Abstract
Diabetes is a noncommunicable disease of carbohydrate, fat and protein metabolism distinguished by increased abstaining from food and after a meal blood sugar levels.The disease consists of a group of disorder demonstrated by hyperglycemia and coming from the mixture of resistance to insulin action, inadequate insulin production, and utmost or improper glucagon secretion. A disease defined by glucose supersensitivity of inconsistent severity with beginning of the earliest phase of pregnancy. Hyperglycemia in pregnancy is found to be related through varied devoted as well as antenatal undesirable outcome.The diabetes can be measured by evaluate the blood sugar levels. The blood sugar level in well man on fasting moderation are 80 mg/dl and in postmeal state is up to 160 mg/dl.Diabetes has a lot of complications related with it as high blood sugar damages organs and tissues throughout the body.The medicinal plants and herbs are being used in extracted forms for their anti diabetic activity.
Keywords
Diabetes Mellitus, Herbal, Types, Symptoms
Introduction
Diabetes mellitus also called as diabetes which was observed as diseases related with “sweet urine” and muscle catabolism. Glucose blood levels are kept up by insulin which is a hormone leberated from the pancreas. When these level increases, insulin is produced from the pancreas and maintained the level of glucose in pancreas. When these level increases, insulin is produced from the pancreas and maintained the level of glucose. In diabetic patients, the production of insulin is absent or less which causes hypoglycemia.?1; Diabetes is a noncommunicable disease of carbohydrate, fat and protein metabolism distinguished by increased abstaining from food and after a meal blood sugar levels. The global commonness of diabetes is estimated to increase, from 4% in 1995 to 5.4% by the year 2025. WHO has predicted that the major intention will occur in developing countries. Studies conducted in India in the last decagon have highlighted that is not only is the regularity of diabetes high but also that it is increasing quickly in the urban citizens.?2;
Diabetes mellitus are three types:
1. Type 1,
2. Type 2
3. gestational diabetes mellitus?3;
1. Type-1 diabetes mellitus
Type 1 diabetes mellitus is known as insulin dependent diabetes mellitus which is due to not functioning of ? cell of islets of Langerhans which is present in pancreas. A lifetime (chronic) illness with elevated potency of sugar (glucose) in the blood.? The rate of cell damage is somewhat incompatible with in this type of diabetes being quick in some persons (chiefly infants and children) and intentional in others (essentially adults). Several patients, mostly child and young adults may begin with diabetic acidosis as the first symptom of the disease. Others comprise reserved fasting increase glucose levels that can speedily alter to severe hyperglycemia and ketoacidosis in occupancy of disease or other strain.?
2. Type -2 diabetes mellitus
Type 2 Diabetes mellitus is known as insulin non dependent diabetes mellitus which is provisional loss of ? cell mass and it is due to genetic susceptibility and mostly occur in corpulent persons and associated with high blood pressure(hypertension) and hyperlipidemia .The aim of treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus is decreases the insulin noncompliance and increases insulin production. ?3; Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus (T2DM) has been specified for long time as non-insulin dependent diabetes, and adult-onset diabetes characterized by insulin resistance, which could progressively aggravate to absolute resistance, but in the past decennium reduced ?-cell function has been recognized as a key problem in T2DM .? The disease consists of a group of disorder demonstrated by hyperglycemia and coming from the mixture of resistance to insulin action, inadequate insulin production, and utmost or improper glucagon secretion.Greatly recurrent and accounts for 90-96% of all diabetes. Adults are mainly affected though recently Type 2 has launched developing in child.?
3. Gestational diabetes mellitus
Gestational diabetes is a type of diabetes which high blood sugar level ( hyperglycemia) in pregnant women. It usually appears in 2-5% pregnancies in 2nd or 3rd trimester duration.?2; The symptoms of diabetes mellitus are excessive thirst (polydipsea), renal disorder ,hyperphagia, drawsiness, fatigue, nausea, vomiting, incapability in men, slow healing wound and cloudy vision and fuzzy vision.? A disease defined by glucose supersensitivity of inconsistent severity with beginning of the earliest phase of pregnancy. Hyperglycemia in pregnancy is found to be related through varied devoted as well as antenatal undesirable outcome. Their offspring will contain a lifetime raise possibility of glucose extremism,courageousness plus metabolic disorder while the mother will contain an elevated threat of metabolic disorder and diabetes in the future.?
