G, Matias PMC, Murtinho D, Valente AJM. Cyclodextrin-Based Nanosponges: Overview and Opportunities. Vol. 10, Frontiers in Chemistry. Frontiers Media S.A.; 2022.
- Kumar A, Rao R. Enhancing efficacy and safety of azelaic acid via encapsulation in cyclodextrin nanosponges: Development, characterization and evaluation. Polymer Bulletin. 2021; 78:5275–5302.
- Loftsson T, Duchêne D. Cyclodextrins and their pharmaceutical applications. Vol. 329, International Journal of Pharmaceutics. Elsevier; 2007. 1–11.
- Trotta F. Cyclodextrin nanosponges and their applications. Cyclodextrins in pharmaceutics, cosmetics, and biomedicine: current and future industrial applications. 2011;323–342.
- Bhowmik H, Venkatesh DN, Kuila A, Kumar KH. Nanosponges: A review. Vol. 10, International Journal of Applied Pharmaceutics. Innovare Academics Sciences Pvt. Ltd; 2018. 1–5.
- Arvapalli S, khan I, Sharma J. Formulation and Invitro evaluation of ?-cyclodextrin based Nanosponges. Scholars Academic Journal of Pharmacy (SAJP) [Internet]. 2017;6(5):175–85.
- Sherje A.P. BRD, KDJM. Cyclodextrin- based nanosponges: A critical review. 2017; 173:37–49.
- Mane PT, Wakure BS, Wakte PS. Cyclodextrin based nanosponges: a multidimensional drug delivery system and its biomedical applications. Curr Drug Deliv. 2021;18(10):1467–1493.
- Kumar S, Dalal P, Rao R. Cyclodextrin Nanosponges: A Promising Approach for Modulating Drug Delivery. In: Colloid Science in Pharmaceutical Nanotechnology. IntechOpen; 2020.
- Tiwari K, Bhattacharya S. The ascension of nanosponges as a drug delivery carrier: preparation, characterization, and applications. J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2022 Mar 4;33(3):28.
- Shringirishi M, Prajapati SK, Mahor A, Alok S, Yadav P, Verma A. Nanosponges: a potential nanocarrier for novel drug delivery-a review. Asian Pac J Trop Dis. 2014;4: 519–526.
- P D NK, Vineetha K, K KK, Shabaraya AR. Nanosponges: A Versatile Novel Drug Delivery System. Int J Pharm Sci Rev Res. 2022 Sep 15;151–156.
- Mandan S CMBYKC. Nanosponges: A New Drug Delivery System, Journal of Drug Delivery and Therapeutics. 2018;8(6-A):141–143.
- Caldera F, Tannous M, Cavalli R, Zanetti M, Trotta F. Evolution of Cyclodextrin Nanosponges. Int J Pharm. 2017 Oct 15;531(2):470–479.
- Garrido B, González S, Hermosilla J, Millao S, Quilaqueo M, Guineo J, et al. Carbonate-?-cyclodextrin-based nanosponge as a nanoencapsulation system for piperine: physicochemical characterization. J Soil Sci Plant Nutr. 2019; 19:620–630.
- Russo M, Saladino ML, Martino DC, Meo P Lo, Noto R. Polyaminocyclodextrin nanosponges: Synthesis, characterization and pH-responsive sequestration abilities. RSC Adv. 2016;6(55):49941–49953.
- Utzeri G, Matias PMC, Murtinho D, Valente AJM. Cyclodextrin-Based Nanosponges: Overview and Opportunities. Front Chem. 2022; 10:859406.
- Pushpalatha R, Selvamuthukumar S, Kilimozhi D. Cross-linked, cyclodextrin-based nanosponges for curcumin delivery-Physicochemical characterization, drug release, stability and cytotoxicity. J Drug Deliv Sci Technol. 2018; 45:45–53.
- Jasim IK, Abd Alhammid SN, Abdulrasool AA. Synthesis and evaluation of B-cyclodextrin based nanosponges of 5-Fluorouracil by using ultrasound assisted method. Iraqi Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences. 2020;29(2):88–98.
- Subramanian S, Singireddy A, Krishnamoorthy K, Rajappan M. Nanosponges: A Novel Class of Drug Delivery System-Review. Vol. 15, J Pharm Pharmaceut Sci. 2012.
- Anandam S, Selvamuthukumar S. Optimization of microwave-assisted synthesis of cyclodextrin nanosponges using response surface methodology. Journal of Porous Materials. 2014; 21:1015–1023.