Symptoms
- Blurry visualization.
- Abnormal deficiency.
- Frequent urination
- slow relieve incision
- Confusing tiredness
- Hasty mass loss (Type 1 diabetes)
- Hypoesthesia or itching in hands or feet.?1;?
Nanoformulations not only increase the drug’s solubility but also have numerous advantages such as reduced dosage, rapid onset of action, controlled drug release profile, less side effects, optimized drug delivery, expanded drug half-life, minimized patient variability and optimized bioavailability and can thus resolve several of the disadvantage of current anti-diabetics.?1;?1;
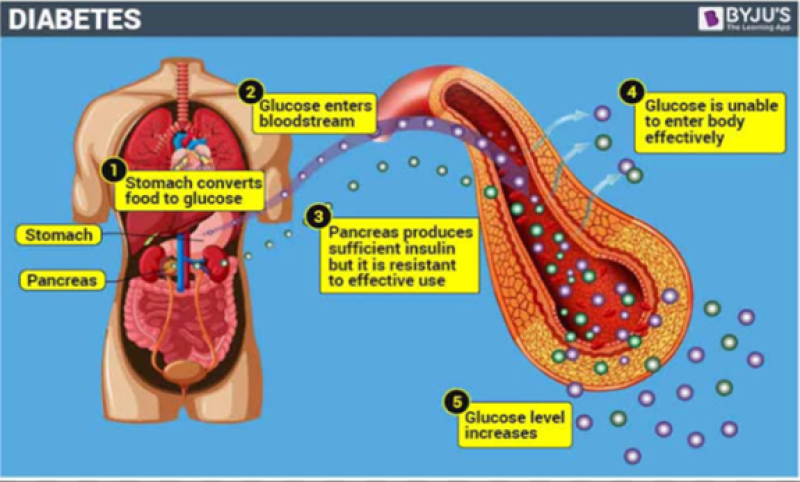
Fig.1 Diabetes Mellitus
Diagnosis of diabetes mellitus
The diabetes can be measured by evaluate the blood sugar levels. The blood sugar level in well man on fasting moderation are 80 mg/dl and in postmeal state is up to 160 mg/dl. Different test for diagnosed of diabetes in laboratory are finger prick blood sugar test, fasting blood sugar, glucose tolerance diagnostic test, glycohemoglobin.?1;?2;
Pathophysiology of diabetes
The equilibrium of glucose in the body is maintained by a number of hormones. However two hormones namely, insulin and glucagon play a important role in the regulation of glucose homeostasis.?1;?3;
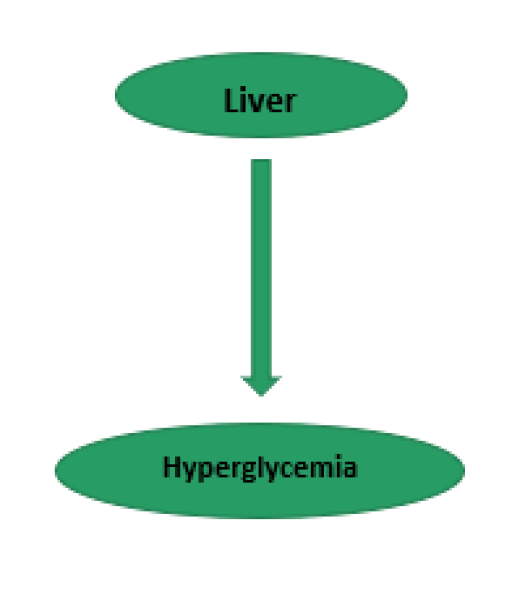
Pathophysiology of diabetes mellitus may include any one or combination of
any mechanisms of as outlined below:
- Increase in lipolysis
- Maximum in reabsorption of glucose by kidney
- Reduced secretion of insulin from ? cells of islets of langerhans
- Impairment or decreased uptake of glucose by peripheral tissues like skeletal muscle, liver and adipose tissue.
- Elevated glucagon secretion from ? cells of islets of langerhans.
- Reduction of effect of incretin in the small intestine.?1;?
Insulin is the essential hormone to control the uptake of glucose from the blood into numerous cells of the body, mainly liver, muscle, as well as adipose tissue. Therefore, its insufficiency or the inappropriate of its receptors depicts a vital task in the entire type of diabetes mellitus.The hormone glucagon essentially controls this process, which acts in the converse manner to insulin.The net result is steadily elevated potency of blood glucose, reduced protein synthesis, plus additional metabolic derangements, insanity such as acidosis.?1;? The imbalance between manufacturing of reactive oxygen species (ROS) and capacity of enzymatic or non enzymatic antioxidant are known as oxidative stress.These ROS can Stimulate various harmful pathway which have important role in growth of diabetes disease.?1;? Diabetes mellitus disease can be prevented by regulating the blood sugar level with various types of medicines, obtaining to different exercise or yoga therapy or diet plan.?1;?

In earliest time doctor and lay person used traditional medicinal plants with their active constituents and properties for the treatment of various diseases such as heart diseases, cancer and diabetes. There is a long history of traditional plants used for the jurisdiction or control of diabetes in India and China. There are various books available such as Charaka Samhita and Susruta Samhita which explains phytopharmacology characteristic of diabetes and its adverse effect.?1;? Diabetes has a lot of complications related with it as high blood sugar damages organs and tissues throughout the body. The longer the body deals with high blood sugar levels, the risk of further complications surfaces up. Complications of diabetes can be microvascular which includes nephropathy, retinopathy, loss of vision and macrovascular like heart diseases, heart attack, stroke, and neuropathy, infections.?1;?
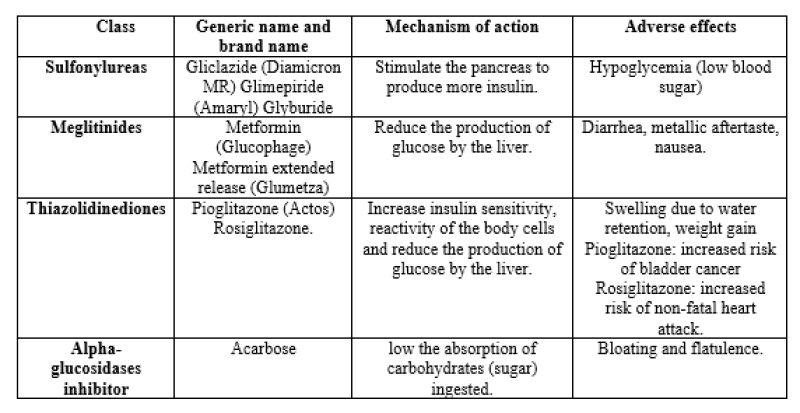
Table:1 Allopathic preparations, mechanism of actions and their adverse effects.
Herbal formulation
Herbal formulations are easily available without prescription. These herbal drugs are used for life threatening and dangerous disease. These drugs are also used when chemical drugs are ineffective in treatment of disease.Herbal drugs permanently cure person and treat the disease while synthetic drugs are temporary cured the diseases. Herbal formulations contain natural herbs and fruits and vegetables extract which are beneficial in treatment of various diseases without any adverse effects.Herbal formulations are available without prescription while all opathic medicines are available with prescription .?2;?
Advantages of herbal formulation.