- Singireddy A, Pedireddi SR, Nimmagadda S, Subramanian S. Beneficial effects of microwave assisted heating versus conventional heating in synthesis of cyclodextrin based nanosponges. Mater Today Proc. 2016;3(10):3951–3959.
- Sharma K, Kadian V, Kumar A, Mahant S, Rao R. Evaluation of solubility, photostability and antioxidant activity of ellagic acid cyclodextrin nanosponges fabricated by melt method and microwave-assisted synthesis. J Food Sci Technol. 2022;1–11.
- Tannous M, Caldera F, Hoti G, Dianzani U, Cavalli R, Trotta F. Drug-encapsulated cyclodextrin nanosponges. Supramolecules in Drug Discovery and Drug Delivery: Methods and Protocols. 2021;247–283.
- Tannous M, Caldera F, Hoti G, Dianzani U, Cavalli R, Trotta F. Drug-Encapsulated Cyclodextrin Nanosponges. 2021. 247–283.
- Simionato I, Domingues FC, Nerin C, Silva F. Encapsulation of cinnamon oil in cyclodextrin nanosponges and their potential use for antimicrobial food packaging. Food and chemical toxicology. 2019; 132:110647.
- Asela I, Donoso-González O, Yutronic N, Sierpe R. ?-cyclodextrin-based nanosponges functionalized with drugs and gold nanoparticles. Pharmaceutics. 2021;13(4).
- Solunke RS, Borge UR, Murthy K, Deshmukh MT, Shete R V. Formulation and evaluation of gliclazide nanosponges. International Journal of Applied Pharmaceutics. 2019 Nov 1;11(6):181–189.
- Abbas N, Sarwar K, Hussain A, Irfan M, Mehmood R, Arshad MS, et al. Formulation and evaluation of indomethacin loaded nanosponges for oral delivery. Acta Poloniae Pharmaceutica - Drug Research. 2018;75(5):1201–1213.
- Ahmed MM, Fatima F, Anwer MK, Ibnouf EO, Kalam MA, Alshamsan A, et al. Formulation and in vitro evaluation of topical nanosponge-based gel containing butenafine for the treatment of fungal skin infection. Saudi Pharmaceutical Journal. 2021 May 1;29(5):467–477.
- Pushpalatha D, Abdul Waris Khan, Manjunath K, Brunda S. Formulation and evaluation of lovastatin loaded nanosponges. World Journal of Advanced Research and Reviews. 2021 Sep 30;11(3):041–056.
- Deng J, Chen QJ, Li W, Zuberi Z, Feng JX, Lin QL, et al. Toward improvements for carrying capacity of the cyclodextrin-based nanosponges: recent progress from a material and drug delivery. J Mater Sci. 2021; 56:5995–6015.
- Manohar DR, Dharan SS. Formulation and Evaluation of Nanosponges Loaded Hydrogel Using Different Polymers Containing Selected Antifungal Drug.
- Arvapalli S, Arvapally S, Harini M, Harshitha G. Formulation and In-vitro Evaluation of Glipizide Nanosponges. Am J PharmTech Res [Internet]. 2017;7(3).
- Kumar S, Pooja, Trotta F, Rao R. Encapsulation of babchi oil in cyclodextrin-based nanosponges: physicochemical characterization, photodegradation, and in vitro cytotoxicity studies. Pharmaceutics. 2018;10(4):169.
- Srivastava S, Mahor A, Singh G, Bansal K, Singh PP, Gupta R, et al. Formulation development, in vitro and in vivo evaluation of topical hydrogel formulation of econazole nitrate-loaded ?- cyclodextrin nanosponges. J Pharm Sci. 2021;110(11):3702–14.
- Pavani A, Rama B. FORMULATION AND IN VITRO CHARACTERIZATION OF FLURBIPROFEN NANOSPONGES 2015, 8.
- Pushpalatha R, Selvamuthukumar S, Kilimozhi D. Cross-linked, cyclodextrin-based nanosponges for curcumin delivery - Physicochemical characterization, drug release, stability and cytotoxicity. J Drug Deliv Sci Technol. 2018 Jun 1; 5:45–53.
- Jawaharlal S, Subramanian S, Palanivel V, Devarajan G, Veerasamy V. Cyclodextrin-based nanosponges as promising carriers for active pharmaceutical ingredient. J Biochem Mol Toxicol. 2024 Jan 30;38(1).
- Argenziano M LCFBTFCFBM. Glutathione/ pH-responsive nanosponges enhance strigolactone delivery to prostate cancer cells. Oncotarget. 2018;35813–35829.