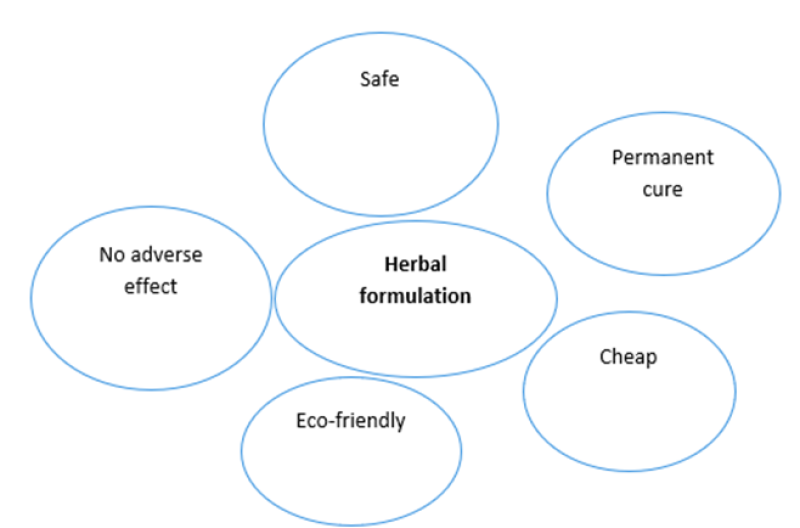
Fig.3 Advantages of herbal formulation
Herbal medicinal plants used in treatment of diabetes mellitus
The medicinal plants and herbs are being used in extracted forms for their anti diabetic activity.Various clinical studies established that medicinal plants extracts shows anti diabetic activity and renovating the action of pancreatic ?- cells.?2;?1;
- Aloe borbadensis (Aloe vera )
It grows in desert climates and is widely distributed in africa, India and other desert areas.?2;?2;It is known as Ghikanvar which belongs to family Liliaceae. It looks like a cactus plant with green blade shaped leaves that are weighty narrowing, hairy and filled with clear clammy gel. Oral administration of aqueous extract of aloe Vera in a dose of 150mg/kg of body weight crucially lowering the blood glucose level.?2;?3;
Blood glucose levels subsequently decreased from 250 mg to 141 mg/dL in the investigational group. The same research team investigated the effects of aloe vera gel in combination with a standard oral antidiabetic therapy and the subjects received either aloe or placebo. Results showed similar decreases in blood glucose in the actively treated group as described in the first trial. However, these studies were neither randomized nor blinded to patient or explorer .?2;?
- Allium Sativum (Garlic)
It belongs to family Liliaceae.Extract of garlic was more efficient than anti diabetic drug glibenclamide. Ethyl acetate, ethanol and petroleum ether extract was observed to show an anti diabetic activity in STZ induced rats. Garlic shows varioustherapeutic effectsuch as anti platelet, antibacterial, lowering the blood pressure and lowering the cholesterol level in the body.?2;?S-allyl cystein sulfoxide (SACS), the precursor of Allicin and garlic oil, is a sulfur containing amino acid, which controlled lipid peroxidation better than glibenclamide and insulin. It also improved diabetic conditions. SACS also stimulated in vitro insulin secretion from beta cells isolated from normal rats. Apart from this, Allium sativum exhibits antimicrobial, anticancer and cardioprotective activities.
- Trigonella Foenum Graecum (Fenugreek)
It belongs to family fabiacae.It is found all over India and the fenugreek seeds are usually used as one of the major constituents of Indian spices. 4-hydroxyleucine, a novel amino acid from fenugreek seeds increased glucose stimulated insulin release by isolated islet cells in both rats and humans .?2;? Administration of fenugreek seeds also improved glucose metabolism and normalized creatinine kinase activity in heart, skeletal muscle and liver of diabetic rats. It also reduced hepatic and renal glucose-6-phosphatase and fructose ?1, 6-biphosphatase activity . This plant also shows antioxidant activity.?2;?
- Ocimum sanctum
It is known as tulsi and belongs to Labiateae family. It is widely found all over India. It is used in Indian ayurvedic medicines for treatment of various diseases. Various animal studies proved that aqueous extract of Ocimum sanctum leaves(200 mg/kg) showed the hypoglycemic activity in streptozotocin induced rats. It is also used for treatment of viral infection, treatment of fungal infection, reduces stress, treatment of tumor and treatment of gastric ulcer.?2;?Significant reduction in fasting blood glucose, uronic acid, total amino acid, total cholesterol, triglyceride and total lipid indicated the hypoglycaemic and hypolipidemic effects of tulsi in diabetic rats.?2;?
- Azadirachta Indica (Neem)
Hydroalcoholic extracts of this plant showed anti-hyperglycaemic activity in streptozotocin treated rats and this effect is because of increase in glucose uptake and glycogen deposition in isolated rat hemi diaphragm.?3;?
- Carica papaya
It is known as papaya which belongs to family caricaceae. Seed and leaves extract shows lowering of blood sugar level, lowering of lipid in the body and healing of wound activities in alloxan induced diabetic rats.?3;?1;
- Catharanthus roseus
It is known as Vinca roseus which belongs to family Apocynaceae. Methanolic extract of leaves and twigs shows decrease in blood sugar level in the alloxan induced diabetic rats. Oral administration of 500 mg/kg dose of leaves and twigs extract was beneficial in animals for lowering in blood sugar level.?3;?2;
CONCLUSION
Diabetes affects people of all ages, genders, races, and ethnicities, and its prevalence has been rising alarmingly in recent years, making it a serious global health concern.
The search for natural resources with anti-diabetic efficacy has shifted due to the side effects of manufactured medications.
REFERENCE
- Bordoloi R, Dutta KN. A Review on Herbs Used in the treatment of Diabetes mellitus.Journal of Pharmaceutical,Chemical and Biological. Sciences;2014(2):86–92
- Ramachandran A, Snehalatha C, Viswanathan V (2002) Burden of type 2 diabetes and its complications- the Indian scenario Curr Sci 83:1471-1476.
- Wannes WA, Marzouk B. Research progress of Tunisian medicinal plants used for acute diabetes. Journalof Acute Disease2016;5(5):357–363.
- Saisho, Y. Importance of Beta Cell Function for the Treatment of Type 2 Diabetes. J. Clin. Med. 2014, 3,923–943.
- Edition;. Edition; http://www.vision2020uk.org.uk/idf-diabetes-atlas-7thedition.
- Cheung KW, Wong SF (2013) Gestational diabetes mellitus update and review of literature. Reproductive System & Sexual Disorders.
- Diagnosis and Classification of Diabetes Mellitus (2004) American Diabetes association Diabetes Care 27: S1.
- Baynes J (2015) Diabetes & Metabolism Classification, Pathophysiology.
- Ozougwu JC (2013) The pathogenesis and pathophysiology of type 1 and type 2 diabetes mellitus. Journal of Physiology and Pathophysiology 4: 46-57.
- Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: Practice Essentials, Background, Pathophysiology.
- S. Uppal, K.S. Italiya, D. Chitkara, A. Mittal, Nanoparticulate-based drug delivery systems for small molecule anti-diabetic drugs: An emerging paradigm for effective therapy, Acta. Biomater. 81 (2018) 20–42, https://doi.org/10.1016/j. actbio.2018.09.049.
- M. Okur, I. Karantas, P. Siafaka, Diabetes Mellitus: A Review on Pathophysiology, Current Status of Oral Pathophysiology, Current Status of Oral Medications and Future Perspectives, ACTA Pharm Sci. 55 (2017) 61, https://doi.org/10.23893/ 1307-2080.aps.0555.
- R. DeFronzo, From the Triumvirate to the Ominous Octet: A New Paradigm for the Treatment of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus, Diabetes 58 (2009) 773–795, https:// doi.org/10.2337/db09-9028.
- R. DeFronzo, From the Triumvirate to the Ominous Octet: A New Paradigm for the Treatment of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus, Diabetes 58 (2009) 773–795, https: doi.org/10.2337/db09-9028.