- Allahyari S, Zahednezhad F, Khatami M, Hashemzadeh N, Zakeri-Milani P, Trotta F. Cyclodextrin nanosponges as potential anticancer drug delivery systems to be introduced into the market, compared with liposomes. J Drug Deliv Sci Technol. 2022; 67:102931.
- Shende PK GRBRPD. Effect of inclusion complexation of meloxicam with ?-cyclodextrin and ?- cyclodextrin-based nanosponges on solubility, in vitro release and stability studies. Colloids and Surfaces B: Biointerfaces. 2015; 136:105–110.
- Shringirishi M, Prajapati SK, Mahor A, Alok S, Yadav P, Verma A. Nanosponges: a potential nanocarrier for novel drug delivery-a review. Asian Pac J Trop Dis. 2014 Sep;4: 519–526.
- Mane PT, Wakure BS, Wakte PS. Cyclodextrin Based Nanosponges: A Multidimensional Drug Delivery System and its Biomedical Applications. Curr Drug Deliv. 2021 Dec;18(10):1467–1493.
- Pawar S, Shende P. A comprehensive patent review on ?-cyclodextrin cross-linked nanosponges for multiple applications. Recent Pat Nanotechnol. 2020;14(1):75–89.
- Sapino S CMCRUEBGGL. Photochemical and antioxidant properties of gamma-oryzanol in beta-cyclodextrin-based nanosponges. Journal of Inclusion Phenomena and Macrocyclic Chemistry. 2013;69–76.
- Kumar S, Pooja, Trotta F, Rao R. Encapsulation of Babchi Oil in Cyclodextrin-Based Nanosponges: Physicochemical Characterization, Photodegradation, and In Vitro Cytotoxicity Studies. Pharmaceutics. 2018 Sep 26;10(4):169.
- Kumar S, Singh KK, Rao R. Enhanced anti-psoriatic efficacy and regulation of oxidative stress of a novel topical babchi oil (Psoralea corylifolia) cyclodextrin-based nanogel in a mouse tail model. J Microencapsul. 2019 Feb 17;36(2):140–155.
- Rezaei A, Varshosaz J, Fesharaki M, Farhang A, Jafari SM. Improving the solubility and in vitro cytotoxicity (anticancer activity) of ferulic acid by loading it into cyclodextrin nanosponges. Int J Nanomedicine. 2019;4589–4599.
- Cavalli R TFTW. Cyclodextrin-based nanosponges for drug delivery. Journal of Inclusion Phenomena and Macrocyclic Chemistry. 2006;209–213.
- Rao M BAKIMGTF. In vitro and in vivo evaluation of ?-cyclodextrin-based nanosponges of telmisartan. Journal of Inclusion Phenomena and Macrocyclic Chemistry. 2013;135–45.
- Olteanu AA, Aram? CC, Radu C, Mih?escu C, Monciu CM. Effect of ?-cyclodextrins based nanosponges on the solubility of lipophilic pharmacological active substances (repaglinide). J Incl Phenom Macrocycl Chem. 2014; 80:17–24.
- Zidan MF, Ibrahim HM, Afouna MI, Ibrahim EA. In vitro and in vivo evaluation of cyclodextrin- based nanosponges for enhancing oral bioavailability of atorvastatin calcium. Drug Dev Ind Pharm. 2018;44(8):1243–12 53.
- Vyas A, Saraf S, Saraf S. Cyclodextrin based novel drug delivery systems. J Incl Phenom Macrocycl Chem. 2008; 62:23–42.
- Pushpalatha R, Selvamuthukumar S, Kilimozhi D. Cyclodextrin nanosponge based hydrogel for the transdermal co-delivery of curcumin and resveratrol: Development, optimization, in vitro and ex vivo evaluation. J Drug Deliv Sci Technol. 2019; 52:55–64.
- Tiwari K, Bhattacharya S. The ascension of nanosponges as a drug delivery carrier: preparation, characterization, and applications. J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2022 Mar 4;33(3):28.


 Kanika* 1
Kanika* 1




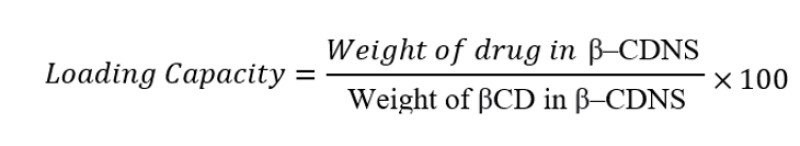





 10.5281/zenodo.10775995
10.5281/zenodo.10775995