- Chawla R, Thakur P, Chowdhry A, Jaiswal S, Sharma A, et al. (2013) Evidence based herbal drug standardization approach in coping with challenges of holistic management of diabetes: a dreadful lifestyle disorder of 21st century.Journal of Diabetes & Metabolic Disorders 12: 35
- Tabatabaeimalazy O. larijani B, Abdollahi M. Targeting metabolic disorders by natural products. Journal of diabetes & metabolic disorder;2015:14–57.
- Narayan DS, Patra VJ, Dinda SC. Diabetes and indian traditional medicines anoverview.International. Journal of Pharmacy and Pharmaceutical Sciences;2012(4).
- Prabhakar PK, Doble M. Mechanism of action of natural products used in the treatment of diabetes mellitus. Chin J integr med;2011(17).
- K. Papatheodorou, M. Banach, E. Bekiari, M. Rizzo, M. Edmonds, Complications of Diabetes 2017, J. Diabetes. Res. 2018 (2018) 1–4, https://doi.org/10.1155/ 2018/3086167.
- Kumar K, Fateh V, Verma B, Pandey S. Some herbal drugs used for treatment of diabetes: review article.International vol. 2014;.
- Gupta R. Bajpai KG, Johri S, Saxenaa M. An overview of indian novel traditional medicinal plants with antidiabetic potentials.Complementary and Alternative. Medicines;2008(5):1–17.
- Gray AM and Flatt PR. Actions of the traditional anti-diabetic plant, Agrimony eupatoria (agrimony): effects onhyperglycaemia, cellular glucose metabolism and insulin secretion. Brazilian Journal of Nutrition 1998; 80: 109-114.
- Malvi R, Jain S, Khatri S, Patel A, Mishra S. A Review on Antidiabetic Medicinal Plants and Marketed Herbal Formulations. International Journal of Pharmaceutical & Biological Archives;2011(2):1344–1355
- Vogler BK, Ernst E (1999) Aloe vera: a systematic review of its clinical effectiveness. Br J Gen Pract 49(447): 823-828.
- Lakshmi MS. Rani KSS, Reddy UKT. A review on di-abetes mellitus and the herbal plants used for its treatment.Asian. journal of pharmaceutical and clinical research;2012(5):15–21.
- Sauvaire Y, Petit P, Broca C, Manteghetti M, Baissac Y,et al. (1998) 4-hydroxyisoleucine: a novel amino acid potentiator of insulin secretion. Diabetes 47(2): 206-210.
- Gupta D, Raju J, Baquer NZ (1999) Modulation of some gluconeogenic enzyme activities in diabetic rat liver and kidney: effect of antidiabetic compounds. Indian J Expt Biol 37: 196-199.
- Kumar D, Trivedi N. Dixit RK. Herbal medicines used in the traditional indian medicinal system as a therapeutic treatment option for diabetes management: A review. World Journal of Pharmacy and Pharmaceutical Sciences2015;4(4).
- Rai V, Iyer U, Mani UV (1997) Effect of Tulasi (Ocimum sanctum) leaf powder supplementation on blood sugar levels, serum lipids and tissue lipid in diabetic rats. Plant Food for Human Nutrition 50(1): 9-16.
- Biswas K, Chattopadhyay I, Banerjee RK, Bandyopadhyay U (2002) Biological activities and medicinal properties of neem (Azadiracta indica). Curr Sci 82: 1336-1345.
- Giovannini P, Jayne MR, Howes E, E S. Medicinal plants used in the traditional management of diabetes and its sequelae in Central America: a review.Journal of. Ethnopharmacology;2016(2).
- Malvi R, Jain S, Khatri S, Patel A, Mishra S. A Review on Antidiabetic Medicinal Plants and Marketed Herbal Formulations. International Journal of Pharmaceutical & Biological Archives;2011(2):1344–1355.


 Suvarna N. Thube *
Suvarna N. Thube *
 Nikita S. Shelke
Nikita S. Shelke
 Dhanshri S. Gunjal
Dhanshri S. Gunjal





 10.5281/zenodo.10893063
10.5281/zenodo.10893063